ON THE ATTACK
In July 1887, the South Island of New Zealand was the scene of a small outbreak at a farmhouse near Omarama. Although the initial stages of the attack are unknown, reports state that by dusk, a group of fourteen armed men dispatched three zombies in the surrounding countryside, then converged on the house for what was to be an easy mop-up. One man was sent to reconnoiter the house. He entered; screams, moans, and shots were heard; then nothing. Another man was sent in. At first all was quiet. He was seen leaning out of an upstairs window, shouting that he had found a half-eaten body but nothing else. Suddenly a decomposing arm appeared behind him, grabbed his hair, and pulled him inside. The others raced in to help him. No sooner had they entered the house when five zombies attacked from all directions. Long hand weapons such as axes and scythes were useless in tight quarters. The same was true of long-barreled rifles. Wild pistol shots accidentally killed three men outright and wounded another two. At the height of the melee, one of the survivors panicked, raced from the house, grabbed a lantern, and threw it through a window. A subsequent search found only charred skeletons.
This chapter is designed to help plan a civilian search-and-destroy mission. As has been stated before, various government agencies will have their own equipment and doctrine (hopefully) for dealing with such unconventional warfare. If they show up, great. Sit back, relax, and watch your tax dollars hard at work. But as has also been stated before, what if those we pay and expect to protect us are nowhere to be found? In this case, responsibility for eradicating the undead menace is up to you and those you can convince to join you. Every rule, every tactic, every tool and weapon in this section have been carefully tailored for just such a contingency. All have been taken from actual combat. All have been tested and proven battle-ready for that moment when retreat has ended and the time has come to hunt the hunters.
GENERAL RULES:
1. COLLECTIVE RESPONSE: As with any other type of combat, undead warfare should never be a solo mission. As stated before, in Western—particularly American—culture, there is the myth of the individual superbeing. One man or woman, well-armed and highly skilled, with nerves of steel, can conquer the world. In truth, anyone believing this should simply strip naked, holler for the undead, then lay down on a silver platter. Not only will going it alone get you killed—it may also create one more zombie. Working together, always together, has shown to be the only successful strategy for annihilating an undead army.
2. KEEP DISCIPLINE: If you take nothing else from this chapter, if correct armament, equipment, communication, and tactics seem a silly waste of time, if only one tool goes with you into battle against the living dead, let it be strict, unwavering, unquestionable discipline. A self-controlled group, regardless of numbers, can inflict infinitely more damage on an undead enemy than any well-armed mob. Since this book is written for civilians, not military personnel, discipline of this caliber is difficult to come by. When selecting your team, make sure that the men and women under your command understand your instructions. Use clear, concise language. Do not resort to military or other coded jargon unless your team are all familiar with its meaning. Make sure there is one leader, acknowledged and respected by the entire group. Make sure there are no personal differences or, at the very least, that they are left far behind. If these demands mean thinning your ranks, so be it. Your team should and must function as one. If not, a plethora of nightmarish possibilities awaits. Large, well-equipped groups have been utterly destroyed when their members have panicked, scattered, or turned on each other. Forget what you’ve seen in movies about loose bands of locals, beer and shotguns in hand, protecting humanity from the zombie menace. In real life, such a gaggle would be little more than a gun-toting buffet.
3. BE ALERT: Maybe you’re elated from a successful fight; maybe you’re tired from days without sleep; maybe hours upon hours of fruitless searching have left you mind-numbingly bored. For whatever reason, never let your guard down. The undead could be anywhere, their sounds muffled, their signs ignored. No matter how safe the area seems, be alert, be alert, be alert!
4. USE GUIDES: Not every battle will occur on home turf. Before entering an area unfamiliar to you or your group, recruit someone with local knowledge. He or she can point out all the hiding places, all the obstacles, all the escape routes, and so on. Groups without guides have been known to accidentally trigger disasters by failing to know that a gas main was within their firing line or that toxic chemicals were stored in the building they had set ablaze. Successful armies throughout history have always employed locals from the territory they sought to conquer. Armies that have entered blind have usually met with defeat.
