
The future tense refers to actions or situations that will be occurring in the time to come. In French, the future has two tenses, the simple future (le futur simple) and the future perfect (le futur antérieur).
In English, the simple future consists of will or shall + verb: I will (shall) go, you will read, he will ask, we will (shall) know, etc. In French, the simple future uses no auxiliary, it consists of one word only. The future meaning is expressed by a specific verb stem and certain endings.
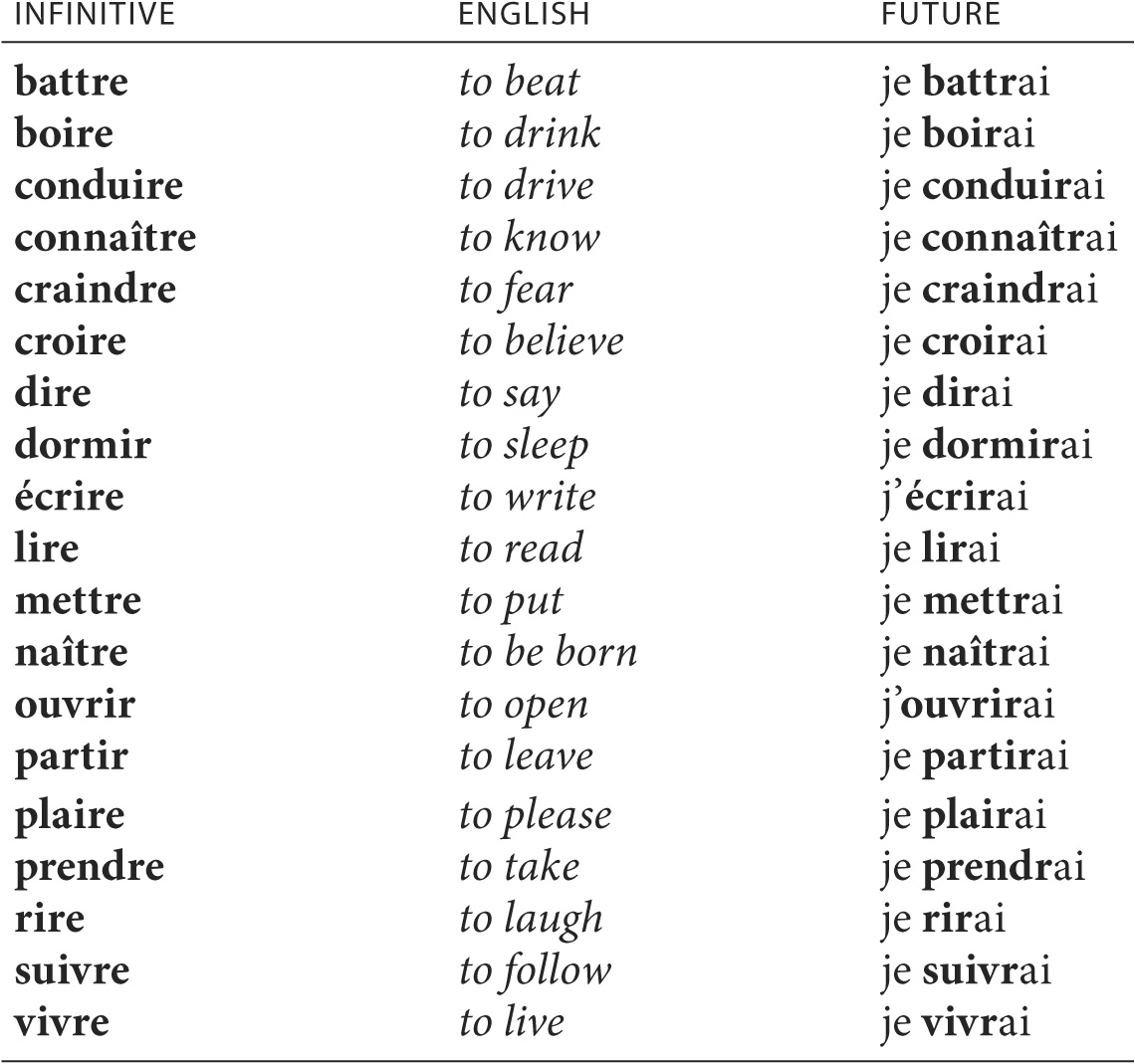
The future stem of regular -er and -ir verbs is the entire infinitive. Regular -re verbs drop the final -e of the infinitive before adding on the endings.
The future endings are: -ai, -as, -a, -ons, -ez, -ont. These endings, taken from the present tense of the verb avoir, are valid for both regular and irregular verbs. Use the following conjugations as models for all regular verbs in the future tense.

