ELECTRONIC CODE OF FEDERAL REGULATIONS
eCFR data is current as of November 9, 2020
PART 61—CERTIFICATION: PILOTS, FLIGHT INSTRUCTORS, AND GROUND INSTRUCTORS
§61.1 Applicability and definitions.
§61.3 Requirement for certificates, ratings, and authorizations.
§61.4 Qualification and approval of flight simulators and flight training devices.
§61.5 Certificates and ratings issued under this part.
§61.7 Obsolete certificates and ratings.
§61.8 Inapplicability of unmanned aircraft operations.
§61.11 Expired pilot certificates and re-issuance.
§61.13 Issuance of airman certificates, ratings, and authorizations.
§61.15 Offenses involving alcohol or drugs.
§61.16 Refusal to submit to an alcohol test or to furnish test results.
§61.18 Security disqualification.
§61.19 Duration of pilot and instructor certificates and privileges.
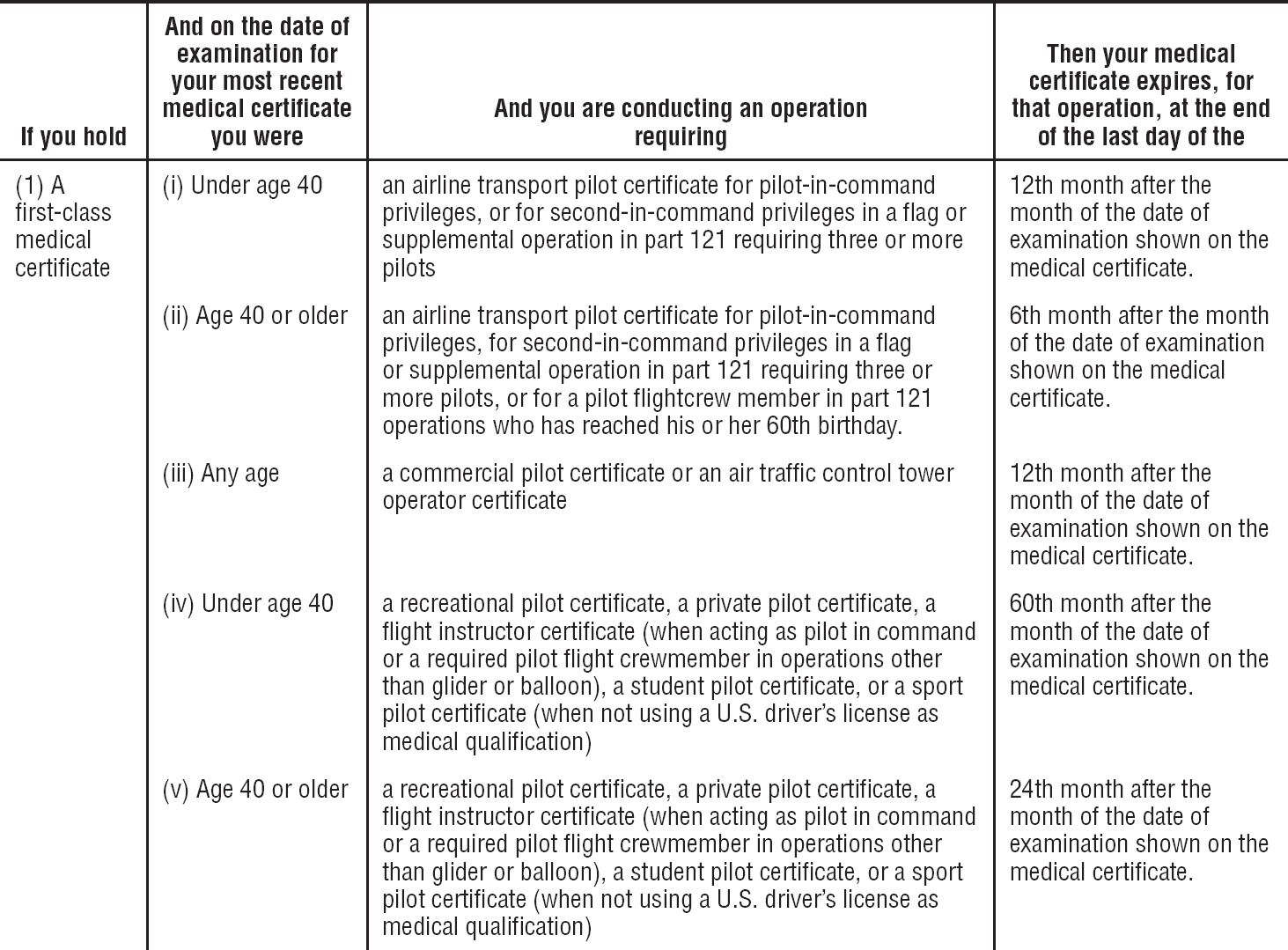
§61.23 Medical certificates: Requirement and duration.
§61.27 Voluntary surrender or exchange of certificate.
§61.29 Replacement of a lost or destroyed airman or medical certificate or knowledge test report.
§61.31 Type rating requirements, additional training, and authorization requirements.
§61.33 Tests: General procedure.
§61.35 Knowledge test: Prerequisites and passing grades.
§61.37 Knowledge tests: Cheating or other unauthorized conduct.
§61.39 Prerequisites for practical tests.
§61.41 Flight training received from flight instructors not certificated by the FAA.
§61.43 Practical tests: General procedures.
§61.45 Practical tests: Required aircraft and equipment.
§61.47 Status of an examiner who is authorized by the Administrator to conduct practical tests.
§61.49 Retesting after failure.
§61.52 Use of aeronautical experience obtained in ultralight vehicles.
§61.53 Prohibition on operations during medical deficiency.
§61.55 Second-in-command qualifications.
§61.57 Recent flight experience: Pilot in command.
Subpart B—Aircraft Ratings and Pilot Authorizations
§61.64 Use of a flight simulator and flight training device.
§61.65 Instrument rating requirements.
§61.66 Enhanced Flight Vision System Pilot Requirements.
§61.67 Category II pilot authorization requirements.
§61.68 Category III pilot authorization requirements.
§61.69 Glider and unpowered ultralight vehicle towing: Experience and training requirements.
§61.71 Graduates of an approved training program other than under this part: Special rules.
§61.73 Military pilots or former military pilots: Special rules.
§61.75 Private pilot certificate issued on the basis of a foreign pilot license.
§61.83 Eligibility requirements for student pilots.
§61.87 Solo requirements for student pilots.
§61.93 Solo cross-country flight requirements.
§61.95 Operations in Class B airspace and at airports located within Class B airspace.
§61.96 Applicability and eligibility requirements: General.
§61.97 Aeronautical knowledge.
§61.99 Aeronautical experience.
§61.100 Pilots based on small islands.
§61.101 Recreational pilot privileges and limitations.
§61.103 Eligibility requirements: General.
§61.105 Aeronautical knowledge.
§61.109 Aeronautical experience.
§61.110 Night flying exceptions.
§61.111 Cross-country flights: Pilots based on small islands.
§61.113 Private pilot privileges and limitations: Pilot in command.
§61.115 Balloon rating: Limitations.
§61.123 Eligibility requirements: General.
§61.125 Aeronautical knowledge.
§61.129 Aeronautical experience.
§61.131 Exceptions to the night flying requirements.
§61.133 Commercial pilot privileges and limitations.
Subpart G—Airline Transport Pilots
§61.153 Eligibility requirements: General.
§61.155 Aeronautical knowledge.
§61.159 Aeronautical experience: Airplane category rating.
§61.160 Aeronautical experience—airplane category restricted privileges.
§61.161 Aeronautical experience: Rotorcraft category and helicopter class rating.
§61.163 Aeronautical experience: Powered-lift category rating.
§61.165 Additional aircraft category and class ratings.
§61.167 Airline transport pilot privileges and limitations.
§61.169 Letters of authorization for institutions of higher education.
Subpart H—Flight Instructors Other than Flight Instructors With a Sport Pilot Rating
§61.183 Eligibility requirements.
§61.185 Aeronautical knowledge.
§61.189 Flight instructor records.
§61.191 Additional flight instructor ratings.
§61.193 Flight instructor privileges.
§61.195 Flight instructor limitations and qualifications.
§61.197 Renewal requirements for flight instructor certification.
§61.199 Reinstatement requirements of an expired flight instructor certificate.
§61.213 Eligibility requirements.
§61.215 Ground instructor privileges.
§61.217 Recent experience requirements.
§61.301 What is the purpose of this subpart and to whom does it apply?
§61.305 What are the age and language requirements for a sport pilot certificate?
§61.307 What tests do I have to take to obtain a sport pilot certificate?
§61.309 What aeronautical knowledge must I have to apply for a sport pilot certificate?
§61.311 What flight proficiency requirements must I meet to apply for a sport pilot certificate?
§61.313 What aeronautical experience must I have to apply for a sport pilot certificate?
§61.315 What are the privileges and limits of my sport pilot certificate?
§61.317 Is my sport pilot certificate issued with aircraft category and class ratings?
§61.327 Are there specific endorsement requirements to operate a light-sport aircraft based on V
Subpart K—Flight Instructors With a Sport Pilot Rating
§61.401 What is the purpose of this subpart?
§61.413 What are the privileges of my flight instructor certificate with a sport pilot rating?
§61.415 What are the limits of a flight instructor certificate with a sport pilot rating?
§61.421 May I give myself an endorsement?
§61.423 What are the recordkeeping requirements for a flight instructor with a sport pilot rating?
§61.425 How do I renew my flight instructor certificate?
§61.427 What must I do if my flight instructor certificate with a sport pilot rating expires?
AUTHORITY: 49 U.S.C. 106(f), 106(g), 40113, 44701-44703, 44707, 44709-44711, 44729, 44903, 45102-45103, 45301-45302; Sec. 2307 Pub. L. 114-190, 130 Stat. 615 (49 U.S.C. 44703 note).
SOURCE: Docket No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997, unless otherwise noted.
Special Federal Aviation Regulation No. 73—Robinson R-22/R-44 Special Training and Experience Requirements
Sections
1. Applicability.
2. Required training, aeronautical experience, endorsements, and flight review.
3. Expiration date.
1. Applicability. Under the procedures prescribed herein, this SFAR applies to all persons who seek to manipulate the controls or act as pilot in command of a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter. The requirements stated in this SFAR are in addition to the current requirements of part 61.
2. Required training, aeronautical experience, endorsements, and flight review.
(a) Awareness Training:
(1) Except as provided in paragraph (a)(2) of this section, no person may manipulate the controls of a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter after March 27, 1995, for the purpose of flight unless the awareness training specified in paragraph (a)(3) of this section is completed and the person’s logbook has been endorsed by a certified flight instructor authorized under paragraph (b)(5) of this section.
(2) A person who holds a rotorcraft category and helicopter class rating on that person’s pilot certificate and meets the experience requirements of paragraph (b)(1) or paragraph (b)(2) of this section may not manipulate the controls of a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter for the purpose of flight after April 26, 1995, unless the awareness training specified in paragraph (a)(3) of this section is completed and the person’s logbook has been endorsed by a certified flight instructor authorized under paragraph (b)(5) of this section.
(3) Awareness training must be conducted by a certified flight instructor who has been endorsed under paragraph (b)(5) of this section and consists of instruction in the following general subject areas:
(i) Energy management;
(ii) Mast bumping;
(iii) Low rotor RPM (blade stall);
(iv) Low G hazards; and
(v) Rotor RPM decay.
(4) A person who can show satisfactory completion of the manufacturer’s safety course after January 1, 1994, may obtain an endorsement from an FAA aviation safety inspector in lieu of completing the awareness training required in paragraphs (a)(1) and (a)(2) of this section.
(b) Aeronautical Experience:
(1) No person may act as pilot in command of a Robinson model R-22 unless that person:
(i) Has had at least 200 flight hours in helicopters, at least 50 flight hours of which were in the Robinson R-22; or
(ii) Has had at least 10 hours dual instruction in the Robinson R-22 and has received an endorsement from a certified flight instructor authorized under paragraph (b)(5) of this section that the individual has been given the training required by this paragraph and is proficient to act as pilot in command of an R-22. Beginning 12 calendar months after the date of the endorsement, the individual may not act as pilot in command unless the individual has completed a flight review in an R-22 within the preceding 12 calendar months and obtained an endorsement for that flight review. The dual instruction must include at least the following abnormal and emergency procedures flight training:
(A) Enhanced training in autorotation procedures,
(B) Engine rotor RPM control without the use of the governor,
(C) Low rotor RPM recognition and recovery, and
(D) Effects of low G maneuvers and proper recovery procedures.
(2) No person may act as pilot in command of a Robinson R-44 unless that person—
(i) Has had at least 200 flight hours in helicopters, at least 50 flight hours of which were in the Robinson R-44. The pilot in command may credit up to 25 flight hours in the Robinson R-22 toward the 50 hour requirement in the Robinson R-44; or
(ii) Has had at least 10 hours dual instruction in a Robinson helicopter, at least 5 hours of which must have been accomplished in the Robinson R-44 helicopter and has received an endorsement from a certified flight instructor authorized under paragraph (b)(5) of this section that the individual has been given the training required by this paragraph and is proficient to act as pilot in command of an R-44. Beginning 12 calendar months after the date of the endorsement, the individual may not act as pilot in command unless the individual has completed a flight review in a Robinson R-44 within the preceding 12 calendar months and obtained an endorsement for that flight review. The dual instruction must include at least the following abnormal and emergency procedures flight training—
(A) Enhanced training in autorotation procedures;
(B) Engine rotor RPM control without the use of the governor;
(C) Low rotor RPM recognition and recovery; and
(D) Effects of low G maneuvers and proper recovery procedures.
(3) A person who does not hold a rotorcraft category and helicopter class rating must have had at least 20 hours of dual instruction in a Robinson R-22 helicopter prior to operating it in solo flight. In addition, the person must obtain an endorsement from a certified flight instructor authorized under paragraph (b)(5) of this section that instruction has been given in those maneuvers and procedures, and the instructor has found the applicant proficient to solo a Robinson R-22. This endorsement is valid for a period of 90 days. The dual instruction must include at least the following abnormal and emergency procedures flight training:
(i) Enhanced training in autorotation procedures,
(ii) Engine rotor RPM control without the use of the governor,
(iii) Low rotor RPM recognition and recovery, and
(iv) Effects of low G maneuvers and proper recovery procedures.
(4) A person who does not hold a rotorcraft category and helicopter class rating must have had at least 20 hours of dual instruction in a Robinson R-44 helicopter prior to operating it in solo flight. In addition, the person must obtain an endorsement from a certified flight instructor authorized under paragraph (b)(5) of this section that instruction has been given in those maneuvers and procedures, and the instructor has found the applicant proficient to solo a Robinson R-44. This endorsement is valid for a period of 90 days. The dual instruction must include at least the following abnormal and emergency procedures flight training:
(i) Enhanced training in autorotation procedures,
(ii) Engine rotor RPM control without the use of the governor,
(iii) Low rotor RPM recognition and recovery, and
(iv) Effects of low G maneuvers and proper recovery procedures.
(5) No certificated flight instructor may provide instruction or conduct a flight review in a Robinson R-22 or R-44 unless that instructor—
(i) Completes the awareness training in paragraph 2(a) of this SFAR.
(ii) For the Robinson R-22, has had at least 200 flight hours in helicopters, at least 50 flight hours of which were in the Robinson R-22, or for the Robinson R-44, has had at least 200 flight hours in helicopters, 50 flight hours of which were in Robinson helicopters. Up to 25 flight hours of Robinson R-22 flight time may be credited toward the 50 hour requirement.
(iii) Has completed flight training in a Robinson R-22, R-44, or both, on the following abnormal and emergency procedures—
(A) Enhanced training in autorotation procedures;
(B) Engine rotor RPM control without the use of the governor;
(C) Low rotor RPM recognition and recovery; and
(D) Effects of low G maneuvers and proper recovery procedures.
(iv) Has been authorized by endorsement from an FAA aviation safety inspector or authorized designated examiner that the instructor has completed the appropriate training, meets the experience requirements and has satisfactorily demonstrated an ability to provide instruction on the general subject areas of paragraph 2(a)(3) of this SFAR, and the flight training identified in paragraph 2(b)(5)(iii) of this SFAR.
(c) Flight Review:
(1) No flight review completed to satisfy §61.56 by an individual after becoming eligible to function as pilot in command in a Robinson R-22 helicopter shall be valid for the operation of R-22 helicopter unless that flight review was taken in an R-22.
(2) No flight review completed to satisfy §61.56 by individual after becoming eligible to function as pilot in command in a Robinson R-44 helicopter shall be valid for the operation of R-44 helicopter unless that flight review was taken in the R-44.
(3) The flight review will include a review of the awareness training subject areas of paragraph 2(a)(3) of this SFAR and the flight training identified in paragraph 2(b) of this SFAR.
(d) Currency Requirements: No person may act as pilot in command of a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter carrying passengers unless the pilot in command has met the recency of flight experience requirements of §61.57 in an R-22 or R-44, as appropriate.
3. Expiration date. This SFAR No. 73 shall remain in effect until it is revised or rescinded.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997, as amended by SFAR 73-1, 63 FR 666, Jan. 7, 1998; 68 FR 43, Jan. 2, 2003; Amdt. 61-120, 73 FR 17246, Apr. 1, 2008; Amdt. SFAR 73-2, 74 FR 25650, May 29, 2009]
Special Federal Aviation Regulation No. 100-2—Relief for U.S. Military and Civilian Personnel Who are Assigned Outside the United States in Support of U.S. Armed Forces Operations
1. Applicability. Flight Standards offices are authorized to accept from an eligible person, as described in paragraph 2 of this SFAR, the following:
(a) An expired flight instructor certificate to show eligibility for renewal of a flight instructor certificate under §61.197, or an expired written test report to show eligibility under part 61 to take a practical test;
(b) An expired written test report to show eligibility under §§63.33 and 63.57 to take a practical test; and
(c) An expired written test report to show eligibility to take a practical test required under part 65 or an expired inspection authorization to show eligibility for renewal under §65.93.
2. Eligibility. A person is eligible for the relief described in paragraph 1 of this SFAR if:
(a) The person served in a U.S. military or civilian capacity outside the United States in support of the U.S. Armed Forces’ operation during some period of time from September 11, 2001, to termination of SFAR 100-2;
(b) The person’s flight instructor certificate, airman written test report, or inspection authorization expired some time between September 11, 2001, and 6 calendar months after returning to the United States or termination of SFAR 100-2, whichever is earlier; and
(c) The person complies with §61.197 or §65.93 of this chapter, as appropriate, or completes the appropriate practical test within 6 calendar months after returning to the United States, or upon termination of SFAR 100-2, whichever is earlier.
