Configuring a Directory Service Account in Outlook 423
LIGHTWEIGHT Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a standard method for querying directory services. For example, you can query LDAP servers for the address, phone number, or other information associated with an entry in the directory. Windows Server uses LDAP as the primary mechanism for accessing Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS).
This chapter explores LDAP and explains how to configure LDAP directory service accounts in Microsoft Outlook 2010.
LDAP was designed to require less overhead and fewer resources than its predecessor, Directory Access Protocol (DAP), which was developed for X.500, a standards-based directory service. LDAP is a standards-based protocol that allows clients to query data in a directory service over a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection. AD DS, Novell eDirectory, IBM WebSphere, and directory services on the Internet such as Bigfoot, InfoSpace, and Yahoo! all employ LDAP to implement searches of their databases.
Note
You will find much more information about LDAP at technet.microsoft.com if you perform a search for LDAP or “Lightweight Directory Access Protocol.”
In addition to supporting email accounts, Outlook 2010 also allows you to add LDAP-based directory service accounts that enable you to query for subscriber information in the remote server’s directory. The LDAP server might be internal to your organization, hosted by another company, or one of several LDAP directories located on the Internet. With an LDAP account in your profile, you can look up names, addresses, and other information stored in the directory.
To set up and configure an LDAP account in Outlook 2010, follow these steps:
Open the Mail item in Control Panel and click E-mail Accounts. Alternatively, if Outlook 2010 is already started, click File, Account Settings, and Account Settings.
Select the Address Books tab, and then click New.
Select Internet Directory Service (LDAP), and then click Next.
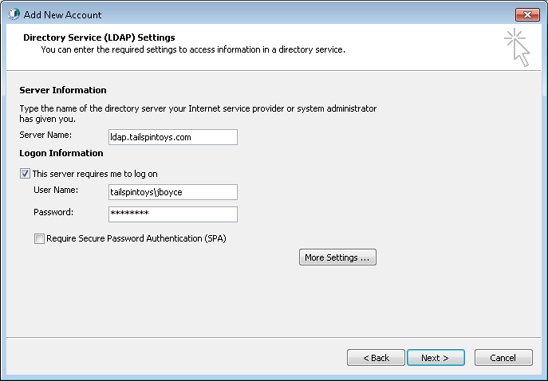
On the Directory Service (LDAP) Settings page of the Add New E-Mail Account wizard, shown in Figure 17-1, type the server name or the Internet Protocol (IP) address in the Server Name box.
If the server requires authentication, select the This Server Requires Me To Log On check box. Specify the logon credentials in the User Name and Password boxes. If you’re authenticating on a Windows Server domain controller, include the domain by entering <domain>\<user> in the User Name box, where <domain> is the domain name and <user> is the user account.
Tip
INSIDE OUT Add the domain for LDAP authentication
Failing to include the domain in the authentication string will result in the authentication error message “Failed to connect to <server> due to invalid authentication.” If you clear the This Server Requires Me To Log On check box and the server requires authentication, you’ll receive the error message “No entries were found. You may need to supply authentication information in order to be able to access the directory.” Clear this check box only if the server allows anonymous LDAP queries.
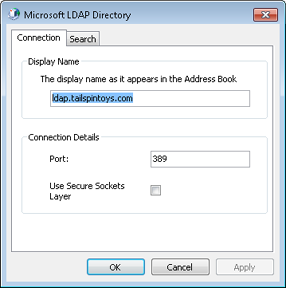
Click More Settings to open the Microsoft LDAP Directory dialog box, shown in Figure 17-2.
Change the name in the Display Name box to the name that you want Outlook 2010 to display in the address book for the directory service.
In the Port box, type the port number required by the LDAP server. The default port is 389, although you can use 3268 for most searches in an AD DS global catalog (GC).
Tip
INSIDE OUT Use two ports
Port 3268 is the default port for the AD DS GC. Certain types of data are available through one specific port, whereas other types of data are accessed through the other. For example, read-only copies of data from other domains are available only through the GC port. For that reason, you might create two directory services, one for each port.
You can select the Use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) check box to connect to the LDAP server through SSL. This option works only if the server allows an SSL connection. If using SSL, the default port is 636 (or 3269 for the GC).
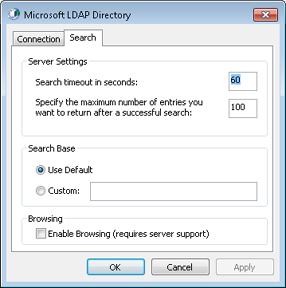
In the Microsoft LDAP Directory dialog box, click the Search tab, shown in Figure 17-3.