Note that the simple future also translates to the English continuous or progressive future (will be … -ing), which does not exist in French (I will be work ing = je travaillerai).
Verbs that show a spelling change in the present tense (except verbs having é in the last syllable of the stem) show the same change in the future, but here, the change affects all persons of the conjugation.
Verbs that contain -e- in the next to last syllable of the infinitive form the future as follows:
1. With some of these verbs, -e- becomes -è- in all persons.
acheter to buy

2. With others, the last consonant of the stem is doubled in all persons.
jeter to throw

Verbs ending in -oyer (except envoyer [to send], which is irregular) and -uyer change the -y- into an -i- in all persons (however, -ayer verbs may keep the -y-, as an alternate spelling).
nettoyer to clean

essayer to try

But verbs that have -é- in the next to last syllable of the infinitive (such as répéter, préférer, etc.) retain the -é- (exceptionally pronounced [ε]) in all persons.
espérer to hope

Note:
 The sound that characterizes the futur simple of all verbs is [R]. There is an [R] sound before the ending in both regular and irregular verbs. If the stem of the verb ends in r, there will be two [R] sounds before the future ending: rentr erai, je montr er ai.
The sound that characterizes the futur simple of all verbs is [R]. There is an [R] sound before the ending in both regular and irregular verbs. If the stem of the verb ends in r, there will be two [R] sounds before the future ending: rentr erai, je montr er ai.
 In many instances, the -e- before the -r- is silent (especially in verbs ending in -ier, -uer, -ouer, -éer): j’oublierai, il/elle/on continuera, tu créeras, nous jouerons, ils/elles achèteront, vous jetterez, j’emploierai, etc.
In many instances, the -e- before the -r- is silent (especially in verbs ending in -ier, -uer, -ouer, -éer): j’oublierai, il/elle/on continuera, tu créeras, nous jouerons, ils/elles achèteront, vous jetterez, j’emploierai, etc.
 In the inverted question form, a -t- is inserted in the third-person singular.
In the inverted question form, a -t- is inserted in the third-person singular.

EXERCICE
9•1
Comment dit-on en français?
1. I will ask. ______________________________________
2. They (masc.) will bring. ______________________________________
3. Will he listen? ______________________________________
4. You (fam.) will not teach. ______________________________________
5. We will give. ______________________________________
6. I will wait. ______________________________________
7. Will you (pol.) work? ______________________________________
8. Will she answer? ______________________________________
9. You (fam.) will lose. ______________________________________
10. It will snow. ______________________________________
11. They (fem.) will forget. ______________________________________
12. I will not go to bed until (avant) midnight. ______________________________________
13. What will they (masc.) buy? ______________________________________
14. I will repeat. ______________________________________
15. We will try. ______________________________________
16. We will employ. ______________________________________
17. You (fam.) will remember. ______________________________________
18. They (masc.) will succeed. ______________________________________
19. I will obey. ______________________________________
20. Everyone will grow old. ______________________________________
Many irregular verbs have regular stems, that is, the entire infinitive or (with -re ending verbs) the infinitive minus final -e. All persons of the future tense use the same stem.
Comment dit-on en français?
1. I will drink beer. ______________________________________
2. She will drive carefully. ______________________________________
3. You (fam.) will not believe this story. ______________________________________
4. You (pol.) will say nothing. ______________________________________
5. Will he sleep well? ______________________________________
6. We will write a term paper. ______________________________________
7. We (On) will read comic strips. ______________________________________
8. Everyone will take pictures. ______________________________________
9. You (fam.) will laugh. ______________________________________
10. They (masc.) will never understand. ______________________________________
The following irregular verbs have irregular stems.