5. HAVE A BASE, HAVE SUPPORT: A team should never go into battle without having established a safe zone. This area should be well outside the target area. It should be manned by a support group with all the necessary facilities to keep you fighting. It should be easily defensible should the tide of battle turn. Fortress, hospital, supply dump, combat information center—all of these should spring to mind when you order your group to “return to base.”
6. USE DAYLIGHT: It is no accident that most horror films take place at night. Darkness has always inspired horror for one simple reason: Homo sapiens are not designed for nocturnal activity. Our lack of night vision and poor hearing and sense of smell make us creatures of the day. Although zombies are no more skilled at night fighting than we are, it has been proven that the margin of safety always drops when confronting them after dark. Daylight not only allows greater visibility but also bestows a psychological lift upon your people.
7. PLAN YOUR ESCAPE: How many zombies are you going up against? Unless you have an exact figure, make sure an escape route is always chosen, scouted, and under guard. Too often, overconfident hunters have sauntered into infested areas only to be overwhelmed by numbers they never considered. Make sure your escape path is clear, close by, and above all, clear of any obstacles. If numbers permit, leave several members of your group to keep this escape passage open. Retreating groups have sometimes been trapped when their escape route was blocked by a mass of walking dead.
8. LET THEM COME TO YOU: More than any other, this tactic allows the living to fully exploit their advantage of intelligence. A human army, knowing an attack is coming, will wait patiently, and safely, on the defense. This is why in conventional human warfare, an attacker always needs at least a three-to-one numerical advantage to ensure success. Not so with the undead. Because zombies are driven simply by instinct, they will attack no matter what the situation. This gives you the advantage of simply waiting near an infested area and letting them come to you. Make as much noise as you can, light bonfires, even send one or two fast scouts in to lure them out. When the dead come, you will be in a position of “aggressive defense,” ready to kill the majority before going in to mop up. Because this tactic has been proven the most effective, different examples of its execution will be discussed later in this chapter.
9. KNOCK!: Before entering a room, locked or otherwise, always listen for activity inside. A zombie could be on the other side of the door—docile, quiet, ready to move at the first sign of prey. How is this possible? Maybe bitten humans succumbed behind their locked doors. Maybe they were put there by other, uninformed humans who believed they were protecting their loved ones. For whatever reasons, the chances of this scenario are at least one in seven. If at first you hear nothing, make some noise. This will either galvanize any silent ghouls or confirm that the room is empty. No matter what, be on your guard.
10. BE THOROUGH: In the early stages of an outbreak, people tend to capture, not kill, zombies they have known in mortal life. When the captors have either fled or been devoured, restrained zombies may remain for years, able to repeat the cycle if released. After an area has been swept for ghouls, sweep it again. Then, sweep it again. Zombies could be anywhere—in sewers, attics, basements, cars, air ducts, crawl spaces, even inside walls or under mounds of debris. Pay particular attention to bodies of water. Zombies wandering at the bottom of lakes, rivers, even reservoirs have been known to surface well after an area has been declared safe. Follow the instructions later in this chapter for proper aquatic search-and-destroy.
11. MAINTAIN COMMUNICATION: Remaining linked to every member of your group is one of the most vital factors in a successful mission. Without proper communication, hunters can become separated, overrun, or accidentally shot by their own people (as in conventional warfare, this happens more than is generally acknowledged). Small, two-way radios—even the inexpensive brands marketed in electronics stores—are the best way to remain in contact. Walkie-talkies are also preferable to cell phones in that their signals do not depend on satellites, relays, or any other external aids.
12. KILL AND LISTEN: After a skirmish, always be wary of secondary zombie groups. The moment a ghoul is put down, cease all activity and listen to the world around you. Chances are that if any zombies are within earshot, they have overheard the battle and are moving in on your position.
13. DISPOSE OF ALL BODIES: Once the area is truly secure, burn both the bodies of the undead and those in your party who have fallen. First, this erases the chance of infected human corpses reanimating as zombies. Second, it prevents the health risk associated with any type of rotting flesh. Freshly slain humans provide an attractive meal for birds, scavenging animals, and, of course, other zombies.
