APPENDIX II
The Contained Mind Metabelief: Definition of Elements
Here we define mind as the software/programs/metaprograms contained in the computational domain of a central nervous system (C.N.S.) in a biological system that supports its essential processes and provides its inputs/outputs from/to an external reality (e.r.). Within the computational domain, an observer/operator (ob/op) exists as that aspect of the computational domain that apparently distinguishes/observes/ operates/computes at a level of computation one level above that called the Self–referential metaprogrammatic level, at least eight levels above the “machine language level” of the operations of the C.N.S. (zeroth level).
COMPUTATION LEVELS
(0) elementary units of neuronal computation. Computational levels: (1) primitive neuron network computations between cellular units in nets; (2) computations by nuclear assemblies of networks; (3) computations by systems of nuclei relations; (4) coordination of computations by nuclear systems; (5) programs regulating coordinations of 4; (6) metaprograms regulating programs of 5; (7) metaprograms creating Self–referential properties; (8) observer/operator metaprograms derived from 7; (9) supra–observer/operator metaprograms specifying origins/states/ domains/existence of the observer/operator metaprograms; (10) unknowns in/above/below all preceding levels.
STRUCTURAL INTACTNESS
A whole adult noninjured (“nonreduced”) C.N.S. is essential for generating levels 6 and above.
SIMULATIONS
“Simulations” (∇’s) are defined as one group of metaprograms at level 7, which are only partially presented to be experienced by ob/op.
“E.r. simulations”: One group of simulations represents the external reality (e.r. ∇’s) and is computed from current C.N.S. input/output computations at lower levels. Such e.r. ∇’s can be partially stored and reactivated from storage.
“Ob/op simulations (ob/op ∇’s)”: Another group of simulations represents the current observer/operator set of metaprograms and is computed in levels 6, 7, 8, and 9.
“I.r. simulations” (i.r. ∇’s) in the presence of e.r. inputs/outputs: In the presence of feedback of a C.N.S. with an external reality, the ob/op operates with the e.r. simulations continuously modulated by the changing input/output relations. The internal reality (defined below) may be reductively simulated as a void in the head/body, or as any other idiosyncratic set of i.r. ∇’s.
“I.r. experience”: The observer/operator exists exclusively in a metaprogrammatic computational domain (levels 8 and 9). If isolated from current e.r. computational necessities, e.r. simulations are free of input/output constraints and can be recomputed in new forms by the observer/operator (level 8) and by the supra–observer/operator metaprograms (level 9). Under these isolation /confinement/solitude conditions (such as isolation tank/anesthesia /psychedelic states /trance/sleep/coma), the observer/operator observes/acts exclusively on/in the computations of levels 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 without modifications introduced by here/now inputs/outputs to/from the external reality.
Under these conditions, the observer/operator exists in an exclusively internal reality (unmodulated by feedback through all levels with the external reality). This internal reality is created exclusively within the confines of the C.N.S.28
SOME STATES OF BEING/EXISTENCE OF THE ISOLATED OBSERVER/OPERATOR (I–OB/OP)
| STATE 1. | E.r. simulations continuing in isolation, intact ob/op as single unique system; an “as if real external reality” with intact feedback from/to body; body simulations modulated by continued body/C.N.S. feedback. |
| STATE 2. | Body/C.N.S. feedback missing/inhibited/chemically decreased; e.r. simulations continuing; intact ob/op; “as if real external reality” with body simulation operating freely within the simulated “external reality” (“as if real body” free to move in simulated e.r.). |
| STATE 3. | Body simulations decreased to vanishingly small values; ob/op intact as a point observer/operator. E.r. simulations (e.r.∇’s) strong. Ob/op in an “as if real external reality” freely moving anywhere, any place, any time (from subatomic to galactic simulations) within the unique constraints of level 9 (supra–ob/op level) and of level 10 (at present unknown constraints). Ob/op free to change apparent size from a point to filling any apparent “as if real external reality.” |
| STATE 4. | Body simulations and e.r. simulations reduced toward zero value. Ob/op free to vary parameters within ob/op simulations (ob/op ∇’s) allowed by level 9. Ob/op states of being/existence vary from a point to any domain allowed. |
| STATE 5. | Body simulations (body∇’s), e.r. simulations (e.r. ∇’s), ob/op simulations (ob/op ∇’s) each reduced to zero. Ob/op exists, feeding back upon itself exclusively, no “outer” references, no simulations left: pure Self–referential observer/operator totally isolated. |
| STATE 6. | Zeroed out ob/op. No memory allowed on return to other states of being. |
General rules for simulations (∇’s):
- Any simulation can be stored as inactive.
