Master AirPlay
With AirPlay, you can play audio and video content from your Mac or iOS device on your Apple TV. You can also mirror your entire screen to the Apple TV, so whatever you see and hear on your device, you also see and hear through the Apple TV. And, in 10.9 Mavericks you can turn the TV attached to your Apple TV into another display for your Mac, just like any other external display. In fact, AirPlay is such a great feature that I’ve decided to use it as a verb—it’s more elegant to write “you can AirPlay a video to your Apple TV” than “you can stream a video to your Apple TV using AirPlay.”
In this chapter, I show you how to AirPlay from iOS, AirPlay from Mac Apps, and Mirror from a Mac, plus how to Extend a Mavericks Desktop to an Apple TV. I even talk about making your Apple TV the source of an AirPlay stream, in AirPlay from an Apple TV.
Lock Down AirPlay
AirPlay is great, but unless you take preventive measures, anyone connected to your Wi-Fi network can AirPlay to your Apple TV. AirPlay always takes precedence, so if you’re trying to watch a movie, a merry prankster could butt in with a music video.
You can keep interlopers out of your TV using either the Onscreen Code option or a password. These options are quite different:
- Code: With a code, when you initiate AirPlay on your device, a 4-digit code appears on your TV screen, where everyone else on the couch can see it too—but not your neighbors in the next apartment. You enter the code on your device, and playback begins. The code is different each time.
- Password: With a password, when you AirPlay to your Apple TV, you are asked to enter the password. The password remains the same each time; it’s whatever you’ve set up, so it keeps out everyone who doesn’t know it.
To enable a code or password, navigate to Settings > AirPlay, and scroll down to the Security heading. Select Onscreen Code or Password and enter one when prompted.
Next time you AirPlay to the Apple TV, you’ll be prompted to enter either the code or the password, depending on which you chose. The code appears on the TV screen (Figure 21).

Figure 21: An AirPlay Code keeps the neighbors from sending media to your Apple TV via AirPlay, but makes it easy for friends and family to beam their content to the big screen.
To turn off a code or password, return to Settings > AirPlay and select None under the Security heading.
AirPlay from iOS
In iOS, AirPlay is supported by many apps. To activate it from within an app that supports it internally, tap the AirPlay ![]() icon and select your Apple TV from the list (Figure 22). You can adjust the volume on the iOS device as you would normally (volume buttons, Control Center, etc.) and the volume change will be reflected on your Apple TV.
icon and select your Apple TV from the list (Figure 22). You can adjust the volume on the iOS device as you would normally (volume buttons, Control Center, etc.) and the volume change will be reflected on your Apple TV.

Figure 22: Activate AirPlay by tapping the AirPlay icon in any app that supports it internally, like the iOS 6 Music app above.
AirPlay remains active in every app that supports it until you turn it off. So if you AirPlay songs from the Music app, and then switch to the Podcasts app and start playing a podcast, that audio will also play through your Apple TV. To turn AirPlay off, tap the AirPlay icon again, then select your device from the popover.
You can also activate or deactivate AirPlay from the multitasking bar in iOS 6 or Control Center in iOS 7. Here’s how.
Activate AirPlay from the Multitasking Bar in iOS 6:
- Double-press the Home button to bring up the multitasking bar. Or if you’re using an iPad and have enabled Multitasking Gestures, swipe up with four fingers.
- Slide the multitasking bar to the right (slide twice on the iPhone and iPod touch).
- Tap the AirPlay
 button.
button. - Select your Apple TV from the popover (Figure 23). Flip the switch if you want to turn AirPlay Mirroring on or off.

Figure 23: To activate AirPlay in iOS 6, bring up the multitasking bar and swipe it to the right to reveal the AirPlay button.
Audio or video that was playing on your device now plays on your Apple TV instead. Or, if you switched on mirroring, the entire screen and audio from your device is duplicated on your Apple TV.
Activate AirPlay from Control Center in iOS 7:
- Bring up Control Center by placing your finger below the bottom edge of the display and swiping up.
- Tap the AirPlay button (Figure 24, left).
- Select your Apple TV from the menu (Figure 24, right). Flip the Mirroring switch if you want to turn AirPlay Mirroring on or off.