3. Required documents. The person must send the Airman Certificate and/or Rating Application (FAA Form 8710-1) to the appropriate Flight Standards office. The person must include with the application one of the following documents, which must show the date of assignment outside the United States and the date of return to the United States:
(a) An official U.S. Government notification of personnel action, or equivalent document, showing the person was a civilian on official duty for the U.S. Government outside the United States and was assigned to a U.S. Armed Forces’ operation some time between September 11, 2001, to termination of SFAR 100-2;
(b) Military orders showing the person was assigned to duty outside the United States and was assigned to a U.S. Armed Forces’ operation some time between September 11, 2001, to termination of SFAR 100-2 ; or
(c) A letter from the person’s military commander or civilian supervisor providing the dates during which the person served outside the United States and was assigned to a U.S. Armed Forces’ operation some time between September 11, 2001, to termination of SFAR 100-2.
4. Expiration date. This Special Federal Aviation Regulation No. 100-2 is effective until further notice.
[Doc. No. FAA-2009-0923, 75 FR 9766, Mar. 4, 2010, as amended by Docket FAA-2018-0119, Amdt. 61-141, 83 FR 9170, Mar. 5, 2018]
Special Federal Aviation Regulation No. 118-2—Relief for Certain Persons During the National Emergency Concerning the Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Public Health Emergency
1. Applicability. This Special Federal Aviation Regulation (SFAR) applies to—
(a) Certain persons who are unable to meet the following requirements during some period between March 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021—
(1) Training, recency, testing and checking requirements specified in parts 61, 91, 107, and 125 of this chapter, and SFAR No. 73 of this part; and
(2) Duration and renewal requirements specified in parts 61, 63, 65, and 141 of this chapter, and SFAR No. 100-2 of this part; and
(b) Certain air carriers and operators who are unable to obtain special flight permits with a continuing authorization under part 21 of this chapter for the purpose of flying the aircraft to a point of storage.
2. Training, recency, testing, and checking requirements.
(a) Applicability. The relief provided by paragraph 2 of this SFAR applies to—
(1) Operations conducted for compensation or hire under parts 91, 125, 133, and 137 of this chapter by persons who are exercising the privileges of at least a commercial pilot certificate issued under this part;
(2) Operations conducted by persons who are exercising the privileges of a private pilot certificate issued under this part, provided the person meets one of the following paragraphs—
(i) The person is conducting a charitable medical flight for a volunteer pilot organization pursuant to an exemption issued under part 11 of this chapter, and the flight involves only the carriage of persons considered essential for the flight;
(ii) The person is conducting an agricultural aircraft operation under a private agricultural aircraft operating certificate issued in accordance with §137.19 of this chapter;
(iii) The person has at least 500 hours of total time as a pilot, that includes at least 400 hours as a pilot in command and at least 50 hours that were accrued within the preceding 12 calendar months, and the person is conducting one of the following operations consistent with the compensation or hire exceptions specified in §61.113:
(A) A flight incidental to that person’s business or employment;
(B) A flight in support of family medical needs or to transport essential goods for personal use;
(C) A flight necessary to fly an aircraft to a location in order to meet a requirement of this chapter; or
(D) A flight to transport essential goods and medical supplies to support public health needs;
(3) For operations conducted under part 91, subpart K, and part 125 of this chapter, persons who are serving as flight attendant crewmembers, check pilots, and flight instructors; and
(4) Operations conducted under part 107 of this chapter by a person who holds a remote pilot certificate issued under part 107 of this chapter.
(b) This Part.
(1) Second-in-command qualifications of §61.55. (i) Airmen requirements. (A) Notwithstanding the period specified in §61.55(c), a person who is required to complete the second-in-command familiarization and currency requirements under §61.55(b)(1) and (2) between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 for purposes of maintaining second-in-command privileges may complete the requirements of §61.55(b)(1) and (2) in the month before or three months after the month in which they are required, provided the pilot meets the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(1)(ii) of this SFAR.
(B) Notwithstanding the period specified in §61.55(c), a person who is required to complete the second-in-command familiarization and currency requirements under §61.55(b)(1) and (2) between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 for purposes of maintaining second-in-command privileges may complete the requirements of §61.55(b)(1) and (2) in the month before or two months after the month in which they are required, provided the pilot meets the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(1)(ii) of this SFAR.
(C) A pilot who meets the requirements of §61.55(b)(1) and (2) in accordance with paragraph 2.(b)(1)(i)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(1)(i)(B) of this SFAR will be considered to have completed the requirements in the month in which they were due.
(ii) Qualification requirements. To complete the requirements of §61.55(b)(1) or (2) within the period specified in paragraph 2.(b)(1)(i)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(1)(i)(B) of this SFAR, the person—
(A) Must review and become familiar with the following information for the specific type of aircraft for which second-in-command privileges are sought—
(1) Operational procedures applicable to the powerplant, equipment, and systems;
(2) Performance specifications and limitations;
(3) Normal, abnormal, and emergency operating procedures;
(4) Flight manual; and
(5) Placards and markings; and
(B) Prior to serving as second-in-command, must have logged at least three takeoffs and landings to a full stop as the sole manipulator of the flight controls within the 180 days preceding the date of the flight.
(2) Flight review requirements of §61.56. A person who has not completed a flight review within the previous 24 calendar months in accordance with §61.56 may continue to act as pilot in command of an aircraft, provided the following requirements are met—
(i) Airmen requirements. The person was current to act as pilot in command of an aircraft in March 2020 and, to maintain currency, is required to complete a flight review under §61.56 between March 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021.
(ii) Qualification requirements. To act as pilot in command of an aircraft during the period specified in paragraph 2.(b)(2)(iii)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(2)(iii)(B) of this SFAR, the person must have—
(A) Within the 12 calendar months preceding the month in which the flight review is due, logged at least 10 hours of flight time as pilot in command in an aircraft for which that pilot is rated; and
(B) Since January 1, 2020 and preceding the date of flight, completed online Wings courses for pilots from the FAA Safety Team website, available at www.faasafety.gov. The online training courses must total at least 3 Wings credits.
(iii) Grace period. (A) A person who is required to complete a flight review under §61.56 between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 may act as pilot in command of an aircraft for a duration of three calendar months from the month in which the flight review was due. Before acting as pilot in command of an aircraft in the fourth month after the month in which the flight review was due, the person must satisfactorily complete a flight review in accordance with §61.56.
(B) A person who is required to complete a flight review under §61.56 between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 may act as pilot in command of an aircraft for a duration of two calendar months from the month in which the flight review was due. Before acting as pilot in command of an aircraft in the third month after the month in which the flight review was due, the person must satisfactorily complete a flight review in accordance with §61.56.
(3) Instrument experience requirements of §61.57. A person who has not performed and logged the tasks required by §61.57(c)(1) within the 6 calendar months preceding the month of the flight may continue to act as pilot in command under IFR or in weather conditions less than the minimums prescribed for VFR, provided the following requirements are met—
(i) Qualification requirements. The person has—
(A) Within the 6 calendar months preceding the month of the flight, performed and logged at least three instrument approaches in actual weather conditions, or under simulated conditions using a view-limiting device; and
(B) Within the 9 calendar months preceding the month of the flight, performed and logged the tasks required by §61.57(c)(1).
(ii) Grace period. Between April 30, 2020 and September 30, 2020, a person who meets the qualification requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(3)(i) of this SFAR may act as pilot in command under IFR or in weather conditions less than the minimums prescribed for VFR.
(iii) Instrument currency after September 30, 2020. Before acting as pilot in command under IFR or in weather conditions less than the minimums prescribed for VFR after September 30, 2020, the person must comply with §61.57(c).
(4) Pilot in command proficiency check requirements of §61.58. (i) Airmen requirements. (A) Notwithstanding the period specified in §61.58(i), a pilot who is required to take a pilot in command proficiency check under §61.58(a)(1) or (2) between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 for purposes of maintaining pilot in command privileges may complete the check in the month before or three months after the month in which it is required, provided the pilot meets the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(4)(ii) of this SFAR.
(B) Notwithstanding the period specified in §61.58(i), a pilot who is required to take a pilot in command proficiency check under §61.58(a)(1) or (2) between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 for purposes of maintaining pilot in command privileges may complete the check in the month before or two months after the month in which it is required, provided the pilot meets the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(4)(ii) of this SFAR.
(C) A pilot who completes the proficiency check within the period prescribed by this paragraph 2.(b)(4)(i)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(4)(i)(B) of this SFAR will be considered to have completed the check in the month in which it was required.
(ii) Qualification requirements. To complete the pilot in command proficiency check required by §61.58(a)(1) or (2) within the period specified in paragraph 2.(b)(4)(i)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(4)(i)(B) of this SFAR, the person—
(A) Must meet the flight experience requirements of §61.57 that are applicable to the operation to be conducted; and
(B) Within the 3 calendar months preceding the month of the flight, must have reviewed the following information for the specific type of aircraft for which pilot in command privileges are sought—
(1) Operational procedures applicable to the powerplant, equipment, and systems;
(2) Performance specifications and limitations;
(3) Normal, abnormal, and emergency operating procedures;
(4) Flight manual; and
(5) Placards and markings.
(5) Flight Crewmember Requirements of Part 91, Subpart K, of this Chapter.
(i) Testing and checking Requirements. (A) Notwithstanding the period specified in §91.1071(a) of this chapter, a crewmember who is required to take a test or a flight check under §91.1065(a), §91.1065(b), §91.1067, §91.1069(a), or §91.1069(b) of this chapter between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 for purposes of maintaining qualification may complete the test or check in the month before or three months after the month it is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR are met.
(B) Notwithstanding the period specified in §91.1071(a) of this chapter, a crewmember who is required to take a test or a flight check under §91.1065(a), §91.1065(b), §91.1067, §91.1069(a), or §91.1069(b) of this chapter between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 for purposes of maintaining qualification may complete the test or check in the month before or two months after the month it is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR are met.
(C) A crewmember who completes a test or check in accordance with paragraph 2.(b)(5)(i)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(5)(i)(B) of this SFAR will be considered to have completed the test or check in the month in which it was required.
(ii) Recurrent training requirements. (A) Notwithstanding the period specified in §91.1073(b) of this chapter, a crewmember who is required to complete recurrent training under §91.1099 or §91.1107(c) of this chapter between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 for purposes of maintaining qualification may complete that training in the month before or three months after the month in which it is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR are met.
(B) Notwithstanding the period specified in §91.1073(b) of this chapter, a crewmember who is required to complete recurrent training under §91.1099 or §91.1107(c) of this chapter between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 for purposes of maintaining qualification may complete that training in the month before or two months after the month in which it is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR are met.
(C) A crewmember who completes recurrent training in accordance with this paragraph 2.(b)(5)(ii)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(5)(ii)(B) will be considered to have completed the training in the month in which it was required.
(iii) Instrument experience.
(A) Precision instrument approaches. A pilot who has not satisfactorily demonstrated the type of precision instrument approach procedure to be used within the previous six months in accordance with §91.1069(c) of this chapter may continue to use that type of approach procedure, provided the following requirements are met—
(1) Airmen requirements. The person was current under §91.1069(c) of this chapter to use that type of precision instrument approach procedure in March 2020, and is required to demonstrate that type of precision instrument approach procedure between March 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021.
(2) Grace period. (i) For a person who is required to demonstrate that type of precision instrument approach procedure between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020, the person satisfactorily demonstrates that type of precision instrument approach procedure within three months after the month in which it was required.
(ii) For a person who is required to demonstrate that type of precision instrument approach procedure between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021, the person satisfactorily demonstrates that type of precision instrument approach procedure within two months after the month in which it was required.
(3) Safety mitigations. The management specification holder satisfies paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR.
(B) Non-precision instrument approaches. A pilot who has not satisfactorily demonstrated either the type of non-precision instrument approach procedure to be used, or any other two different types of non-precision approach procedures, within the previous six months in accordance with §91.1069(c) of this chapter may continue to use that type of non-precision instrument approach procedure, provided the following requirements are met—
(1) Airmen requirements. The person was current under §91.1069(c) of this chapter to use that type of non-precision instrument approach procedure in March 2020, and is required to demonstrate that type of non-precision instrument approach procedure, or any other two different types of non-precision instrument approach procedures, between March 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021.
(2) Grace period. (i) For a person who is required to demonstrate that type of non-precision instrument approach procedure between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020, the person satisfactorily demonstrates that type of non-precision instrument approach procedure within three months after the month in which it was required.
(ii) For a person who is required to demonstrate that type of non-precision instrument approach procedure between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021, the person satisfactorily demonstrates that type of non-precision instrument approach procedure within two months after the month in which it was required.
(3) Safety mitigations. The management specification holder satisfies paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR.
(iv) Check pilot (simulator) and flight instructor (simulator) requirements. (A) Notwithstanding the period specified in §§91.1089(g) and 91.1091(g) of this chapter, a check pilot (simulator) or flight instructor (simulator) who is required to complete the flight segments or line-observation program under §91.1089(f) or §91.1091(f) of this chapter between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 for purposes of maintaining qualification may complete the flight segments or line-observation program requirements in the month before or three months after the month they are required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR are met.
(B) Notwithstanding the period specified in §§91.1089(g) and 91.1091(g) of this chapter, a check pilot (simulator) or flight instructor (simulator) who is required to complete the flight segments or line-observation program under §91.1089(f) or §91.1091(f) of this chapter between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 for purposes of maintaining qualification may complete the flight segments or line-observation program requirements in the month before or two months after the month they are required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR are met.
(C) A check pilot (simulator) or flight instructor (simulator) who completes the flight segments or line-observation program requirements in accordance with this paragraph 2.(b)(5)(iv) will be considered to have completed the requirements in the month in which they were due.
(v) Check pilot and flight instructor observation check requirements. (A) Notwithstanding the period specified in §§91.1093(b) and 91.1095(b) of this chapter, a check pilot or flight instructor who is required to complete an observation check under §91.1093(a)(2) or §91.1095(a)(2) of this chapter between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 for purposes of maintaining qualification may complete the observation check in the month before or three months after the month it is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR are met.
(B) Notwithstanding the period specified in §§91.1093(b) and 91.1095(b) of this chapter, a check pilot or flight instructor who is required to complete an observation check under §91.1093(a)(2) or §91.1095(a)(2) of this chapter between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 for purposes of maintaining qualification may complete the observation check in the month before or two months after the month it is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(5)(vi) of this SFAR are met.
(C) A check pilot or flight instructor who completes an observation check in accordance with this paragraph 2.(b)(5)(v) will be considered to have completed the check in the month it which it was due.
(vi) Safety mitigations. The management specification holder must provide an acceptable plan to the responsible Flight Standards office that contains the following information—
(A) A safety analysis and corresponding risk mitigations to be implemented by the management specification holder; and
(B) The method the management specification holder will use to ensure that each crewmember complying with paragraph 2.(b)(5) of this SFAR remains adequately tested and currently proficient for each aircraft, duty position, and type of operation in which the person serves.
(6) Mitsubishi MU-2B Series Special Training, Experience, and Operating Requirements of Part 91, Subpart N, of this Chapter.
(i) Recurrent training. (A) Notwithstanding the period specified in §91.1705(e) of this chapter, a person who is required to complete recurrent training under §91.1703(e) of this chapter between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 for purposes of complying with §91.1705(a) and (b) may complete the recurrent training in the month before or three months after the month the recurrent training is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(6)(iii) of this SFAR are met.
(B) Notwithstanding the period specified in §91.1705(e) of this chapter, a person who is required to complete recurrent training under §91.1703(e) of this chapter between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 for purposes of complying with §91.1705(a) and (b) may complete the recurrent training in the month before or two months after the month the recurrent training is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(6)(iii) of this SFAR are met.
(C) A person who completes the recurrent training in accordance with this paragraph 2.(b)(6)(i) will be considered to have completed the training in the month it was required.
(ii) Flight review. A person who has not completed a flight review in accordance with §§61.56 and 91.1715(c) of this chapter in a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane or an MU-2B Simulator approved for landings with an approved course conducted under part 142 of this chapter may continue to act as pilot in command of a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane, providing the following requirements are met—
(A) Airmen requirements. The person was—
(1) Current to act as pilot in command of a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane in March 2020 and, to maintain currency, is required to complete a flight review in a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane between March 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021; and
(2) The requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(6)(iii) of this SFAR are met.
(B) Grace period. (1) A person who is required to complete a flight review in a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 may act as pilot in command of a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane for a duration for three calendar months from the month in which the flight review was due. Before acting as pilot in command of an aircraft in the fourth month after the month in which the flight review was due, the person must satisfactorily complete a flight review in accordance with §§61.56 and 91.1715(c) of this chapter in a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane or an MU-2B Simulator approved for landings with an approved course conducted under part 142 of this chapter.
(2) A person who is required to complete a flight review in a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 may act as pilot in command of a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane for a duration for two calendar months from the month in which the flight review was due. Before acting as pilot in command of an aircraft in the third month after the month in which the flight review was due, the person must satisfactorily complete a flight review in accordance with §§61.56 and 91.1715(c) of this chapter in a Mitsubishi MU-2B series airplane or an MU-2B Simulator approved for landings with an approved course conducted under part 142 of this chapter.
(iii) Qualification requirements. To complete the recurrent training during the period provided under paragraph 2.(b)(6)(i)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(6)(i)(B) of this SFAR or to complete the flight review during the period provided under paragraph 2.(b)(6)(ii)(A) or paragraph 2.(b)(6)(ii)(B) of this SFAR, the person must—
(A) Within the 12 calendar months preceding the month the recurrent training or flight review is due, logged at least 10 hours of flight time in an MU-2B series airplane that includes at least 3 hours of flight time in the 3 calendar months preceding the month in which the recurrent training or flight review is due;
(B) Since January 1, 2020, completed online Wings courses for pilots from FAA Safety Team website, available at www.faasafety.gov. The online training courses must total at least 3 Wings credits; and
(C) Prior to manipulating the controls of an MU-2B series airplane, completed three hours of self-study, since January 1, 2020 and preceding the date of the flight, on the following subjects—
(1) The ground training curriculum required by §91.1705(h)(1) of this chapter;
(2) The Special Emphasis Items listed in the approved MU-2B training program that the pilot last completed;
(3) The limitations, procedures, aircraft performance, and MU-2B Cockpit Checklist procedures applicable to the MU-2B model to be flown, which are contained in the flight training curriculum required by §91.1705(h)(2) of this chapter; and
(4) The current general operating and flight rules of part 91 of this chapter.
