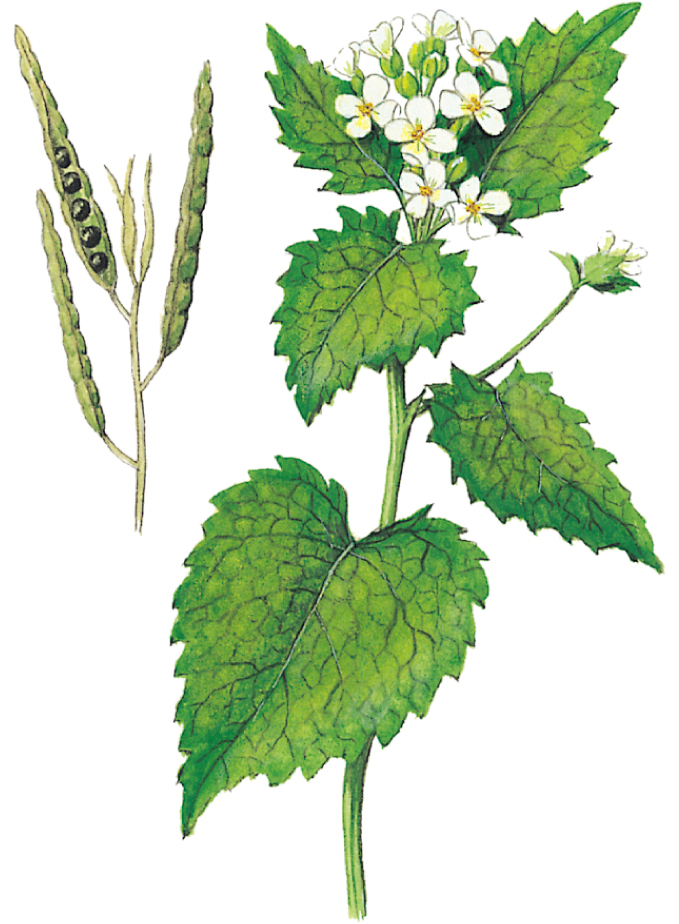

Garlic Mustard
Alliaria petiolata

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Erect biennial to 1.2m tall. Leaves are heart-shaped, toothed at the margins and smell of garlic when bruised. Flowers are white with four petals, and are followed by slender fruits 6–20mm long. Also called Jack-by-the-Hedge.
DISTRIBUTION
Found throughout Europe, North Africa, and western and central Asia.
USES
Tastes mildly of garlic. Picked before flowering, the leaves can be used in salads and sauces.
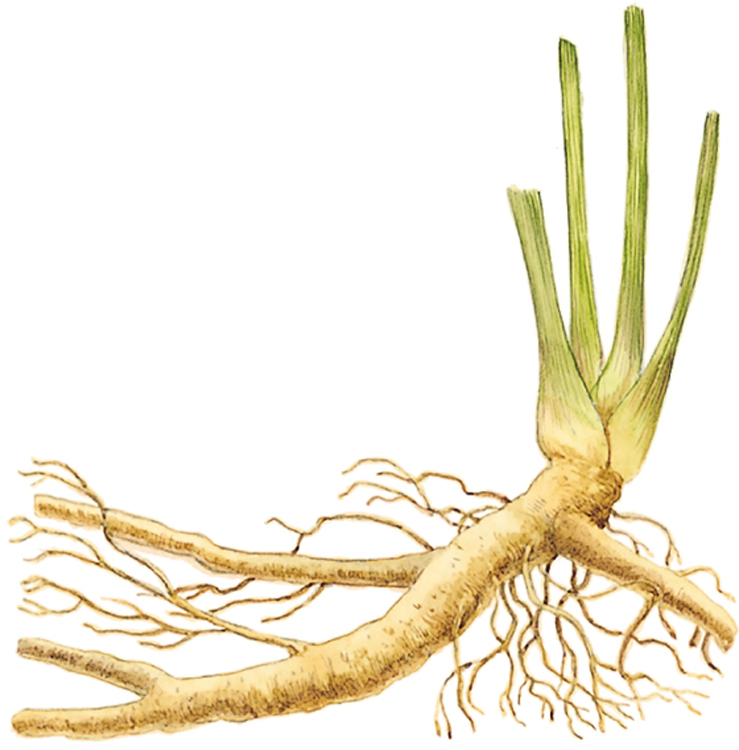
Horseradish
Armoracia rusticana
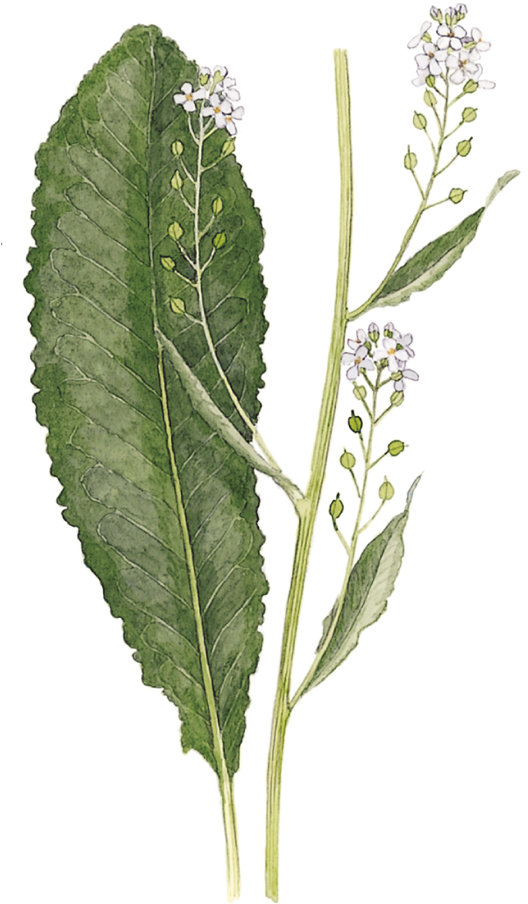

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Robust perennial to 1.2m tall, with a stout taproot. Large leaves are glossy, stalked, oblong to ovate, and have toothed margins. Flowering stems are leafy, erect and branching. Flowers are white with four petals. Also called Red Cole.
DISTRIBUTION
Native to southern Europe and western Asia; cultivated and naturalized in many temperate areas.
USES
Grated and mixed with cream, the pungent acrid root yields horseradish sauce. Young leaves can be added to salads. Stimulatory and antibiotic properties; the herb is used for coughs and sinus congestion, and for urinary infections, gout, arthritis and circulatory problems.