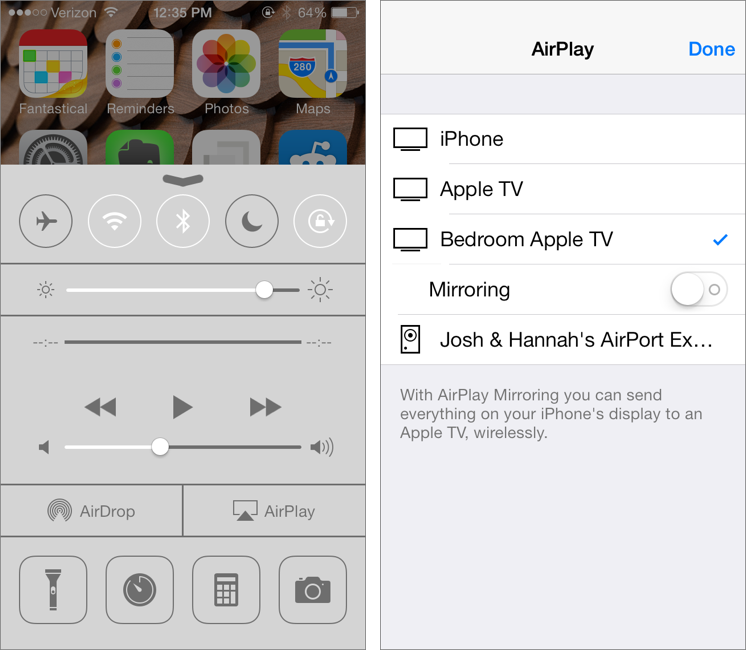
Figure 24: To turn on AirPlay in iOS 7, slide your finger up from beneath the bottom of the screen to pull up Control Center and tap AirPlay (left). In the AirPlay screen, tap the Apple TV that you want to send content to (right).
Media that was playing on your device now plays on your Apple TV instead. Or, if you turned on mirroring, the entire screen and audio from your device is duplicated on your Apple TV.
AirPlay from Mac Apps
Unfortunately, few Mac apps support AirPlay natively. iTunes is one notable exception, and Safari can support AirPlay video via a couple of third-party extensions.
AirPlay from iTunes
Let’s take iTunes as a likely example of an app that you’d want to AirPlay from. To send audio or video from iTunes to a single device, click the AirPlay icon near the top of the window, then select your Apple TV from the popover (Figure 25). The icon turns blue to indicate that AirPlay is active. To turn AirPlay off, select your computer from the popover.
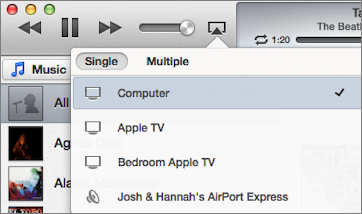
Figure 25: In iTunes 11, sending audio or video to your Apple TV is as simple as clicking the AirPlay icon and selecting your Apple TV from the list.
You can also turn AirPlay on or off while watching a video by clicking the AirPlay icon in the video controls. Unfortunately, some videos purchased from iTunes disable AirPlay (but you can work around this by mirroring your display).
AirPlay Video from Safari
Want to send a video from your Web browser to the Apple TV? Safari doesn’t have a built-in AirPlay feature, so you might try mirroring your entire display, but that can cause choppy video. Instead, try the Media Center Safari extension by Marc Hoyois. Media Center can AirPlay HTML5 videos.
To begin, visit the Media Center page, download the extension, and then double-click the downloaded .safariextz file (it’s probably in your Downloads folder). When asked by Safari if you want to install the extension, click Install.
Next, configure Media Center for your Apple TV:
- On your Apple TV, go to Settings > General > About, and look at the IP Address field. You should see a number like
10.0.1.41or192.168.4.12. That’s the IP address of your Apple TV. Keep it showing on your TV screen or write it down on a slip of paper. - In Safari, choose Safari > Preferences (Command-,) and click the Extensions button in the toolbar.
- In the left column, select Media Center.
- At the bottom right, in the “AirPlay device hostname” field, enter the Apple TV’s IP address from Step 1 (Figure 26).
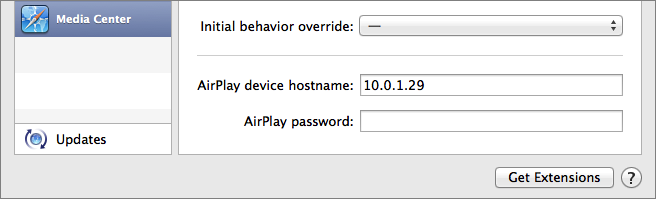
Figure 26: Working at the bottom right of the Safari Preferences window, tell the Media Center Safari extension how to find your Apple TV by telling it the Apple TV’s IP address (hostname).