(7) Aeronautical Knowledge Recency Requirements of §107.65 of this Chapter. A person who has not satisfied the aeronautical knowledge recency requirements of §107.65(a) or (b) of this chapter within the previous 24 calendar months may operate a small unmanned aircraft system under part 107 of this chapter, provided that person meets the following requirements—
(i) Airmen requirements. The person was current to exercise the privileges of a remote pilot certificate in March 2020 and, to maintain aeronautical currency, is required to meet the aeronautical recency requirements in §107.65(a) or (b) of this chapter between April 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020.
(ii) Qualification requirements. The person must have completed an FAA-developed initial or recurrent online training course, available at www.faasafety.gov, covering the areas of knowledge specified in §107.74(a) or (b) of this chapter. Each person is eligible to take an online training course specified in this paragraph 2.(b)(7)(ii) one time for the purpose of obtaining the six calendar month period specified in paragraph 2.(b)(7)(iii) of this SFAR;
(iii) Grace period. The person may operate a small unmanned aircraft system under part 107 of this chapter for a duration of six calendar months from the month in which the person completed the online training course specified in paragraph 2.(b)(7)(ii) of this SFAR. Before operating a small unmanned aircraft system under part 107 in the seventh month after the month in which the person completed the online training course, the person must satisfy §107.65 of this chapter.
(8) Flight Crewmember Requirements of Part 125 of this Chapter.
(i) Recent experience requirements. A person who has not satisfied the recent experience requirements of §125.285(a) of this chapter may be used by a certificate holder (or holder of an A125 letter of deviation authority), and may serve as a required pilot flight crewmember, in operations conducted under part 125 of this chapter, provided the following requirements are met—
(A) Grace period. (1) For flights between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020, the person has made at least three takeoffs and landings, within the preceding 150 days, in the type of airplane in which that person is to serve.
(2) For flights between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021, the person has made at least three takeoffs and landings, within the preceding 120 days, in the type of airplane in which that person is to serve.
(B) Safety Mitigations. The certificate holder complies with paragraph 2.(b)(8)(iii) of this SFAR.
(ii) Testing and checking requirements. (A) Notwithstanding the period specified in §125.293(a) of this chapter, a crewmember who is required to take a test or check under §125.287(a), §125.287(b), §125.289, or §125.291(a) of this chapter between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 for purposes of maintaining qualifications may complete the test or check in the month before or three months after the month it is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(8)(iii) of this SFAR are met.
(B) Notwithstanding the period specified in §125.293(a) of this chapter, a crewmember who is required to take a test or check under §125.287(a), §125.287(b), §125.289, or §125.291(a) of this chapter between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 for purposes of maintaining qualifications may complete the test or check in the month before or two months after the month it is required, provided the requirements of paragraph 2.(b)(8)(iii) of this SFAR are met.
(C) A crewmember who completes the test or check in accordance with this paragraph 2.(b)(8)(ii) will be considered to have completed the test or check in the month in which it was required.
(iii) Safety mitigations. The certificate holder (or holder of an A125 letter of deviation authority) must provide an acceptable plan to its assigned principal operations inspector that contains the following information—
(A) A safety analysis and corresponding risk mitigations to be implemented by the certificate holder (or holder of an A125 letter of deviation authority); and
(B) The method the certificate holder (or holder of an A125 letter of deviation authority) will use to ensure that each crewmember complying with paragraph 2.(b)(8) of this SFAR remains adequately tested and currently proficient for each aircraft, duty position, and type of operation in which the person serves.
(9) Robinson R-22/R-44 Special Training and Experience Requirements of SFAR No. 73 of this Part. A person who has not completed a flight review in a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate, within the preceding 24 calendar months in accordance with paragraph 2(c) of SFAR No. 73 and §61.56, may continue to act as pilot in command of a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate, providing the following requirements are met—
(i) Airmen requirements. The person was current to act as pilot in command of a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate, in March 2020 and, to maintain currency, is required to complete a flight review in a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate, between March 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021.
(ii) Qualification requirements. The person must—
(A) Satisfy the qualification requirements specified in paragraph 2.(b)(2)(ii) of this SFAR, except
(1) The 10 hours of flight time as pilot in command must be obtained in a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate to the privileges sought;
(2) At least 3 hours of flight time must be obtained within the 3 calendar months preceding the month in which the flight review is due; and
(3) The courses required by paragraphs 2.(b)(9)(ii)(C) and (D) of this SFAR may count towards the 3 Wings credits.
(B) Complete three hours of self-study, since January 1, 2020 and preceding the date of flight, on the following subjects—
(1) The awareness training subject areas specified in paragraphs 2.(a)(3)(i) through (v) of SFAR No. 73 of this part;
(2) The current general operating and flight rules of part 91 of this chapter;
(3) Robinson R-22 or R-44 Maneuvers Guide, as applicable to the model(s) in which the airmen holds pilot in command privileges;
(C) Complete Course ALC-103: Helicopter Weight and Balance, Performance at www.faasafety.gov; and
(D) Complete Course ALC-104: Helicopter—General and Flight Aerodynamics at www.faasafety.gov.
(iii) Grace period. (A) A person who is required to complete a flight review under §61.56 between March 1, 2020 and September 30, 2020 may act as a pilot in command of a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate, for a duration of three calendar months from the month in which the flight review was due. Before acting as pilot in command of an aircraft in the fourth month after the month in which the flight review was due, the person must satisfactorily complete a flight review in a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate to the privileges sought, in accordance with paragraph 2(c) of SFAR No. 73 of this part and §61.56.
(B) A person who is required to complete a flight review under §61.56 between October 1, 2020 and January 31, 2021 may act as a pilot in command of a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate, for a duration of two calendar months from the month in which the flight review was due. Before acting as pilot in command of an aircraft in the third month after the month in which the flight review was due, the person must satisfactorily complete a flight review in a Robinson model R-22 or R-44 helicopter, as appropriate to the privileges sought, in accordance with paragraph 2(c) of SFAR No. 73 of this part and §61.56.
3. Duration and renewal requirements.
(a) This Part.
(1) Extension of medical certificate duration requirements. (i) The expiration date of a first-, second-, or third-class medical certificate that expires between March 31, 2020 and January 31, 2021 is extended three calendar months from the duration established in §61.23(d) of this part as follows:
(A) For first-, second-, and third-class medical certificates that expire between March 31, 2020 and September 30, 2020, the expiration date is extended for three calendar months;
(B) Except as provided in paragraph 3.(a)(1)(i)(C) of this SFAR, for first-, second-, and third-class medical certificates that expire between October 31, 2020 and January 31, 2021, the expiration date is extended for two calendar months; and
(C) For first-, second-, and third-class medical certificates that expire between October 31, 2020 and January 31, 2021, the expiration date is extended for three calendar months if the holder of the medical certificate resides in or serves as a pilot of an aircraft in the State of Alaska.
(ii) A certificate extended under this paragraph 3.(a)(1) is considered valid under §61.2(a)(5).
(iii) Unless otherwise prohibited by a foreign country, a person may operate outside of the United States under this paragraph 3.(a)(1) if the person—
(A) Has access to this SFAR when outside the United States; and
(B) Presents a copy of this SFAR for inspection upon request by a foreign Civil Aviation Authority in accordance with the Convention on International Civil Aviation (Chicago Convention), and its Annexes.
(2) Extension of knowledge test duration requirements in §61.39. An applicant for a certificate or rating issued under part 61 of this chapter may satisfy the eligibility requirement in §61.39(a)(1) by passing the required knowledge test:
(i) Within the 27-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test, if a knowledge test is required, provided the knowledge test was passed between March 1, 2018 and September 30, 2018;
(ii) Within the 63-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test for those applicants who complete the airline transport pilot certification training program in §61.156 and pass the knowledge test for an airline transport pilot certificate with a multiengine class rating, provided the knowledge test was passed between March 1, 2015 and September 30, 2015;
(iii) Within the 26-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test, if a knowledge test is required, provided the knowledge test was passed between October 1, 2018 and January 31, 2019; or
(iv) Within the 62-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test for those applicants who complete the airline transport pilot certification training program in §61.156 and pass the knowledge test for an airline transport pilot certificate with a multiengine class rating, provided the knowledge test was passed between October 1, 2015 and January 31, 2016.
(3) Extension of renewal requirements for flight instructor certification. The holder of a flight instructor certificate that expires between March 31, 2020 and May 31, 2020 may renew his or her flight instructor certificate by submitting a completed and signed application to the FAA and satisfactorily completing one of the renewal requirements specified in §61.197(a)(2)(i) through (iv) before June 30, 2020.
(b) Part 63 of this Chapter.
(1) Extension of medical certificate duration requirements. (i) For a person acting as a flight engineer of an aircraft, the expiration date of a second-class (or higher) medical certificate that expires between March 31, 2020 and September 30, 2020 is extended 3 calendar months from the original expiration date.
(ii) Except as provided in paragraph 3.(b)(1)(iii) of this SFAR, for a person acting as a flight engineer of an aircraft, the expiration date of a second-class (or higher) medical certificate that expires between October 31, 2020 and January 31, 2021 is extended 2 calendar months from the original expiration date.
(iii) For a person acting as a flight engineer of an aircraft, the expiration date of a second-class (or higher) medical certificate that expires between October 31, 2020 and January 31, 2021 is extended 3 calendar months from the original expiration date if the flight engineer resides in or serves as a flight engineer in an aircraft in the State of Alaska.
(iv) Unless otherwise prohibited by a foreign country, a person may operate outside of the United States under this paragraph 3.(b)(1) if the person:
(A) Has access to this SFAR when outside the United States; and
(B) Presents a copy of this SFAR for inspection upon request by a foreign Civil Aviation Authority in accordance with the Convention on International Civil Aviation (Chicago Convention), and its Annexes.
(2) Extension of written test duration requirements in §63.35 of this chapter. (i) An applicant for a flight engineer certificate or rating may satisfy the knowledge requirement in §63.35(d) of this chapter by passing the required written test within the 27-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test, provided the written test was passed between March 1, 2018 and September 30, 2018.
(ii) An applicant for a flight engineer certificate or rating may satisfy the knowledge requirement in §63.35(d) of this chapter by passing the required written test within the 26-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test, provided the written test was passed between October 1, 2018 and January 31, 2019.
(c) Part 65 of this Chapter.
(1) Extension of knowledge test duration requirements in §65.55 of this chapter. (i) An applicant for an aircraft dispatcher certificate may satisfy the knowledge requirement in §65.55(b) of this chapter by presenting satisfactory evidence that the applicant passed the knowledge test within the 27-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test, provided the knowledge test was passed between March 1, 2018 and September 30, 2018.
(ii) An applicant for an aircraft dispatcher certificate may satisfy the knowledge requirement in §65.55(b) of this chapter by presenting satisfactory evidence that the applicant passed the knowledge test within the 26-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test, provided the knowledge test was passed between October 1, 2018 and January 31, 2019.
(2) Extension of testing period in §65.71 of this chapter. (i) A person may show eligibility for a mechanic certificate or rating under §65.71 of this chapter by passing all the prescribed tests of part 65, subpart D, of this chapter within a period of 27 months, provided the testing period began between March 1, 2018 and September 30, 2018.
(ii) A person may show eligibility for a mechanic certificate or rating under §65.71 of this chapter by passing all the prescribed tests of part 65, subpart D, of this chapter within a period of 26 months, provided the testing period began between October 1, 2018 and January 31, 2019.
(3) Renewal of inspection authorizations in §65.93 of this chapter.
(i) Grace period for meeting renewal requirements. Notwithstanding the requirement in §65.93(c) of this chapter, an inspection authorization holder who did not complete one of the activities in §65.93(a)(1) through (5) of this chapter by March 31, 2020 of the first year may still be eligible for renewal of an inspection authorization for a 2-year period in March 2021. To be eligible for renewal, the inspection authorization holder must show completion of one of the five activities in §65.93(a)(1) through (5) of this chapter by June 30, 2020, and completion of the one of the five activities in §65.93(a)(1) through (5) of this chapter during the second year of the 2-year period. A person who completes one of the five activities by June 30, 2020 will be considered to have completed the activity by March 31, 2020 of the first year for purposes of determining eligibility under §65.93 of this chapter.
(ii) Inspection authorization privileges after June 2020. If the inspection authorization holder does not complete one of the five activities in §65.93(a)(1) through (5) of this chapter by June 30, 2020, the inspection authorization holder may not exercise inspection authorization privileges after June 30, 2020. The inspection authorization holder may resume exercising inspection authorization privileges only after passing an oral test from an FAA inspector in accordance with §65.93(c) of this chapter.
(4) Military riggers or former military riggers: Special certification rule of §65.117 of this chapter. A person may satisfy the requirements of §65.117(a) and (b) of this chapter for a senior parachute rigger certificate by presenting satisfactory documentary evidence that the person was honorably discharged or released from any status covered by §65.117(a) of this chapter between March 2019 and June 2019, and has served as a parachute rigger for an Armed Force within the 15 months before the date of application.
(d) Relief for U.S. Military and Civilian Personnel Who are Assigned Outside the United States in Support of U.S. Armed Forces Operations. Notwithstanding the six calendar month period specified in paragraph 2 of SFAR No. 100-2 of this part, a person may exercise the relief specified in paragraph 1 of SFAR No. 100-2 for a duration of nine calendar months after returning to the United States, provided the person—
(i) Is eligible in accordance with paragraph 2 of SFAR No. 100-2 of this part;
(ii) Complies with the documentation requirements specified in paragraph 3 of SFAR No. 100-2 of this part; and
(iii) Returned to the United States from deployment between October 2019 and March 2020.
(e) Part 141 of this Chapter.
(1) Pilot school certificate requirements of §141.5 of this chapter.
(i) Provisional pilot school. Notwithstanding the period specified in §141.5 of this chapter, a provisional pilot school may apply for, and the FAA may issue, a pilot school certificate with the appropriate ratings if the following requirements are met—
(A) The provisional pilot school must satisfy the requirements of §141.5(a) through (e) of this chapter before December 31, 2020;
(B) The provisional pilot school certificate must expire between April 2020 and June 2020; and
(C) The provisional pilot school meets the requirements of paragraph 3.(e)(1)(ii) of this SFAR.
(ii) Safety mitigations.
(A) The provisional pilot school must notify its responsible Flight Standards office that it is applying for a pilot school certificate in accordance with this SFAR.
(B) Each provisional pilot school must include in its notification an acceptable plan that explains the method to meet the requirements of §141.5(d) and (e) of this chapter, including—
(1) Ensuring each instructor used for ground or flight training is current and proficient; and
(2) Evaluating students to determine if they are assigned to the proper stage of the training course and if additional training is necessary.
(2) Renewal of certificates and ratings in §141.27 of this Chapter.
(i) Pilot school. A pilot school may apply for renewal of its pilot school certificate and ratings after the expiration of its pilot schools certificate, provided the school applies for renewal before December 31, 2020 and the following requirements are met—
(A) The pilot school must meet §141.27(a)(2) of this chapter before December 31, 2020;
(B) The pilot school certificate must expire between April 2020 and June 2020; and
(C) The pilot school meets the requirements of paragraph 3.(e)(2)(ii) of this SFAR.
(ii) Safety mitigations.
(A) Each pilot school must submit to the responsible Flight Standards office notification that it will renew its pilot school certificate in accordance with this SFAR.
(B) Each pilot school must include in its notification an acceptable plan that explains the method to regain currency, including—
(1) Ensuring each instructor used for ground or flight training is current and proficient; and
(2) Evaluating students to determine if they are assigned to the proper stage of the training course and if additional training is necessary.
4. Other relief for special flight permits issued under §21.197(c) of this chapter. In addition to the purposes specified in §21.197(c) of this chapter, notwithstanding §§119.5(l) and 91.1015(a) of this chapter, a special flight permit with a continuing authorization may be issued under §21.197(c) of this chapter through March 31, 2021, for aircraft that may not meet applicable airworthiness requirements, but are capable of safe flight for the purpose of flying the aircraft to a point of storage, provided the following requirements are met—
(a) The air carrier or operator must hold a special flight permit with continuing authorization to conduct a ferry flight program issued under §21.197(c) of this chapter; and
(b) The certificate holder or management specification holder must notify the responsible Flight Standards office each time the special flight permit is used for the purpose of flying the aircraft to a point of storage.
5. Expiration date. This SFAR is effective until April 30, 2021. The FAA may amend, rescind, or extend the SFAR as necessary.
6. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) control number. The Paperwork Reduction Act of 1995 (44 U.S.C. 3501-3520) requires the FAA to get approval from OMB for our information collection activities. The OMB control number assigned to the FAA’s information collection associated with this SFAR is 2120-0788.
[Doc. No. FAA-2020-0446; Amdt. 61-147, 85 FR 62966, Oct. 6, 2020]
EFFECTIVE DATE NOTE: Doc. No. FAA-2020-0446; Amdt. No. 61-147, 85 FR 62966, Oct. 6, 2020SFAR 118-2 to part 61 was added, effective Oct. 1, 2020 through Apr. 30, 2021.
Subpart A—General
§61.1 Applicability and definitions.
(a) Except as provided in part 107 of this chapter, this part prescribes:
(1) The requirements for issuing pilot, flight instructor, and ground instructor certificates and ratings; the conditions under which those certificates and ratings are necessary; and the privileges and limitations of those certificates and ratings.
(2) The requirements for issuing pilot, flight instructor, and ground instructor authorizations; the conditions under which those authorizations are necessary; and the privileges and limitations of those authorizations.
(3) The requirements for issuing pilot, flight instructor, and ground instructor certificates and ratings for persons who have taken courses approved by the Administrator under other parts of this chapter.
(b) For the purpose of this part:
Accredited has the same meaning as defined by the Department of Education in 34 CFR 600.2.
Aeronautical experience means pilot time obtained in an aircraft, flight simulator, or flight training device for meeting the appropriate training and flight time requirements for an airman certificate, rating, flight review, or recency of flight experience requirements of this part.
Authorized instructor means—
(i) A person who holds a ground instructor certificate issued under part 61 of this chapter and is in compliance with §61.217, when conducting ground training in accordance with the privileges and limitations of his or her ground instructor certificate;
(ii) A person who holds a flight instructor certificate issued under part 61 of this chapter and is in compliance with §61.197, when conducting ground training or flight training in accordance with the privileges and limitations of his or her flight instructor certificate; or
(iii) A person authorized by the Administrator to provide ground training or flight training under part 61, 121, 135, or 142 of this chapter when conducting ground training or flight training in accordance with that authority.
Aviation training device means a training device, other than a full flight simulator or flight training device, that has been evaluated, qualified, and approved by the Administrator.
