15.7 Automatic Material Requirements Planning
Automatic MRP (automatic procurement) is responsible for punctual and accurate goods procurement. In this process, procurement processes are triggered systematically. Automatic MRP focuses on an optimal supply, primarily of the production and stores, with materials and supplies used for manufacturing. Its goal is to ensure availability of the materials, while keeping the storage costs to a minimum. The benefit is less capital commitment, shorter lead times, higher on-time delivery performance, and more flexibility in production. To conclude the chapter on MM, we’ll introduce automatic MRP.
Automatic MRP is used to monitor stocks at the plant level and at the MRP area. MRP at the plant level refers to the plant and all its assigned storage locations. An MRP area, on the other hand, is an independently planning organizational unit.
Automatic planning runs determine shortages (i.e., the stock is about to fall below a defined threshold) and can create the following procurement elements, if necessary:
- PReq
- Planned order
- Delivery schedules
A delivery schedule is an outline agreement with a vendor defining which materials are delivered at certain dates.
Procurement elements can only be created if certain system settings are configured both in the material and vendor master and in the purchasing info record.
MRP can be consumption-based or plan-based. With consumption-based MRP, the current stock level of a material is considered; with plan-based MRP, the current and the future sales are considered. As an example, we’ll now contemplate the simple consumption-based MRP, which only considers stock levels, while reservations and sales orders aren’t taken into consideration.
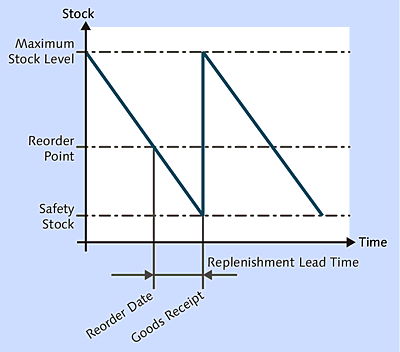
Figure 15.27 shows the stock levels of a material at a plant. If the stock level reaches the reorder point, procurement processes are triggered (e.g., a PReq is created). The material is then replenished to the maximum stock level, and the process is started all over again. A previously defined safety stock can only be withdrawn after an explicit approval. When using this procedure, the delivery time and the GR processing time must be considered for the respective material.
Figure 15.27 Consumption-Based MRP