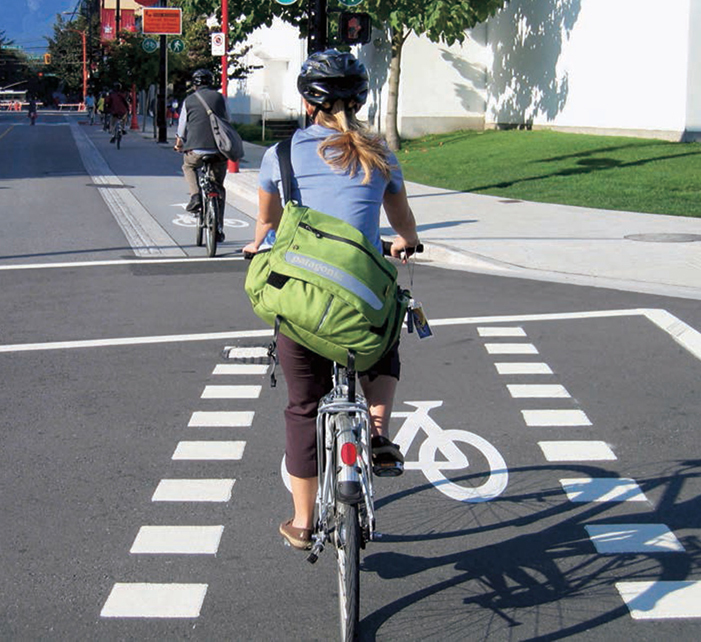

Intersection Crossing Markings

VANCOUVER, BC (PHOTO: WWW.PEDBIKEIMAGES.ORG, CARL SUNDSTROM)
Intersection crossing markings indicate the intended path of bicyclists. They guide bicyclists on a safe and direct path through intersections, including driveways and ramps. They provide a clear boundary between the paths of through bicyclists and either through or crossing motor vehicles in the adjacent lane.
This guidance covers a number of different marking strategies currently in use in the United States and Canada. Cities considering implementing markings through intersections should consider standardizing future designs to avoid confusion.
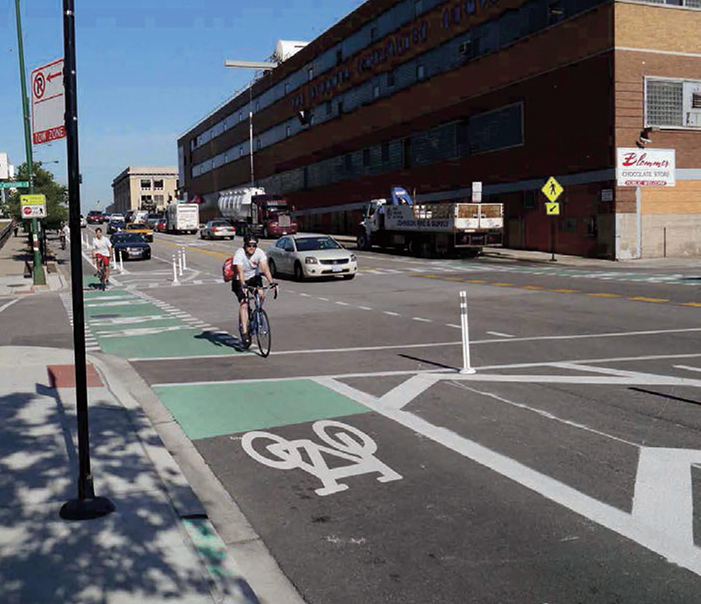

CHICAGO, IL
Benefits
Raises awareness for both bicyclists and motorists to potential conflict areas.60
Reinforces that through bicyclists have priority over turning vehicles or vehicles entering the roadway (from driveways or cross streets).61
Guides bicyclists through the intersection in a straight and direct path.
Reduces bicyclist stress by delineating the bicycling zone.62
Makes bicycle movements more predictable.
Increases the visibility of bicyclists. Reduces conflicts between bicyclists and turning motorists.63

NEW YORK, NY
Best estimates for safety effects of one blue cycle crossing in a junction are a reduction of 10% in accidents and 19% in injuries.
Jensen, S. U. (2008). Safety effects of blue cycle crossings: A before-after study. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 40(2), 742-750.

