3.6 For all Supply Chain Elements: SAP Supply Chain Management
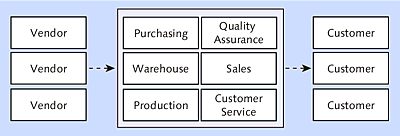
SAP Supply Chain Management (SAP SCM) includes functions for the entire supply chain, from the supplier to the customer. The software offers advanced functions for complex business processes in logistics (Figure 3.4).
Figure 3.4 Advanced Supply Chain
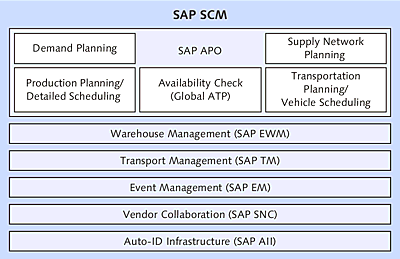
SAP SCM is an extremely powerful software solution with diverse individual components. Due to its wide functional scope, the following list only provides a short overview of SAP SCM (illustrated in Figure 3.5):
-
Warehouse management
SAP Extended Warehouse Management (SAP EWM) is the SAP SCM solution for warehouse management, and it has options that go far beyond the Warehouse Management component (WM) in SAP ERP. SAP EWM is deployed for all processes in warehouse management. -
Transportation management
SAP SCM provides a separate solution in the transportation area called SAP Transportation Management (SAP TM). In contrast to SAP Logistics Execution System (SAP LES) in SAP ERP, this solution was also developed for transport service providers. -
Tracking of logistics processes
SAP Event Management (SAP EM) was designed for tracking and status management tasks. -
Support of RFID processes
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) allows for the noncontact identification and localization of objects (which are provided with an RFID label) using RFID readers. This facilitates data entry. In this context, the SAP component, SAP Auto-ID Infrastructure (AII), represents a link between the RFID reader and the SAP system. -
Supplier collaboration
By means of SAP Supply Network Collaboration (SAP SNC), you can achieve closer cooperation of external suppliers by letting them respond to customer stocks and requirements independently. -
Planning and optimization of the supply chain
SAP Advanced Planning and Optimization (SAP APO) consists of a very widespread task area with functions for production planning, sales planning, availability checks, transportation planning, and so on.
Figure 3.5 Overview of SAP SCM Components
If you take a close look at the usage areas of SAP SCM, you may notice some overlap of SAP ERP components. For example, there is a component for warehouse management within SAP ERP (i.e., WM) and SAP SCM (i.e., SAP EWM), respectively; the latter, however, has more refined options than the former.