Complex airplane means an airplane that has a retractable landing gear, flaps, and a controllable pitch propeller, including airplanes equipped with an engine control system consisting of a digital computer and associated accessories for controlling the engine and propeller, such as a full authority digital engine control; or, in the case of a seaplane, flaps and a controllable pitch propeller, including seaplanes equipped with an engine control system consisting of a digital computer and associated accessories for controlling the engine and propeller, such as a full authority digital engine control.
Cross-country time means—
(i) Except as provided in paragraphs (ii) through (vi) of this definition, time acquired during flight—
(A) Conducted by a person who holds a pilot certificate;
(B) Conducted in an aircraft;
(C) That includes a landing at a point other than the point of departure; and
(D) That involves the use of dead reckoning, pilotage, electronic navigation aids, radio aids, or other navigation systems to navigate to the landing point.
(ii) For the purpose of meeting the aeronautical experience requirements (except for a rotorcraft category rating), for a private pilot certificate (except for a powered parachute category rating), a commercial pilot certificate, or an instrument rating, or for the purpose of exercising recreational pilot privileges (except in a rotorcraft) under §61.101 (c), time acquired during a flight—
(A) Conducted in an appropriate aircraft;
(B) That includes a point of landing that was at least a straight-line distance of more than 50 nautical miles from the original point of departure; and
(C) That involves the use of dead reckoning, pilotage, electronic navigation aids, radio aids, or other navigation systems to navigate to the landing point.
(iii) For the purpose of meeting the aeronautical experience requirements for a sport pilot certificate (except for powered parachute privileges), time acquired during a flight conducted in an appropriate aircraft that—
(A) Includes a point of landing at least a straight line distance of more than 25 nautical miles from the original point of departure; and
(B) Involves, as applicable, the use of dead reckoning; pilotage; electronic navigation aids; radio aids; or other navigation systems to navigate to the landing point.
(iv) For the purpose of meeting the aeronautical experience requirements for a sport pilot certificate with powered parachute privileges or a private pilot certificate with a powered parachute category rating, time acquired during a flight conducted in an appropriate aircraft that—
(A) Includes a point of landing at least a straight line distance of more than 15 nautical miles from the original point of departure; and
(B) Involves, as applicable, the use of dead reckoning; pilotage; electronic navigation aids; radio aids; or other navigation systems to navigate to the landing point.
(v) For the purpose of meeting the aeronautical experience requirements for any pilot certificate with a rotorcraft category rating or an instrument-helicopter rating, or for the purpose of exercising recreational pilot privileges, in a rotorcraft, under §61.101(c), time acquired during a flight—
(A) Conducted in an appropriate aircraft;
(B) That includes a point of landing that was at least a straight-line distance of more than 25 nautical miles from the original point of departure; and
(C) That involves the use of dead reckoning, pilotage, electronic navigation aids, radio aids, or other navigation systems to navigate to the landing point.
(vi) For the purpose of meeting the aeronautical experience requirements for an airline transport pilot certificate (except with a rotorcraft category rating), time acquired during a flight—
(A) Conducted in an appropriate aircraft;
(B) That is at least a straight-line distance of more than 50 nautical miles from the original point of departure; and
(C) That involves the use of dead reckoning, pilotage, electronic navigation aids, radio aids, or other navigation systems.
(vii) For a military pilot who qualifies for a commercial pilot certificate (except with a rotorcraft category rating) under §61.73 of this part, time acquired during a flight—
(A) Conducted in an appropriate aircraft;
(B) That is at least a straight-line distance of more than 50 nautical miles from the original point of departure; and
(C) That involves the use of dead reckoning, pilotage, electronic navigation aids, radio aids, or other navigation systems.
Examiner means any person who is authorized by the Administrator to conduct a pilot proficiency test or a practical test for an airman certificate or rating issued under this part, or a person who is authorized to conduct a knowledge test under this part.
Flight training means that training, other than ground training, received from an authorized instructor in flight in an aircraft.
Ground training means that training, other than flight training, received from an authorized instructor.
Institution of higher education has the same meaning as defined by the Department of Education in 34 CFR 600.4.
Instrument approach means an approach procedure defined in part 97 of this chapter.
Instrument training means that time in which instrument training is received from an authorized instructor under actual or simulated instrument conditions.
Knowledge test means a test on the aeronautical knowledge areas required for an airman certificate or rating that can be administered in written form or by a computer.
Nationally recognized accrediting agency has the same meaning as defined by the Department of Education in 34 CFR 600.2.
Night vision goggles means an appliance worn by a pilot that enhances the pilot’s ability to maintain visual surface reference at night.
Night vision goggle operation means the portion of a flight that occurs during the time period from 1 hour after sunset to 1 hour before sunrise where the pilot maintains visual surface reference using night vision goggles in an aircraft that is approved for such an operation.
Pilot time means that time in which a person—
(i) Serves as a required pilot flight crewmember;
(ii) Receives training from an authorized instructor in an aircraft, full flight simulator, flight training device, or aviation training device;
(iii) Gives training as an authorized instructor in an aircraft, full flight simulator, flight training device, or aviation training device; or
(iv) Serves as second in command in operations conducted in accordance with §135.99(c) of this chapter when a second pilot is not required under the type certification of the aircraft or the regulations under which the flight is being conducted, provided the requirements in §61.159(c) are satisfied.
Practical test means a test on the areas of operations for an airman certificate, rating, or authorization that is conducted by having the applicant respond to questions and demonstrate maneuvers in flight, in a flight simulator, or in a flight training device.
Set of aircraft means aircraft that share similar performance characteristics, such as similar airspeed and altitude operating envelopes, similar handling characteristics, and the same number and type of propulsion systems.
Student pilot seeking a sport pilot certificate means a person who has received an endorsement—
(i) To exercise student pilot privileges from a certificated flight instructor with a sport pilot rating; or
(ii) That includes a limitation for the operation of a light-sport aircraft specified in §61.89(c) issued by a certificated flight instructor with other than a sport pilot rating.
Technically advanced airplane (TAA) means an airplane equipped with an electronically advanced avionics system.
Training time means training received—
(i) In flight from an authorized instructor;
(ii) On the ground from an authorized instructor; or
(iii) In a flight simulator or flight training device from an authorized instructor.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40893, July 30, 1997 as amended by Amdt. 61-110, 69 FR 44864, July 27, 2004; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42546, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-128, 76 FR 54105, Aug. 31, 2011; Amdt. 61-130, 78 FR 42372, July 15, 2013; Amdt. 61-137, 81 FR 42208, June 28, 2016; Amdt. 61-142, 83 FR 30276, June 27, 2018]
§61.2 Exercise of Privilege.
(a) Validity. No person may:
(1) Exercise privileges of a certificate, rating, endorsement, or authorization issued under this part if the certificate, rating or authorization is surrendered, suspended, revoked or expired.
(2) Exercise privileges of a flight instructor certificate if that flight instructor certificate is surrendered, suspended, revoked or expired.
(3) Exercise privileges of a foreign pilot certificate to operate an aircraft of foreign registry under §61.3(b) if the certificate is surrendered, suspended, revoked or expired.
(4) Exercise privileges of a pilot certificate issued under §61.75, or an authorization issued under §61.77, if the foreign pilot certificate relied upon for the issuance of the U.S. pilot certificate or authorization is surrendered, suspended, revoked or expired.
(5) Exercise privileges of a medical certificate issued under part 67 to meet any requirements of part 61 if the medical certificate is surrendered, suspended, revoked or expired according to the duration standards set forth in §61.23(d).
(6) Use an official government issued driver’s license to meet any requirements of part 61 related to holding that driver’s license, if the driver’s license is surrendered, suspended, revoked or expired.
(b) Currency. No person may:
(1) Exercise privileges of an airman certificate, rating, endorsement, or authorization issued under this part unless that person meets the appropriate airman and medical recency requirements of this part, specific to the operation or activity.
(2) Exercise privileges of a foreign pilot license within the United States to conduct an operation described in §61.3(b), unless that person meets the appropriate airman and medical recency requirements of the country that issued the license, specific to the operation.
[Doc. No. FAA-2006-26661, 74 FR 42546, Aug. 21, 2009]
§61.3 Requirement for certificates, ratings, and authorizations.
(a) Required pilot certificate for operating a civil aircraft of the United States. No person may serve as a required pilot flight crewmember of a civil aircraft of the United States, unless that person:
(1) Has in the person’s physical possession or readily accessible in the aircraft when exercising the privileges of that pilot certificate or authorization—
(i) A pilot certificate issued under this part and in accordance with §61.19;
(ii) A special purpose pilot authorization issued under §61.77;
(iii) A temporary certificate issued under §61.17;
(iv) A document conveying temporary authority to exercise certificate privileges issued by the Airmen Certification Branch under §61.29(e);
(v) When engaged in a flight operation within the United States for a part 119 certificate holder authorized to conduct operations under part 121 or 135 of this chapter, a temporary document provided by that certificate holder under an approved certificate verification plan;
(vi) When engaged in a flight operation within the United States for a fractional ownership program manager authorized to conduct operations under part 91, subpart K, of this chapter, a temporary document provided by that program manager under an approved certificate verification plan; or
(vii) When operating an aircraft within a foreign country, a pilot license issued by that country may be used.
(2) Has a photo identification that is in that person’s physical possession or readily accessible in the aircraft when exercising the privileges of that pilot certificate or authorization. The photo identification must be a:
(i) Driver’s license issued by a State, the District of Columbia, or territory or possession of the United States;
(ii) Government identification card issued by the Federal government, a State, the District of Columbia, or a territory or possession of the United States;
(iii) U.S. Armed Forces’ identification card;
(iv) Official passport;
(v) Credential that authorizes unescorted access to a security identification display area at an airport regulated under 49 CFR part 1542; or
(vi) Other form of identification that the Administrator finds acceptable.
(b) Required pilot certificate for operating a foreign-registered aircraft within the United States. No person may serve as a required pilot flight crewmember of a civil aircraft of foreign registry within the United States, unless—
(1) That person’s pilot certificate or document issued under §61.29(e) is in that person’s physical possession or readily accessible in the aircraft when exercising the privileges of that pilot certificate; and
(2) Has been issued in accordance with this part, or has been issued or validated by the country in which the aircraft is registered.
(c) Medical certificate. (1) A person may serve as a required pilot flight crewmember of an aircraft only if that person holds the appropriate medical certificate issued under part 67 of this chapter, or other documentation acceptable to the FAA, that is in that person’s physical possession or readily accessible in the aircraft. Paragraph (c)(2) of this section provides certain exceptions to the requirement to hold a medical certificate.
(2) A person is not required to meet the requirements of paragraph (c)(1) of this section if that person—
(i) Is exercising the privileges of a student pilot certificate while seeking a pilot certificate with a glider category rating, a balloon class rating, or glider or balloon privileges;
(ii) Is exercising the privileges of a student pilot certificate while seeking a sport pilot certificate with other than glider or balloon privileges and holds a U.S. driver’s license;
(iii) Is exercising the privileges of a student pilot certificate while seeking a pilot certificate with a weight-shift-control aircraft category rating or a powered parachute category rating and holds a U.S. driver’s license;
(iv) Is exercising the privileges of a sport pilot certificate with glider or balloon privileges;
(v) Is exercising the privileges of a sport pilot certificate with other than glider or balloon privileges and holds a U.S. driver’s license. A person who has applied for or held a medical certificate may exercise the privileges of a sport pilot certificate using a U.S. driver’s license only if that person—
(A) Has been found eligible for the issuance of at least a third-class airman medical certificate at the time of his or her most recent application; and
(B) Has not had his or her most recently issued medical certificate suspended or revoked or most recent Authorization for a Special Issuance of a Medical Certificate withdrawn.
(vi) Is holding a pilot certificate with a balloon class rating and is piloting or providing training in a balloon as appropriate;
(vii) Is holding a pilot certificate or a flight instructor certificate with a glider category rating, and is piloting or providing training in a glider, as appropriate;
(viii) Is exercising the privileges of a flight instructor certificate, provided the person is not acting as pilot in command or as a required pilot flight crewmember;
(ix) Is exercising the privileges of a ground instructor certificate;
(x) Is operating an aircraft within a foreign country using a pilot license issued by that country and possesses evidence of current medical qualification for that license;
(xi) Is operating an aircraft with a U.S. pilot certificate, issued on the basis of a foreign pilot license, issued under §61.75, and holds a medical certificate issued by the foreign country that issued the foreign pilot license, which is in that person’s physical possession or readily accessible in the aircraft when exercising the privileges of that airman certificate;
(xii) Is a pilot of the U.S. Armed Forces, has an up-to-date U.S. military medical examination, and holds military pilot flight status;
(xiii) Is exercising the privileges of a student, recreational or private pilot certificate for operations conducted under the conditions and limitations set forth in §61.113(i) and holds a U.S. driver’s license; or
(xiv) Is exercising the privileges of a flight instructor certificate and acting as pilot in command for operations conducted under the conditions and limitations set forth in §61.113(i) and holds a U.S. driver’s license.
(d) Flight instructor certificate. (1) A person who holds a flight instructor certificate issued under this part must have that certificate, or other documentation acceptable to the Administrator, in that person’s physical possession or readily accessible in the aircraft when exercising the privileges of that flight instructor certificate.
(2) Except as provided in paragraph (d)(3) of this section, no person other than the holder of a flight instructor certificate issued under this part with the appropriate rating on that certificate may—
(i) Give training required to qualify a person for solo flight and solo cross-country flight;
(ii) Endorse an applicant for a—
(A) Pilot certificate or rating issued under this part;
(B) Flight instructor certificate or rating issued under this part; or
(C) Ground instructor certificate or rating issued under this part;
(iii) Endorse a pilot logbook to show training given; or
(iv) Endorse a logbook for solo operating privileges.
(3) A flight instructor certificate issued under this part is not necessary—
(i) Under paragraph (d)(2) of this section, if the training is given by the holder of a commercial pilot certificate with a lighter-than-air rating, provided the training is given in accordance with the privileges of the certificate in a lighter-than-air aircraft;
(ii) Under paragraph (d)(2) of this section, if the training is given by the holder of an airline transport pilot certificate with a rating appropriate to the aircraft in which the training is given, provided the training is given in accordance with the privileges of the certificate and conducted in accordance with an approved air carrier training program approved under part 121 or part 135 of this chapter;
(iii) Under paragraph (d)(2) of this section, if the training is given by a person who is qualified in accordance with subpart C of part 142 of this chapter, provided the training is conducted in accordance with an approved part 142 training program;
(iv) Under paragraphs (d)(2)(i), (d)(2)(ii)(C), and (d)(2)(iii) of this section, if the training is given by the holder of a ground instructor certificate in accordance with the privileges of the certificate; or
(v) Under paragraph (d)(2)(iii) of this section, if the training is given by an authorized flight instructor under §61.41 of this part.
(e) Instrument rating. No person may act as pilot in command of a civil aircraft under IFR or in weather conditions less than the minimums prescribed for VFR flight unless that person holds:
(1) The appropriate aircraft category, class, type (if required), and instrument rating on that person’s pilot certificate for any airplane, helicopter, or powered-lift being flown;
(2) An airline transport pilot certificate with the appropriate aircraft category, class, and type rating (if required) for the aircraft being flown;
(3) For a glider, a pilot certificate with a glider category rating and an airplane instrument rating; or
(4) For an airship, a commercial pilot certificate with a lighter-than-air category rating and airship class rating.
(f) Category II pilot authorization. Except for a pilot conducting Category II operations under part 121 or part 135, a person may not:
(1) Act as pilot in command of a civil aircraft during Category II operations unless that person—
(i) Holds a Category II pilot authorization for that category or class of aircraft, and the type of aircraft, if applicable; or
(ii) In the case of a civil aircraft of foreign registry, is authorized by the country of registry to act as pilot in command of that aircraft in Category II operations.
(2) Act as second in command of a civil aircraft during Category II operations unless that person—
(i) Holds a pilot certificate with category and class ratings for that aircraft and an instrument rating for that category aircraft;
(ii) Holds an airline transport pilot certificate with category and class ratings for that aircraft; or
(iii) In the case of a civil aircraft of foreign registry, is authorized by the country of registry to act as second in command of that aircraft during Category II operations.
(g) Category III pilot authorization. Except for a pilot conducting Category III operations under part 121 or part 135, a person may not:
(1) Act as pilot in command of a civil aircraft during Category III operations unless that person—
(i) Holds a Category III pilot authorization for that category or class of aircraft, and the type of aircraft, if applicable; or
(ii) In the case of a civil aircraft of foreign registry, is authorized by the country of registry to act as pilot in command of that aircraft in Category III operations.
(2) Act as second in command of a civil aircraft during Category III operations unless that person—
(i) Holds a pilot certificate with category and class ratings for that aircraft and an instrument rating for that category aircraft;
(ii) Holds an airline transport pilot certificate with category and class ratings for that aircraft; or
(iii) In the case of a civil aircraft of foreign registry, is authorized by the country of registry to act as second in command of that aircraft during Category III operations.
(h) Category A aircraft pilot authorization. The Administrator may issue a certificate of authorization for a Category II or Category III operation to the pilot of a small aircraft that is a Category A aircraft, as identified in §97.3(b)(1) of this chapter if:
(1) The Administrator determines that the Category II or Category III operation can be performed safely by that pilot under the terms of the certificate of authorization; and
(2) The Category II or Category III operation does not involve the carriage of persons or property for compensation or hire.
(i) Ground instructor certificate. (1) Each person who holds a ground instructor certificate issued under this part must have that certificate or a temporary document issued under §61.29(e) in that person’s physical possession or immediately accessible when exercising the privileges of that certificate.
(2) Except as provided in paragraph (i)(3) of this section, no person other than the holder of a ground instructor certificate, issued under this part or part 143, with the appropriate rating on that certificate may—
(i) Give ground training required to qualify a person for solo flight and solo cross-country flight;
(ii) Endorse an applicant for a knowledge test required for a pilot, flight instructor, or ground instructor certificate or rating issued under this part; or
(iii) Endorse a pilot logbook to show ground training given.
(3) A ground instructor certificate issued under this part is not necessary—
(i) Under paragraph (i)(2) of this section, if the training is given by the holder of a flight instructor certificate issued under this part in accordance with the privileges of that certificate;
(ii) Under paragraph (i)(2) of this section, if the training is given by the holder of a commercial pilot certificate with a lighter-than-air rating, provided the training is given in accordance with the privileges of the certificate in a lighter-than-air aircraft;
(iii) Under paragraph (i)(2) of this section, if the training is given by the holder of an airline transport pilot certificate with a rating appropriate to the aircraft in which the training is given, provided the training is given in accordance with the privileges of the certificate and conducted in accordance with an approved air carrier training program approved under part 121 or part 135 of this chapter;
(iv) Under paragraph (i)(2) of this section, if the training is given by a person who is qualified in accordance with subpart C of part 142 of this chapter, provided the training is conducted in accordance with an approved part 142 training program; or
(v) Under paragraph (i)(2)(iii) of this section, if the training is given by an authorized flight instructor under §61.41 of this part.