AUSTIN, TX (PHOTO: AUSTIN TRANSPORTATION DEPARTMENT)
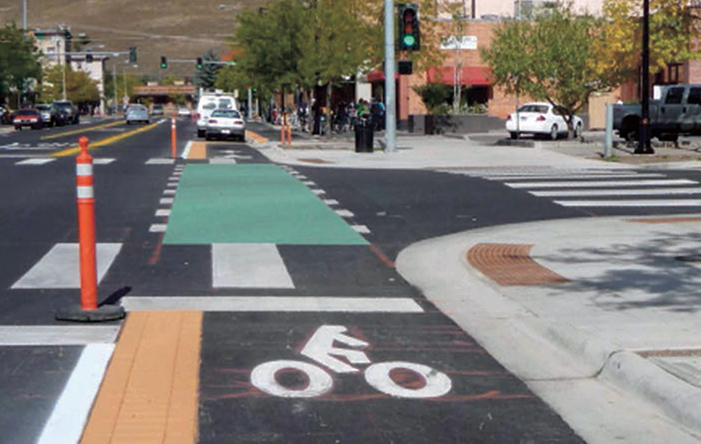

MISSOULA, MT
Typical Applications
Across signalized intersections, particularly through wide or complex intersections where the bicycle path may be unclear.
Along roadways with bike lanes or cycle tracks.
Across driveways and Stop or Yield-controlled cross-streets.
Where typical vehicle movements frequently encroach into bicycle space, such as across ramp-style exits and entries where the prevailing speed of ramp traffic at the conflict point is low enough that motorist yielding behavior can be expected.
May not be applicable for crossings in which bicycles are expected to yield priority, such as when the street with the bicycle route has Stop or Yield control at an intersection.

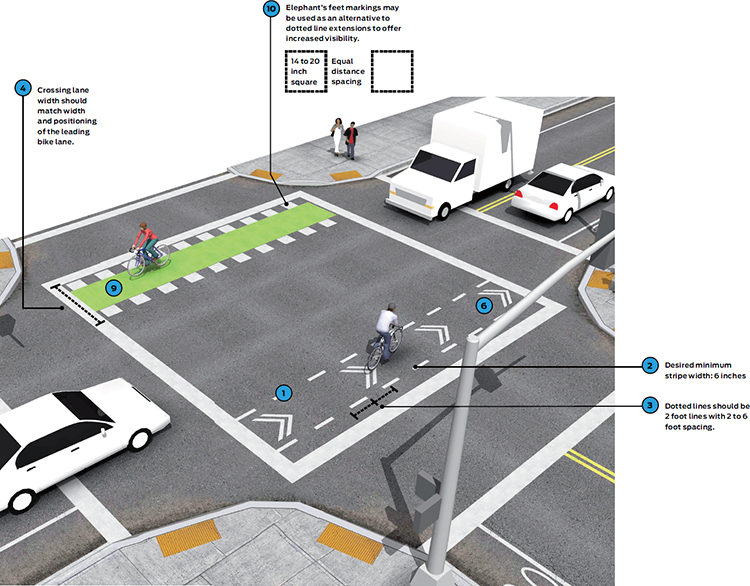
Required Features
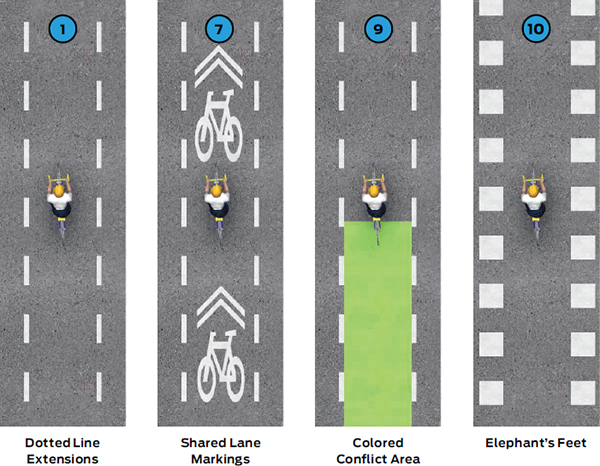
 Dotted lines shall bind the bicycle crossing space. See MUTCD Section 3B.08 for dotted line extensions through intersections.64
Dotted lines shall bind the bicycle crossing space. See MUTCD Section 3B.08 for dotted line extensions through intersections.64
 Striping width shall be a minimum of 6 inches adjacent to motor vehicle travel lanes and shall otherwise match the width and lateral positioning of leading bike lane striping, except when using elephant’s feet markings.65
Striping width shall be a minimum of 6 inches adjacent to motor vehicle travel lanes and shall otherwise match the width and lateral positioning of leading bike lane striping, except when using elephant’s feet markings.65
Recommended Features
 Dotted lines should be 2 foot lines with 2 to 6 foot spacing. Markings should be white, skid resistant and retro-reflective.
Dotted lines should be 2 foot lines with 2 to 6 foot spacing. Markings should be white, skid resistant and retro-reflective.
 Crossing lane width should match width and positioning of the leading bike lane.
Crossing lane width should match width and positioning of the leading bike lane.
 On crossings of two-way paths and cycle tracks, markings should indicate that there is two-way traffic either by marking the path center line through the intersection, or by marking bicycle silhouettes and/or chevrons in opposite directions in the two lanes. See Two-Way Cycle Tracks.
On crossings of two-way paths and cycle tracks, markings should indicate that there is two-way traffic either by marking the path center line through the intersection, or by marking bicycle silhouettes and/or chevrons in opposite directions in the two lanes. See Two-Way Cycle Tracks.
Optional Features
 Chevrons may be used for increased visibility within conflict areas or across entire intersections. Placement shall be in the middle of the moving lanes, and close to crosswalks.
Chevrons may be used for increased visibility within conflict areas or across entire intersections. Placement shall be in the middle of the moving lanes, and close to crosswalks.
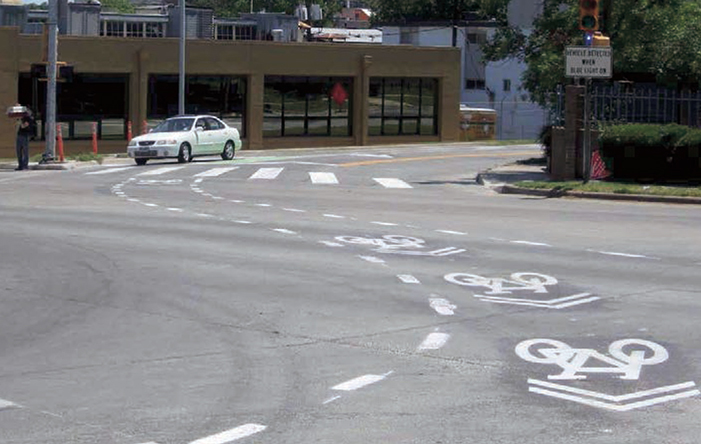
 Shared lane markings (MUTCD Figure 9C-9) may be used for increased visibility within conflict areas or across entire intersections. Placement shall be in the middle of the moving lanes, and close to crosswalks.66
Shared lane markings (MUTCD Figure 9C-9) may be used for increased visibility within conflict areas or across entire intersections. Placement shall be in the middle of the moving lanes, and close to crosswalks.66
 Helmeted rider or bicycle symbol pavement markings may be used for increased visibility within conflict areas or across entire intersections. Placement should consider a rotated symbol facing cross-traffic in the middle of the bicycle lane.67
Helmeted rider or bicycle symbol pavement markings may be used for increased visibility within conflict areas or across entire intersections. Placement should consider a rotated symbol facing cross-traffic in the middle of the bicycle lane.67
 Colored pavement may be used for increased visibility within conflict areas or across entire intersections.68
Colored pavement may be used for increased visibility within conflict areas or across entire intersections.68
 Elephant’s feet markings may be used as an alternative to dotted line extensions to offer increased visibility. If used, the markings should be 14 to 20 inches square, with equal distance spacing between markings. Markings should be positioned on outside of lane.69
Elephant’s feet markings may be used as an alternative to dotted line extensions to offer increased visibility. If used, the markings should be 14 to 20 inches square, with equal distance spacing between markings. Markings should be positioned on outside of lane.69
 Combinations of several of the listed strategies may be considered to increase visibility.
Combinations of several of the listed strategies may be considered to increase visibility.
 Yield Lines, also known as “Sharks Teeth” may be used when crossing driveways and alleyways to mark the edge of the bike lane.70
Yield Lines, also known as “Sharks Teeth” may be used when crossing driveways and alleyways to mark the edge of the bike lane.70