14. INCENDIARY CONTROL: When using fire, make sure you keep in mind the larger implications. Can you control the blaze? If not, the fire will endanger your group. Is the zombie threat serious enough to warrant destroying great amounts of personal property? The answer may seem obvious, but why burn down half a town to kill three zombies that could be destroyed by rifle fire? As stated previously, fire can be as powerful an enemy as it is an ally. Use it only when necessary. Make sure your team can easily escape a wild blaze. Make sure you know where all explosive and poisonous chemicals are stored and if their destruction could endanger your team. Make sure you practice with your incendiary tools (blowtorch, Molotov, flare, etc.) before entering a combat zone so you know what they are capable of. Be aware of flammable fumes such as a leaking gas main. Even without resorting to fire as a weapon, the danger of these fumes, spilled chemicals, leaking fuel tanks on automobiles, and a host of other hazards are enough to prohibit smoking during any search-and-destroy mission.
15. NEVER GO OFF ALONE!: There may be times when it seems wasteful to send an entire team to do one person’s job. Wouldn’t five individuals cover more ground than a group all bunched together? In terms of time and efficiency, yes. For safety, the priority of any zombie sweep, staying together is mandatory. A separated individual could easily be surrounded and consumed. Even worse, hunters have come up against walking dead who only hours before were members of their own party!
WEAPONS AND GEAR
Arming and equipping a civilian, antizombie team should follow the same pattern as a military unit. Each person should have a standard “kit” in addition to certain items required for the whole team.
Every member should carry:
• Primary firearm (rifle or semiautomatic carbine)
• Fifty rounds of ammunition
• Cleaning kit
• Secondary weapon (preferably a pistol)
• Twenty-five rounds of ammunition
• Hand-to-hand weapon (large or small)
• Knife
• Flashlight
• Two emergency flares
• Signaling mirror
• Two-way radio
• Two ways of making fire (matches, lighter, etc.)
• Full quart canteen
• Daily rations
• Personal mess kit
• Hiking or combat boots
• Two pairs of socks
• Bedroll or pad
Each group (ten people or fewer) should have:
• Two silent weapons (could be carried as secondary weapons)
• Three explosive devices
• Two grappling hooks
• 500 feet of rope (nylon construction, 7⁄16" diameter, tensile strength 6,500 lbs., load absorption 1,450 ft./lb.)
• Two pairs of binoculars (minimum 50mm lenses/10X power)
• Two crowbars (could be carried as hand-to-hand weapons)
• Two bolt cutters
• Tool kit (must include: hammer-claw and ball-peen 4 oz., diagonal 4" pliers with spring, 4–6" longnose pliers with cutter, Phillips screwdrivers [3", 4", and stubby], slot screwdriver [4–5"], jeweler’s screwdrivers set, 12" × ½" hacksaw, 3M electrical tape, adjustable wrench, hand drill with 2–5mm bit set)
• Ax or hand hatchet (could be carried as hand-to-hand weapon)
• Medical kit (must include: bandages, cotton rolls/balls, two arm slings, scissors, medical tape, Merthiolate vials, antiseptic swab sticks, antiseptic and cleaning towelettes, bacterial soap, sterile gauze/eye pads, petrolatum, sterile lancets)
• Three gallons extra potable water
• Two maps (immediate zone/surrounding area)
• Two compasses
• Extra batteries for all electronic devices
• Ten extra emergency flares
• Four compact entrenching tools (could be carried as hand-to-hand weapons)
TRANSPORTATION
Unlike the scenario described in “On the Run,” the goal of this section is to help you not escape an area but sweep it. The undead are not to be avoided but attracted. Also, unlike the previous chapter, you will not be alone, and the support area should make fueling and servicing a vehicle much easier. With this in mind, using the noise from a car’s engine will act like a lure. (See “Strategies.”) In this instance, removing the rubber from a bicycle’s tires can accomplish the same result. Do not become too dependent on your vehicles. Unless applied to a specific strategy (see below), use them more as a means of getting to and from a battle site. Once in the target area, dismount and search on foot. This will allow for greater flexibility, particularly in urban areas.
TERRAIN TYPES
At first, this section might seem redundant. However, unlike “On the Run,” which teaches how to use terrain to escape, this will teach you how to use it to hunt. This time you are not simply passing through your environment as quickly, quietly, and easily as possible. As a hunter, you are here to reclaim this land—hold it, sweep it, cleanse it until every trace of the undead is gone. This section includes only information necessary to do just that.

