APPENDIX 3-1
Human Disease Conditions and the Probiotics Known to Promote Health in These Conditions
| Condition | Probiotic Therapy | Results |
|---|
| Diarrhea (infectious) | B. bifidum | Less frequent stools |
| Diarrhea | B. lactis | Less frequent stools |
| (antibiotic-associated) | S. thermophilus | Decreases incidence |
| Candida | L. acidophilus | Weakens the infection |
| Chlamydia | E. faecium | Reduces infection |
| C. rodentium | L. acidophilus | Reduces cell growth |
| L. rhamnosus | in colon |
| Giardia | E. faecium | Reduces infection |
| Helicobacter pylori | L. acidophilus | Reduces |
| L. rhamnosus | inflammation |
| L. gasseri | Decreases H. pylori |
| L. reuteri | growth |
| Salmonella | B. longum | Reduces infection |
| S. cerevisiae | |
| L. reuteri | |
| C. difficile | S. cerevisiae | Reduces rate of death in patients |
APPENDIX 3-2
Bifidobacteria Species Known to Inhibit Infection of Pathogens That Cause Disease in Humans
| Bifidobacteria Species | Pathogen Inhibited | Reference |
|---|
| B. longum | Salmonella typhimurium | Silva et al. 1999 |
| B. breve | E. coli | Asahara et al. 2004 |
| B. pseudocatenulatum | E. coli | Gagnon et al. 2004 |
| Bifidobacterium | Listeria monocytogenes | Toure et al. 2003 |
| Campylobacter jejuni | Fooks and Gibson 2003 |
| Bacteroides vulgatus | Shiba et al. 2003 |
APPENDIX 4-1
Common Commercially Used Probiotic Species
| Lactobacillus |
| L. acidophilus |
| L. delbrueckii ssp bulgaricus |
| L. fermentum |
| L. gasseri |
| L. johnsonii |
| L. lactis |
| L. paracasei |
| L. plantarum |
| L. reuteri |
| L. rhamnosus GG (L. casei) |
| L. salivarius |
| Bifidobacterium |
| B. adolescentis |
| B. animalis |
| B. bifidum |
| B. breve |
| B. catenulatum |
| B. infantis |
| B. lactis |
| B. longum |
| B. regularis (B. animalis) |
| Enterococcus |
| E. faecium |
| E. faecalis |
| Streptococcus |
| S. thermophilus |
| Other |
| Saccharomyces boulardii (S. cerevisiae) |
| Oxalobacter formigenes |
| Bacillus cereus |
| Bacillus subtilis |
| Bacillus coagulans |
| Escherichia coli |
| Streptococcus thermophilus |
| Propionibacterium freudenrechii |
APPENDIX 4-2
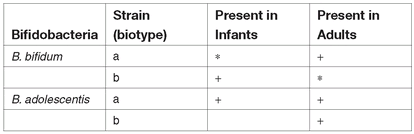
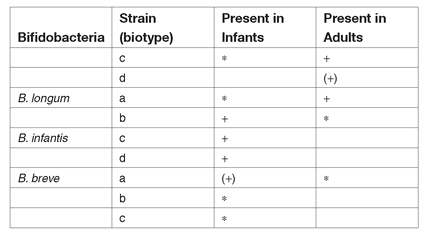
Bifidobacterium species in the intestine of infants and adults (according to Lerche and Reuter, 1961; Reuter, 1963, 1971; Mitsuoka, 1969, 1982).
Frequency:
+ frequently (+) moderately * occasionally
Source: Lerche and Reuter, 1961; Reuter, 1963, 1971; Mitsuoka, 1969, 1982.
APPENDIX 4-3
Some of the Human Disease Conditions Known to Benefit from Oral Administration of Certain Probiotic Species.