- In the next field, enter your Apple TV’s AirPlay password, if it has one. (If you forget to input the password, you’ll be presented with an undismissable password prompt when you try to AirPlay a video, requiring you to quit Safari to continue.)
With Media Center configured, try watching an HTML5 video. Control-click the video and choose Send via AirPlay (Figure 27). The video begins playing on your Apple TV!
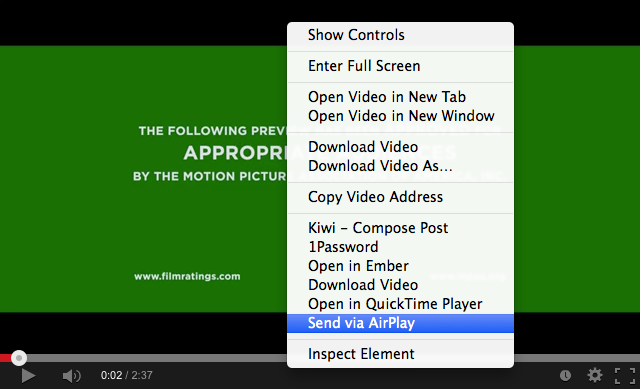
Figure 27: Once Media Center is configured, you can AirPlay any HTML5 video with a couple of clicks.
To work around the fact that Flash and Silverlight videos aren’t supported, or if you have trouble with YouTube videos, you may need to install the ClickToPlugin Safari extension (also by Marc Hoyois) and the YouTube5 Safari extension (donationware by Vertical Forest). These extensions cause many video sites to fall back to the necessary HTML5 video format instead of Flash or Silverlight. Open Safari’s preferences and configure them in a similar manner to how you configured Media Center.
Mirror from a Mac
10.8 Mountain Lion and 10.9 Mavericks can mirror audio and video to your Apple TV—that is, whatever you see or hear on your Mac is duplicated on the Apple TV. This enables you to give presentations, view content not available on Apple TV or iOS, or even play Mac games—though you’ll have to deal with a little lag.
To turn on mirroring, click the AirPlay icon in the menu bar and choose your Apple TV. The icon turns blue, indicating that AirPlay is active. Alternatively, you can turn AirPlay on or off in the Displays pane of System Preferences.
Mirror from Windows & Older Macs
AirPlay Mirroring is great, but what if you use Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard or Windows? AirParrot ($9.99) is a third-party alternative that supports 10.6.8 Snow Leopard or later and Windows XP or later.
Once launched, AirParrot lives in your menu bar on the Mac or the System Tray in Windows. Select the Apple TV to mirror your display to, then select which screen you wish to mirror. By default, AirParrot only displays video. If you want audio mirroring as well, select Start Audio from the menu and follow the onscreen prompts to install the required audio driver.
AirParrot has one advantage over AirPlay Mirroring: it can mirror a single window instead of the whole screen. From the menu, choose Specific App, then the desired app, then the specific window.
Extend a Mavericks Desktop
In Mavericks, by default, AirPlay Display mirrors your Desktop, but you can instead “extend” your Desktop right onto your TV screen through your Apple TV. You might do this to display content on the TV while you continue to work on your Mac. To accomplish this, first click the AirPlay icon in the menu bar and choose Apple TV. Second, open the AirPlay menu again and choose Extend Desktop (Figure 28).
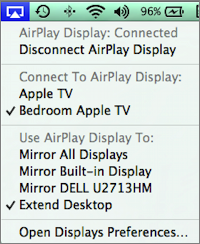
Figure 28: To use your TV screen as an additional Mac monitor, choose both your Apple TV and the Extend Desktop command from the AirPlay menu in the menu bar.
Your TV now acts as an additional monitor—if you’ve never used a Mac with two displays before, note that you can move your pointer and drag your windows between the two screens!
To see how your monitors are arranged or to change their virtual arrangement, open the Displays pane of System Preferences and click Arrangement. In the Arrangement view, you can drag the screens to adjust their positions; for example, you might want your laptop to be “below” the Apple TV screen so that when you mouse off the bottom of the TV screen, your pointer appears at the top of your laptop screen (For a detailed analysis of multiple displays in Mavericks, see Jason Snell’s Macworld article.)
AirPlay from an Apple TV
Your Apple TV isn’t just an AirPlay receiver; it’s also an AirPlay audio transmitter. It can send audio to AirPlay speakers, an AirPort Express base station (with a connected AirPlay speaker), or even another Apple TV!
You could use this capability, for example, to supplement lousy TV speakers without fussing with a receiver or shelling out for a soundbar. Or, you can keep your Apple TV’s overall volume lower by putting an AirPlay speaker next to the couch.