(j) Age limitation for certain operations. (1) Age limitation. No person who holds a pilot certificate issued under this part may serve as a pilot on a civil airplane of U.S. registry in the following operations if the person has reached his or her 60th birthday or, in the case of operations with more than one pilot, his or her 65th birthday:
(i) Scheduled international air services carrying passengers in turbojet-powered airplanes;
(ii) Scheduled international air services carrying passengers in airplanes having a passenger-seat configuration of more than nine passenger seats, excluding each crewmember seat;
(iii) Nonscheduled international air transportation for compensation or hire in airplanes having a passenger-seat configuration of more than 30 passenger seats, excluding each crewmember seat; or
(iv) Scheduled international air services, or nonscheduled international air transportation for compensation or hire, in airplanes having a payload capacity of more than 7,500 pounds.
(2) Definitions. (i) “International air service,” as used in this paragraph (j), means scheduled air service performed in airplanes for the public transport of passengers, mail, or cargo, in which the service passes through the airspace over the territory of more than one country.
(ii) “International air transportation,” as used in this paragraph (j), means air transportation performed in airplanes for the public transport of passengers, mail, or cargo, in which the service passes through the airspace over the territory of more than one country.
(k) Special purpose pilot authorization. Any person that is required to hold a special purpose pilot authorization, issued in accordance with §61.77 of this part, must have that authorization and the person’s foreign pilot license in that person’s physical possession or have it readily accessible in the aircraft when exercising the privileges of that authorization.
(l) Inspection of certificate. Each person who holds an airman certificate, temporary document in accordance with paragraph (a)(1)(v) or (vi) of this section, medical certificate, documents establishing alternative medical qualification under part 68 of this chapter, authorization, or license required by this part must present it and their photo identification as described in paragraph (a)(2) of this section for inspection upon a request from:
(1) The Administrator;
(2) An authorized representative of the National Transportation Safety Board;
(3) Any Federal, State, or local law enforcement officer; or
(4) An authorized representative of the Transportation Security Administration.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40894, July 30, 1997; Amdt. 61-111, 67 FR 65861, Oct. 28, 2002; Amdt. 61-110, 69 FR 44864, July 27, 2004; Amdt. 61-123, 74 FR 34234, July 15, 2009; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42546, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-124A, 74 FR 53644, Oct. 20, 2009; Amdt. 61-131, 78 FR 56828, Sept. 16, 2013; Amdt. 61-134, 80 FR 33400, June 12, 2015; Docket FAA-2010-1127, Amdt. 61-135, 81 FR 1306, Jan. 12, 2016; Doc. No. FAA-2016-9157, Amdt. 61-140, 82 FR 3164, Jan. 11, 2017; Amdt. 60-6, 83 FR 30276, June 27, 2018]
§61.4 Qualification and approval of flight simulators and flight training devices.
(a) Except as specified in paragraph (b) or (c) of this section, each flight simulator and flight training device used for training, and for which an airman is to receive credit to satisfy any training, testing, or checking requirement under this chapter, must be qualified and approved by the Administrator for—
(1) The training, testing, and checking for which it is used;
(2) Each particular maneuver, procedure, or crewmember function performed; and
(3) The representation of the specific category and class of aircraft, type of aircraft, particular variation within the type of aircraft, or set of aircraft for certain flight training devices.
(b) Any device used for flight training, testing, or checking that has been determined to be acceptable to or approved by the Administrator prior to August 1, 1996, which can be shown to function as originally designed, is considered to be a flight training device, provided it is used for the same purposes for which it was originally accepted or approved and only to the extent of such acceptance or approval.
(c) The Administrator may approve a device other than a flight simulator or flight training device for specific purposes.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40895, July 30, 1997]
§61.5 Certificates and ratings issued under this part.
(a) The following certificates are issued under this part to an applicant who satisfactorily accomplishes the training and certification requirements for the certificate sought:
(1) Pilot certificates—
(i) Student pilot.
(ii) Sport pilot.
(iii) Recreational pilot.
(iv) Private pilot.
(v) Commercial pilot.
(vi) Airline transport pilot.
(2) Flight instructor certificates.
(3) Ground instructor certificates.
(b) The following ratings are placed on a pilot certificate (other than student pilot) when an applicant satisfactorily accomplishes the training and certification requirements for the rating sought:
(1) Aircraft category ratings—
(i) Airplane.
(ii) Rotorcraft.
(iii) Glider.
(iv) Lighter-than-air.
(v) Powered-lift.
(vi) Powered parachute.
(vii) Weight-shift-control aircraft.
(2) Airplane class ratings—
(i) Single-engine land.
(ii) Multiengine land.
(iii) Single-engine sea.
(iv) Multiengine sea.
(3) Rotorcraft class ratings—
(i) Helicopter.
(ii) Gyroplane.
(4) Lighter-than-air class ratings—
(i) Airship.
(ii) Balloon.
(5) Weight-shift-control aircraft class ratings—
(i) Weight-shift-control aircraft land.
(ii) Weight-shift-control aircraft sea.
(6) Powered parachute class ratings—
(i) Powered parachute land.
(ii) Powered parachute sea.
(7) Aircraft type ratings—
(i) Large aircraft other than lighter-than-air.
(ii) Turbojet-powered airplanes.
(iii) Other aircraft type ratings specified by the Administrator through the aircraft type certification procedures.
(iv) Second-in-command pilot type rating for aircraft that is certificated for operations with a minimum crew of at least two pilots.
(8) Instrument ratings (on private and commercial pilot certificates only)—
(i) Instrument—Airplane.
(ii) Instrument—Helicopter.
(iii) Instrument—Powered-lift.
(c) The following ratings are placed on a flight instructor certificate when an applicant satisfactorily accomplishes the training and certification requirements for the rating sought:
(1) Aircraft category ratings—
(i) Airplane.
(ii) Rotorcraft.
(iii) Glider.
(iv) Powered-lift.
(2) Airplane class ratings—
(i) Single-engine.
(ii) Multiengine.
(3) Rotorcraft class ratings—
(i) Helicopter.
(ii) Gyroplane.
(4) Instrument ratings—
(i) Instrument—Airplane.
(ii) Instrument—Helicopter.
(iii) Instrument—Powered-lift.
(5) Sport pilot rating.
(d) The following ratings are placed on a ground instructor certificate when an applicant satisfactorily accomplishes the training and certification requirements for the rating sought:
(1) Basic.
(2) Advanced.
(3) Instrument.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-110, 69 FR 44864, July 27, 2004; Amdt. 61-113, 70 FR 45271, Aug. 4, 2005]
§61.7 Obsolete certificates and ratings.
(a) The holder of a free-balloon pilot certificate issued before November 1, 1973, may not exercise the privileges of that certificate.
(b) The holder of a pilot certificate that bears any of the following category ratings without an associated class rating may not exercise the privileges of that category rating:
(1) Rotorcraft.
(2) Lighter-than-air.
(3) Helicopter.
(4) Autogyro.
§61.8 Inapplicability of unmanned aircraft operations.
Any action conducted pursuant to part 107 of this chapter or Subpart E of part 101 of this chapter cannot be used to meet the requirements of this part.
[Docket FAA-2015-0150, Amdt. 61-137, 81 FR 42208, June 28, 2016]
§61.9 [Reserved]
§61.11 Expired pilot certificates and re-issuance.
(a) No person who holds an expired pilot certificate or rating may act as pilot in command or as a required pilot flight crewmember of an aircraft of the same category or class that is listed on that expired pilot certificate or rating.
(b) The following pilot certificates and ratings have expired and will not be reissued:
(1) An airline transport pilot certificate issued before May 1, 1949, or an airline transport pilot certificate that contains a horsepower limitation.
(2) A private or commercial pilot certificate issued before July 1, 1945.
(3) A pilot certificate with a lighter-than-air or free-balloon rating issued before July 1, 1945.
(c) An airline transport pilot certificate that was issued after April 30, 1949, and that bears an expiration date but does not contain a horsepower limitation, may have that airline transport pilot certificate re-issued without an expiration date.
(d) A private or commercial pilot certificate that was issued after June 30, 1945, and that bears an expiration date, may have that pilot certificate reissued without an expiration date.
(e) A pilot certificate with a lighter-than-air or free-balloon rating that was issued after June 30, 1945, and that bears an expiration date, may have that pilot certificate reissued without an expiration date.
[Doc. No. FAA-2006-26661, 74 FR 42547, Aug. 21, 2009]
§61.13 Issuance of airman certificates, ratings, and authorizations.
(a) Application. (1) An applicant for an airman certificate, rating, or authorization under this part must make that application on a form and in a manner acceptable to the Administrator.
(2) An applicant must show evidence that the appropriate fee prescribed in appendix A to part 187 of this chapter has been paid when that person applies for airmen certification services administered outside the United States.
(3) An applicant who is neither a citizen of the United States nor a resident alien of the United States may be refused issuance of any U.S. airman certificate, rating or authorization by the Administrator.
(4) Except as provided in paragraph (a)(3) of this section, an applicant who satisfactorily accomplishes the training and certification requirements for the certificate, rating, or authorization sought is entitled to receive that airman certificate, rating, or authorization.
(b) Limitations. (1) An applicant who cannot comply with certain areas of operation required on the practical test because of physical limitations may be issued an airman certificate, rating, or authorization with the appropriate limitation placed on the applicant’s airman certificate provided the—
(i) Applicant is able to meet all other certification requirements for the airman certificate, rating, or authorization sought;
(ii) Physical limitation has been recorded with the FAA on the applicant’s medical records; and
(iii) Administrator determines that the applicant’s inability to perform the particular area of operation will not adversely affect safety.
(2) A limitation placed on a person’s airman certificate may be removed, provided that person demonstrates for an examiner satisfactory proficiency in the area of operation appropriate to the airman certificate, rating, or authorization sought.
(c) Additional requirements for Category II and Category III pilot authorizations. (1) A Category II or Category III pilot authorization is issued by a letter of authorization as part of an applicant’s instrument rating or airline transport pilot certificate.
(2) Upon original issue, the authorization contains the following limitations:
(i) For Category II operations, the limitation is 1,600 feet RVR and a 150-foot decision height; and
(ii) For Category III operations, each initial limitation is specified in the authorization document.
(3) The limitations on a Category II or Category III pilot authorization may be removed as follows:
(i) In the case of Category II limitations, a limitation is removed when the holder shows that, since the beginning of the sixth preceding month, the holder has made three Category II ILS approaches with a 150-foot decision height to a landing under actual or simulated instrument conditions.
(ii) In the case of Category III limitations, a limitation is removed as specified in the authorization.
(4) To meet the experience requirements of paragraph (c)(3) of this section, and for the practical test required by this part for a Category II or a Category III pilot authorization, a flight simulator or flight training device may be used if it is approved by the Administrator for such use.
(d) Application during suspension or revocation. (1) Unless otherwise authorized by the Administrator, a person whose pilot, flight instructor, or ground instructor certificate has been suspended may not apply for any certificate, rating, or authorization during the period of suspension.
(2) Unless otherwise authorized by the Administrator, a person whose pilot, flight instructor, or ground instructor certificate has been revoked may not apply for any certificate, rating, or authorization for 1 year after the date of revocation.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 40895, July 30, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-116, 72 FR 18558, Apr. 12, 2007; Amdt. 61-132, 78 FR 77572, Dec. 24, 2013]
§61.14 [Reserved]
§61.15 Offenses involving alcohol or drugs.
(a) A conviction for the violation of any Federal or State statute relating to the growing, processing, manufacture, sale, disposition, possession, transportation, or importation of narcotic drugs, marijuana, or depressant or stimulant drugs or substances is grounds for:
(1) Denial of an application for any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part for a period of up to 1 year after the date of final conviction; or
(2) Suspension or revocation of any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part.
(b) Committing an act prohibited by §91.17(a) or §91.19(a) of this chapter is grounds for:
(1) Denial of an application for a certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part for a period of up to 1 year after the date of that act; or
(2) Suspension or revocation of any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part.
(c) For the purposes of paragraphs (d), (e), and (f) of this section, a motor vehicle action means:
(1) A conviction after November 29, 1990, for the violation of any Federal or State statute relating to the operation of a motor vehicle while intoxicated by alcohol or a drug, while impaired by alcohol or a drug, or while under the influence of alcohol or a drug;
(2) The cancellation, suspension, or revocation of a license to operate a motor vehicle after November 29, 1990, for a cause related to the operation of a motor vehicle while intoxicated by alcohol or a drug, while impaired by alcohol or a drug, or while under the influence of alcohol or a drug; or
(3) The denial after November 29, 1990, of an application for a license to operate a motor vehicle for a cause related to the operation of a motor vehicle while intoxicated by alcohol or a drug, while impaired by alcohol or a drug, or while under the influence of alcohol or a drug.
(d) Except for a motor vehicle action that results from the same incident or arises out of the same factual circumstances, a motor vehicle action occurring within 3 years of a previous motor vehicle action is grounds for:
(1) Denial of an application for any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part for a period of up to 1 year after the date of the last motor vehicle action; or
(2) Suspension or revocation of any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part.
(e) Each person holding a certificate issued under this part shall provide a written report of each motor vehicle action to the FAA, Civil Aviation Security Division (AMC-700), P.O. Box 25810, Oklahoma City, OK 73125, not later than 60 days after the motor vehicle action. The report must include:
(1) The person’s name, address, date of birth, and airman certificate number;
(2) The type of violation that resulted in the conviction or the administrative action;
(3) The date of the conviction or administrative action;
(4) The State that holds the record of conviction or administrative action; and
(5) A statement of whether the motor vehicle action resulted from the same incident or arose out of the same factual circumstances related to a previously reported motor vehicle action.
(f) Failure to comply with paragraph (e) of this section is grounds for:
(1) Denial of an application for any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part for a period of up to 1 year after the date of the motor vehicle action; or
(2) Suspension or revocation of any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part.
§61.16 Refusal to submit to an alcohol test or to furnish test results.
A refusal to submit to a test to indicate the percentage by weight of alcohol in the blood, when requested by a law enforcement officer in accordance with §91.17(c) of this chapter, or a refusal to furnish or authorize the release of the test results requested by the Administrator in accordance with §91.17(c) or (d) of this chapter, is grounds for:
(a) Denial of an application for any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part for a period of up to 1 year after the date of that refusal; or
(b) Suspension or revocation of any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this part.
§61.17 Temporary certificate.
(a) A temporary pilot, flight instructor, or ground instructor certificate or rating is issued for up to 120 days, at which time a permanent certificate will be issued to a person whom the Administrator finds qualified under this part.
(b) A temporary pilot, flight instructor, or ground instructor certificate or rating expires:
(1) On the expiration date shown on the certificate;
(2) Upon receipt of the permanent certificate; or
(3) Upon receipt of a notice that the certificate or rating sought is denied or revoked.
§61.18 [Reserved]
§61.19 Duration of pilot and instructor certificates and privileges.
(a) General. (1) The holder of a certificate with an expiration date may not, after that date, exercise the privileges of that certificate.
(2) Except for a certificate issued with an expiration date, a pilot certificate is valid unless it is surrendered, suspended, or revoked.
(b) Paper student pilot certificate. A student pilot certificate issued under this part prior to April 1, 2016 expires:
(1) For student pilots who have not reached their 40th birthday, 60 calendar months after the month of the date of examination shown on the medical certificate.
(2) For student pilots who have reached their 40th birthday, 24 calendar months after the month of the date of examination shown on the medical certificate.
(3) For student pilots seeking a glider rating, balloon rating, or a sport pilot certificate, 60 calendar months after the month of the date issued, regardless of the person’s age.
(c) Pilot certificates. (1) A pilot certificate (including a student pilot certificate issued after April 1, 2016 issued under this part is issued without a specific expiration date.
(2) The holder of a pilot certificate issued on the basis of a foreign pilot license may exercise the privileges of that certificate only while that person’s foreign pilot license is effective.
(d) Flight instructor certificate. Except as specified in §61.197(b), a flight instructor certificate expires 24 calendar months from the month in which it was issued, renewed, or reinstated, as appropriate.
(e) Ground instructor certificate. A ground instructor certificate is issued without a specific expiration date.
(f) Return of certificates. The holder of any airman certificate that is issued under this part, and that has been suspended or revoked, must return that certificate to the FAA when requested to do so by the Administrator.
(g) Duration of pilot certificates. Except for a temporary certificate issued under §61.17 or a student pilot certificate issued under paragraph (b) of this section, the holder of a paper pilot certificate issued under this part may not exercise the privileges of that certificate after March 31, 2010.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-118, 73 FR 10668, Feb. 28, 2008; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42547, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-124A, 74 FR 53644, Oct. 20, 2009; Docket FAA-2010-1127, Amdt. 61-135, 81 FR 1306, Jan. 12, 2016]
§61.21 Duration of a Category II and a Category III pilot authorization (for other than part 121 and part 135 use).
(a) A Category II pilot authorization or a Category III pilot authorization expires at the end of the sixth calendar month after the month in which it was issued or renewed.
(b) Upon passing a practical test for a Category II or Category III pilot authorization, the authorization may be renewed for each type of aircraft for which the authorization is held.
(c) A Category II or Category III pilot authorization for a specific type aircraft for which an authorization is held will not be renewed beyond 12 calendar months from the month the practical test was accomplished in that type aircraft.
(d) If the holder of a Category II or Category III pilot authorization passes the practical test for a renewal in the month before the authorization expires, the holder is considered to have passed it during the month the authorization expired.
§61.23 Medical certificates: Requirement and duration.
(a) Operations requiring a medical certificate. Except as provided in paragraphs (b) and (c) of this section, a person—
(1) Must hold a first-class medical certificate:
(i) When exercising the pilot-in-command privileges of an airline transport pilot certificate;
(ii) When exercising the second-in-command privileges of an airline transport pilot certificate in a flag or supplemental operation in part 121 of this chapter that requires three or more pilots; or
(iii) When serving as a required pilot flightcrew member in an operation conducted under part 121 of this chapter if the pilot has reached his or her 60th birthday.