Black Mustard
Brassica nigra

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Slender annual to 2m tall. Leaves are pinnately cut and bristly, with the terminal lobe much larger than the other lobes. Flowers are yellow with four petals. Fruits are slender-beaked, contain dark brown seeds and are pressed against the stem.
DISTRIBUTION
Widespread throughout most temperate regions, and commonly cultivated.
USES
Leaves and flowers can be used in salads, stir-fries and sandwiches, ground seeds to make a mustard condiment. Warming stimulant with an antibiotic effect; used to ease muscular pain and for respiratory tract infections.
White Mustard
Sinapis alba
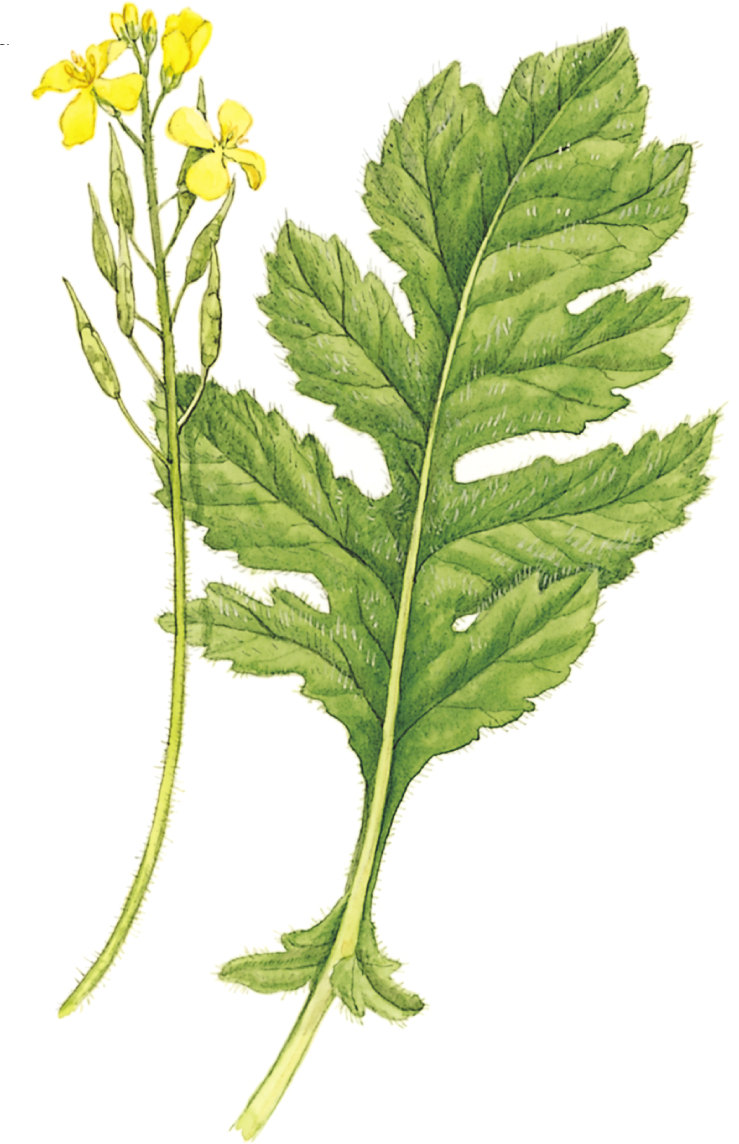
SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Similar to Black Mustard, but flowers are slightly larger and fruits have broad beaks and spread out from the stem. Seeds are pale. Also called Salad Mustard and Yellow Mustard.
DISTRIBUTION
Occurs across most of Europe and the Near East; introduced into many other areas.
USES
Similar to those of Black Mustard. White form is milder. Whole seeds are added to pickles, and seedlings can be used with cress in salads and sandwiches.
Water-cress
Rorippa nasturtium-aquaticum

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Perennial to 60cm tall, with creeping rooting stems that grow upwards to flower. Leaves are glossy, and pinnate with rounded leaflets. Flowers are white, small and have four petals. Fruits are slender, with seeds in two rows on each side.
DISTRIBUTION
Grows in shallow water in most of Europe, North Africa and western Asia.
USES
Leaves have a pungent hot taste, and a high vitamin and mineral content, particularly of vitamin C and iron. They may be used in soups and salads, but can be confused with unrelated poisonous species; additionally, in some areas wild plants harbour parasitic liver flukes that can damage the liver. Wild plants are therefore best avoided. Antibacterial and antifungal properties; used for respiratory tract ailments.
Common Scurvygrass
Cochlearia officinalis

