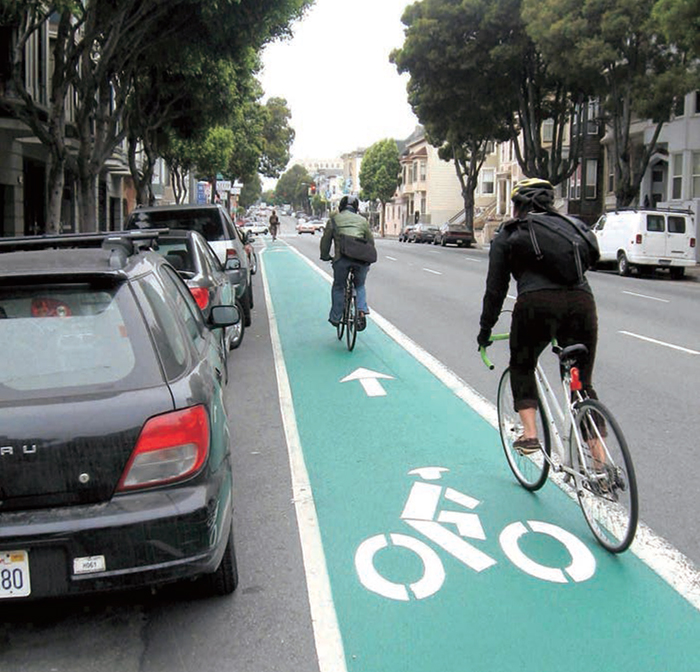

Colored Bike Facilities

SAN FRANCISCO, CA
Colored pavement within a bicycle lane increases the visibility of the facility, identifies potential areas of conflict, and reinforces priority to bicyclists in conflict areas and in areas with pressure for illegal parking. Colored pavement can be utilized either as a corridor treatment along the length of a bike lane or cycle track, or as a spot treatment, such as a bike box, conflict area, or intersection crossing marking. Color can be applied along the entire length of bike lane or cycle track to increase the overall visibility of the facility. Consistent application of color across a bikeway corridor is important to promote clear understanding for all users.
Benefits
Promotes the multi-modal nature of a corridor.
Increases the visibility of bicyclists. Discourages illegal parking in the bike lane.
When used in conflict areas, raises motorist and bicyclist awareness to potential areas of conflict.
Increases bicyclist comfort though clearly delineated space.93
Increases motorist yielding behavior.94
Helps reduce bicycle conflicts with turning motorists.
Anecdotally, most cyclists like the green paint treatment and believe that it is more effective at keeping cars from parking in bike lanes than regular striping. In particular, cyclists cite the conspicuousness of cars parked in green painted lanes as a deterrent to drivers parking there.
New York City Department of Transportation. (2011). Evaluation of Solid Green Bicycle Lanes, to Increase Compliance and Bicycle Safety.
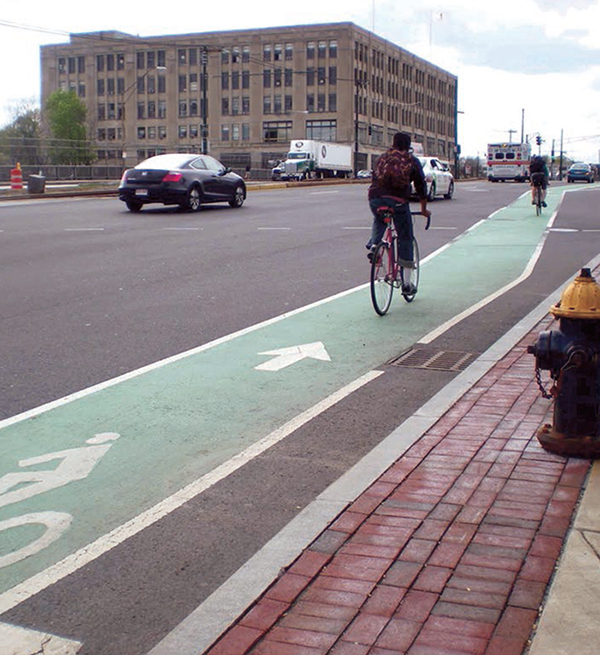

