48
Gastrointestinal obstruction
Most of the conditions causing gastrointestinal obstructions are serious but their prognosis has improved with advances in medical, anesthetic and surgical care. They are relatively uncommon but are important to recognize because:
- failure or delay in diagnosis may result in electrolyte imbalance, dehydration and shock
- malrotation with midgut volvulus is a surgical emergency in order to avoid bowel necrosis.
Causes – see Fig. 48.1

Fig. 48.1 Causes of intestinal obstruction.
Diagnostic clues
Prenatal:
- Polyhydramnios – from obstruction to the passage of amniotic fluid through the gastrointestinal tract.
- Abnormal ultrasound – dilated bowel, hyperechoic bowel, ascites, calcified lesions. May be difficult to diagnose.
- Fetus with trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) – 30% have associated duodenal atresia.
- Family history of cystic fibrosis – associated with meconium ileus.
Delivery room:
- Bubbly oral secretions – esophageal atresia.
- Peri-umbilical abdominal wall discoloration – in utero bowel perforation.
Clinical presentation
- Vomiting – usually bile (yellow-green) stained. Bile is present if the obstruction is distal to ampulla of Vater. Presents within 24–48 hours of birth with high gastrointestinal lesions, may be delayed for several days for lower lesions. Hematemesis (blood-stained vomit) may occur with malrotation.
- Feeding intolerance.
- Abdomen – distension with visible loops of bowel or peristalsis, erythema/edema of abdominal wall, abdominal mass, peritonitis and shock.
- Failure to pass meconium within 48 hours of birth.
- Blood in stool (fresh or altered).
Diagnosis
Abdominal X-ray:
- Bowel obstruction – distended loops of bowel with air-fluid levels, with absence of gas distally (see Fig. 47.2).
- Bowel perforation – free air under diaphragm, intrahepatic or around falciform ligament.
Management
- Abdominal decompression with nasal or orogastric tube. In esophageal atresia, aspirate pouch to avoid aspiration pneumonia.
- Intravenous fluids for resuscitation and maintenance. Early parenteral nutrition (PN).
- Antibiotics preoperatively.
- Evaluate and correct bleeding diathesis.
- Surgical intervention for most lesions.
- Evaluate for other anomalies. Karyotype and microarray analysis may be necessary.
Some specific conditions
Esophageal atresia (Chapter 47)
Pyloric stenosis
Hypertrophy of circular smooth muscle of pylorus of stomach.
- Presentation – projectile vomiting in a hungry infant at 4–8 weeks of age. Occurs at same age in preterm infants.
- Examination – visible peristalsis. A firm, olive-like mass is palpable in right upper abdomen during feeds.
- Investigation – abdominal ultrasound – hypertrophy of pylorus.
- Management – correct electrolyte imbalance (hypochloremic hypokalemic alkalosis). Surgery-muscle incision (pyloromyotomy).
Duodenal atresia
- Lesion – obstruction may be due to atresia, webs, stenosis or fibrous cord.
- Incidence – 1 in 7500 births. Check for trisomy 21 and other anomalies.
- Antenatal – polyhydramnios, distended fluid-filled stomach on ultrasound.
- Presentation – vomiting – bilious or non-bilious, upper abdominal distension and feeding intolerance.
- Diagnosis – double bubble on X-ray (Fig. 48.2). May be accentuated by injecting 20 mL of air through gastric tube.
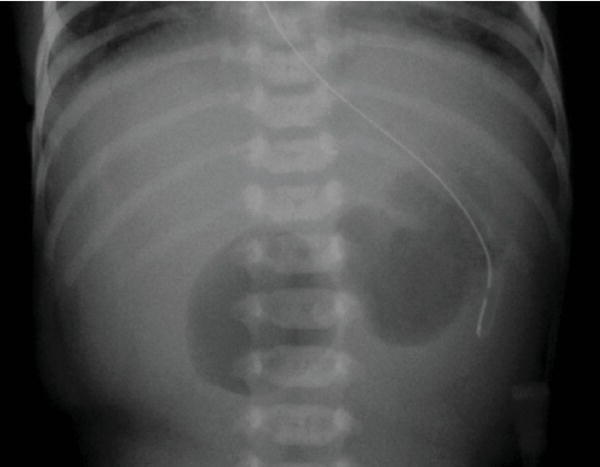
Fig. 48.2 Abdominal X-ray showing double bubble in duodenal atresia.
(Courtesy of Dr Sheila Berlin.)