(2) Must hold at least a second class medical certificate when exercising:
(i) Second-in-command privileges of an airline transport pilot certificate in part 121 of this chapter (other than operations specified in paragraph (a)(1)(ii) of this section); or
(ii) Privileges of a commercial pilot certificate; or
(3) Must hold at least a third-class medical certificate—
(i) When exercising the privileges of a private pilot certificate, recreational pilot certificate, or student pilot certificate, except when operating under the conditions and limitations set forth in §61.113(i);
(ii) When exercising the privileges of a flight instructor certificate and acting as the pilot in command or as a required flightcrew member, except when operating under the conditions and limitations set forth in §61.113(i);
(iii) When taking a practical test in an aircraft for a recreational pilot, private pilot, commercial pilot, or airline transport pilot certificate, or for a flight instructor certificate, except when operating under the conditions and limitations set forth in §61.113(i); or
(iv) When performing the duties as an Examiner in an aircraft when administering a practical test or proficiency check for an airman certificate, rating, or authorization.
(b) Operations not requiring a medical certificate. A person is not required to hold a medical certificate—
(1) When exercising the privileges of a student pilot certificate while seeking—
(i) A sport pilot certificate with glider or balloon privileges; or
(ii) A pilot certificate with a glider category rating or balloon class rating;
(2) When exercising the privileges of a sport pilot certificate with privileges in a glider or balloon;
(3) When exercising the privileges of a pilot certificate with a glider category rating or balloon class rating in a glider or a balloon, as appropriate;
(4) When exercising the privileges of a flight instructor certificate with—
(i) A sport pilot rating in a glider or balloon; or
(ii) A glider category rating;
(5) When exercising the privileges of a flight instructor certificate if the person is not acting as pilot in command or serving as a required pilot flight crewmember;
(6) When exercising the privileges of a ground instructor certificate;
(7) When serving as an Examiner or check airman and administering a practical test or proficiency check for an airman certificate, rating, or authorization conducted in a glider, balloon, flight simulator, or flight training device;
(8) When taking a practical test or a proficiency check for a certificate, rating, authorization or operating privilege conducted in a glider, balloon, flight simulator, or flight training device; or
(9) When a military pilot of the U.S. Armed Forces can show evidence of an up-to-date medical examination authorizing pilot flight status issued by the U.S. Armed Forces and—
(i) The flight does not require higher than a third-class medical certificate; and
(ii) The flight conducted is a domestic flight operation within U.S. airspace.
(c) Operations requiring either a medical certificate or U.S. driver’s license. (1) A person must hold and possess either a medical certificate issued under part 67 of this chapter or a U.S. driver’s license when—
(i) Exercising the privileges of a student pilot certificate while seeking sport pilot privileges in a light-sport aircraft other than a glider or balloon;
(ii) Exercising the privileges of a sport pilot certificate in a light-sport aircraft other than a glider or balloon;
(iii) Exercising the privileges of a flight instructor certificate with a sport pilot rating while acting as pilot in command or serving as a required flight crewmember of a light-sport aircraft other than a glider or balloon;
(iv) Serving as an Examiner and administering a practical test for the issuance of a sport pilot certificate in a light-sport aircraft other than a glider or balloon;
(v) Exercising the privileges of a student, recreational or private pilot certificate if the flight is conducted under the conditions and limitations set forth in §61.113(i); or
(vi) Exercising the privileges of a flight instructor certificate and acting as the pilot in command or as a required flight crewmember if the flight is conducted under the conditions and limitations set forth in §61.113(i).
(2) A person using a U.S. driver’s license to meet the requirements of paragraph (c) while exercising sport pilot privileges must—
(i) Comply with each restriction and limitation imposed by that person’s U.S. driver’s license and any judicial or administrative order applying to the operation of a motor vehicle;
(ii) Have been found eligible for the issuance of at least a third-class airman medical certificate at the time of his or her most recent application (if the person has applied for a medical certificate);
(iii) Not have had his or her most recently issued medical certificate (if the person has held a medical certificate) suspended or revoked or most recent Authorization for a Special Issuance of a Medical Certificate withdrawn; and
(iv) Not know or have reason to know of any medical condition that would make that person unable to operate a light-sport aircraft in a safe manner.
(3) A person using a U.S. driver’s license to meet the requirements of paragraph (c) while operating under the conditions and limitations of §61.113(i) must meet the following requirements—
(i) The person must—
(A) Comply with all medical requirements or restrictions associated with his or her U.S. driver’s license;
(B) At any point after July 14, 2006, have held a medical certificate issued under part 67 of this chapter;
(C) Complete the medical education course set forth in §68.3 of this chapter during the 24-calendar months before acting as pilot in command in an operation conducted under §61.113(i) and retain a certification of course completion in accordance with §68.3(b)(1) of this chapter;
(D) Receive a comprehensive medical examination from a State-licensed physician during the 48 months before acting as pilot in command of an operation conducted under §61.113(i) and that medical examination is conducted in accordance with the requirements in part 68 of this chapter; and
(E) If the individual has been diagnosed with any medical condition that may impact the ability of the individual to fly, be under the care and treatment of a State-licensed physician when acting as pilot in command of an operation conducted under §61.113(i).
(ii) The most recently issued medical certificate—
(A) May include an authorization for special issuance;
(B) May be expired; and
(C) Cannot have been suspended or revoked.
(iii) The most recently issued Authorization for a Special Issuance of a Medical Certificate cannot have been withdrawn; and
(iv) The most recent application for an airman medical certificate submitted to the FAA cannot have been completed and denied.
(d) Duration of a medical certificate. Use the following table to determine duration for each class of medical certificate:


[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40895, July 30, 1997; Amdt. 61-110, 69 FR 44864, July 27, 2004, as amended by Amdt. 61-121, 73 FR 43064, July 24, 2008; Amdt. 61-121, 73 FR 48125, Aug. 18, 2008; Amdt. 61-123, 74 FR 34234, July 15, 2009; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42547, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-129, 76 FR 78143, Dec. 16, 2011; Amdt. 61-129A, 77 FR 61721, Oct. 11, 2012; Amdt. 61-130, 78 FR 42372, July 15, 2013; Docket FAA-2016-9157, Amdt. 61-140, 82 FR 3164, Jan. 11, 2017]
§61.25 Change of name.
(a) An application to change the name on a certificate issued under this part must be accompanied by the applicant’s:
(1) Airman certificate; and
(2) A copy of the marriage license, court order, or other document verifying the name change.
(b) The documents in paragraph (a) of this section will be returned to the applicant after inspection.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42548, Aug. 21, 2009]
§61.27 Voluntary surrender or exchange of certificate.
(a) The holder of a certificate issued under this part may voluntarily surrender it for:
(1) Cancellation;
(2) Issuance of a lower grade certificate; or
(3) Another certificate with specific ratings deleted.
(b) Any request made under paragraph (a) of this section must include the following signed statement or its equivalent: “This request is made for my own reasons, with full knowledge that my (insert name of certificate or rating, as appropriate) may not be reissued to me unless I again pass the tests prescribed for its issuance.”
§61.29 Replacement of a lost or destroyed airman or medical certificate or knowledge test report.
(a) A request for the replacement of a lost or destroyed airman certificate issued under this part must be made:
(1) By letter to the Department of Transportation, FAA, Airmen Certification Branch, P.O. Box 25082, Oklahoma City, OK 73125, and must be accompanied by a check or money order for the appropriate fee payable to the FAA; or
(2) In any other manner and form approved by the Administrator including a request online to Airmen Services at http://www.faa.gov, and must be accompanied by acceptable form of payment for the appropriate fee.
(b) A request for the replacement of a lost or destroyed medical certificate must be made:
(1) By letter to the Department of Transportation, FAA, Aerospace Medical Certification Division, P.O. Box 26200, Oklahoma City, OK 73125, and must be accompanied by a check or money order for the appropriate fee payable to the FAA; or
(2) In any other manner and form approved by the Administrator and must be accompanied by acceptable form of payment for the appropriate fee.
(c) A request for the replacement of a lost or destroyed knowledge test report must be made:
(1) By letter to the Department of Transportation, FAA, Airmen Certification Branch, P.O. Box 25082, Oklahoma City, OK 73125, and must be accompanied by a check or money order for the appropriate fee payable to the FAA; or
(2) In any other manner and form approved by the Administrator and must be accompanied by acceptable form of payment for the appropriate fee.
(d) The letter requesting replacement of a lost or destroyed airman certificate, medical certificate, or knowledge test report must state:
(1) The name of the person;
(2) The permanent mailing address (including ZIP code), or if the permanent mailing address includes a post office box number, then the person’s current residential address;
(3) The certificate holder’s date and place of birth; and
(4) Any information regarding the—
(i) Grade, number, and date of issuance of the airman certificate and ratings, if appropriate;
(ii) Class of medical certificate, the place and date of the medical exam, name of the Airman Medical Examiner (AME), and the circumstances concerning the loss of the original medical certificate, as appropriate; and
(iii) Date the knowledge test was taken, if appropriate.
(e) A person who has lost an airman certificate, medical certificate, or knowledge test report may obtain, in a form or manner approved by the Administrator, a document conveying temporary authority to exercise certificate privileges from the FAA Aeromedical Certification Branch or the Airman Certification Branch, as appropriate, and the:
(1) Document may be carried as an airman certificate, medical certificate, or knowledge test report, as appropriate, for up to 60 days pending the person’s receipt of a duplicate under paragraph (a), (b), or (c) of this section, unless the person has been notified that the certificate has been suspended or revoked.
(2) Request for such a document must include the date on which a duplicate certificate or knowledge test report was previously requested.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40896, July 30, 1997; Amdt. 61-121, 73 FR 43065, July 24, 2008; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42548, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-131, 78 FR 56828, Sept. 16, 2013]
§61.31 Type rating requirements, additional training, and authorization requirements.
(a) Type ratings required. A person who acts as a pilot in command of any of the following aircraft must hold a type rating for that aircraft:
(1) Large aircraft (except lighter-than-air).
(2) Turbojet-powered airplanes.
(3) Other aircraft specified by the Administrator through aircraft type certificate procedures.
(b) Authorization in lieu of a type rating. A person may be authorized to operate without a type rating for up to 60 days an aircraft requiring a type rating, provided—
(1) The Administrator has authorized the flight or series of flights;
(2) The Administrator has determined that an equivalent level of safety can be achieved through the operating limitations on the authorization;
(3) The person shows that compliance with paragraph (a) of this section is impracticable for the flight or series of flights; and
(4) The flight—
(i) Involves only a ferry flight, training flight, test flight, or practical test for a pilot certificate or rating;
(ii) Is within the United States;
(iii) Does not involve operations for compensation or hire unless the compensation or hire involves payment for the use of the aircraft for training or taking a practical test; and
(iv) Involves only the carriage of flight crewmembers considered essential for the flight.
(5) If the flight or series of flights cannot be accomplished within the time limit of the authorization, the Administrator may authorize an additional period of up to 60 days to accomplish the flight or series of flights.
(c) Aircraft category, class, and type ratings: Limitations on the carriage of persons, or operating for compensation or hire. Unless a person holds a category, class, and type rating (if a class and type rating is required) that applies to the aircraft, that person may not act as pilot in command of an aircraft that is carrying another person, or is operated for compensation or hire. That person also may not act as pilot in command of that aircraft for compensation or hire.
(d) Aircraft category, class, and type ratings: Limitations on operating an aircraft as the pilot in command. To serve as the pilot in command of an aircraft, a person must—
(1) Hold the appropriate category, class, and type rating (if a class or type rating is required) for the aircraft to be flown; or
(2) Have received training required by this part that is appropriate to the pilot certification level, aircraft category, class, and type rating (if a class or type rating is required) for the aircraft to be flown, and have received an endorsement for solo flight in that aircraft from an authorized instructor.
(e) Additional training required for operating complex airplanes. (1) Except as provided in paragraph (e)(2) of this section, no person may act as pilot in command of a complex airplane, unless the person has—
(i) Received and logged ground and flight training from an authorized instructor in a complex airplane, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of a complex airplane, and has been found proficient in the operation and systems of the airplane; and
(ii) Received a one-time endorsement in the pilot’s logbook from an authorized instructor who certifies the person is proficient to operate a complex airplane.
(2) The training and endorsement required by paragraph (e)(1) of this section is not required if—
(i) The person has logged flight time as pilot in command of a complex airplane, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of a complex airplane prior to August 4, 1997; or
(ii) The person has received ground and flight training under an approved training program and has satisfactorily completed a competency check under §135.293 of this chapter in a complex airplane, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of a complex airplane which must be documented in the pilot’s logbook or training record.
(f) Additional training required for operating high-performance airplanes. (1) Except as provided in paragraph (f)(2) of this section, no person may act as pilot in command of a high-performance airplane (an airplane with an engine of more than 200 horsepower), unless the person has—
(i) Received and logged ground and flight training from an authorized instructor in a high-performance airplane, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of a high-performance airplane, and has been found proficient in the operation and systems of the airplane; and
(ii) Received a one-time endorsement in the pilot’s logbook from an authorized instructor who certifies the person is proficient to operate a high-performance airplane.
(2) The training and endorsement required by paragraph (f)(1) of this section is not required if—
(i) The person has logged flight time as pilot in command of a high-performance airplane, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of a high-performance airplane prior to August 4, 1997; or
(ii) The person has received ground and flight training under an approved training program and has satisfactorily completed a competency check under §135.293 of this chapter in a high performance airplane, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of a high performance airplane which must be documented in the pilot’s logbook or training record.
(g) Additional training required for operating pressurized aircraft capable of operating at high altitudes. (1) Except as provided in paragraph (g)(3) of this section, no person may act as pilot in command of a pressurized aircraft (an aircraft that has a service ceiling or maximum operating altitude, whichever is lower, above 25,000 feet MSL), unless that person has received and logged ground training from an authorized instructor and obtained an endorsement in the person’s logbook or training record from an authorized instructor who certifies the person has satisfactorily accomplished the ground training. The ground training must include at least the following subjects:
(i) High-altitude aerodynamics and meteorology;
(ii) Respiration;
(iii) Effects, symptoms, and causes of hypoxia and any other high-altitude sickness;
(iv) Duration of consciousness without supplemental oxygen;
(v) Effects of prolonged usage of supplemental oxygen;
(vi) Causes and effects of gas expansion and gas bubble formation;
(vii) Preventive measures for eliminating gas expansion, gas bubble formation, and high-altitude sickness;
(viii) Physical phenomena and incidents of decompression; and
(ix) Any other physiological aspects of high-altitude flight.
(2) Except as provided in paragraph (g)(3) of this section, no person may act as pilot in command of a pressurized aircraft unless that person has received and logged training from an authorized instructor in a pressurized aircraft, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of a pressurized aircraft, and obtained an endorsement in the person’s logbook or training record from an authorized instructor who found the person proficient in the operation of a pressurized aircraft. The flight training must include at least the following subjects:
(i) Normal cruise flight operations while operating above 25,000 feet MSL;
(ii) Proper emergency procedures for simulated rapid decompression without actually depressurizing the aircraft; and
(iii) Emergency descent procedures.
(3) The training and endorsement required by paragraphs (g)(1) and (g)(2) of this section are not required if that person can document satisfactory accomplishment of any of the following in a pressurized aircraft, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of a pressurized aircraft:
(i) Serving as pilot in command before April 15, 1991;
(ii) Completing a pilot proficiency check for a pilot certificate or rating before April 15, 1991;
(iii) Completing an official pilot-in-command check conducted by the military services of the United States; or
(iv) Completing a pilot-in-command proficiency check under part 121, 125, or 135 of this chapter conducted by the Administrator or by an approved pilot check airman.
(h) Additional aircraft type-specific training. No person may serve as pilot in command of an aircraft that the Administrator has determined requires aircraft type-specific training unless that person has—
(1) Received and logged type-specific training in the aircraft, or in a full flight simulator or flight training device that is representative of that type of aircraft; and
(2) Received a logbook endorsement from an authorized instructor who has found the person proficient in the operation of the aircraft and its systems.
(i) Additional training required for operating tailwheel airplanes. (1) Except as provided in paragraph (i)(2) of this section, no person may act as pilot in command of a tailwheel airplane unless that person has received and logged flight training from an authorized instructor in a tailwheel airplane and received an endorsement in the person’s logbook from an authorized instructor who found the person proficient in the operation of a tailwheel airplane. The flight training must include at least the following maneuvers and procedures:
(i) Normal and crosswind takeoffs and landings;
(ii) Wheel landings (unless the manufacturer has recommended against such landings); and
(iii) Go-around procedures.
(2) The training and endorsement required by paragraph (i)(1) of this section is not required if the person logged pilot-in-command time in a tailwheel airplane before April 15, 1991.
(j) Additional training required for operating a glider. (1) No person may act as pilot in command of a glider—
(i) Using ground-tow procedures, unless that person has satisfactorily accomplished ground and flight training on ground-tow procedures and operations, and has received an endorsement from an authorized instructor who certifies in that pilot’s logbook that the pilot has been found proficient in ground-tow procedures and operations;
(ii) Using aerotow procedures, unless that person has satisfactorily accomplished ground and flight training on aerotow procedures and operations, and has received an endorsement from an authorized instructor who certifies in that pilot’s logbook that the pilot has been found proficient in aerotow procedures and operations; or
(iii) Using self-launch procedures, unless that person has satisfactorily accomplished ground and flight training on self-launch procedures and operations, and has received an endorsement from an authorized instructor who certifies in that pilot’s logbook that the pilot has been found proficient in self-launch procedures and operations.
(2) The holder of a glider rating issued prior to August 4, 1997, is considered to be in compliance with the training and logbook endorsement requirements of this paragraph for the specific operating privilege for which the holder is already qualified.
(k) Additional training required for night vision goggle operations. (1) Except as provided under paragraph (k)(3) of this section, a person may act as pilot in command of an aircraft using night vision goggles only if that person receives and logs ground training from an authorized instructor and obtains a logbook or training record endorsement from an authorized instructor who certifies the person completed the ground training. The ground training must include the following subjects:
(i) Applicable portions of this chapter that relate to night vision goggle limitations and flight operations;
(ii) Aeromedical factors related to the use of night vision goggles, including how to protect night vision, how the eyes adapt to night, self-imposed stresses that affect night vision, effects of lighting on night vision, cues used to estimate distance and depth perception at night, and visual illusions;
(iii) Normal, abnormal, and emergency operations of night vision goggle equipment;
(iv) Night vision goggle performance and scene interpretation; and
(v) Night vision goggle operation flight planning, including night terrain interpretation and factors affecting terrain interpretation.
(2) Except as provided under paragraph (k)(3) of this section, a person may act as pilot in command of an aircraft using night vision goggles only if that person receives and logs flight training from an authorized instructor and obtains a logbook or training record endorsement from an authorized instructor who found the person proficient in the use of night vision goggles. The flight training must include the following tasks:
(i) Preflight and use of internal and external aircraft lighting systems for night vision goggle operations;
(ii) Preflight preparation of night vision goggles for night vision goggle operations;
(iii) Proper piloting techniques when using night vision goggles during the takeoff, climb, enroute, descent, and landing phases of flight; and
(iv) Normal, abnormal, and emergency flight operations using night vision goggles.