It’s easy to set up. On the Apple TV, open Settings > AirPlay, scroll down to Speakers, and select your desired speaker (Figure 29). Unfortunately, it’s a pain to flip back and forth between different speakers, making it annoying, for instance, to play iTunes Radio music through different speakers than you want to use when watching TV.
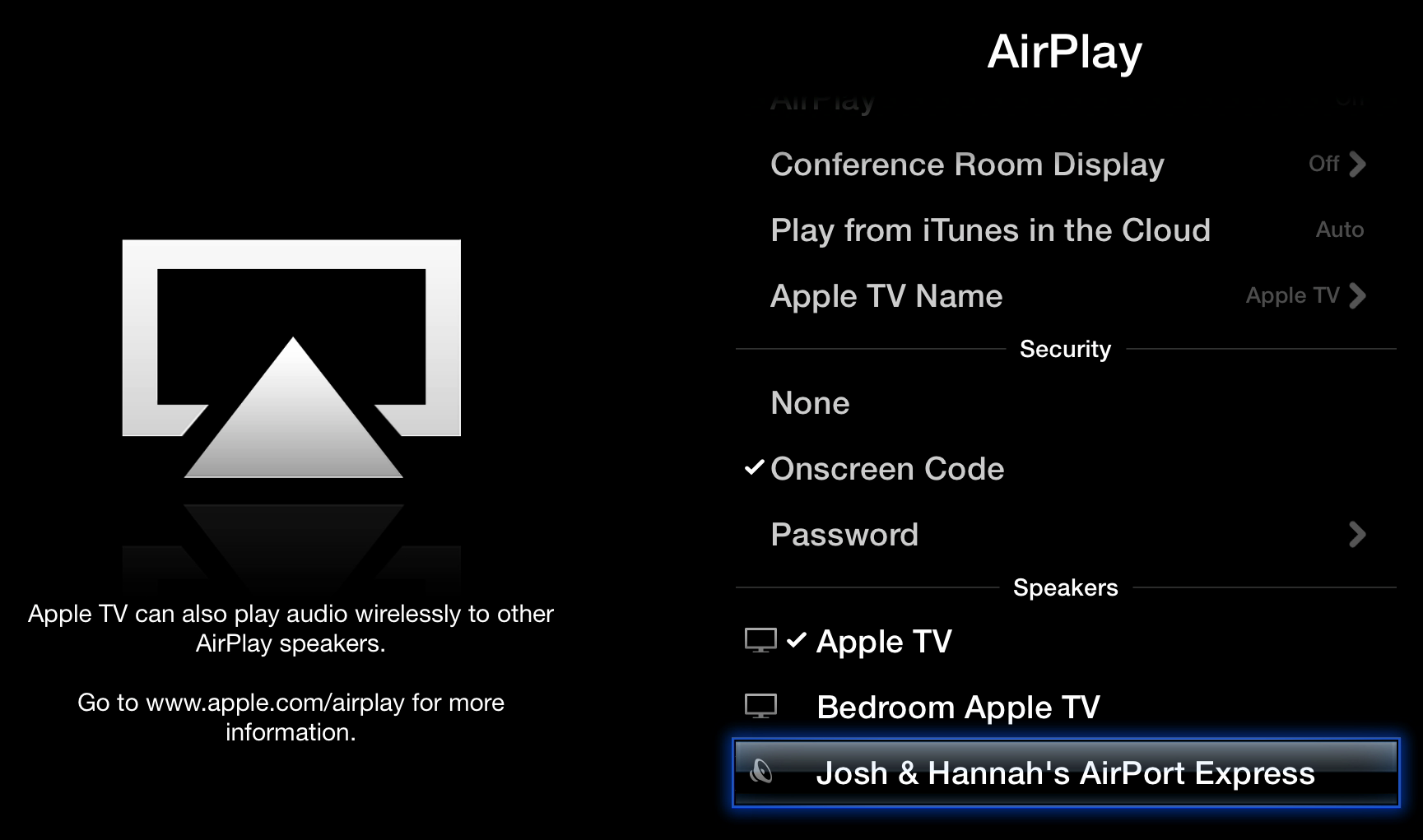
Figure 29: You can send audio from the Apple TV to any AirPlay receiver—even another Apple TV!
I’ll cover adjusting the output volume in later chapters, as it’s a bit different for movies and music, but regardless, you can access the AirPlay volume control by holding down the Select button on the Apple Remote while watching a video or listening to audio.