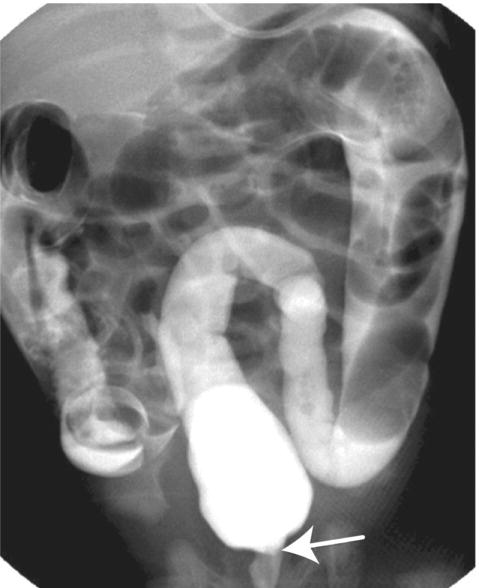
Fig. 48.3 Barium enema showing transition zone between normal and aganglionic bowel in Hirschsprung disease.
(Courtesy of Dr Sheila Berlin.)
Malrotation
Failure of the developing bowel to undergo the normal counter-clockwise rotation during the 4th to 10th weeks of embryogenesis. Peritoneal bands (which normally attach the bowel to the central body axis posteriorly and are also known as Ladd bands) compress the duodenum, partially obstructing it. Because the mesentery is not fixed, malrotation predisposes to midgut volvulus (twisting of a loop of bowel around its mesenteric attachment). In addition to intestinal obstruction, compression of the superior mesenteric artery leads to ischemia of the small bowel.
Presentation
Sudden bilious vomiting is malrotation until proven otherwise. Usually in first few weeks of life but can occur at any age. With acute volvulus also abdominal distension and tenderness followed by shock. Hematemesis may occur.
Investigation
Doppler ultrasound of mesenteric vessels may be helpful at the bedside. Upper gastrointestinal exam (contrast swallow) is diagnostic. The normal position of the duodenal-jejunal junction (Treitz angle) is to the left of the spine. Any other position indicates malrotation. Volvulus classically appears as a spiral corkscrew of the duodenum (see Fig. 47.1).
Management
Volvulus is a surgical emergency. Ischemia can lead to small bowel infarction requiring bowel resection. Extensive resection of the small bowel carries a poor prognosis.
To relieve the obstruction, the peritoneal bands around the duodenum are divided. Appendectomy is also performed to avoid future confusion if the child has abdominal pain.
Meconium ileus
- Small bowel obstruction from inspissated, putty-like, sticky meconium.
- Affects 10–15% of patients with cystic fibrosis, whereas 95% of infants with meconium ileus have cystic fibrosis.
Presentation
Bilious vomiting, failure to pass meconium, abdominal distension, abdominal mass. Edema of abdominal wall suggests peritonitis. Complications include volvulus and perforation.
Investigation and management
- Abdominal X-ray – dilated loops of bowel, air fluid levels and ground glass soap-bubble appearance of meconium.
- Intra-abdominal calcification indicates intrauterine perforation and peritonitis.
- Gastrograffin (water-soluble contrast) enema may wash out the meconium, otherwise surgery is required.
- Test for cystic fibrosis.
Meconium plug syndrome
Presentation – low bowel obstruction, as in Hirschsprung disease.
Hirschsprung disease
- Congenital absence of ganglionic cells in the myenteric plexus secondary to defective migration of ganglion cell precursors from neural crest to hind gut. Abnormal bowel extends from rectum for variable distance of large bowel. Proximal bowel is normal.
- Incidence – 1 in 5000 births, male: female ratio 5:1.
- May be associated with trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).
- Accounts for 20–25% of cases of neonatal intestinal obstruction.
Presentation
- Delayed passage of stools – more than 50% do not stool for 48 hours.
- About 50% of affected children present with abdominal distension (see Fig. 47.3) and vomiting in neonatal period, others when older with constipation.
- May present with enterocolitis – explosive liquid stools, fever and shock.
Investigation
Abdominal X-ray shows distal bowel obstruction – multiple distended loops of bowel with lack of air in the rectum.
Diagnosis
- Rectal suction biopsy for histology.
- Barium enema – excludes other causes of intestinal obstruction and may show transition zone between normal and aganglionic bowel (Fig. 48.3).
Treatment
Rectal washouts, followed by surgical repair.