CHAPTER 6
The Human Body and Health
Body Systems
The human body is composed of organ systems that work interactively to carry out the functions of life. The following table identifies the 11 major organ systems and the functions involved with the different body systems.


Interaction Between Body Systems
Most tasks in the body need the support of two or more organ systems working together. In your body, organ systems work together to complete the tasks needed to keep you alive.
The circulatory, digestive, and respiratory systems work together to carry out the process of cellular respiration. The respiratory system brings oxygen into the lungs, and the digestive system breaks down food into nutrients such as glucose. The circulatory system transports glucose from the digestive system to the cells. It also moves oxygen from the lungs to the cells and returns carbon dioxide waste to the lungs.
Another example is the organ system teamwork needed to walk, run, or lift an object. The muscular, skeletal, and nervous systems must all cooperate to produce even the most simple movements that propel our bodies. The following diagram highlights some specific ways that these systems work together.

EXERCISE 1
Body Systems
Directions: Choose the best answer for each of the following items.
1. Which organ system regulates both the volume and pH of blood?
A. circulatory
B. respiratory
C. lymphatic
D. urinary
2. Complete the statement with terms from the section.
The three organ systems primarily responsible for the running motion of an athlete in a relay race are ____________________, ____________________, and ____________________.
Answers are on page 661.
Homeostasis
Your body’s ability to adjust to external changes while maintaining a stable internal environment is known as homeostasis. Humans are able to function in a wide range of environments because our bodies have a system of feedback controls. This allows body systems to regulate the internal conditions and make adjustments.
Homeostatic feedback loops are constantly being carried out in big and small ways in your body. Even a mild scrape on your arm triggers a series of responses designed to heal and maintain your body’s homeostasis. The following diagram illustrates how a homeostatic feedback loop works.

There are two main types of feedback loops. Negative feedback is a process that happens when body systems need to slow down or completely stop a process that is occurring. Your digestive system uses a negative feedback loop to regulate the use of your stomach. You don’t need your stomach churning if you are not eating!
Positive feedback encourages a physiological process. It amplifies your body’s response to a stimulus until negative feedback can take over. Take, for example, the process of digestion. Your body makes an enzyme called pepsin that helps to digest food. Before that takes place, your body usually secretes an inactive enzyme called pepsinogen in your stomach. As pepsinogen is converted to a different enzyme, pepsin, it triggers a process that helps convert other pepsinogen molecules. This cascade effect quickly supplies your stomach with enough pepsin molecules needed to digest proteins.
Effects of External Environments
Homeostatic feedback also occurs in response to changes in the external environment. It can be clearly seen when your body regulates temperature. For example, think about how you feel when you are standing in the hot sun and becoming overheated. In this situation, the response to overheating is stimulation of the sweat glands. Receptors in your skin monitor and sense the rising body temperature. The receptors respond by sending a message to your brain, which then alerts the sweat glands in the skin. The sweat glands act as effectors when they respond to your brain’s message to make a change. Sweating cools you and reduces body temperature, thus restoring homeostasis.
Now, suppose that it is very cold and you go outside without a coat. Your body wants to maintain its normal 98.6°F temperature, so it automatically adjusts. To stay warm, hair follicles on your arms tighten and stand up higher to retain heat. Your muscles will also shiver to generate heat through movement. If your body failed to respond, you would be at risk of hypothermia, a life-threateningly cold body temperature.
EXERCISE 2
Homeostasis
Directions: Choose the best answer for each of the following items.
1. Indicate your answer choice by connecting the terms to correct places in the homeostatic feedback loop. (Note: On the real GED® test, you will click on the words you choose and “drag” each one into position in the diagram.)