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Biennial or perennial to 50cm tall. Basal leaves are kidney-shaped, long-stalked and grow in a loose rosette; stem leaves are clasping and fleshy. Flowers are white or occasionally lilac.
DISTRIBUTION
Occurs around the coasts of north-west Europe and in the Alps.
USES
Relatively bitter leaves may be added to soups, salads and sauces. Fresh leaves were once eaten by sailors on long voyages to prevent scurvy that was caused by vitamin C deficiency. A tonic was also made in the form of scurvygrass ale.
Winter-cress
Barbarea vulgaris
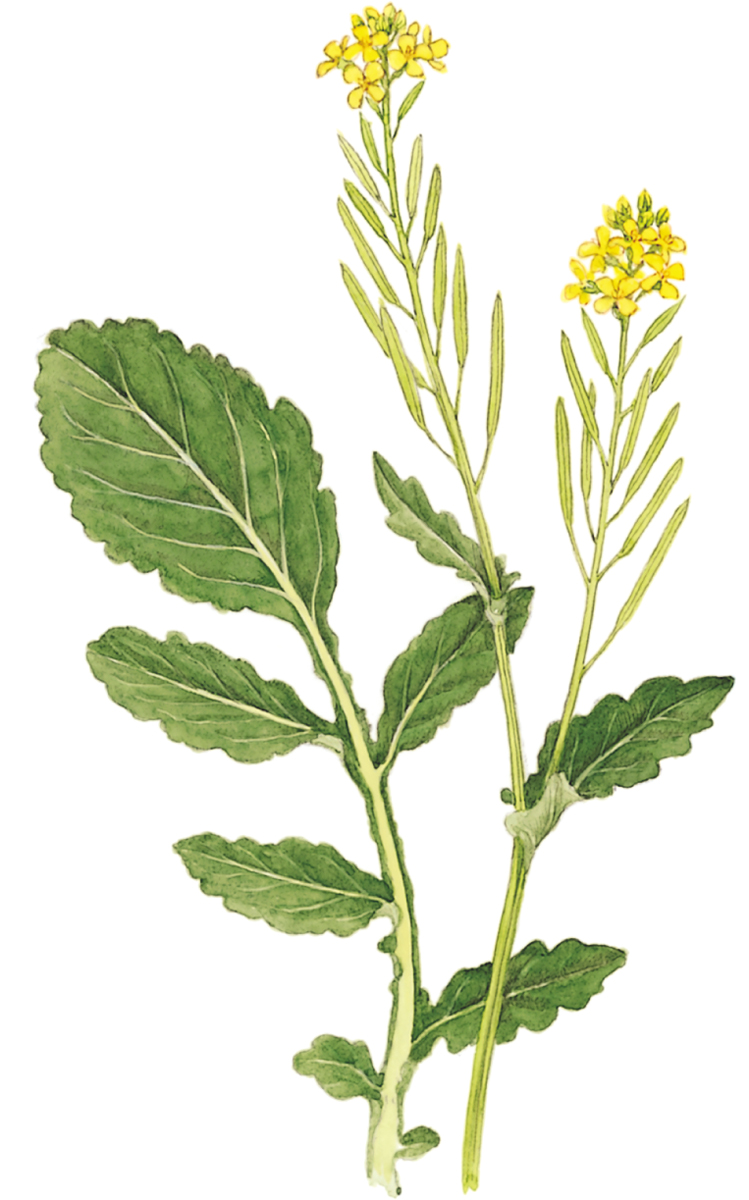