BOSTON, MA

SEATTLE, WA
Typical Applications
Within bike lanes or cycle tracks.
Across turning conflict areas such as vehicle right turn lanes.
Across intersections, particularly through wide or complex intersections where the bicycle path may be unclear.95
Across driveways and Stop or Yield-controlled cross-streets.
Where typical vehicle movements frequently encroach into bicycle space, such as across ramp-style exits and entries where the prevailing speed of turning traffic at the conflict point is low enough that motorist yielding behavior can be expected.
Color may be applied along an entire corridor, with gaps in coloring to denote crossing areas.96
Facility designers should match coloring strategy to desired design outcomes of projects.
May not be applicable for crossings in which bicycles are expected to yield right of way, such as when the street with the bicycle route has Stop or Yield control at an intersection.
Bicyclists familiar with more traditional sharrows have noted that the additional emphasis resulting from the green pavement paint appears to be creating an heightened awareness by the motorists in the lane.
City of Long Beach. (2010). Final Report: Second Street Sharrows and Green Lane in the City of Long Beach, California (RTE 9-113E).
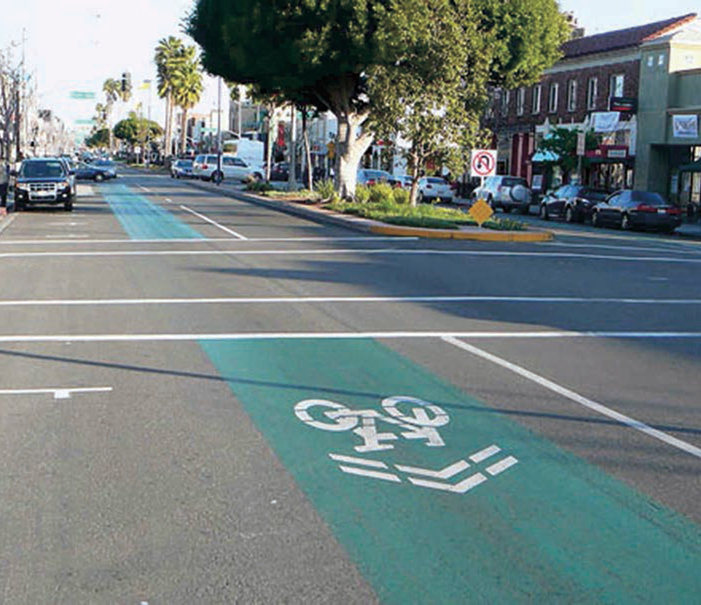