CHICAGO, IL
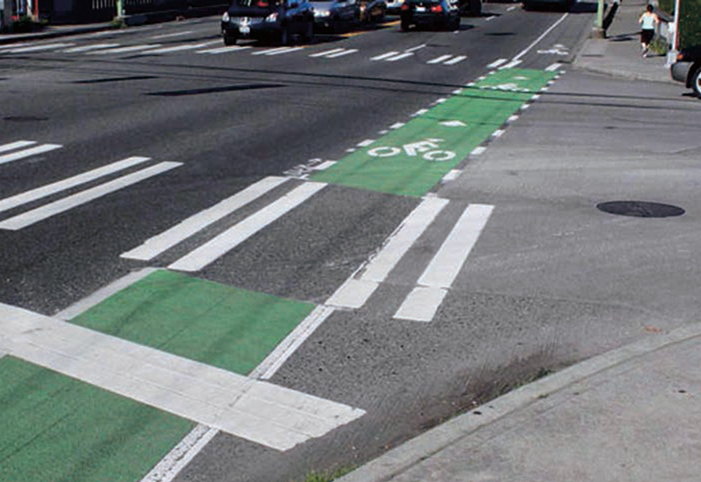

SEATTLE, WA
Maintenance
Routine roadway/utility maintenance.
Because the effectiveness of marked crossings depends entirely on their visibility, maintaining marked crossings should be a high priority.
Treatment Adoption and Professional Consensus
Commonly used in dozens of European bicycle friendly cities.
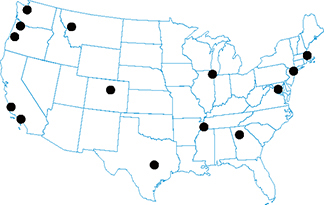
Seen in the form of dotted line extensions in most US bicycle-friendly cities.
• Austin, TX
• Boston, MA
• Cambridge, MA
• Chicago, IL
• Decatur, GA
• Denver, CO
• Eugene, OR
• Long Beach, CA
• Memphis, TN
• Missoula, MT
• New York, NY
• Portland, OR
• San Francisco, CA
• Seattle, WA
• Washington, DC

CHICAGO, IL