(3) The requirements under paragraphs (k)(1) and (2) of this section do not apply if a person can document satisfactory completion of any of the following pilot proficiency checks using night vision goggles in an aircraft:
(i) A pilot proficiency check on night vision goggle operations conducted by the U.S. Armed Forces.
(ii) A pilot proficiency check on night vision goggle operations under part 135 of this chapter conducted by an Examiner or Check Airman.
(iii) A pilot proficiency check on night vision goggle operations conducted by a night vision goggle manufacturer or authorized instructor, when the pilot—
(A) Is employed by a Federal, State, county, or municipal law enforcement agency; and
(B) Has logged at least 20 hours as pilot in command in night vision goggle operations.
(l) Exceptions. (1) This section does not require a category and class rating for aircraft not type-certificated as airplanes, rotorcraft, gliders, lighter-than-air aircraft, powered-lifts, powered parachutes, or weight-shift-control aircraft.
(2) The rating limitations of this section do not apply to—
(i) An applicant when taking a practical test given by an examiner;
(ii) The holder of a student pilot certificate;
(iii) The holder of a pilot certificate when operating an aircraft under the authority of—
(A) A provisional type certificate; or
(B) An experimental certificate, unless the operation involves carrying a passenger;
(iv) The holder of a pilot certificate with a lighter-than-air category rating when operating a balloon;
(v) The holder of a recreational pilot certificate operating under the provisions of §61.101(h); or
(vi) The holder of a sport pilot certificate when operating a light-sport aircraft.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 40896, July 30, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-104, 63 FR 20286, Apr. 23, 1998; Amdt. 61-110, 69 FR 44865, July 27, 2004; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42548, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-128, 76 FR 54105, Aug. 31, 2011; Amdt. 61-142, 83 FR 30276, June 27, 2018]
§61.33 Tests: General procedure.
Tests prescribed by or under this part are given at times and places, and by persons designated by the Administrator.
§61.35 Knowledge test: Prerequisites and passing grades.
(a) An applicant for a knowledge test must have:
(1) Received an endorsement, if required by this part, from an authorized instructor certifying that the applicant accomplished the appropriate ground-training or a home-study course required by this part for the certificate or rating sought and is prepared for the knowledge test;
(2) After July 31, 2014, for the knowledge test for an airline transport pilot certificate with an airplane category multiengine class rating, a graduation certificate for the airline transport pilot certification training program specified in §61.156; and
(3) Proper identification at the time of application that contains the applicant’s—
(i) Photograph;
(ii) Signature;
(iii) Date of birth, which shows:
(A) For issuance of certificates other than the ATP certificate with an airplane category multiengine class rating, the applicant meets or will meet the age requirements of this part for the certificate sought before the expiration date of the airman knowledge test report;
(B) Prior to August 1, 2014, for issuance of an ATP certificate with an airplane category multiengine class rating under the aeronautical experience requirements of §§61.159 or 61.160, the applicant is at least 21 years of age at the time of the knowledge test; and
(C) After July 31, 2014, for issuance of an ATP certificate with an airplane category multiengine class rating obtained under the aeronautical experience requirements of §§61.159 or 61.160, the applicant is at least 18 years of age at the time of the knowledge test;
(iv) If the permanent mailing address is a post office box number, then the applicant must provide a current residential address.
(b) The Administrator shall specify the minimum passing grade for the knowledge test.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-104, 63 FR 20286, Apr. 23, 1998; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42548, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-130, 78 FR 42373, July 15, 2013; Amdt. 61-130B, 78 FR 77573, Dec. 24, 2013]
§61.37 Knowledge tests: Cheating or other unauthorized conduct.
(a) An applicant for a knowledge test may not:
(1) Copy or intentionally remove any knowledge test;
(2) Give to another applicant or receive from another applicant any part or copy of a knowledge test;
(3) Give assistance on, or receive assistance on, a knowledge test during the period that test is being given;
(4) Take any part of a knowledge test on behalf of another person;
(5) Be represented by, or represent, another person for a knowledge test;
(6) Use any material or aid during the period that the test is being given, unless specifically authorized to do so by the Administrator; and
(7) Intentionally cause, assist, or participate in any act prohibited by this paragraph.
(b) An applicant who the Administrator finds has committed an act prohibited by paragraph (a) of this section is prohibited, for 1 year after the date of committing that act, from:
(1) Applying for any certificate, rating, or authorization issued under this chapter; and
(2) Applying for and taking any test under this chapter.
(c) Any certificate or rating held by an applicant may be suspended or revoked if the Administrator finds that person has committed an act prohibited by paragraph (a) of this section.
§61.39 Prerequisites for practical tests.
(a) Except as provided in paragraphs (b), (c), and (e) of this section, to be eligible for a practical test for a certificate or rating issued under this part, an applicant must:
(1) Pass the required knowledge test:
(i) Within the 24-calendar-month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test, if a knowledge test is required; or
(ii) Within the 60-calendar month period preceding the month the applicant completes the practical test for those applicants who complete the airline transport pilot certification training program in §61.156 and pass the knowledge test for an airline transport pilot certificate with a multiengine class rating after July 31, 2014;
(2) Present the knowledge test report at the time of application for the practical test, if a knowledge test is required;
(3) Have satisfactorily accomplished the required training and obtained the aeronautical experience prescribed by this part for the certificate or rating sought, and if applying for the practical test with flight time accomplished under §61.159(c), present a copy of the records required by §135.63(a)(4)(vi) and (x) of this chapter;
(4) Hold at least a third-class medical certificate, if a medical certificate is required;
(5) Meet the prescribed age requirement of this part for the issuance of the certificate or rating sought;
(6) Have an endorsement, if required by this part, in the applicant’s logbook or training record that has been signed by an authorized instructor who certifies that the applicant—
(i) Has received and logged training time within 2 calendar months preceding the month of application in preparation for the practical test;
(ii) Is prepared for the required practical test; and
(iii) Has demonstrated satisfactory knowledge of the subject areas in which the applicant was deficient on the airman knowledge test; and
(7) Have a completed and signed application form.
(b) An applicant for an airline transport pilot certificate with an airplane category multiengine class rating or an airline transport pilot certificate with an airplane type rating may take the practical test with an expired knowledge test only if the applicant passed the knowledge test after July 31, 2014, and is employed:
(1) As a flightcrew member by a part 119 certificate holder conducting operations under parts 125 or 135 of this chapter at the time of the practical test and has satisfactorily accomplished that operator’s approved pilot-in-command training or checking program; or
(2) As a flightcrew member by a part 119 certificate holder conducting operations under part 121 of this chapter at the time of the practical test and has satisfactorily accomplished that operator’s approved initial training program; or
(3) By the U.S. Armed Forces as a flight crewmember in U.S. military air transport operations at the time of the practical test and has completed the pilot in command aircraft qualification training program that is appropriate to the pilot certificate and rating sought.
(c) An applicant for an airline transport pilot certificate with a rating other than those ratings set forth in paragraph (b) of this section may take the practical test for that certificate or rating with an expired knowledge test report, provided that the applicant is employed:
(1) As a flightcrew member by a part 119 certificate holder conducting operations under parts 125 or 135 of this chapter at the time of the practical test and has satisfactorily accomplished that operator’s approved pilot-in-command training or checking program; or
(2) By the U.S. Armed Forces as a flight crewmember in U.S. military air transport operations at the time of the practical test and has completed the pilot in command aircraft qualification training program that is appropriate to the pilot certificate and rating sought.
(d) In addition to the requirements in paragraph (a) of this section, to be eligible for a practical test for an airline transport pilot certificate with an airplane category multiengine class rating or airline transport pilot certificate obtained concurrently with an airplane type rating, an applicant must:
(1) If the applicant passed the knowledge test after July 31, 2014, present the graduation certificate for the airline transport pilot certification training program in §61.156, at the time of application for the practical test;
(2) If applying for the practical test under the aeronautical experience requirements of §61.160(a), the applicant must present the documents required by that section to substantiate eligibility; and
(3) If applying for the practical test under the aeronautical experience requirements of §61.160(b), (c), or (d), the applicant must present an official transcript and certifying document from an institution of higher education that holds a letter of authorization from the Administrator under §61.169.
(e) A person is not required to comply with the provisions of paragraph (a)(6) of this section if that person:
(1) Holds a foreign pilot license issued by a contracting State to the Convention on International Civil Aviation that authorizes at least the privileges of the pilot certificate sought;
(2) Is only applying for a type rating; or
(3) Is applying for an airline transport pilot certificate or an additional rating to an airline transport pilot certificate in an aircraft that does not require an aircraft type rating practical test.
(f) If all increments of the practical test for a certificate or rating are not completed on the same date, then all the remaining increments of the test must be completed within 2 calendar months after the month the applicant began the test.
(g) If all increments of the practical test for a certificate or rating are not completed within 2 calendar months after the month the applicant began the test, the applicant must retake the entire practical test.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40897, July 30, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-104, 63 FR 20286, Apr. 23, 1998; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42548, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-130, 78 FR 42373, July 15, 2013; Amdt. 61-130B, 78 FR 77573, Dec. 24, 2013; Amdt. 61-142, 83 FR 30726, June 27, 2018]
§61.41 Flight training received from flight instructors not certificated by the FAA.
(a) A person may credit flight training toward the requirements of a pilot certificate or rating issued under this part, if that person received the training from:
(1) A flight instructor of an Armed Force in a program for training military pilots of either—
(i) The United States; or
(ii) A foreign contracting State to the Convention on International Civil Aviation.
(2) A flight instructor who is authorized to give such training by the licensing authority of a foreign contracting State to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, and the flight training is given outside the United States.
(b) A flight instructor described in paragraph (a) of this section is only authorized to give endorsements to show training given.
§61.43 Practical tests: General procedures.
(a) Completion of the practical test for a certificate or rating consists of—
(1) Performing the tasks specified in the areas of operation for the airman certificate or rating sought;
(2) Demonstrating mastery of the aircraft by performing each task successfully;
(3) Demonstrating proficiency and competency within the approved standards; and
(4) Demonstrating sound judgment.
(b) The pilot flight crew complement required during the practical test is based on one of the following requirements that applies to the aircraft being used on the practical test:
(1) If the aircraft’s FAA-approved flight manual requires the pilot flight crew complement be a single pilot, then the applicant must demonstrate single pilot proficiency on the practical test.
(2) If the aircraft’s type certification data sheet requires the pilot flight crew complement be a single pilot, then the applicant must demonstrate single pilot proficiency on the practical test.
(3) If the FAA Flight Standardization Board report, FAA-approved aircraft flight manual, or aircraft type certification data sheet allows the pilot flight crew complement to be either a single pilot, or a pilot and a copilot, then the applicant may demonstrate single pilot proficiency or have a copilot on the practical test. If the applicant performs the practical test with a copilot, the limitation of “Second in Command Required” will be placed on the applicant’s pilot certificate. The limitation may be removed if the applicant passes the practical test by demonstrating single-pilot proficiency in the aircraft in which single-pilot privileges are sought.
(c) If an applicant fails any area of operation, that applicant fails the practical test.
(d) An applicant is not eligible for a certificate or rating sought until all the areas of operation are passed.
(e) The examiner or the applicant may discontinue a practical test at any time:
(1) When the applicant fails one or more of the areas of operation; or
(2) Due to inclement weather conditions, aircraft airworthiness, or any other safety-of-flight concern.
(f) If a practical test is discontinued, the applicant is entitled credit for those areas of operation that were passed, but only if the applicant:
(1) Passes the remainder of the practical test within the 60-day period after the date the practical test was discontinued;
(2) Presents to the examiner for the retest the original notice of disapproval form or the letter of discontinuance form, as appropriate;
(3) Satisfactorily accomplishes any additional training needed and obtains the appropriate instructor endorsements, if additional training is required; and
(4) Presents to the examiner for the retest a properly completed and signed application.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42549, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-142, 83 FR 30276, June 27, 2018]
§61.45 Practical tests: Required aircraft and equipment.
(a) General. Except as provided in paragraph (a)(2) of this section or when permitted to accomplish the entire flight increment of the practical test in a flight simulator or a flight training device, an applicant for a certificate or rating issued under this part must furnish:
(1) An aircraft of U.S. registry for each required test that—
(i) Is of the category, class, and type, if applicable, for which the applicant is applying for a certificate or rating; and
(ii) Has a standard airworthiness certificate or special airworthiness certificate in the limited, primary, or light-sport category.
(2) At the discretion of the examiner who administers the practical test, the applicant may furnish—
(i) An aircraft that has an airworthiness certificate other than a standard airworthiness certificate or special airworthiness certificate in the limited, primary, or light-sport category, but that otherwise meets the requirements of paragraph (a)(1) of this section;
(ii) An aircraft of the same category, class, and type, if applicable, of foreign registry that is properly certificated by the country of registry; or
(iii) A military aircraft of the same category, class, and type, if aircraft class and type are appropriate, for which the applicant is applying for a certificate or rating, and provided—
(A) The aircraft is under the direct operational control of the U.S. Armed Forces;
(B) The aircraft is airworthy under the maintenance standards of the U.S. Armed Forces; and
(C) The applicant has a letter from his or her commanding officer authorizing the use of the aircraft for the practical test.
(b) Required equipment (other than controls). (1) Except as provided in paragraph (b)(2) of this section, an aircraft used for a practical test must have—
(i) The equipment for each area of operation required for the practical test;
(ii) No prescribed operating limitations that prohibit its use in any of the areas of operation required for the practical test;
(iii) Except as provided in paragraphs (e) and (f) of this section, at least two pilot stations with adequate visibility for each person to operate the aircraft safely; and
(iv) Cockpit and outside visibility adequate to evaluate the performance of the applicant when an additional jump seat is provided for the examiner.
(2) An applicant for a certificate or rating may use an aircraft with operating characteristics that preclude the applicant from performing all of the tasks required for the practical test. However, the applicant’s certificate or rating, as appropriate, will be issued with an appropriate limitation.
(c) Required controls. Except for lighter-than-air aircraft, and a glider without an engine, an aircraft used for a practical test must have engine power controls and flight controls that are easily reached and operable in a conventional manner by both pilots, unless the Examiner determines that the practical test can be conducted safely in the aircraft without the controls easily reached by the Examiner.
(d) Simulated instrument flight equipment. An applicant for a practical test that involves maneuvering an aircraft solely by reference to instruments must furnish:
(1) Equipment on board the aircraft that permits the applicant to pass the areas of operation that apply to the rating sought; and
(2) A device that prevents the applicant from having visual reference outside the aircraft, but does not prevent the examiner from having visual reference outside the aircraft, and is otherwise acceptable to the Administrator.
(e) Aircraft with single controls. A practical test may be conducted in an aircraft having a single set of controls, provided the:
(1) Examiner agrees to conduct the test;
(2) Test does not involve a demonstration of instrument skills; and
(3) Proficiency of the applicant can be observed by an examiner who is in a position to observe the applicant.
(f) Light-sport aircraft with a single seat. A practical test for a sport pilot certificate may be conducted in a light-sport aircraft having a single seat provided that the—
(1) Examiner agrees to conduct the test;
(2) Examiner is in a position to observe the operation of the aircraft and evaluate the proficiency of the applicant; and
(3) Pilot certificate of an applicant successfully passing the test is issued a pilot certificate with a limitation “No passenger carriage and flight in a single-seat light-sport aircraft only.”
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40897, July 30, 1997; Amdt. 61-104, 63 FR 20286, Apr. 23, 1998; Amdt. 61-110, 69 FR 44865, July 27, 2004; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42549, Aug. 21, 2009]
§61.47 Status of an examiner who is authorized by the Administrator to conduct practical tests.
(a) An examiner represents the Administrator for the purpose of conducting practical tests for certificates and ratings issued under this part and to observe an applicant’s ability to perform the areas of operation on the practical test.
(b) The examiner is not the pilot in command of the aircraft during the practical test unless the examiner agrees to act in that capacity for the flight or for a portion of the flight by prior arrangement with:
(1) The applicant; or
(2) A person who would otherwise act as pilot in command of the flight or for a portion of the flight.
(c) Notwithstanding the type of aircraft used during the practical test, the applicant and the examiner (and any other occupants authorized to be on board by the examiner) are not subject to the requirements or limitations for the carriage of passengers that are specified in this chapter.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40897, July 30, 1997]
§61.49 Retesting after failure.
(a) An applicant for a knowledge or practical test who fails that test may reapply for the test only after the applicant has received:
(1) The necessary training from an authorized instructor who has determined that the applicant is proficient to pass the test; and
(2) An endorsement from an authorized instructor who gave the applicant the additional training.
(b) An applicant for a flight instructor certificate with an airplane category rating or, for a flight instructor certificate with a glider category rating, who has failed the practical test due to deficiencies in instructional proficiency on stall awareness, spin entry, spins, or spin recovery must:
(1) Comply with the requirements of paragraph (a) of this section before being retested;
(2) Bring an aircraft to the retest that is of the appropriate aircraft category for the rating sought and is certificated for spins; and
(3) Demonstrate satisfactory instructional proficiency on stall awareness, spin entry, spins, and spin recovery to an examiner during the retest.
§61.51 Pilot logbooks.
(a) Training time and aeronautical experience. Each person must document and record the following time in a manner acceptable to the Administrator:
(1) Training and aeronautical experience used to meet the requirements for a certificate, rating, or flight review of this part.
(2) The aeronautical experience required for meeting the recent flight experience requirements of this part.
(b) Logbook entries. For the purposes of meeting the requirements of paragraph (a) of this section, each person must enter the following information for each flight or lesson logged:
(1) General—
(i) Date.
(ii) Total flight time or lesson time.
(iii) Location where the aircraft departed and arrived, or for lessons in a full flight simulator or flight training device, the location where the lesson occurred.
(iv) Type and identification of aircraft, full flight simulator, flight training device, or aviation training device, as appropriate.
(v) The name of a safety pilot, if required by §91.109 of this chapter.
(2) Type of pilot experience or training—
(i) Solo.
(ii) Pilot in command.
(iii) Second in command.
(iv) Flight and ground training received from an authorized instructor.
(v) Training received in a full flight simulator, flight training device, or aviation training device from an authorized instructor.
(3) Conditions of flight—
(i) Day or night.
(ii) Actual instrument.
(iii) Simulated instrument conditions in flight, a full flight simulator, flight training device, or aviation training device.
(iv) Use of night vision goggles in an aircraft in flight, in a full flight simulator, or in a flight training device.