1. FOREST
When hunting, watch for freshly eaten carcasses. Try to determine if the predator was an animal or a zombie. Also, use the trees to extend your visibility: Each one can serve as a lookout post or sniper platform. Set fires only as a last-ditch effort.

2. PLAINS
Vast, open areas provide great visibility, allowing full use of long-range sharpshooting weapons. One team of five with adequately sighted rifles and plenty of ammunition can clear several square miles in the course of a single day. Of course, great visibility allows the undead to see you as readily as you see them. Hunter groups operating on plains or prairie have reported being sighted and stalked by ghouls from as far as ten miles away. Another slight but still potential danger is posed by the odd zombie who may be lying in the tall grass. Undead who have lost their legs or had their spinal columns severed can remain undetected until it is too late. If your team is traveling through tall grass, travel slowly, watch the ground, and listen for any rustling or moans.

3. FIELDS
Unsuspecting hunters have chased zombies through a field only to be grabbed by another one lurking inches away! Unless you are ordered to protect the harvest, or the food itself is of vital importance, this is one case in which fire should be used first. Although almost every other word in this book stresses the control of incendiary warfare, common sense dictates that no human life is worth an acre or two of maize.
4. TUNDRA
One potential danger, not experienced in other environments, is that of a multigenerational outbreak. Because of cold weather’s preservative ability, zombies may remain frozen for decades. When thawed, they will join the ranks of the recently reanimated and, in some cases, can re-infect an entire area. Frozen tundra, more than any other environment, requires not only a tireless search but a heightened alert status during the next year’s spring thaw.

5. HILLS
Rolling terrain can be as treacherous and pose as great a threat from zombies as it can from any human enemy. If possible, always take the high ground and hold it. This allows greater visibility for you. As crazy as this sounds, remember that ghouls have limited dexterity. Apply this fact to their climbing skills, and what you have is a mass of zombies struggling unsuccessfully to get up the slope while you pick them off one by one.

6. DESERT
The problems discussed in “On the Run” are doubled when operating in a desert. Unlike the escapee, your team of hunters will be out during the brightest, hottest, most excruciating part of the day. Make sure each hunter is well supplied with water and antisunstroke accessories. Combat, unlike travel, will require more energy and therefore increase the risk of dehydration. Do not ignore the signs. One incapacitated member can cripple an entire team, allowing the undead to quickly turn the tables on you. Losing touch with your supply base, becoming isolated even for a day, takes on a whole new meaning in this life-threatening environment.

7. URBAN
If the goal were only to kill zombies, an urban area could simply be bombed or burned to the ground. That would “secure” it, but where would the survivors live with their homes a pile of rubble? Urban combat is the most difficult for a variety of reasons. For starters, it takes the longest amount of time because every building, every room, every subway tunnel, every car, every sewer pipe, every nook and cranny of this massive maze must be searched. Chances are, given a city’s importance, your civilian group will be working side by side with government forces. If this is not the case, however, be extremely cautious. Always think conservatively when it comes to team members, time, and resources (food, water, ammo). Cities have a way of swallowing them all up.

8. JUNGLE
This is a close-combat nightmare. Sniper rifles and other long-range weapons such as crossbows will be next to useless. Equip your team with carbines and/or shotguns. Machetes must be carried by each hunter, both for clearing foliage and for hand-to-hand combat. Use of fire will not be an option because the intense moisture will dampen most attempts to start one. Keep your team together at all times, be hyperalert, and listen carefully to the sounds of nearby wildlife. As with forests and swamps, they will be your only warning system.
9. SWAMP
Many of the aspects of jungle warfare can apply to marshes as well. They may not always be as hot or as dense, but this does not mean they are any safer. Pay close attention to the water. All equipment and tactics applied to subaquatic warfare and discussed later will most likely be employed in this scenario as well.

