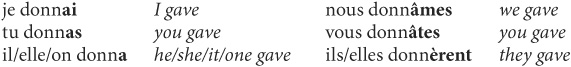
The passé simple is a literary past tense that replaces the passé composé in formal speeches and writing. You will never use the passé simple in conversation, but you will see it in newspaper articles and when you read French literature.
A. The passé simple of all -er ending verbs (including the irregular verb aller) is formed by adding the endings -ai, -as, -a, -âmes, -âtes, -èrent to the stem of the infinitive.
donner to give
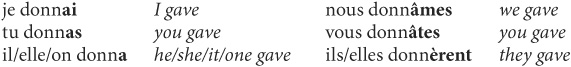
Note:
 -cer ending verbs add a cédille to the c before a (i.e., in all persons except the third-person plural)
-cer ending verbs add a cédille to the c before a (i.e., in all persons except the third-person plural)
commencer to begin

 -ger ending verbs insert e after g before a (i.e., in all persons except the third-person plural)
-ger ending verbs insert e after g before a (i.e., in all persons except the third-person plural)
manger to eat

B. The passé simple of both -ir and -re ending verbs is formed by adding the endings -is, -is, -it, -îmes, -îtes, -irent to the stem of the infinitive.
Some irregular verbs take the endings -is, -is, -it, -îmes,* -îtes,* -irent (as regular -ir and -re ending verbs); other irregular verbs take the endings -us, -us, -ut, -ûmes,* -ûtes,* -urent.
*Note that the nous and vous forms of all regular and irregular verbs (except haïr [to hate]) have an accent circonflexe (â, î, û) in the passé simple.
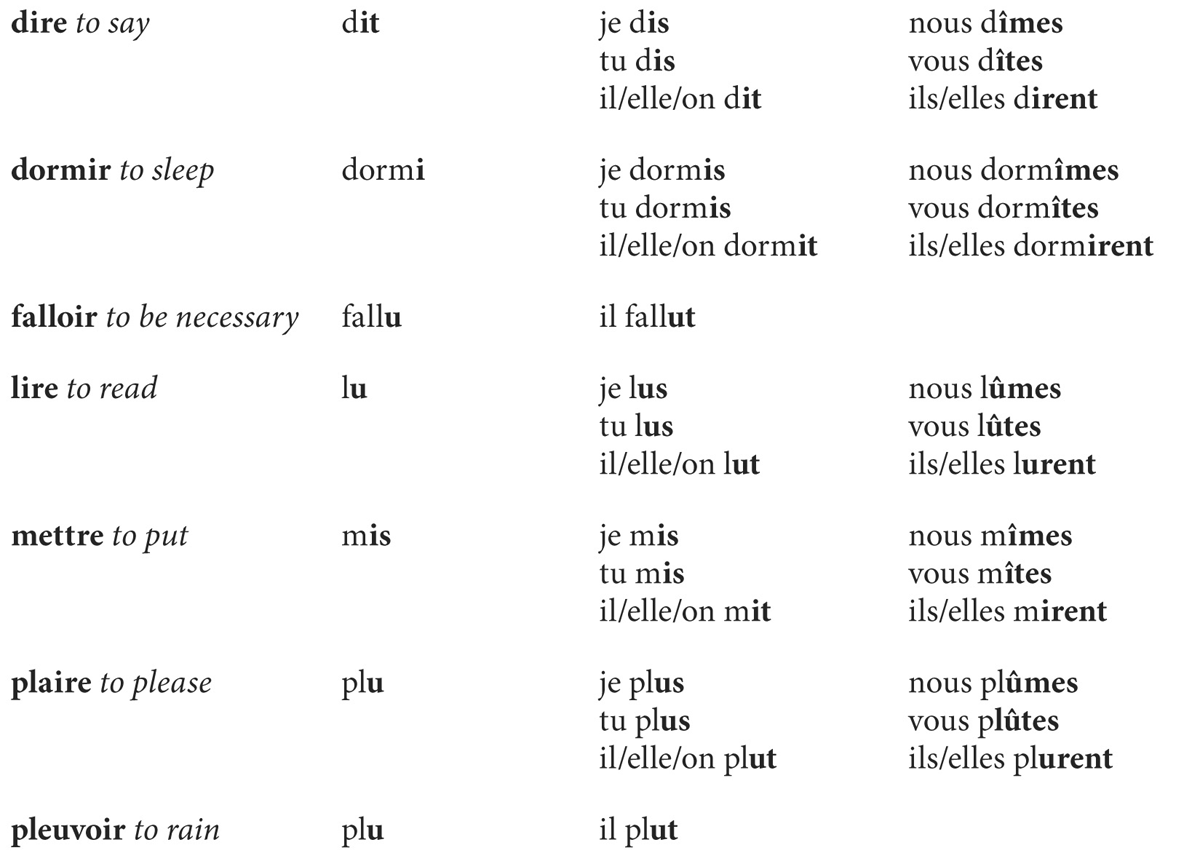
A. The passé simple of the following irregular verbs can be derived from their past participle. If the past participle of the verb ends in -i, -is, or -it, the first series of the above mentioned endings (with i) form its passé simple. If the past participle of the verb ends in -u, the second series of the above mentioned endings (with u) form its passé simple.