 The future of il y a (there is, there are) is il y aura (there will be).
The future of il y a (there is, there are) is il y aura (there will be).
 Most compound irregular verbs have the same future stem as the main or model verbs:
Most compound irregular verbs have the same future stem as the main or model verbs:
devenir  je deviendrai
je deviendrai
revenir  je reviendrai
je reviendrai
se souvenir  je me souviendrai
je me souviendrai
promettre  je promettrai
je promettrai
sourire  je sourirai
je sourirai
comprendre  je comprendrai
je comprendrai
apprendre  j’apprendrai
j’apprendrai
reconnaître 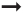 je reconnaîtrai, etc.
je reconnaîtrai, etc.
EXERCICE
9•3
Donnez la forme correcte du verbe au futur.
1. Ils (aller) ______________ à Monte Carlo.
2. Je (prendre) ______________ le train.
3. Il (savoir) ______________ beaucoup de choses.
4. Nous (devoir) ______________ faire un choix.
5. Je (faire) ______________ tout ce que tu (vouloir) ______________.
6. Elles (voir) ______________ l’Airbus A380.
7. Vous (envoyer) ______________ le fichier en pièce jointe.
8. (venir) ______________ -tu avec moi?
9. Vous (être) ______________ mieux chez vous.
10. J’(avoir) ______________ trente ans en septembre.
11. Il (falloir) ______________ se lever tôt.
12. Je ne (pouvoir) ______________ pas venir.
EXERCICE
9•4
Vrai ou faux?
À votre avis, est-ce que les prédictions suivantes pour l’an 2050 sont bonnes?
_______ 1. On pourra éviter la guerre, et on vivra en paix.
_______ 2. Nous passerons nos vacances sur la lune.
_______ 3. Les robots nettoieront nos maisons.
_______ 4. Il n’y aura plus de maladies incurables.
_______ 5. Les centrales nucléaires n’existeront plus.
_______ 6. Les éoliennes (aerogenerators) produiront toute notre électricité.
_______ 7. Je parlerai couramment (fluently) le français.
EXERCICE
9•5
Comment dit-on en français?
1. I will sit down. ______________________________________
2. We (On) will see. ______________________________________
3. I will go to the butcher shop. ______________________________________
4. Where will she go? ______________________________________
5. Will we have enough money? ______________________________________
6. Will there be a meeting tonight? ______________________________________
7. She will have to pay for the dinner. ______________________________________
8. They (fem.) will be happy. ______________________________________
9. Will that (Ça) be all? ______________________________________
10. What will you (fam.) do? ______________________________________
11. You (pol.) will remember. ______________________________________
12. It will be necessary to hurry. ______________________________________
13. What will the weather be like? —It will rain. ______________________________________
14. We will not be able to come. ______________________________________
15. They (masc.) will receive a phone call (un coup de téléphone). ______________________________________
As in English, the simple future is used
1. to describe a future action or situation. Often along with expressions of time such as:
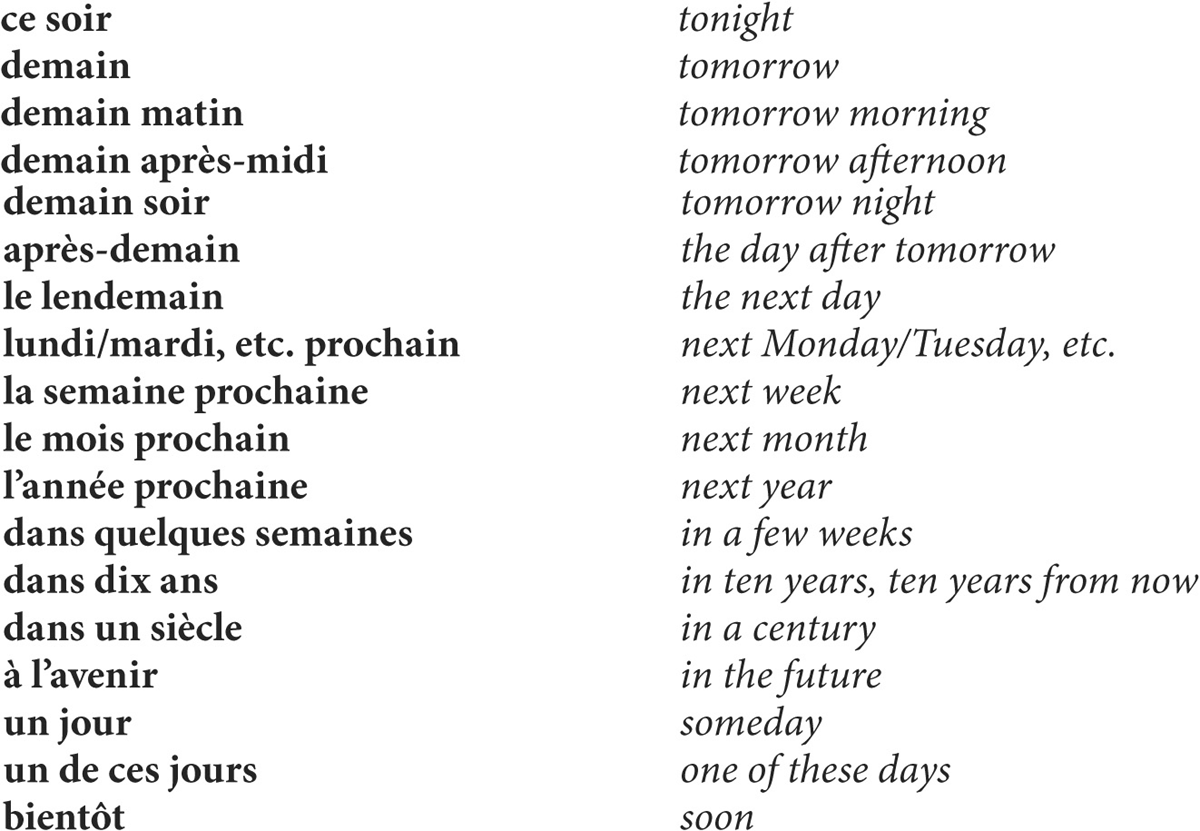
2. after si meaning whether if the action in the subordinate clause refers to the future, and if the introductory verb (i.e., the verb in the main clause) is in the present tense. This is also called indirect discourse.