STRATEGIES
1. LURE AND DESTROY
Use one or more vehicles, large pickup trucks, or SUVs to enter an infested area. Once inside, make as much noise as possible to draw the undead to you. Exit the area slowly, matching the speed of your pursuers. Like the Pied Piper, you will soon acquire a tail of zombies, a grisly parade slouching after you. At this point, sharpshooters posted at the back of the vehicles can proceed to take them down. The pursuing ghouls will not realize what is happening, as their primitive brains will not notice that their comrades are falling all around them. Continue to lead them from the area, thinning their ranks until none are left. Use this tactic in urban zones (when the roads are clear) or where natural environments allow long vehicular journeys.

2. THE BARRICADE
This tactic works similarly to “Lure and Destroy,” only instead of leading the undead on for miles, your bait will draw them to a fixed position. This position could be constructed of debris, hastily erected barbed wire, wrecked cars, or your own vehicles. From the fixed position, your team will stand its ground, killing the zombies before they can overrun the barricade. In this instance, incendiary devices are ideal. Chances are, that the approaching zombies will be tightly packed by the time they reach your position. Molotovs or (and only in this one case) a flamethrower would utterly destroy their ranks. Barbed wire or other similar obstacles should be used to slow an advance and further concentrate targets. If incineration is not an option, simple marksmanship will accomplish the same task. Make sure your distances are measured and your rounds are expended wisely. Always watch your flanks. If possible, make sure the zone of approach is narrow and contained. Always have your escape route ready, but keep control of the team to avoid a premature retreat. Use the Barricade tactic in urban areas or those that provide great visibility. Specifically exclude jungles, swamps, or thick forests.
3. THE TOWER
Find an area high above ground (a tree, building, water tower, etc.). Stock this position with enough ammunition and basic supplies for a protracted battle (longer than one full day). Once all these tasks have been accomplished, do everything you can to attract the dead. As they gather around your position, begin the slaughter. Be careful when using incendiaries, as fire may spread to the tower or smoke may become a health risk.
4. MOBILE TOWER
Drive a garbage truck, semi, or other tall vehicle into the heart of an infested area. Establish a kill zone with good visibility, park, and commence the attack. The advantages of this tactic include never being shackled to an existing tower, already luring the dead with your vehicle’s engine, and (provided your cabin is always clear) a guaranteed means of escape.

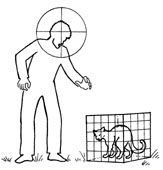
5. THE CAGE
If you don’t believe in cruelty to animals, don’t try this on a sweep. It basically involves placing an animal in a cage, positioning your team within weapons range of that cage, then picking off the zombies that come to devour said animal. Of course, several factors need to be considered for this tactic to work. The live bait must be loud enough to attract any nearby ghouls. The cage must be strong enough to resist an attack and anchored well enough to resist being pushed. Your team needs to be hidden so as not to attract zombies to its position. They must also take care not to hit and kill the caged animal. Silent, dead bait will quickly foil the cage strategy. Environments least suited to a cage approach are those with little or no cover for your team. Avoid its use in plains, tundra, or open desert.
6. THE TANK
Obviously, any civilian group will not have access to a real tank or armored personnel carrier. What might be available is an armored car, the type used to transport valuable commodities. In this case, the commodity will be your team. Using a “tank” is very similar to the cage tactic in that your goal is to attract the zombies to a specific location, then dispose of them with rifle fire. But unlike the cage, your team members within the tank’s cabin are not simply live bait. Firing slits enable them to add another level of firepower to those of the external snipers. Be aware, however, of the possibility that undead may tip your armored car on its side.
7. THE STAMPEDE
Of all hunting methods used against the dead, this is perhaps the most theatrical. Basically, the “process” involves dividing your party into teams, boarding a number of motor vehicles, driving through the infested area, and running over every zombie they find. Despite the image of a modern-day stampede, from which this tactic gets its name, it has been all but abandoned by knowledgeable hunting groups. Hitting a ghoul with a vehicle rarely results in a kill. More likely, the animated corpse is left crippled, crawling around with a shattered spinal column and useless legs. Always plan to follow up your “high-speed chase” with hours of mopping up by a team of dismounted hunters. If you do decide on the stampede tactic, use it in plains, desert, tundra, and other wide-open areas. Urban zones present too many obstacles, such as wrecked cars or abandoned barricades. Too often, stampeding hunters have found their paths blocked and their situation radically reversed. Avoid swamps or wetlands entirely.