LONG BEACH, CA

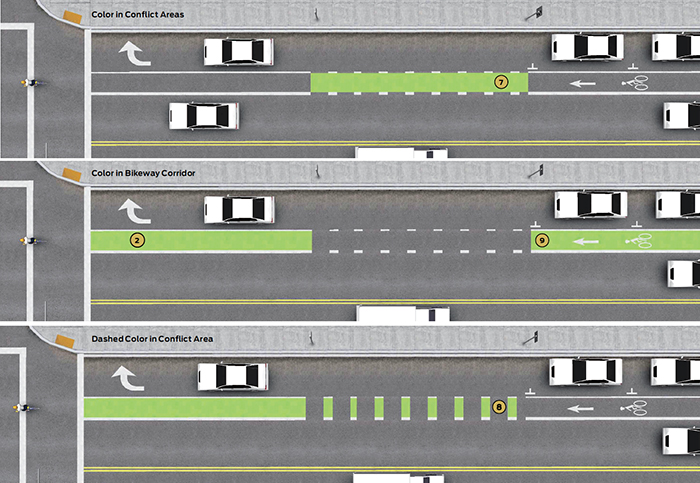
Required Features
 The color green shall be used to minimize confusion with other standard traffic control markings.97
The color green shall be used to minimize confusion with other standard traffic control markings.97
 Color shall be applied to the road surface to delineate space, increase visibility, and emphasize proper vehicle priority.98
Color shall be applied to the road surface to delineate space, increase visibility, and emphasize proper vehicle priority.98
 Normal white bike lane lines shall be provided along the edges of the colored lane to provide consistency with other facilities and to enhance nighttime visibility.
Normal white bike lane lines shall be provided along the edges of the colored lane to provide consistency with other facilities and to enhance nighttime visibility.
Recommended Features
 The colored surface should be skid resistant and retro-reflective.
The colored surface should be skid resistant and retro-reflective.
 A “Yield to Bikes” sign should be used at intersections or driveway crossings to reinforce that bicyclists have the right-of-way at colored bike lane areas.99
A “Yield to Bikes” sign should be used at intersections or driveway crossings to reinforce that bicyclists have the right-of-way at colored bike lane areas.99
 The configuration of color should be consistently applied throughout the corridor.
The configuration of color should be consistently applied throughout the corridor.
Optional Features
 Color may be applied within conflict areas for increased visibility of bicyclists.
Color may be applied within conflict areas for increased visibility of bicyclists.
 Color may be applied along a dashed pattern within a dashed bicycle lane to indicate merging areas. Dashed application of colored pavement mimics typical traffic striping layouts, where dashed markings indicate areas where merging maneuvers are permitted.100
Color may be applied along a dashed pattern within a dashed bicycle lane to indicate merging areas. Dashed application of colored pavement mimics typical traffic striping layouts, where dashed markings indicate areas where merging maneuvers are permitted.100
 Color may be applied along a corridor, with gaps in coloring to denote crossing areas. When used in this fashion, color can distinguish the bicycle facility along its entire length. This is particularly useful in high traffic situations or areas where traffic may encroach into the bike facility.101
Color may be applied along a corridor, with gaps in coloring to denote crossing areas. When used in this fashion, color can distinguish the bicycle facility along its entire length. This is particularly useful in high traffic situations or areas where traffic may encroach into the bike facility.101
 Color may be used to supplement shared lane markings for added visibility.102
Color may be used to supplement shared lane markings for added visibility.102
Best estimates for safety effects of one blue cycle crossing in a junction are a reduction of 10% in accidents and 19% in injuries.
Jensen, S. U. (2008). Safety effects of blue cycle crossings: A before-after study. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 40(2): 742-750.

TUSCON, AZ

SAN FRANCISCO, CA (PHOTO: SFSTREETSBLOG)

CHICAGO, IL
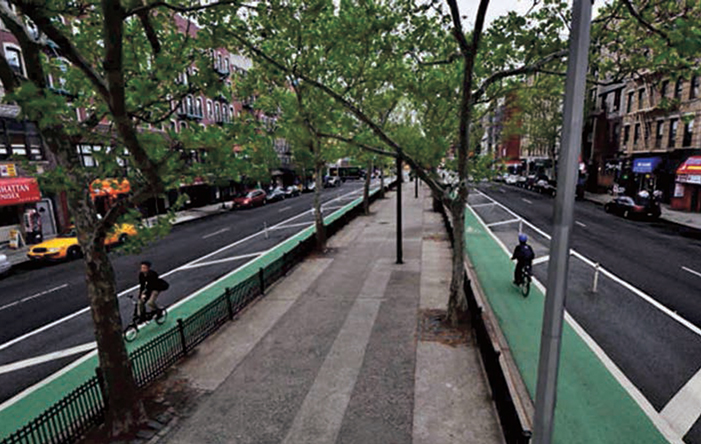

NEW YORK, NY

SEATTLE, WA

AUSTIN, TX
Maintenance
Colored pavement requires varying levels of maintenance depending on materials.
Because the effectiveness of markings depends entirely on their visibility, maintaining markings should be a high priority.
Colored facilities should be maintained to be free of potholes, broken glass, and other debris.
AUSTIN, TX
Treatment Adoption and Professional Consensus
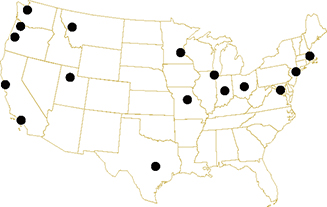
Application of colored pavement is seen in the following US cities:
• Austin, TX
• Boston, MA
• Cambridge, MA
• Chicago, IL
• Columbia, MO
• Columbus, OH
• Eugene, OR
• Indianapolis, IN
• Long Beach, CA
• Madison, WI
• Minneapolis, MN
• Missoula, MT
• New York, NY
• Portland, OR
• Salt Lake City, UT
• San Francisco, CA
• Seattle, WA
• Washington, DC