| Disease Condition | Probiotic Therapy | Results |
|---|
| Asthma | L. rhamnosus | Decreased incidence |
| Atopic dermatitis | B. lactis | Reduced symptoms |
| L. casei* | |
| L. fermentum | |
| L. reuteri | |
| L. rhamnosus | |
| Bladder cancer | L. casei Shirota | Reduced recurrence |
| Candida | L. acidophilus | Reduced infection |
| L. crispatus | |
| L. fermentum | |
| L. jensenii | |
| L. rhamnosus | |
| C. difficile | S. cerevisiae | Reduced risk of death |
| Colic | L. reuteri | Reduced crying time |
| Colon cancer | B. animalis | Reduced risk |
| B. breve |
| B. lactis |
| B. longum |
| L. rhamnosus |
| Common Cold | B. bifidum | Reduced incidence |
| B. longum |
| L. gasseri |
| Diarrhea (infectious) | B. bifidum | Less frequent stools |
| B. breve |
| B. lactis |
| L. casei * |
| L. reuteri |
| L. rhamnosus |
| S. thermophilus |
| Diarrhea (antibiotic-associated) | B. bifidum | Less frequent stools Decreased incidence of diarrhea |
| B. lactis |
| B. longum |
| E. faecium |
| L. acidophilus |
| L. bulgaricus |
| S. boulardii |
| S. thermophilus |
| E. coli | L. acidophilus | Reduced infection |
| L. rhamnosus |
| Giardia | E. faecium | Reduced infection |
| Helicobacter pylori | L. acidophilus | Decreased H. pylori or inhibited growth |
| L. brevis |
| L. casei * |
| L. gasseri |
| L. johnsonii La1 |
| L. reuteri | |
| L. rhamnosus | |
| L. salivarius | |
| S. boulardii | |
| High Cholesterol | B. longum | Improved cholesterol |
| E. faecium | levels |
| L. acidophilus | |
| Irritable Bowel Disease | B. breve | Reduced bowel |
| (Crohn’s disease) | B. infantis | movements |
| B. longum | |
| L. acidophilus | |
| L. bulgaricus | |
| L. casei * | |
| L. plantarum | |
| L. salivarus | |
| S. thermophilus | |
| S. boulardii | |
| VSL#3 | |
| Irritable Bowel Disease | L. casei* | Clinical remission/ |
| (Ulcerative colitis) | S. boulardii | Reduced inflammation |
| S. thermophilus | and infection |
| VSL#3 | |
| Irritable Bowel | B. infantis | Less bloating/ |
| Syndrome (IBS) | B. lactis L. acidophilus | Decreased pain |
| L. paracasei | |
| L. plantarum | |
| L. rhamnosus | |
| L. salivarius | |
| VSL#3 | |
| Lactose intolerance | B. animalis | Assist lactose digestion |
| B. longum | |
| L. acidophilus | |
| L. bulgaricus | |
| S. thermophilus | |
| Liver cancer | L. rhamnosus | Reduced carcinogens |
| P. freudenreichii | |
| Oral health (dental | L. casei * | Improved health |
| carries) | L. bulgaricus | Reduced development |
| L. lactis | of dental carries |
| L. paracasei | |
| L. rhamnosus | |
| S. thermophilus | |
| Pouchitis | L. casei* | |
| S. thermophilus | |
| VSL#3 | |
| Salmonella | B. longum | Reduced infection |
| L. reuteri | |
| S. cerevisiae | |
| Traveler’s Diarrhea | L. casei* | Reduced incidences |
| S. boulardii | |
| Ulcers | L. casei | Speeds healing time |
| Urinary Tract Infection | L. casei Shirota | Prevented infection |
| (UTI) | L. crispatus | |
| L. fermentum | |
| L. reuteri | |
| L. rhamnosus | |
| Vaginosis | L. acidophilus | Prevented infection |
| L. crispatus | |
| L. delbrueckii | |
| L. fermentum | |
| L. paracasei | |
| L. rhamnosus | |
| Yeast Infections | L. acidophilus | Reduced infection |
| L. fermentum | |
| L. rhamnosus | |
| *L. rhamnosus GG is commonly called L. casei |
APPENDIX 6-1
Bad Microbes That Can Cause Diarrhea
| Diarrhea-Causing Microbes | Examples |
|---|
| Bacteria | Campylobacter, Salmonella, Shigella, Escherichia coli |
| Viral | Rotavirus, Norwalk, Cytomegalovirus, Hepatitis |
| Parasite | Giardia lambia, Entamoeba histolytica, Cryptosporidium |
| Food Intolerance | Unable to digest food components, e.g., lactose |