8. MOTORIZED SWEEP
Almost the polar opposite of a Stampede, the Motorized Sweep is a slow, calm, methodical approach. Your hunters, traveling in large, powerful, well-protected vehicles, at speeds no greater than ten miles an hour, patrol the infested area. Sharpshooters pick off the undead, one shot at a time, until none are left standing. Trucks work best because they offer snipers an easier, safer vantage point from the roof. Although this tactic reduces the mop-up time of a Stampede, each body will still have to be inspected and disposed of. Open areas are ideal for the Motorized Sweep, although the slower speed involved allows limited use of this tactic in urban areas. As with all motorized vehicles, avoid dense and/or tropical areas. Once again, as with the Stampede, you will still need to plan for an extensive mopping-up period. Taking potshots from the roof of your Chevrolet Suburban will not get that last zombie at the bottom of the pond, locked in a closet, wandering the sewers, or lurking in a basement.
9. AIRBORNE SWEEP
What could be safer than attacking your enemy from the air? With several helicopters, couldn’t your team cover more ground in less time with no risk at all? In theory, yes; in practice, no. Any student of conventional warfare will acknowledge the need for ground troops, no matter how superior an air force is. This applies tenfold for hunting the undead. Forget using air attacks in urban, forest, jungle, swamp, or any other canopied terrain. Chances are your kill rate will drop to under 10 percent. Forget also the idea of a clean, painless sweep, even in a high-visibility zone. Your team will still have to mop up no matter how secure it appears. Air support does have its uses, especially in forward spotting and transport. Planes or helicopters, scouting in open areas, can provide zombie location data for multiple hunter teams simultaneously. Blimps have the advantage of lingering over the infested area all day, providing a constant stream of information and warning against possible ambushes. Helicopters can provide immediate assistance to those in trouble, lifting one team to the aid of another. Be cautious, however, about using your “eye in the sky,” so far ahead of the group. Mechanical failures could cause a forced landing in highly infested areas. Not only would the chopper crew be endangered—so would any team member attempting to rescue them.
What about parachuting hunters into an infested zone? This theory has been suggested many times although never put into practice. It is daring, it is courageous, it is heroic, and it is utterly insipid! Forget being injured on impact, tangled in trees, blown off course, lost on landing—forget all the possibilities associated with normal parachute jumps in regular peacetime conditions. If you want to know the true danger of an airborne attack against zombies, try dropping a square centimeter of meat on a swarming anthill. Chances are, that meat will never touch the ground. In short, air support is just that: “support.” People who believe it to be a war-winner have no business planning, orchestrating, or participating in any conflict with the living dead.
10. THE FIRESTORM
Provided the blaze can be controlled, the area in question is suitably flammable, and property protection is not an issue, nothing works better than an artificial blaze. Zone boundaries must be clearly delineated. Set a simultaneous fire to the entire perimeter so that the flames march steadily inward. Do not allow for an escape route, no matter how narrow. Keep watch for zombies that may have wandered through the flames. In theory, the storm will herd the dead into a tight perimeter, incinerating them in minutes. Mopping up will still be required, however, especially in urban areas, where basements and other rooms may have shielded zombies from the flames. As always, use caution, and be ready to deal with fire as a secondary enemy.
11. UNDERWATER BATTLES
Never forget the possibility of ghouls stumbling into nearby water before you declare an area secure. Too often humans have repopulated “cleared” zones only to be attacked days, weeks, even months later by zombies who have just recently found their way back to dry land. Because the undead can exist, operate, even kill in a liquid environment, hunting them may require occasional underwater warfare. This can be extremely hazardous, as water is not the natural environment for humans. The obvious problems of breathing and lack of communication, mobility, and visibility make an underwater zone the most difficult for hunting the undead. Unlike escaping by water, in which you have the advantage over them, searching and sweeping this alien environment will tip the balance firmly in a zombie’s favor. This does not mean that an underwater hunt is impossible. Far from it. Ironically, its difficulty has been known to keep hunters more alert and focused than in more familiar environments. The following general rules apply to any successful subaquatic hunt.