But si meaning if (expressing a condition) can never be followed by the future. The present tense is used instead.

3. in the main clause of sentences expressing a condition when the present tense is used in the si-clause and when a future action or situation is referred to.
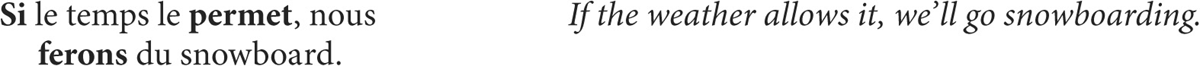
Contrary to English, the simple future is used
1. in subordinate clauses, after the verb espérer (to hope) when it refers to a future action or situation. (English generally uses the present tense, not the future, in this context.)
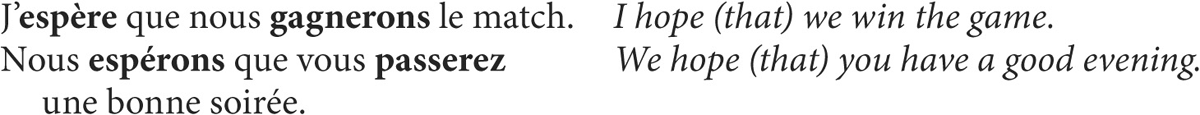
2. in subordinate clauses after the conjunctions quand (when), lorsque (when), dès que (as soon as), aussitôt que (as soon as), when the verb in the main clause is in the future or imperative and when a future action or situation is referred to. (English uses the present tense, not the future, in this context.)

3. to express an order (i.e., replace an imperative).

EXERCICE
9•6
Comment dit-on en français? (Use the futur simple throughout.)
1. Tomorrow afternoon, there will be a party. ______________________________________
2. Tonight, I will send a letter to my aunt. ______________________________________
3. I hope (that) the weather is nice next week. ______________________________________
4. In the future, he will be more careful. ______________________________________
5. When will you (fam.) be leaving? ______________________________________
6. I don’t know whether I will go to the meeting. ______________________________________
7. Will you (fam.) have the time to do it? ______________________________________
8. He will come back in July. ______________________________________
9. I will never know the answer. ______________________________________
10. Will you (fam.) be able to join us? ______________________________________
11. Someday, this house will be worth a fortune. ______________________________________
12. He will want to see your (votre) passport. ______________________________________
13. My mother will buy me a laptop computer when I am fifteen. ______________________________________
14. She will call as soon as she can. ______________________________________
15. From now on (Désormais) take (pol.) the subway! ______________________________________
16. If it rains, we will stay at home. ______________________________________
17. I will leave when I want. ______________________________________
18. In a few weeks, this factory will close its doors. ______________________________________
19. The strike will only last twenty-four hours. ______________________________________
20. I will be back (de retour) in five minutes. ______________________________________
Prédisez (Predict ) l’avenir d’un(e) ami(e) ou d’un membre de votre famille.
Exemple: Tu seras riche et heureux (heureuse), tu ne travailleras pas, etc.