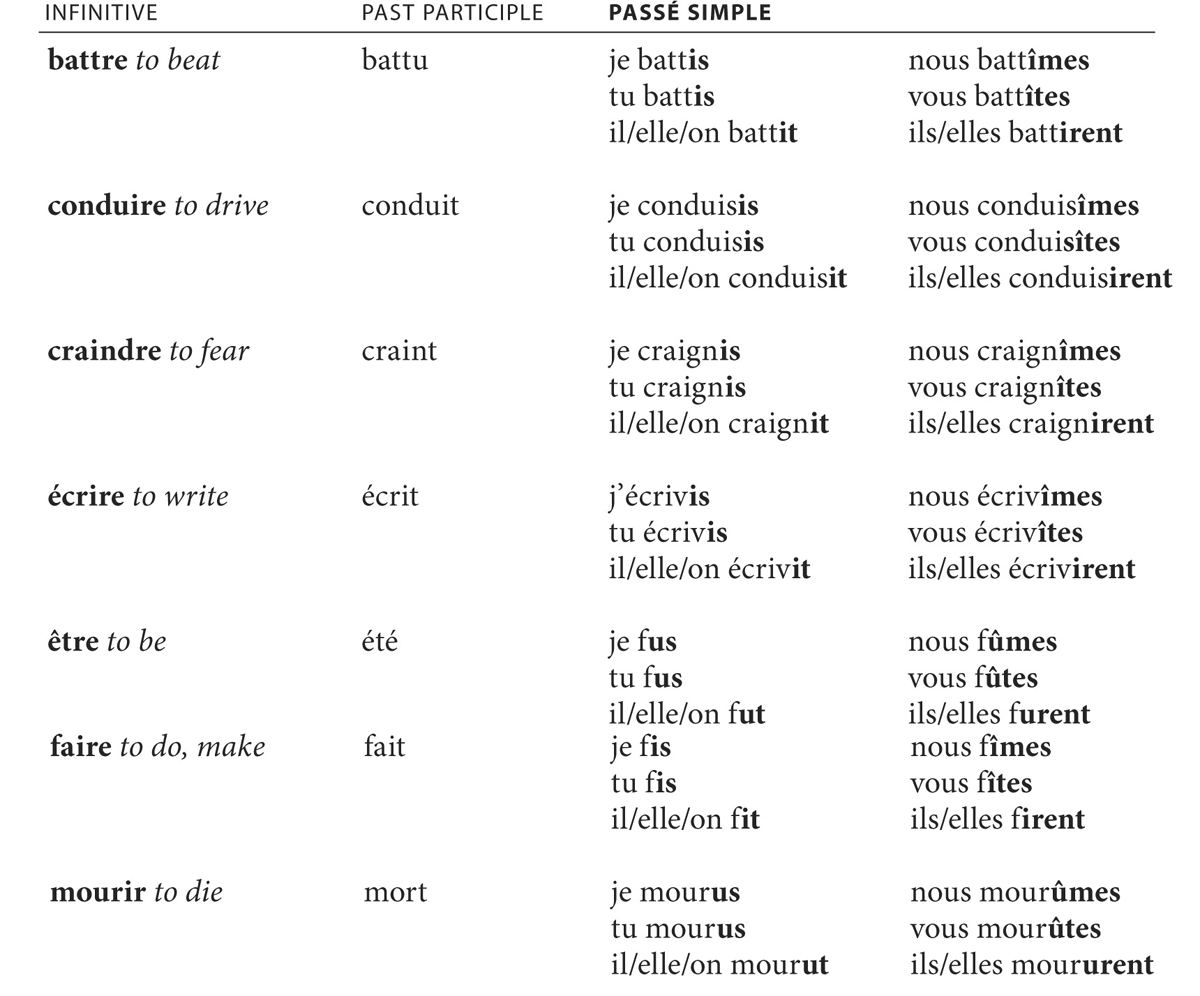
B. The passé simple of the following irregular verbs cannot be derived from their past participle.
The passé simple is used instead of the passé composé in literary and historical texts as well as in very formal speeches to state punctual and completed actions in the past.

Comment dit-on en anglais?
1. il fut ________________
2. il fit ________________
3. il vit ________________
4. nous vînmes ________________
5. nous reçûmes ________________
6. elle écrivit ________________
7. il fallut ________________
8. il prit ________________
9. ils dirent ________________
10. il voulut ________________
11. ils mirent ________________
12. elle alla ________________
13. je bus ________________
14. il vécut ________________
15. il dut ________________
16. nous eûmes ________________
17. il lut ________________
18. il courut ________________
EXERCICE
8•3
Napoléon Bonaparte. Dans le passage suivant, mettez au passé composé les verbes qui sont au passé simple.
Napoléon Bonaparte (naquit) (1) ______________ à Ajaccio en 1769. Il (prit) (2) ______________ le pouvoir en 1799 et (se maria) (3) ______________ avec Joséphine de Beauharnais. Il (devint) (4) ______________ l’empereur en 1804. Quand il (se rendit) (5) ______________ compte que Josephine et lui ne pouvaient pas avoir d’enfants, il (divorça) (6) ______________ d’avec sa femme et (épousa) (7) ______________ la princesse Marie-Louise d’Autriche. Ils (eurent) (8) ______________ un fils qui (reçut) (9) ______________ immédiatement ______________ le titre de « Roi de Rome ». Napoléon (créa) (10) ______________ le Code Civil qui reste actuellement la base de la jurisprudence française. Il (fonda) (11) ______________ aussi les lycées (et le baccalauréat) qui existent encore aujourd’hui. Napoléon (fit) (12) ______________ beaucoup de guerres. La campagne de Russie (commença) (13) ______________ en 1812, et Napoléon (gagna) (14) ______________ sa première victoire importante à Borodino. Cette victoire lui (ouvrit) (15) ______________ la route de Moscou. Bientôt, l’armée française (arriva) (16) ______________ devant la capitale russe. Napoléon (passa) (17) ______________ cinq semaines dans cette ville. Quand il (vit) (18) ______________ que l’hiver russe tuait ses soldats, il (décida) (19) ______________ de retourner en France. Quand il (fallut) (20) ______________ traverser la Bérézina, des milliers d’hommes (perdirent) (21) ______________ la vie. Après avoir perdu la bataille de Leipzig, Napoléon (abdiqua) (22) ______________ et (s’en alla) (23) ______________ à l’île d’Elbe dans la Méditerranée. Le frère de Louis XVI (revint) (24) ______________ à Paris et (fut) (25) ______________ proclamé roi de France sous le nom de Louis XVIII. Le premier mars 1815, Napoléon (s’échappa) (26) ______________ de l’île d’Elbe et (retourna) (27) ______________ à Paris pour régner encore cent jours jusqu’à sa défaite à Waterloo. Finalement, Napoléon (dut) (28) ______________ partir en exil à Sainte-Hélène. Il y (mourut) (29) ______________ en 1821.
Traduisez en anglais cette épigramme de Voltaire.
L’autre jour, au fond d’un vallon, ____________________________________
Un serpent piqua Jean Fréron. ____________________________________
Que pensez-vous qu’il arriva? ____________________________________
Ce fut le serpent qui creva. ____________________________________