A. Know Your Zone
How deep is the body of water in question? How wide? Is it landlocked (pond, lake, reservoir)? If not, where are the exits to larger bodies of water? How is underwater visibility? Are there any sunken obstacles? Answer all these questions before proceeding with the hunt.
B. Scan from the Surface
Hooking on scuba gear and blindly diving into zombie-infested water is a wonderful way to mix the two childhood terrors of being eaten and drowning. Never submerge before thoroughly searching the area from shore, dock, or boat. If murky conditions or extreme depth prevent the use of naked eyesight, artificial means can always be employed. Sonar devices, common echo rangers found in civilian fishing boats, can easily detect something as large as a human body. Surface scans do not always confirm whether a zone is infested or clear. Underwater obstacles such as trees, rock formations, or sunken debris can obscure a zombie’s shape. If even a single one turns up, however, the next rule should be observed.
C. Consider Drainage
Why place your team in a hostile environment if that environment can be removed? Ask yourself the question: Is it possible to just empty the body of water? If so, even if it costs more time and effort than a submarine hunt, by all means proceed. Most of the time, however, this is not a viable option. To eliminate the menace below, your team will have to follow it down.
D. Find an Expert
Are any of your team licensed scuba divers? Have any of them ever worn scuba gear? How about simply snorkeling while on vacation? Sending inexperienced men and women underwater could kill them all even before they make contact with zombies. Drowning, asphyxiation, nitrogen narcosis, and hypothermia are only a few of the numerous ways that air-breathing animals such as ourselves can meet their fate beneath the waves. If time permits—for instance, if zombies are cornered in a landlocked body of water—find someone to either train and lead your team, or even to undertake the mission on his own. But if you believe that zombies have fallen into a river and could wind up near another town soon, waiting for the experts is not an option. Be ready to take the plunge, but be ready for the consequences.
E. Prepare Your Gear
As with land warfare, the right equipment and weapons will be crucial to your survival. The most common respiratory aid is scuba (Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus). If none is available, jury-rigged compressors and rubber hoses provide a workable if not perfect substitute. Handheld searchlights are a necessity. Even in the clearest water, zombies could be lurking in sheltered, darkened nooks. Spear guns should always be thought of as a primary weapon. Their ability for skull penetration from a safe distance is shared by no other aquatic weapon. Another powerful device is the diver’s “bang stick,” essentially a twelve-gauge shotgun shell at the end of a metal pole. Both these weapons are rare, however, in all but coastal areas. In their absence, look for nets, hooks, or homemade harpoons.
F. Integrated Attack
Nothing is more frightening than surfacing from an underwater sweep to find zombies waiting on your boat! Always work in concert with surface units. If your team consists of ten people, take five underwater and leave the rest “on the roof.” This will allow for a quick rescue if the tide of battle turns. A surface group can also aid in scouting, killing, and calling in reinforcements from land. As a general rule of all combat strategies, the more dangerous the environment, the more support is necessary.
G. Observe Wildlife
We have already established that birds and animals can signal the approach of zombies. The same is true for fish. It has been proven that aquatic wildlife can detect even minute traces of Solanum-infected flesh as it floats off a zombie’s body. Once they do they consistently and immediately flee the area. Underwater hunters have always reported zones completely devoid of fish right before encountering an underwater zombie.
H. Killing Methods
Do not discount any of these tactics as fantastic or unreliable. As ludicrous as some of them may sound, all have been repeatedly tested in antizombie, underwater combat. All have shown remarkable success.
1. Sniping: Substitute a speargun for a rifle and water for air, and it is basically the same tactic. As a speargun requires less range than a rifle, the diver will find himself in greater danger. If the first shot misses, never reload on the spot! Swim to a safe distance, lock in another spear, then re-engage your target.
2. Spearfishing: This is used if a head shot proves too difficult. Attach a metal line to the end of the spear, and aim for the ribcage. Once the zombie is skewered, your surface team can haul it up for disposal. Keep in mind that these zombies still have the ability to attack. If possible, try for a head shot from a rifle the second they break the surface. This will require great coordination between a diver and the surface team. One past foul-up resulted in an unwary team hauling what they believed was a destroyed zombie to the surface. Their screams were not heard by the incompetent diver below.