EXERCICE
9•8
Comment sera le monde dans trente ans? Utilisez votre imagination.

Votre amie Anne est allée voir une diseuse de bonne aventure pour savoir ce que l’avenir lui réserve. Dites en français ce que la dame lui a dit.
You will live in Europe, and you will travel a lot. You will work for a French company, and later you will become a fashion model and a movie star. You will have the lead in many movies, and you will see the whole world. Everybody will admire you. You will be able to buy many things because you will be extremely rich. When you are thirty, you will meet the man of your dreams. You will get married in Paris, and you will spend your honeymoon in Tahiti, where the sun will shine all the time. You will have three beautiful children, one boy and two girls. The boy’s name will be Antoine, and the girls’ names will be Chantal and Denise. Your husband will love you, and you will adore your husband. You will go on many trips together. Your children will attend Harvard University. They will be successful, and they will become rich and famous also. You will be very happy, and you will live a long time.
VOCABULAIRE

EXERCICE
9•10
Répondez aux questions suivantes. (If the questions don’t apply, invent an answer.)
1. Où iras-tu l’été prochain? ______________________________________
2. À quelle heure te coucheras-tu ce soir? ______________________________________
3. Qu’est-ce que tu feras le week-end prochain? ______________________________________
4. Pourras-tu sortir ce soir? ______________________________________
5. Combien d’enfants auras-tu un jour? ______________________________________
6. Seras-tu marié(e) dans dix ans? ______________________________________
7. Selon la météo, pleuvra-t-il demain ou fera-t-il beau? ______________________________________
8. Quand obtiendras-tu ton diplôme? ______________________________________
9. Est-ce que tu verras tes parents la semaine prochaine? ______________________________________
10. Est-ce que tu enverras des e-mails à tes amis cet après-midi? ______________________________________
An event or situation in the future, especially when it is the near future, can also be expressed by the futur proche, which consists of the present tense of aller + infinitive. As we have seen earlier, the English equivalent of this construction is to be going to + infinitive.

Remplacez le futur proche par le futur simple.
Exemple: Il va le savoir. Il le saura.
1. Tu vas avoir mal au cœur. ______________________________________
2. Il va faire meilleur demain. ______________________________________
3. Elle va finir ses études dans six ans. ______________________________________
4. Nous allons nous asseoir sur un banc. ______________________________________
5. Tu vas être surpris. ______________________________________
6. Je vais me marier en octobre prochain. ______________________________________
7. Il va pleuvoir. ______________________________________
8. Il va pleurer. ______________________________________
9. Ils vont mourir. ______________________________________
10. Je vais courir. ______________________________________
11. Il va y avoir un orage. ______________________________________
12. Vous allez voir. ______________________________________
English will (+ infinitive) does not always correspond to the future tense in French. The French futur simple translates will only if a future action or situation is expressed (I will ask = je demanderai). Otherwise, will must be translated differently.
English will is translated by the present tense of vouloir:
 in polite requests
in polite requests