| Reaction to Medicine | Antibiotics, some blood pressure and cancer medications |
| Intestinal Disease | Colitis, Crohn’s disease, Celiac disease |
| Functional Bowel Disorders | Irritable bowel syndrome |
| Vitamin C | Over dosage of vitamin C can cause diarrhea |
APPENDIX 6-2
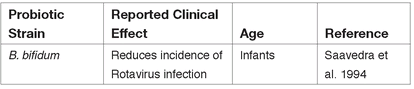
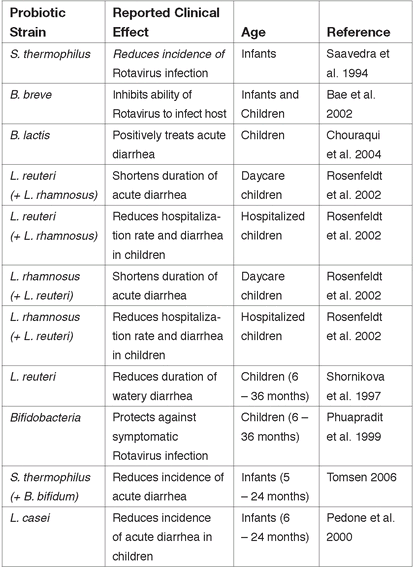
Reported Effects of Probiotic Species on Diarrhea in Children and Infants
APPENDIX 12-1
Food Sources of Calcium
| Food Item | Portion | Calcium (mg) |
|---|
| Almonds | 3 oz | 210 |
| Broccoli (cooked) | 2 stalks | 250 |
| Collard greens (cooked) | 6 oz | 225 |
| Dried apricots | 3 oz | 80 |
| Egg yolk | 1 | 25 |
| Fortified margarine | 2 tsp | 51 |
| Fortified orange juice | 1/2 cup | 45 |
| Fortified rice or soy beverage | 1 cup | 80 |
| Herring or trout, cooked | 75 g | 156 |
| Mackerel, cooked | 75 g | 80 |
| Milk | 1 cup | 100 |
| Salmon, Atlantic, cooked | 75 g | 225 |
| Salmon, canned or cooked* | 75 g | 608 |
| Sardines, Atlantic, canned | 75 g | 70 |
| Sardines, Pacific, canned | 75 g | 360 |
| Sunflower seeds | 2 oz | 80 |
| Tuna, canned, light or white | 75 g | 41 |
| Tuna, canned, yellow fin (albacore, ahi) | 75 g | 105 |
| Yogurt | 6 oz | 300 |
| *includes Chinook, Coho, Humpback (pink), Sockeye |
APPENDIX 18-1
| Origins of Some Probiotic Species |
| Human Origins |
| B. adolescentis - adult feces |
| B. angulatum - adult feces |
| B. bifidum - child and adult feces, vagina |
| B. breve - child feces, vagina |
| B. catenulatum - child and adult feces, vagina |
| B. denticolens - buccal cavity |
| B. dentium - buccal cavity, adult feces |
| B. gallicum - adult feces |
| B. infantis - child feces, vagina |
| B. inopinatum - buccal cavity |
| B. longum - child and adult feces and vagina |
| B. pseudocatenulatum - child feces |
| Environmental and Food Origins |
| B. lactis - fermented milk |
| B. minimum - sewage |
| B. subtile - sewage |
| B. thermacidophilum - anaerobic digester |
| Animal Origins |
| B. animalis - rat, chicken, rabbit and calf feces |
| B. asteroides - bees |
| B. boum - rumen, piglet feces |
| B. choerinum -piglet feces |
| B. coryneforme - bees |
| B. cuniculi - rabbit feces |
| B. gallinarum - chicken feces |
| B. indicum - bees |
| B. magnum - rabbit feces |
| B. merycicuum - rumen |
| B. pseudolongum - piglet, chicken, calf, rat feces |
| B. pullorum - chicken feces |
| B. ruminantium - rumen |
| B. saeculare - rabbit feces |
| B. suis - piglet feces |
| B. thermophilum - piglet, chicken and calf feces |
APPENDIX 18-2
Some Commercial Food Products with Added Probiotics
| Strain(s) | Commercial Products |
|---|
| L. casei DN114001 (L. casei Defensis ™) | DanActive® fermented milk |
| B. lactis Bb-12 | Good Start Natural Cultures® infant formula |
| L. casei Shirota, B. breve strain Yakult | Yakult® |
| L. acidophilus, L. casei (CL 1285) | Bio-K+® |
| B. animalis DN173 010 (Bifidis regularis™) | Danone Activia® yogurt |
| L. johnsonii Lj-1 (same as NCC533 and formerly L. acidophilus La-1) | LC1® Go! |
| L. reuteri SD2112 | Stonyfield Farms yogurts |
| L. rhamnosus GG (LGG) | Dannon Danimals® |
| Lactobacillus bulgaricus, | Horizon® Organic Yogurts |
| Streptococcus thermophilus, | |
| Lactobacillus casei | |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus LA5, Bifidobacterium lactis BB12 | Yoplait Yoptimal Immun+ |
| L. casei Defensive, L. casei Immunitass | Danone Actimel |
| L. casei | Kashi Vive Cereal |
| L. acidophilus (LAFTI ®L10), | Attune Snack Bars |
| L. casei (LAFTI® L26), B. lactis | |
| (LAFTI® B94) | |
| L. rhamnosus, B. lactis | Kraft LiveActive |