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Stout perennial or biennial to 80cm tall, with upright branches. Lower leaves are pinnately lobed; upper leaves are smaller and have wavy margins. Yellow flowers are borne in terminal clusters. Also called Bittercress, Poor Man’s Cabbage and Yellow Rocket.
DISTRIBUTION
Common throughout much of Europe.
USES
Hot taste similar to that of Water-cress. Once commonly cultivated in Europe as a salad vegetable. Leaves may be cooked and used like spinach, and young shoots can be steamed or stir-fried.
Hairy Bitter-cress
Cardamine hirsuta
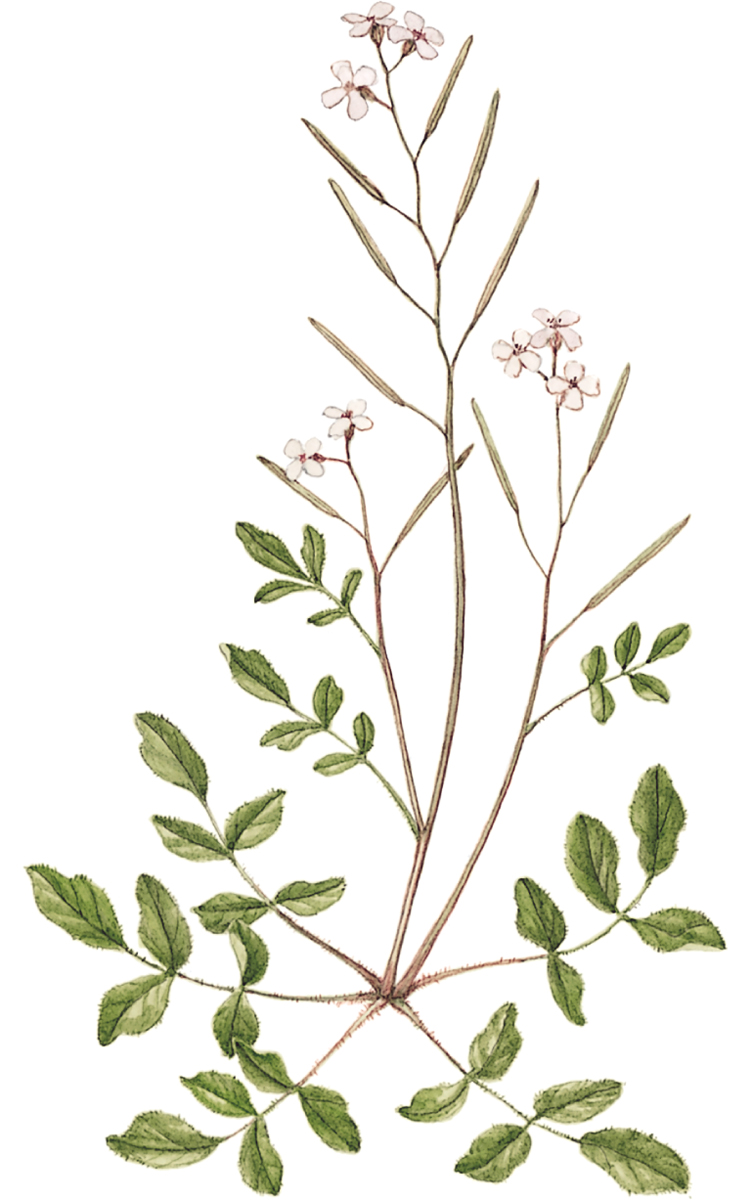

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Annual to 30cm tall, with upright stems. Leaves are pinnate with oval leaflets. Flowers are small, white and borne in loose terminal clusters. Fruits are long and narrow pods. Also called Lamb’s Cress.
DISTRIBUTION
Common throughout Europe.
USES
Sharp flavour that is not as hot as that of Water-cress. May be used in salads or cooked like spinach.
Shepherd’s-purse
Capsella bursa-pastoris
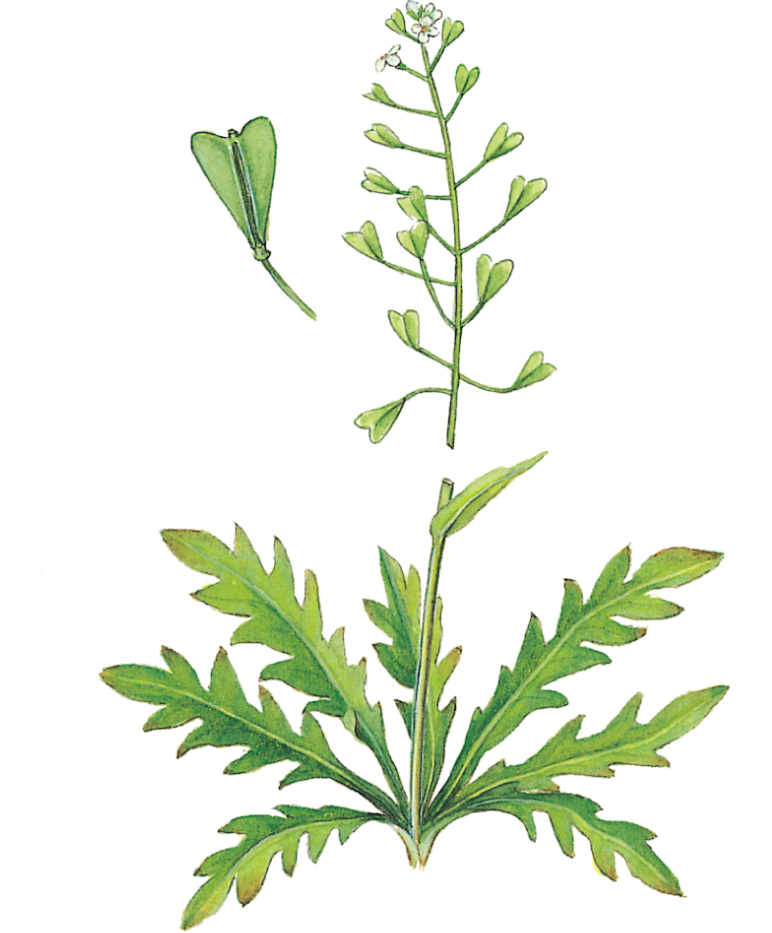