Specify the search time-out and the maximum number of entries you want returned in a search. In the Search Base box, either select Use Default (the Users container) or type the root for your search in the directory. If you’re searching AD DS, for example, you might enter dc=<domain>,dc=<suffix>, where <domain> is your domain name (without the domain suffix). Specify the domain suffix (net, com, org, or us, for example) as the last data item. (See the following section, Setting the Search Base, for more details.) To be able to browse the directory, select the Enable Browsing (Requires Server Support) check box. The AD DS domain controller must allow browsing for this feature to work.
Click OK to close the dialog box, and then click Next and click Finish to complete the account setup.
Note
Queries to AD DS using SSL should be directed to port 636. GC queries using SSL should be directed to port 3269.
You can use the directory service accounts created in Outlook 2010 to perform LDAP queries from within Outlook 2010.
The search base for an LDAP query specifies the container in the directory service where the query will be performed. You can set the search base to target more closely the information that you’re trying to find, but to do so, you must understand what the search base really is. (For AD DS queries, you can generally use the Default search base to locate users.)
Each entry in the directory has a Distinguished Name (DN), which is a fully qualified name that identifies that specific object. Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs) are concatenated to form the DN, which uniquely identifies the object in the directory. RDNs include the following:
cn= Common name
ou= Organizational unit
o= Organization
c= Country
dc= Domain
For example, assume that you want to search the Users container in the domain tailspintoys.com. The search base would be as follows:
cn=users,dc=tailspintoys,dc=com
Notice that the domain is represented by two dc attributes. If the domain that you are searching is microsoft.com, you would use dc=microsoft,dc=com instead.
In some cases, the part of the directory you want to search will be in a specific organizational unit (OU), or you might be setting up multiple LDAP accounts in Outlook 2010, each configured to search a specific OU. For example, perhaps your company has Sales, Marketing, Support, External Contacts, and a handful of other OUs, and you want to configure an LDAP query for each one. One solution is to add an LDAP service for each and configure the search base accordingly. For example, let’s say we’re configuring an LDAP service account to query the Support OU in the tailspintoys.com domain. The search base would be as follows: ou=support,dc=tailspintoys,dc=com.
Keep the following points in mind when deciding on a search base:
Specifying no search bases causes Outlook 2010 to retrieve objects from the entire directory.
Specifying a search base sets the branch of the directory to search in the directory tree.
If you decide to include a search base, determine the common name for the object or OU, and then add the domain. You can’t specify just the ou or cn attribute without the domain, but you can specify the domain by itself to perform a top-down search of the domain.
Note
If you need to search different branches of the directory tree, you can add multiple LDAP service accounts to your profile, each with the appropriate search base. Alternatively, add only one LDAP service account and then simply change its search base when you need to query a different branch.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Your LDAP query returns this error message: “There are no entries in the directory service that match your search criteria”
Sooner or later, you’ll attempt to query an LDAP server that you know contains at least one item meeting your search criteria, but you’ll receive an error message telling you that no entries in the directory service match your criteria. One possible cause of this problem is that the search option specified at the LDAP server might be preventing the query from completing successfully. For example, you might be issuing an “any” query, but the server is configured to treat such queries as initial queries.
You might also receive this error message if you’ve incorrectly set the LDAP directory service account properties—for example, you might have configured the account to use port 389 when the server requires SSL. Check your directory service account settings to ensure that you have specified the proper server name or address, port, and search base.
You can perform LDAP queries in Outlook 2010 by using directory service accounts you add to Outlook 2010. Follow these steps to perform an LDAP query with an LDAP server in Outlook 2010:
In Outlook 2010, click Address Book on the Home tab of the ribbon to open the Address Book window.
In the Outlook Address Book, select the directory service in the Address Book drop-down list. Depending on how the directory service account is configured (whether or not Enable Browsing is enabled), Outlook 2010 might display the contents of the directory immediately in the Address Book. When browsing is enabled, Outlook can access directory information and display it in the Address Book automatically. For information about how to enable browsing, see the section Configuring a Directory Service Account in Outlook, on page 423, and Figure 17-3. If Enable Browsing is not selected, no names will be listed. Type your search keywords and click Go to perform a search.
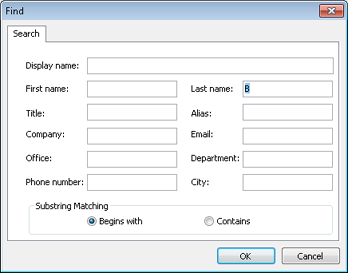
To search using specific criteria, click the Advanced Find link or choose Tools, Find. Either action opens the Find dialog box, shown in Figure 17-4.
Specify the criteria for the search, and then click OK. If objects meeting the search criteria exist within the LDAP directory, the results will show a list of all matching objects.