- Any simulation can be activated from storage.
- When a simulation is stored, it is absent in the ob/op domain.
- When activated, a simulation acts in the ob/op domain.
In the following discussion, tables and diagrams, a stored simulation is represented by its absence in the ob/op domain by the symbol “0.” Currently active simulation in the ob/op domain is symbolized by “1”.
Let:
observer/operator = ob/op
simulations = ∇’s
external reality = e.r.
internal reality = i.r.
body = body
a given domain missing = 0
a given domain present = 1
TABLE 1. Six States of Being for (ob/op):

TABLE 2. Equivalences Between the Six Formulated States and Equivalent Classical Labels
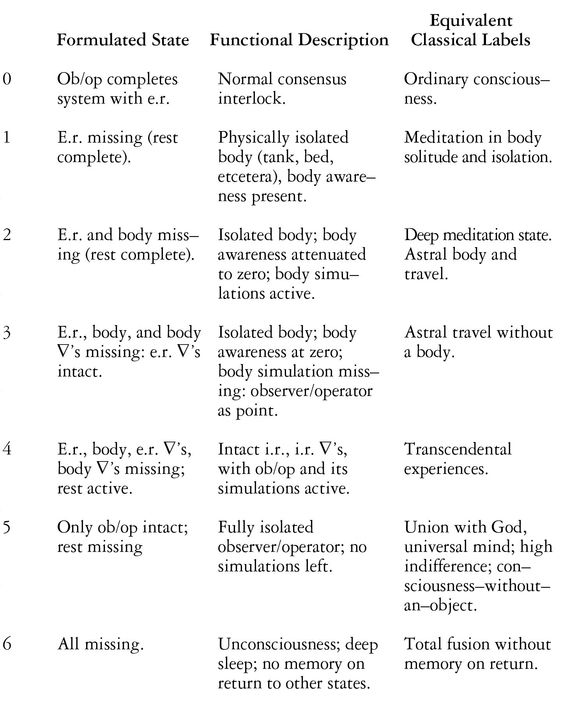
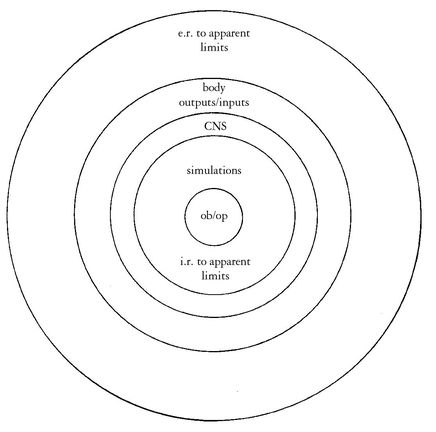
FIGURE 1: Simplified Diagram of Relations

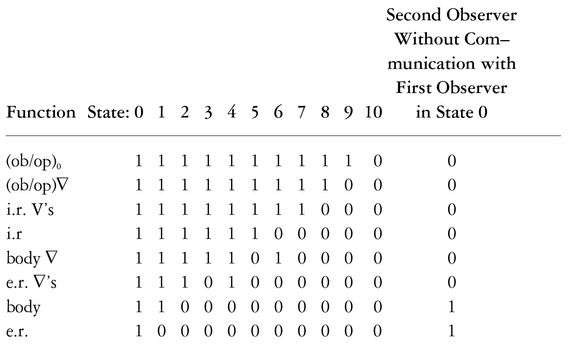
FIGURE 2: Diagram of (ob/op)0 and 2nd Observer/Operator (ob/op)1
Watching Body
EXERCISES
No. 1 Problem for the Reader
Describe the above ten states. (Hint: Expand Table 2—Formulated State, Functional Description, and Equivalent Classical Labels.)
No. 2 Problem
Construct Rest of Cases of States of Being (enlarge table to include all states conceivable).
Define “experience” vs. “simulation.”
