In this chapter, you learn about exponents and exponentiation.
Exponential Notation
An exponent is a small raised number written to the upper right of a quantity, which is called the base for the exponent. For example, consider the product 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3, in which the same number is repeated as a factor multiple times. The exponential form for 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 is 35. The number 3 is the base, and the small 5 to the upper right of 3 is the exponent.
Most commonly, you read 35 as either “three to the fifth” or “three raised to the fifth power.” When the exponent is 1, as in 71, you say, “seven to the first.” When 2 is the exponent, as in 62, you say, “six squared,” and when 3 is the exponent, as in 53, you say, “five cubed.”
Problem
Express the exponential form in words.
a. 25
b. 56
c. 43
d. (−13)2
e. 101
a. 25

Step 1. Identify the base.
The base is 2.
Step 2. Identify the exponent.
The exponent is 5.
Step 3. Express 25 in words.
25 is “two to the fifth.”
b. 26

Step 1. Identify the base.
The base is 5.
Step 2. Identify the exponent.
The exponent is 6.
Step 3. Express 56 in words.
56 is “five to the sixth.”
c. 43

Step 1. Identify the base.
The base is 4.
Step 2. Identify the exponent.
The exponent is 3.
Step 3. Express 43 in words.
43 is “four cubed.”
d. (−13)2

Step 1. Identify the base.
The base is −13.
Step 2. Identify the exponent.
The exponent is 2.
Step 3. Express (−13)2 in words.
(−13)2 is “negative thirteen squared.”
e. 101

Step 1. Identify the base.
The base is 10.
Step 2. Identify the exponent.
The exponent is 1.
Step 3. Express 101 in words.
101 is “ten to the first” or because 101 = 10, simply “10.”
Natural Number Exponents
When the exponent is a natural number, it tells you how many times to use the base as a factor.
Problem
Write the indicated product in exponential form.
a. 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
b. (−3)(−3)(−3)(−3)(−3)(−3)
Solution
a. 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
Step 1. Count how many times 2 is a factor.
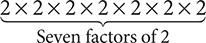
Step 2. Write the indicated product as an exponential expression with 2 as the base and 7 as the exponent.
2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 27
b. (−3)(−3)(−3)(−3)(−3)(−3)
Step 1. Count how many times −3 is a factor.
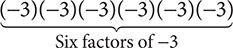
Step 2. Write the indicated product as an exponential expression with −3 as the base and 6 as the exponent.
(−3)(−3)(−3)(−3)(−3)(−3) = (−3)6
In the above problem, you must enclose the −3 in parentheses to show that −3 is the number that is used as a factor six times.
To evaluate the exponential form 35, you do to the base what the exponent tells you to do. The result you get is the fifth power of 3, as shown in Figure 3.1.
Problem
Evaluate 35.
Solution

Step 1. Write 35 in product form, using 3 as a factor five times.
35 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3
Step 2. Do the multiplication.
35 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 243 (fifth power of 3)
Note: To express 35 = 243 in words, say either “three to the fifth is two hundred forty-three” or “three raised to the fifth power is two hundred forty-three.”
Problem
Evaluate the expression.
a. 25
b. 56
c. 43
d. (−13)2
e. 101
a. 25

Step 1. Write 25 in product form, using 2 as a factor five times.
25 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
Step 2. Do the multiplication.
2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 32
Step 3. Review the main results.
25 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 32
b. 56

Step 1. Write 56 in product form, using 5 as a factor six times.
56 = 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5
Step 2. Do the multiplication.
5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 = 15,625
Step 3. Review the main results.
56 = 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 × 5 = 15,625
c. 43

Step 1. Write 43 in product form, using 4 as a factor three times.
43 = 4 × 4 × 4
Step 2. Do the multiplication.
4 × 4 × 4 = 64
Step 3. Review the main results.
43 = 4 × 4 × 4 = 64
d. (−13)2

Step 1. Write (−13)2 in product form, using −13 as a factor two times.
(−13)=(−13)(−13)
Step 2. Do the multiplication.
(−13)(−13) = 169
Step 3. Review the main results.
(−13)2 = (—13)(—13) = 169
e. 101