(c) Logging of pilot time. The pilot time described in this section may be used to:
(1) Apply for a certificate or rating issued under this part or a privilege authorized under this part; or
(2) Satisfy the recent flight experience requirements of this part.
(d) Logging of solo flight time. Except for a student pilot performing the duties of pilot in command of an airship requiring more than one pilot flight crewmember, a pilot may log as solo flight time only that flight time when the pilot is the sole occupant of the aircraft.
(e) Logging pilot-in-command flight time. (1) A sport, recreational, private, commercial, or airline transport pilot may log pilot in command flight time for flights-
(i) Except when logging flight time under §61.159(c), when the pilot is the sole manipulator of the controls of an aircraft for which the pilot is rated, or has sport pilot privileges for that category and class of aircraft, if the aircraft class rating is appropriate;
(ii) When the pilot is the sole occupant in the aircraft;
(iii) When the pilot, except for a holder of a sport or recreational pilot certificate, acts as pilot in command of an aircraft for which more than one pilot is required under the type certification of the aircraft or the regulations under which the flight is conducted; or
(iv) When the pilot performs the duties of pilot in command while under the supervision of a qualified pilot in command provided—
(A) The pilot performing the duties of pilot in command holds a commercial or airline transport pilot certificate and aircraft rating that is appropriate to the category and class of aircraft being flown, if a class rating is appropriate;
(B) The pilot performing the duties of pilot in command is undergoing an approved pilot in command training program that includes ground and flight training on the following areas of operation—
(1) Preflight preparation;
(2) Preflight procedures;
(3) Takeoff and departure;
(4) In-flight maneuvers;
(5) Instrument procedures;
(6) Landings and approaches to landings;
(7) Normal and abnormal procedures;
(8) Emergency procedures; and
(9) Postflight procedures;
(C) The supervising pilot in command holds—
(1) A commercial pilot certificate and flight instructor certificate, and aircraft rating that is appropriate to the category, class, and type of aircraft being flown, if a class or type rating is required; or
(2) An airline transport pilot certificate and aircraft rating that is appropriate to the category, class, and type of aircraft being flown, if a class or type rating is required; and
(D) The supervising pilot in command logs the pilot in command training in the pilot’s logbook, certifies the pilot in command training in the pilot’s logbook and attests to that certification with his or her signature, and flight instructor certificate number.
(2) If rated to act as pilot in command of the aircraft, an airline transport pilot may log all flight time while acting as pilot in command of an operation requiring an airline transport pilot certificate.
(3) A certificated flight instructor may log pilot in command flight time for all flight time while serving as the authorized instructor in an operation if the instructor is rated to act as pilot in command of that aircraft.
(4) A student pilot may log pilot-in-command time only when the student pilot—
(i) Is the sole occupant of the aircraft or is performing the duties of pilot of command of an airship requiring more than one pilot flight crewmember;
(ii) Has a solo flight endorsement as required under §61.87 of this part; and
(iii) Is undergoing training for a pilot certificate or rating.
(5) A commercial pilot or airline transport pilot may log all flight time while acting as pilot in command of an operation in accordance with §135.99(c) of this chapter if the flight is conducted in accordance with an approved second-in-command professional development program that meets the requirements of §135.99(c) of this chapter.
(f) Logging second-in-command flight time. A person may log second-in-command time only for that flight time during which that person:
(1) Is qualified in accordance with the second-in-command requirements of §61.55, and occupies a crewmember station in an aircraft that requires more than one pilot by the aircraft’s type certificate;
(2) Holds the appropriate category, class, and instrument rating (if an instrument rating is required for the flight) for the aircraft being flown, and more than one pilot is required under the type certification of the aircraft or the regulations under which the flight is being conducted; or
(3) Serves as second in command in operations conducted in accordance with §135.99(c) of this chapter when a second pilot is not required under the type certification of the aircraft or the regulations under which the flight is being conducted, provided the requirements in §61.159(c) are satisfied.
(g) Logging instrument time. (1) A person may log instrument time only for that flight time when the person operates the aircraft solely by reference to instruments under actual or simulated instrument flight conditions.
(2) An authorized instructor may log instrument time when conducting instrument flight instruction in actual instrument flight conditions.
(3) For the purposes of logging instrument time to meet the recent instrument experience requirements of §61.57(c) of this part, the following information must be recorded in the person’s logbook—
(i) The location and type of each instrument approach accomplished; and
(ii) The name of the safety pilot, if required.
(4) A person may use time in a full flight simulator, flight training device, or aviation training device for acquiring instrument aeronautical experience for a pilot certificate or rating provided an authorized instructor is present to observe that time and signs the person’s logbook or training record to verify the time and the content of the training session.
(5) A person may use time in a full flight simulator, flight training device, or aviation training device for satisfying instrument recency experience requirements provided a logbook or training record is maintained to specify the training device, time, and the content.
(h) Logging training time. (1) A person may log training time when that person receives training from an authorized instructor in an aircraft, full flight simulator, flight training device, or aviation training device.
(2) The training time must be logged in a logbook and must:
(i) Be endorsed in a legible manner by the authorized instructor; and
(ii) Include a description of the training given, the length of the training lesson, and the authorized instructor’s signature, certificate number, and certificate expiration date.
(i) Presentation of required documents. (1) Persons must present their pilot certificate, medical certificate, logbook, or any other record required by this part for inspection upon a reasonable request by—
(i) The Administrator;
(ii) An authorized representative from the National Transportation Safety Board; or
(iii) Any Federal, State, or local law enforcement officer.
(2) A student pilot must carry the following items in the aircraft on all solo cross-country flights as evidence of the required authorized instructor clearances and endorsements—
(i) Pilot logbook;
(ii) Student pilot certificate; and
(iii) Any other record required by this section.
(3) A sport pilot must carry his or her logbook or other evidence of required authorized instructor endorsements on all flights.
(4) A recreational pilot must carry his or her logbook with the required authorized instructor endorsements on all solo flights—
(i) That exceed 50 nautical miles from the airport at which training was received;
(ii) Within airspace that requires communication with air traffic control;
(iii) Conducted between sunset and sunrise; or
(iv) In an aircraft for which the pilot does not hold an appropriate category or class rating.
(5) A flight instructor with a sport pilot rating must carry his or her logbook or other evidence of required authorized instructor endorsements on all flights when providing flight training.
(j) Aircraft requirements for logging flight time. For a person to log flight time, the time must be acquired in an aircraft that is identified as an aircraft under §61.5(b), and is—
(1) An aircraft of U.S. registry with either a standard or special airworthiness certificate;
(2) An aircraft of foreign registry with an airworthiness certificate that is approved by the aviation authority of a foreign country that is a Member State to the Convention on International Civil Aviation Organization;
(3) A military aircraft under the direct operational control of the U.S. Armed Forces; or
(4) A public aircraft under the direct operational control of a Federal, State, county, or municipal law enforcement agency, if the flight time was acquired by the pilot while engaged on an official law enforcement flight for a Federal, State, County, or Municipal law enforcement agency.
(k) Logging night vision goggle time. (1) A person may log night vision goggle time only for the time the person uses night vision goggles as the primary visual reference of the surface and operates:
(i) An aircraft during a night vision goggle operation; or
(ii) A full flight simulator or flight training device with the lighting system adjusted to represent the period beginning 1 hour after sunset and ending 1 hour before sunrise.
(2) An authorized instructor may log night vision goggle time when that person conducts training using night vision goggles as the primary visual reference of the surface and operates:
(i) An aircraft during a night goggle operation; or
(ii) A full flight simulator or flight training device with the lighting system adjusted to represent the period beginning 1 hour after sunset and ending 1 hour before sunrise.
(3) To log night vision goggle time to meet the recent night vision goggle experience requirements under §61.57(f), a person must log the information required under §61.51(b).
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40897, July 30, 1997; Amdt. 61-104, 63 FR 20286, Apr. 23, 1998; Amdt. 61-110, 69 FR 44865, July 27, 2004; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42549, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-128, 76 FR 54105, Aug. 31, 2011; Amdt. 61-142, 83 FR 30277, June 27, 2018]
§61.52 Use of aeronautical experience obtained in ultralight vehicles.
(a) Before January 31, 2012, a person may use aeronautical experience obtained in an ultralight vehicle to meet the requirements for the following certificates and ratings issued under this part:
(1) A sport pilot certificate.
(2) A flight instructor certificate with a sport pilot rating;
(3) A private pilot certificate with a weight-shift-control or powered parachute category rating.
(b) Before January 31, 2012, a person may use aeronautical experience obtained in an ultralight vehicle to meet the provisions of §61.69.
(c) A person using aeronautical experience obtained in an ultralight vehicle to meet the requirements for a certificate or rating specified in paragraph (a) of this section or the requirements of paragraph (b) of this section must—
(1) Have been a registered ultralight pilot with an FAA-recognized ultralight organization when that aeronautical experience was obtained;
(2) Document and log that aeronautical experience in accordance with the provisions for logging aeronautical experience specified by an FAA-recognized ultralight organization and in accordance with the provisions for logging pilot time in aircraft as specified in §61.51;
(3) Obtain the aeronautical experience in a category and class of vehicle corresponding to the rating or privilege sought; and
(4) Provide the FAA with a certified copy of his or her ultralight pilot records from an FAA-recognized ultralight organization, that —
(i) Document that he or she is a registered ultralight pilot with that FAA-recognized ultralight organization; and
(ii) Indicate that he or she is recognized to operate the category and class of aircraft for which sport pilot privileges are sought.
[Doc. No. FAA-2001-11133, 69 FR 44865, July 27, 2004, as amended by Amdt. 61-125, 75 FR 5220, Feb. 1, 2010]
§61.53 Prohibition on operations during medical deficiency.
(a) Operations that require a medical certificate. Except as provided for in paragraph (b) of this section, no person who holds a medical certificate issued under part 67 of this chapter may act as pilot in command, or in any other capacity as a required pilot flight crewmember, while that person:
(1) Knows or has reason to know of any medical condition that would make the person unable to meet the requirements for the medical certificate necessary for the pilot operation; or
(2) Is taking medication or receiving other treatment for a medical condition that results in the person being unable to meet the requirements for the medical certificate necessary for the pilot operation.
(b) Operations that do not require a medical certificate. For operations provided for in §61.23(b) of this part, a person shall not act as pilot in command, or in any other capacity as a required pilot flight crewmember, while that person knows or has reason to know of any medical condition that would make the person unable to operate the aircraft in a safe manner.
(c) Operations requiring a medical certificate or a U.S. driver’s license. For operations provided for in §61.23(c), a person must meet the provisions of—
(1) Paragraph (a) of this section if that person holds a medical certificate issued under part 67 of this chapter and does not hold a U.S. driver’s license.
(2) Paragraph (b) of this section if that person holds a U.S. driver’s license.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997, as amended by Amdt. 61-110, 69 FR 44866, July 27, 2004; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42550, Aug. 21, 2009]
§61.55 Second-in-command qualifications.
(a) A person may serve as a second-in-command of an aircraft type certificated for more than one required pilot flight crewmember or in operations requiring a second-in-command pilot flight crewmember only if that person holds:
(1) At least a private pilot certificate with the appropriate category and class rating; and
(2) An instrument rating or privilege that applies to the aircraft being flown if the flight is under IFR; and
(3) At least a pilot type rating for the aircraft being flown unless the flight will be conducted as domestic flight operations within the United States airspace.
(b) Except as provided in paragraph (e) of this section, no person may serve as a second-in-command of an aircraft type certificated for more than one required pilot flight crewmember or in operations requiring a second-in-command unless that person has within the previous 12 calendar months:
(1) Become familiar with the following information for the specific type aircraft for which second-in-command privileges are requested—
(i) Operational procedures applicable to the powerplant, equipment, and systems.
(ii) Performance specifications and limitations.
(iii) Normal, abnormal, and emergency operating procedures.
(iv) Flight manual.
(v) Placards and markings.
(2) Except as provided in paragraph (g) of this section, performed and logged pilot time in the type of aircraft or in a flight simulator that represents the type of aircraft for which second-in-command privileges are requested, which includes—
(i) Three takeoffs and three landings to a full stop as the sole manipulator of the flight controls;
(ii) Engine-out procedures and maneuvering with an engine out while executing the duties of pilot in command; and
(iii) Crew resource management training.
(c) If a person complies with the requirements in paragraph (b) of this section in the calendar month before or the calendar month after the month in which compliance with this section is required, then that person is considered to have accomplished the training and practice in the month it is due.
(d) A person may receive a second-in-command pilot type rating for an aircraft after satisfactorily completing the second-in-command familiarization training requirements under paragraph (b) of this section in that type of aircraft provided the training was completed within the 12 calendar months before the month of application for the SIC pilot type rating. The person must comply with the following application and pilot certification procedures:
(1) The person who provided the training must sign the applicant’s logbook or training record after each lesson in accordance with §61.51(h)(2) of this part. In lieu of the trainer, it is permissible for a qualified management official within the organization to sign the applicant’s training records or logbook and make the required endorsement. The qualified management official must hold the position of Chief Pilot, Director of Training, Director of Operations, or another comparable management position within the organization that provided the training and must be in a position to verify the applicant’s training records and that the training was given.
(2) The trainer or qualified management official must make an endorsement in the applicant’s logbook that states “[Applicant’s Name and Pilot Certificate Number] has demonstrated the skill and knowledge required for the safe operation of the [Type of Aircraft], relevant to the duties and responsibilities of a second in command.”
(3) If the applicant’s flight experience and/or training records are in an electronic form, the applicant must present a paper copy of those records containing the signature of the trainer or qualified management official to a Flight Standards office or Examiner.
(4) The applicant must complete and sign an Airman Certificate and/or Rating Application, FAA Form 8710-1, and present the application to a Flight Standards office or to an Examiner.
(5) The person who provided the ground and flight training to the applicant must sign the “Instructor’s Recommendation” section of the Airman Certificate and/or Rating Application, FAA Form 8710-1. In lieu of the trainer, it is permissible for a qualified management official within the organization to sign the applicant’s FAA Form 8710-1.
(6) The applicant must appear in person at a Flight Standards office or to an Examiner with his or her logbook/training records and with the completed and signed FAA Form 8710-1.
(7) There is no practical test required for the issuance of the “SIC Privileges Only” pilot type rating.
(e) A person may receive a second-in-command pilot type rating for the type of aircraft after satisfactorily completing an approved second-in-command training program, proficiency check, or competency check under subpart K of part 91, part 125, or part 135, as appropriate, in that type of aircraft provided the training was completed within the 12 calendar months before the month of application for the SIC pilot type rating. The person must comply with the following application and pilot certification procedures:
(1) The person who provided the training must sign the applicant’s logbook or training record after each lesson in accordance with §61.51(h)(2) of this part. In lieu of the trainer, it is permissible for a qualified management official within the organization to sign the applicant’s training records or logbook and make the required endorsement. The qualified management official must hold the position of Chief Pilot, Director of Training, Director of Operations, or another comparable management position within the organization that provided the training and must be in a position to verify the applicant’s training records and that the training was given.
(2) The trainer or qualified management official must make an endorsement in the applicant’s logbook that states “[Applicant’s Name and Pilot Certificate Number] has demonstrated the skill and knowledge required for the safe operation of the [Type of Aircraft], relevant to the duties and responsibilities of a second in command.”
(3) If the applicant’s flight experience and/or training records are in an electronic form, the applicant must provide a paper copy of those records containing the signature of the trainer or qualified management official to a Flight Standards office, an Examiner, or an Aircrew Program Designee.
(4) The applicant must complete and sign an Airman Certificate and/or Rating Application, FAA Form 8710-1, and present the application to a Flight Standards office or to an Examiner or to an authorized Aircrew Program Designee.
(5) The person who provided the ground and flight training to the applicant must sign the “Instructor’s Recommendation” section of the Airman Certificate and/or Rating Application, FAA Form 8710-1. In lieu of the trainer, it is permissible for a qualified management official within the organization to sign the applicant’s FAA Form 8710-1.
(6) The applicant must appear in person at a Flight Standards office or to an Examiner or to an authorized Aircrew Program Designee with his or her logbook/training records and with the completed and signed FAA Form 8710-1.
(7) There is no practical test required for the issuance of the “SIC Privileges Only” pilot type rating.
(f) The familiarization training requirements of paragraph (b) of this section do not apply to a person who is:
(1) Designated and qualified as pilot in command under subpart K of part 91, part 121, 125, or 135 of this chapter in that specific type of aircraft;
(2) Designated as the second in command under subpart K of part 91, part 121, 125, or 135 of this chapter in that specific type of aircraft;
(3) Designated as the second in command in that specific type of aircraft for the purpose of receiving flight training required by this section, and no passengers or cargo are carried on the aircraft; or
(4) Designated as a safety pilot for purposes required by §91.109 of this chapter.
(g) The holder of a commercial or airline transport pilot certificate with the appropriate category and class rating is not required to meet the requirements of paragraph (b)(2) of this section, provided the pilot:
(1) Is conducting a ferry flight, aircraft flight test, or evaluation flight of an aircraft’s equipment; and
(2) Is not carrying any person or property on board the aircraft, other than necessary for conduct of the flight.
(h) For the purpose of meeting the requirements of paragraph (b) of this section, a person may serve as second in command in that specific type aircraft, provided:
(1) The flight is conducted under day VFR or day IFR; and
(2) No person or property is carried on board the aircraft, other than necessary for conduct of the flight.
(i) The training under paragraphs (b) and (d) of this section and the training, proficiency check, and competency check under paragraph (e) of this section may be accomplished in a flight simulator that is used in accordance with an approved training course conducted by a training center certificated under part 142 of this chapter or under subpart K of part 91, part 121 or part 135 of this chapter.
(j) When an applicant for an initial second-in-command qualification for a particular type of aircraft receives all the training in a flight simulator, that applicant must satisfactorily complete one takeoff and one landing in an aircraft of the same type for which the qualification is sought. This requirement does not apply to an applicant who completes a proficiency check under part 121 or competency check under subpart K, part 91, part 125, or part 135 for the particular type of aircraft.
[Doc. No. 25910, 62 FR 16298, Apr. 4, 1997; Amdt. 61-103, 62 FR 40898, July 30, 1997; Amdt. 61-109, 68 FR 54559, Sept. 17, 2003; Amdt. 61-113, 70 FR 45271, Aug. 4, 2005; Amdt. 61-109, 70 FR 61890, Oct. 27, 2005; Amdt. 61-124, 74 FR 42550, Aug. 21, 2009; Amdt. 61-128, 76 FR 54105, Aug. 31, 2011; Amdt. 61-130, 78 FR 42374, July 15, 2013; Docket FAA-2018-0119, Amdt. 61-141, 83 FR 9170, Mar. 5, 2018]