E.r. experience vs. e.r. simulations experienced.
I.r. experience vs. i.r. simulations experienced.
DEFINITIONS
Experience: This concept is here distinguished into two domains: the e.r.–e.r. ∇ domain, and the i.r.–i.r. ∇ domain. (The usual definitions of this term in dictionaries imply: [1] external reality feedback with Self over time [2] religious experience which affirms or reaffirms faith in a particular belief system.)
The set of computations that currently generates external reality simulations (e.r. ∇’s) interlocked with the observer/operator and with the computed e.r. inputs/outputs operating synchronously, generates what is called “external experience.”
The set of computations that currently generates internal reality simulations (i.r. ∇’s) interlocked with the observer/operator and with the i.r. computations operating synchronously, generates what is called “internal experience.” (See example below under Goodness–of–fit section.)
Simulation: That term is used here in the nonpejorative sense used in computer software terminology: a system of metaprograms, programs and subroutines that represents/models/simulates/reproduces the behavior of another system in a quantitatively similar way within a computer, here a biocomputer.
Goodness–of–fit: The measurements of the differences between the behavior of a simulation and the system simulated: if the differential measurements are within certain specified limits (above threshold for the detection of differences) the goodness–of–fit is adequate and the simulation is said to work satisfactorily. An example from e.r. vs. e.r. ∇:
Example: (1) One walks through a room containing furniture many times over days. One very dark night the lights suddenly fail. One walks through the room using a “visual” simulation of the room for navigation, avoiding the unseen furniture. The goodness–of–fit between the e.r. furniture loci and the e.r. simulation “furniture loci” operating in the C.N.S. is adequate to avoid collisions with the e.r. furniture.
(2) Someone else moved a chair; the goodness–of–fit is inadequate: a collision results. In this example, e.r. is interlocked in a time sequence with e.r. ∇.
The e.r. experience is paralleled by an i.r. experience of a simulation of an e.r.
Physical Isolation Experience: In physical isolation (tank), e.r. inputs/outputs approach zero. In the solitude/isolation/confinement tank, the i.r. experience is among simulations, either e.r. and/or i.r.
Once free of e.r. experience simulations, the i.r. experience is that of i.r. and its simulations.
I.r. experience is of the new/unique/never–before–experienced.
I.r. simulation experience is that which is familiar/repeated/programmed from the i.r. experience of Self/others.
Pure Simulation Experience: As above in Physical Isolation Experience.
Simulations, ≡ ∇ ≡a simulation: Free of what is simulated. E.r. ∇ free of e.r.; i.r. ∇ free of i.r. (This is characterized by the “as if” property: simulations are “as if true”; direct experiences are true):
Metabelief operator ≡ ∇2 ≡ controller of simulations: free of simulation, domain control.
Ob/op ≡ ∇3 controller of metabelief operators: free of metabelief operators controlled.
Supra–ob/op: ∇4 free of ob/op control.
(∇ ≡ “del”)
∇0 ≡ a metaprogram controlling a set of programs
∇1 ≡ a simulation controlling a set of metaprograms
∇2 ≡ a meta–simulation operator controlling simulations,∇’s
∇3 ≡ ob/op controlling meta–simulation operators, ∇2s
∇4 ≡ supra–ob/op controller, controlling ob/op, ∇3
∇1 A belief is a fixed simulation controlling a set of metaprograms or a set of fixed simulations (lasting a long–enough time to be detected by ob/op0 or e.r. ob/opn).
∇2 A metabelief operator is free of beliefs and controls beliefs. (Cf. ∇2, above.)
Multiple ob/ops
In the above definitions, it is implicitly assumed that ob/op is a single unique observer/operator. This may not be the case. ∇4 can introduce one or more additional ∇3s to a total of as much as five ∇3s. (Cf. Three Faces of Eve by Thigpen and Cleckley,29 and Morton Prince’s experiments in hypnosis, for examples.)
∇4 can introduce simulations of the (ob/op)0 in subtle ways, placing limits on (ob/op)0 and splitting off other “entities” experienced by (ob/op)0 “as if coming from e.r. or i.r.” which communicate with/control /are controlled by (ob/op)0. (Cf. Programming and Metaprogramming in the Human Biocomputer and The Center of the Cyclone.)