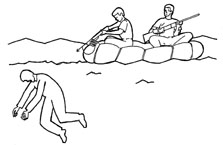
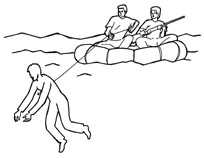
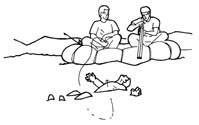
3. Hook and Line: Attach a harpoon to a section of rope. Use it to spear the targeted zombie, then have your surface team haul it up. Boat or meathooks, fastened to the end of the harpoon, decrease the chances of losing your target during the ascent. If the water is clear and shallow enough, the process of harpooning could be conducted entirely from aboard a boat. Again, as with the spearfishing, the “reeled-in” ghoul must be disposed of before it comes close enough to strike.
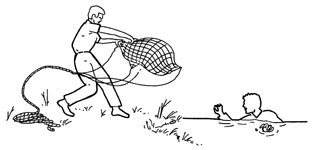
4. Netting: Surface teams will be your primary source of attack, with divers acting only as scouts. Fish or cargo nets should be dropped on the targeted ghoul, then used to bring them to the surface. One major advantage of netting is that the zombies you haul aboard should be too tangled in the net to strike out at you. Of course, “should” is a very dangerous word. Many a hunter was fatally wounded by zombies that “should” have been easy kills.

I. Specific Rules
Think of bodies of water as different types of terrain. Each will have its own set of conditions and can be as different from one another as a desert is from a swamp. About the only thing some bodies of water have in common is the H2O that covers them. You already have one deadly enemy to contend with. Don’t make another one.
1. Rivers: Constant currents can be both a blessing and a curse. Depending on the strength of its currents a river can wash any and all zombies well away from the initial infested area. Ghouls that fall into the Mississippi near Winona, Minnesota, could easily wash ashore a week later in downtown New Orleans. This creates a sense of urgency not found with landlocked pools. If possible, set up nets at the narrowest points. Monitor them carefully, and exercise extreme caution when sending divers in to investigate. A strong current can carry them right into the waiting arms and open mouths of their “targets.”
2. Lakes and Ponds: Because they are landlocked (generally), there is little chance for zombies to escape from a lake or a pond. Any undead wandering back to shore could be sighted and killed. Those remaining submerged will be eventually fished out and destroyed. The lack of any current makes them an ideal location for divers. Lakes and ponds that freeze over present a multigenerational problem. If they freeze solid, the submerged will become entombed for the winter, making them almost impossible to find. If only the surface freezes, zombies could still prowl the water’s dark depths.
3. Swamps: These are easily the most frustrating places for an underwater hunt. Their murky waters make diving next to impossible. Their root-riddled bottoms confound echo sounders. In most cases, their shallow bottoms make it easy for a zombie to simply reach up and either grab a hunter or capsize his boat. Hunting in large numbers with extensive use of searchlights and probing poles is the only proven method for sweeping this environment. After one of these arduous campaigns, you will know why so many tales of terror have their origin in the swamp.
4. Oceans: Unless the area in question is a harbor or other semi-enclosed area, forget about any successful hunts in the open seas. There is simply too much space for a real sweep, with depths beyond the reach of all but the rarest and most expensive submersibles. As problematic as this is for aggressive hunting, the threat posed by these undersea undead will probably be negligible. Most will simply wander the ocean floor, never seeing dry land again, until they eventually decay to nothing. This does not mean, however, that the threat should be ignored. Once it has been confirmed that zombies have been washed out to sea, determine the deep-water currents in that area and if—and where—they might take the undead close to land. All coastal inhabitants should be warned and a system of surveillance maintained for some time after that. Unlikely as it sounds, zombies have been known to slouch out of the surf months after an outbreak and on beaches thousands of miles away.
So let’s assume that you have followed all these instructions correctly. The battle is over, the area is secure, the victims have been mourned, the zombies have been burned. Hopefully, this will be the last time you will ever have to raise your hand to undead flesh. But what if it isn’t? What if your struggle was merely one small theater of a greater, all-out war between the living and the dead? What if, heaven forbid, it is a war humanity loses?