 in refusals (will not or won’t)
in refusals (will not or won’t)
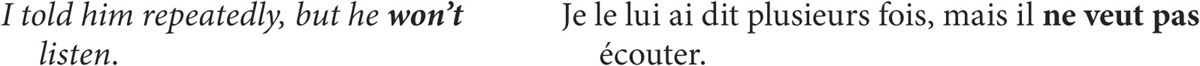
English will is also translated by the present tense of the verb in question when repetition or habit is implied.
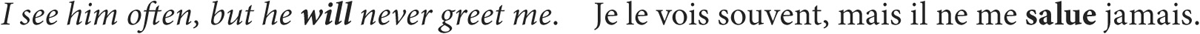
Comment dit-on en français?
1. Will you (pol.) follow me? ______________________________________
2. Will you (fam.) help me? ______________________________________
3. Will you (fam.) do me a favor? ______________________________________
4. These things (Ce sont des choses qui) will happen. ______________________________________
5. The car will not start (démarrer). ______________________________________
6. He won’t (= refuses to) do it. ______________________________________
In English, the future perfect consists of will have or shall have + past participle of the verb in question: I will (shall) have gone, you will have read, he will have known, we will (shall) have seen, etc.
In French, the future perfect (le futur antérieur) consists of the simple future of avoir or être + past participle of the verb in question. Here are two model conjugations:
*The agreement of the past participle in the future perfect is made as in all other compound tenses of verbs conjugated with être.
Note: Whereas the simple future describes an action or situation that will be taking place at some time in the future, the future perfect refers to an action or situation that is seen as completed by or at a specific time in the future. Compare:
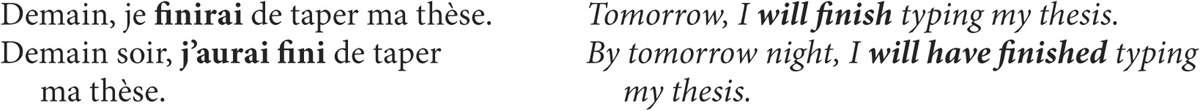
EXERCICE
9•13
Comment dit-on en français?
1. I will have bought a car. ______________________________________
2. She will have gone to the dentist (chez le dentiste). ______________________________________
3. We will have gone to bed. ______________________________________
4. You (fam.) will already have left. ______________________________________
5. They (masc.) will have seen the movie. ______________________________________
6. I will have had a good time. ______________________________________
7. You (pol.) will have understood. ______________________________________
As in English, the future perfect is used for actions and situations that will be completed at or by a specified time in the future.
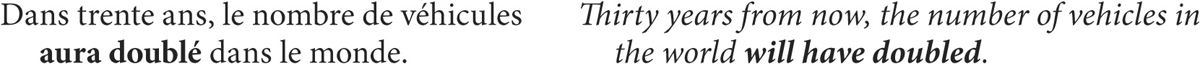
EXERCICE
9•14
Comment dit-on en français?
1. The day after tomorrow, I will have finished my report. ______________________________________
2. By the end of the year (D’ici la fin de l’année), we will have spent one thousand euros on medication (en médicaments). ______________________________________
3. By (En) July, this factory will have laid off one hundred workers. ______________________________________
4. Ten years from now (D’ici dix ans), these birds will have disappeared. ______________________________________
5. I hope that she will have left when you (fam.) come back. ______________________________________
6. Will you (pol.) have written the recommendation (la recommandation) by tonight (ce soir)? ______________________________________
EXERCICE
9•15
What will you have done by the end of the year? Answer with oui or non.
D’ici la fin de l’année…
_______ 1. j’aurai lu cinq livres.
_______ 2. je serai allé(e) en France.
_______ 3. je me serai marié(e).
_______ 4. j’aurai acheté une nouvelle voiture.
_______ 5. j’aurai dîné chez MacDo dix fois.
_______ 6. j’aurai gagné beaucoup d’argent.
_______ 7. j’aurai écrit mille courriels.
_______ 8. j’aurai maigri de trois kilos.
_______ 9. j’aurai vu au moins huit films étrangers.
_______ 10. j’aurai appris le français.
Contrary to English, the future perfect is used after the conjunctions dès que (as soon as), aussitôt que (as soon as), quand (when), lorsque (when), une fois que (once), tant que (as long as), and après que (after) for actions and situations that will be completed before another future action. In these sentences, the verb in the main clause is in the simple future or imperative. (English uses the present perfect in this context.)

EXERCICE
9•16
Comment dit-on en français?
1. Call (pol.) me as soon as you have received this message. ______________________________________
2. It will be your turn (Ce sera votre tour) when I have finished. ______________________________________
3. We (On) will know more when he has had an X-ray. ______________________________________
4. Once we have retrieved (récupérer) our suitcases, we will take a taxi. ______________________________________
5. As long as you (fam.) haven’t done your homework, you will not be able to go out. ______________________________________
6. I will write to you (fam.) after we have arrived. ______________________________________
Contrary to English, the future perfect is used to express an assumption on the part of the speaker, i.e., the probability of a past action or situation. (English uses must have + past participle in this context.)
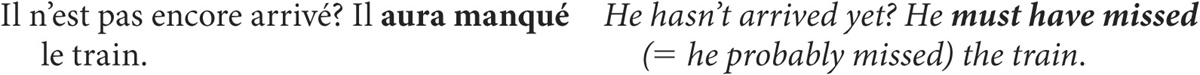
Comment dit-on en français?
1. That is not possible. She must have made a mistake. ______________________________________
2. He is coming back. He must have forgotten something. ______________________________________
3. I cannot find my pen. My colleague (Mon collègue) must have taken it. ______________________________________
4. She hasn’t called yet? You (fam.) must have given her the wrong (mauvais) number. ______________________________________
5. They (masc.) are not hungry? They must have already eaten. ______________________________________