Step 1. Write 10 as a factor one time.
101 = 10
You likely are most familiar with natural number exponents, but natural numbers are not the only numbers you can use as exponents. Here are two other types of exponents.
Zero Exponents
A zero exponent on a nonzero number tells you to put 1 as the answer when you evaluate. Caution: It’s important to remember that when you use 0 as an exponent, the base cannot be 0. The expression 00 has no meaning. You say, “zero to the zero power is undefined.”
Problem
Evaluate.
a. 20
b. (−25)0
c. 00
d. 1000
e. 10
Solution
a. 20

Step 1. The exponent is 0, so put 1 as the answer.
20 = 1
b. (−25)°

Step 1. The exponent is 0, so put 1 as the answer.
(−25)° = 1

Step 1. The exponent is 0, but 00 has no meaning, so put undefined as the answer.
00 is undefined.
d. 1000

Step 1. The exponent is 0, so put 1 as the answer. 1000 = 1
e. 10

Step 1. The exponent is 0, so put 1 as the answer.
10 = 1
Negative Exponents
A negative exponent on a nonzero number tells you to obtain the reciprocal of the corresponding expression that has a positive exponent. Caution: You cannot use 0 as a base for negative exponents. When you evaluate such expressions, you get 0 in the denominator, meaning that you have division by 0, which is undefined.
Problem
Evaluate.
a. 2−5
b. 5−6
c. 4−3
d. (−13)−2
e. 10−1
f. 0−3
Solution
a. 2−5

Step 1. Write the expression using 5 instead of −5 as the exponent.
25
Step 2. Write the reciprocal of 25.
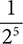
Step 3. Evaluate the denominator, 25.

Step 4. Review the main results.
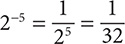
b. 5−6

Step 1. Write the expression using 6 instead of −6 as the exponent.
56
Step 2. Write the reciprocal of 56.
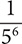
Step 3. Evaluate the denominator, 56.
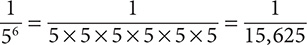
Step 4. Review the main results.
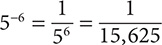
c. 4−3

Step 1. Write the expression using 3 instead of −3 as the exponent.
43
Step 2. Write the reciprocal of 43.
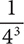
Step 3. Evaluate the denominator, 43.
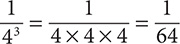
Step 4. Review the main results.

d. (−13)−2

Step 1. Write the expression using 2 instead of −2 as the exponent.
(−13)2
Step 2. Write the reciprocal of (−13)2.
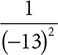
Step 3. Evaluate the denominator, (−13)2.
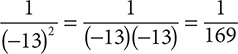
Step 4. Review the main results.
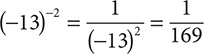
e. 10−1

Step 1. Write the expression using 1 instead of −1 as the exponent.
101 = 10
Step 2. Write the reciprocal of 10.
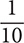
Step 3. Review the main results.
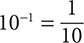
f. 0−3

Step 1. The base is 0, so the expression is undefined.
0−3 is undefined.
 Exercise 3
Exercise 3
For 1−4, express the exponential form in words.
1. 65
2. (−5)4
3. 40
4. (−9)2
For 5 and 6, write the indicated product in exponential form.
5. (−4)(−4)(−4)(−4)(−4)
6. 8 × 8 × 8 × 8 × 8 × 8 × 8
For 7−15, evaluate, if possible.
7. 28
8. 54
9. (−4)5
10. 09
11. (−2)°
12. 0−4
13. 3−4
14. (−15)−2
15. 4−2
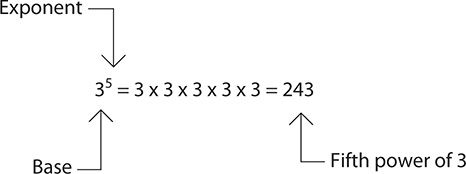
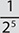 .
.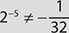 . A negative exponent does not make a power negative.
. A negative exponent does not make a power negative. 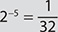 .
.