2. Prolonged exposure to the sun at the beach would most likely disrupt homeostasis in the
A. skin because of the potential for a sunburn.
B. liver because of increased liquid consumption.
C. muscles because of exhaustion from swimming.
D. lungs because of secondhand smoke and exhaust fumes.
Answers are on page 661.
Nutrition
Your body’s ability to carry out all the chemical reactions needed to maintain homeostasis depends on six types of nutrients. The following table identifies the essential nutrients, the roles they play in helping your body to function properly, and some foods in which the nutrients are found.
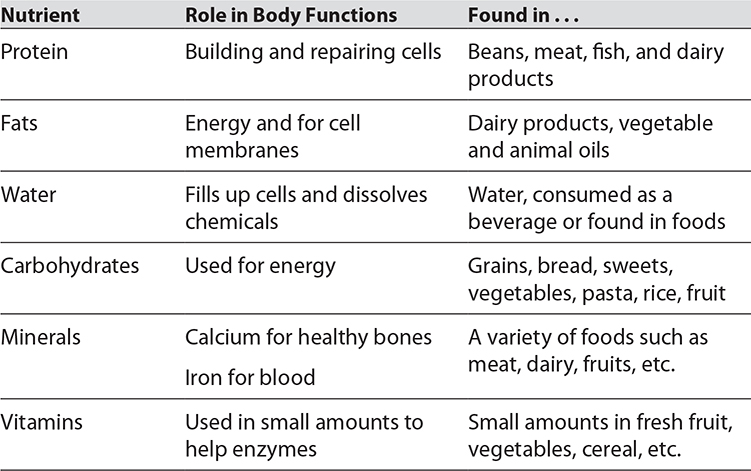
Another source of nutrients is bacteria. Many types of helpful bacteria live inside your digestive system. These symbiotic bacteria assist in breaking down food and make the essential vitamins B and K. In return, the bacteria benefit from a stable environment inside your intestines.
Nutrition Concepts
A well-balanced diet is an important component of your overall health. Deficiencies in certain types of nutrients can even lead to disease. For example, a lack of vitamin D can result in bones not hardening properly. Too little of the mineral iron can lead to anemia, a disorder affecting red blood cells.
The energy your body needs is measured in calories. The number of calories in a food tells how much energy that food provides. The following chart shows the amount of energy, in calories, found in 1 gram of fat, protein, and carbohydrate.
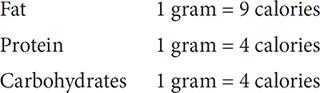
Eating the proper amount of each type of nutrient is one key to staying healthy. Just as deficiencies in nutrients can cause problems, so also can too much of a certain type of nutrient. Excessive amounts of protein in a diet can lead to a buildup of toxins that can harm your kidneys. Excessive amounts of fat can eventually lead to obesity.
Information about the types and amounts of nutrients in packaged food can be found on the nutritional labels. The following illustration points out important details found on labels, such as the number of calories and the amount of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals per serving size.
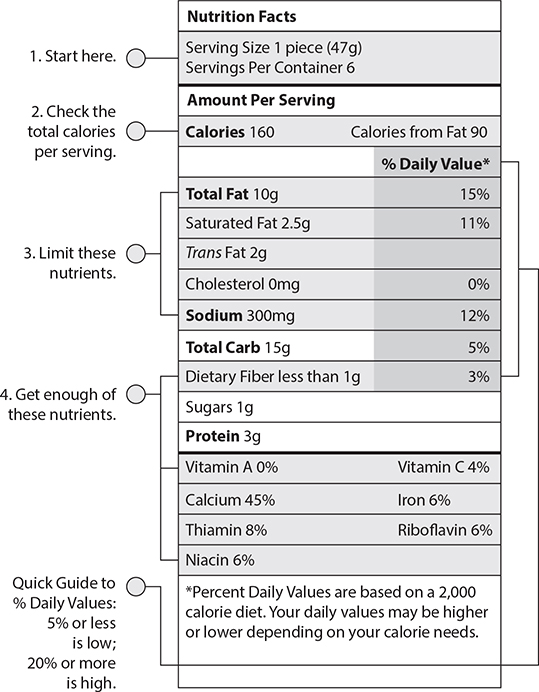
EXERCISE 3
Nutrition
Directions: Choose the best answer for each of the following items.
1. How many calories are in 9 grams of fat?
A. 9
B. 10
C. 18
D. 81
2. Which of the following nutrients is important for bone health?
A. vitamins
B. minerals
C. proteins
D. carbohydrates
3. A person taking antibiotics for a long time might be at risk for which of the following?
A. anemia
B. reduced energy
C. vitamin K deficiency
D. toxicity of the kidneys
Answers are on page 661.
Disease and Pathogens
Another way that your body’s homeostasis can be disrupted is through disease and pathogens. Pathogens are microorganisms or viruses that cause disease. The following table identifies five of the most common ways in which pathogens can be transmitted, or spread.

Prevention of Disease
Many diseases can be prevented by simple sanitation methods. Adopting healthy behaviors such as washing your hands often and covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze can reduce and prevent illness. Being aware of what you eat and drink and how carefully you prepare the food is also important for good health.
Immunizations are another way to prevent infections. Many infectious diseases, such as measles, polio, tetanus, and diphtheria, can be controlled with vaccines. A vaccine introduced into your body enables you to develop immunity without suffering from the actual disease that the vaccine prevents.
Effects of Disease on Populations
Prior to vaccinations, many infectious diseases had devastating results. Millions of lives were lost in widespread viral epidemics. Between the 15th and 18th centuries, the arrival of European colonists to the Americas introduced several deadly viruses. Some Native American populations were reduced by 80 percent from diseases such as smallpox, measles, and influenza. The damage done by these viruses helped the colonists to conquer the native populations and changed the course of history. Widespread outbreaks of diseases still have the power to change demographics and even lead to extinction.
EXERCISE 4
Disease and Pathogens
Directions: Choose the best answer for each of the following items.
1. The best way to prevent Salmonella poisoning is by
A. boiling your water.
B. using mosquito repellant.
C. covering your mouth when you sneeze.
D. not consuming raw foods such as eggs.
Questions 2 through 4 are based on the following passage.
A scientist designed an experiment in which he took a random sample of patients who tested positive for measles and found out whether, prior to their infection with the disease, they had received no measles vaccine, one dose of vaccine, or two doses of vaccine. He surveyed 100 patients who tested positive for measles and found that 7 people had received one dose of measles vaccine, 3 people had received two doses, and 90 people had not had the vaccine.
2. The experiment is designed to answer which of the following questions?
A. Why do so many people not receive the measles vaccine?
B. Can people who have had the measles in the past get it again?
C. How effective is the measles vaccine?
D. Are older people more susceptible to measles than younger people?
3. What is the effectiveness of two doses of measles vaccine at preventing measles? Express your answer as a percent. Two doses of the measles vaccine are ____________% effective at preventing measles.
4. The scientist repeated the experiment with a different set of 100 measles patients and found that 5 people had received one dose of measles vaccine, 3 people had received two doses, and 92 people had not had the vaccine. How can he best reconcile the data from these two studies to state a conclusion?
A. The measles vaccine is 90% effective at preventing measles.
B. The measles vaccine is highly effective at preventing measles and is most effective with two doses.
C. The effectiveness of the measles vaccine is variable based on when it is received.
D. Three doses of measles vaccine can completely protect people from measles.