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Annual or biennial to 40cm tall. Basal rosette of pinnately divided leaves; stem leaves are stalkless and clasping. Minute white flowers are borne in loose spikes. Fruits are heart-shaped capsules resembling the purses people used to hang from their belts in the Middle Ages, hence the plant’s common name.
DISTRIBUTION
Common throughout Europe.
USES
Young leaves, collected before the plant flowers, may be added to salads, soups, sauces and stews, and stir-fried. As a herbal remedy, used mainly for haemorrhages.
Field Penny-cress
Thlaspi arvense
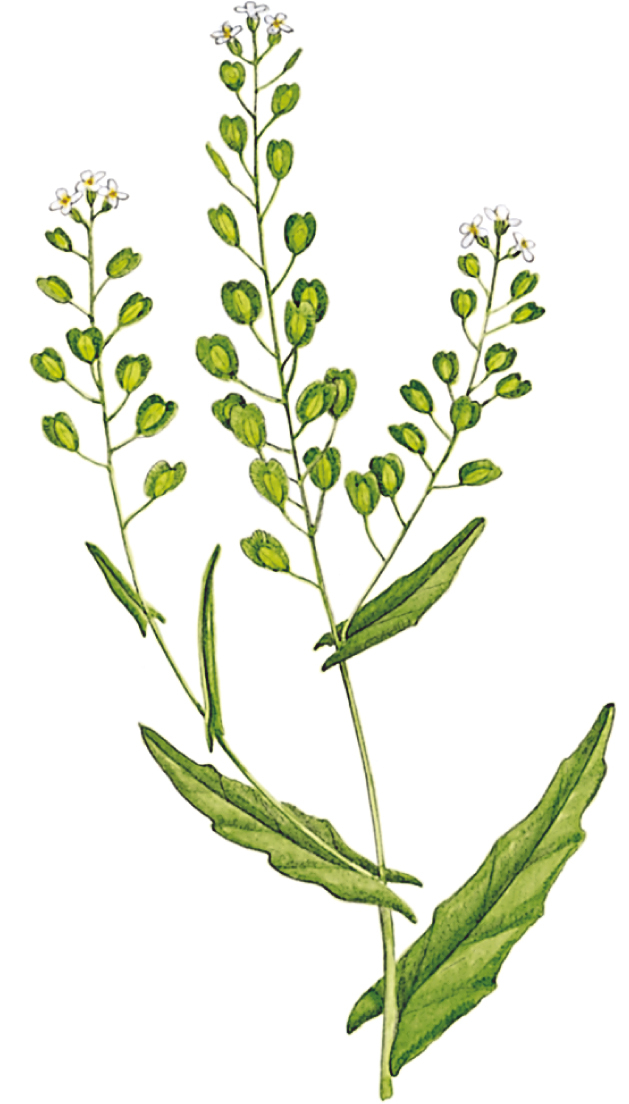

SIZE AND DESCRIPTION
Annual to 50cm tall. First leaves are oval and pointed, forming a basal rosette; stem leaves are clasping, with arrow-shaped bases and toothed margins. Flowers are small, with white petals, and are arranged in an ascending spike. Fruits are large heart-shaped capsules. Also called Boor’s Mustard, French Weed, Stinkweed and Treaclewort.
DISTRIBUTION
Common throughout much of Europe, but less frequent in the north.
USES
Slightly bitter flavour. Small amounts may be finely chopped and added to salads, soups and sauces.