Web servers offer us more than the content of the web pages that I discussed in Chapter 5. As part of their transactions with browsers , they reveal information about themselves and offer important insights into the operation of server-side scripts that cannot be found in the web pages they produce. This chapter describes the various types of HTTP header and shows the important role they can play in Internet forensics.
In a typical HTTP transaction, the browser requests a specific page from the server. Along with the request, the browser sends several lines of header information. These tell the server what types of data the browser can handle, what type of browser it is, and so forth, which I discuss in detail in Chapter 7. The server responds with the content that was requested, but it precedes that with its own header lines. These are not usually revealed to the end user, but they can tell us a great deal about the server and the pages that it hosts.
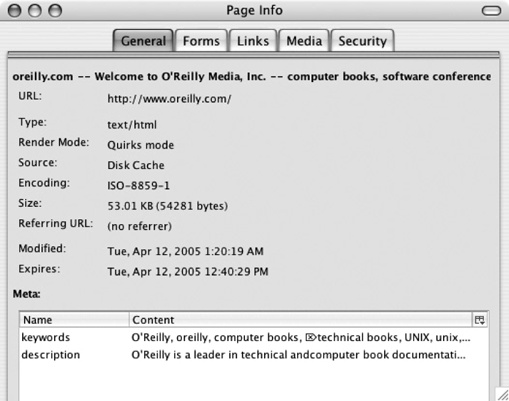
Certain browsers are able to display these headers. Mozilla Firefox, for example, makes some of them available under the General tab of its Page Info window as shown in Figure 6-1.
Using a browser for this purpose can be convenient, but in order
to capture the headers directly to a file, a better solution is to
return to the command tool wget,
described in Chapter 5.
Supplying the -S option to wget causes the HTTP headers to be displayed at the same time as the content is saved
to a file:
% wget -S http://www.oreilly.com/index.html
--09:08:11-- http://www.oreilly.com/index.html
=> `index.html'
Resolving www.oreilly.com... 208.201.239.37, 208.201.239.36
Connecting to www.oreilly.com[208.201.239.37]:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response...
1 HTTP/1.1 200 OK 2 Date: Thu, 20 Jan 2005 17:08:11 GMT
3 Server: Apache/1.3.33 (Unix) PHP/4.3.10 mod_perl/1.29
4 P3P: policyref="http://www.oreillynet.com/w3c/p3p.xml",
CP="CAO DSP COR [...]"
5 Last-Modified: Thu, 20 Jan 2005 09:19:26 GMT
6 ETag: "a4524-d5f6-41ef779e"
7 Accept-Ranges: bytes
8 Content-Length: 54774
9 Content-Type: text/html
10 X-Cache: MISS from www.oreilly.com
11 Keep-Alive: timeout=15, max=500
12 Connection: Keep-Alive
100%[==========================================================>] 54,77
4 136.85K/s
09:08:11 (136.46 KB/s) - `index.html' saved [54774/54774]By default, these are sent to Standard Error, but you can direct
them to a file using the -o
(lowercase o) option. For example, this command directs them to the file
headers.txt.
% wget -S -o headers.txt http://www.oreilly.com/index.html