Chapter 10

To be productive with Windows, you need to know how to work with documents. In this chapter, you learn what documents are, as well as how to create, save, open, edit, and print documents.
Understanding Documents
Documents are files that you create or edit yourself. The four examples shown here are the basic document types that you can create by using the programs that come with Windows.
Text Document

A text document is one that includes only the characters that you see on your keyboard, plus a few others. A text document contains no special formatting, such as colored text or bold formatting, although you can change the font. In Windows, you normally use the Notepad program to create text documents.
Word Processing Document
A word processing document contains text and other symbols, and you can format those characters to improve the look of the document. For example, you can change the size, color, and typeface, and you can make words bold or italic. In Windows, you use the WordPad program to create word processing — or Rich Text Format — documents.
Drawing
A drawing in this context is a digital image you create using special “tools” that create lines, boxes, polygons, special effects, and free-form shapes. In Windows, you use the Paint program to create drawings.
An e-mail message is a document that you send to another person via the Internet. Most e-mail messages use plain text, but some programs support formatted text, images, and other effects. In Windows, you create and send e-mail messages using the Mail app (see Chapter 5).
Create a Document
When you are ready to create something using Windows, in most cases you begin by launching a program and then using that program to create a new document to hold your work. Many Windows programs (such as WordPad and Paint) create a new document for you automatically when you begin the program. However, you can also use these programs to create another new document after you have started the program.
Create a Document

 Click File.
Click File.
 Click New
Click New
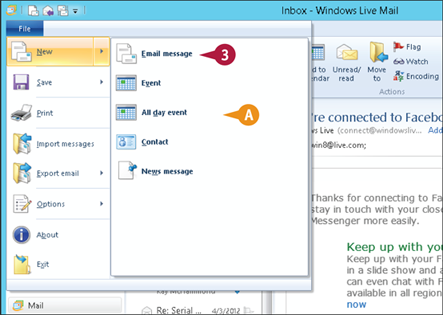
A If the program supports more than one type of file, the program asks which type you want to create.
Note: Some programs display a dialog box with a list of document types.
 Click the document type you want.
Click the document type you want.
The program creates the new document.
Note: In most programs, you can also press  +
+ to create a new document.
to create a new document.
Save a Document
After you create a document and make any changes to it, you can save the document to preserve your work. When you work on a document, Windows stores the changes in your computer's memory. However, Windows erases the contents of your PC's memory each time you shut down or restart the computer. This means that the changes you have made to your document are lost when you turn off or restart your PC. Saving the document preserves your changes on your computer's hard drive.
Save a Document

 Click File.
Click File.
 Click Save.
Click Save.
Note: In most programs, you can also press  +
+ or click Save (
or click Save ( ).
).
Note: If you saved the document previously, your changes are now preserved. You do not need to follow the rest of the steps in this section.
If this is a new document that you have never saved before, the Save As dialog box appears.
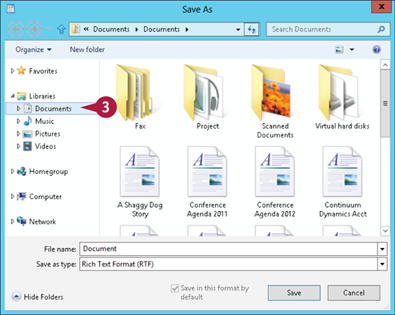
Note: In most programs, the Documents library is selected automatically when you save a document.

A Windows opens the Documents library.
 Click in the File name text box and type the name you want to use for the document.
Click in the File name text box and type the name you want to use for the document.
Note: The name you type can be up to 255 characters long, but it cannot include the following characters: < >, ?: “ \ *.
 Click Save.
Click Save.
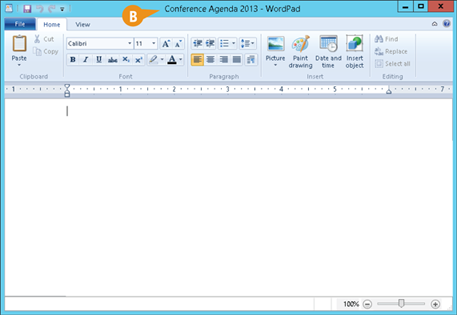
B The filename you typed appears in the program's title bar.
Open a Document
To work with a document that you have saved in the past, you typically need to open the document in the program that you used to create it. When you save a document, you save its contents to your PC's hard drive, and those contents are stored in a separate file. When you open the document using the same application that you used to save it, Windows loads the file's contents into memory and displays the document in the application. You can then view or edit the document as needed.
Open a Document
 Start the program you want to work with.
Start the program you want to work with.
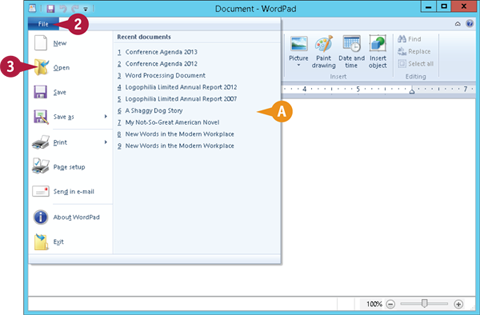
 File
File
A If you see the document you want in a list of the most recently used documents on the File menu, click the name to open it. You can then skip the rest of the steps in this section.
 Click Open.
Click Open.
Note: In most programs, you can also press  +
+ or click Open (
or click Open ( ).
).
The Open dialog box appears.
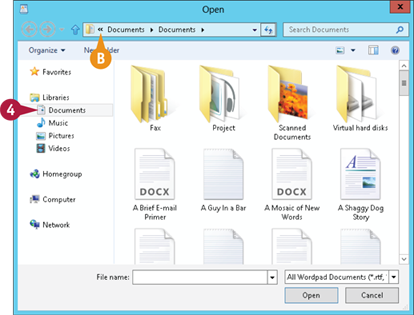
 Click Documents.
Click Documents.
Note: In most programs, the Documents library is selected automatically when you open a document.
B If you want to open the document from some other folder, click here, click your username, and then double-click the folder.
C The document appears in the program window.
 Windows opens the Documents library.
Windows opens the Documents library.
 Click Open.
Click Open.
D The document appears in the program window.
Edit Document Text
When you work with a character-based file, such as a text or word processing document or an e-mail message, you need to know the basic techniques for editing, selecting, copying, and moving text. Text you enter into a document is rarely perfect the first time through. The text likely contains errors that require correcting, or words, sentences, or paragraphs that appear in the wrong place. To get your document text the way you want it, you need to know how to edit text, including deleting characters, selecting the text you want to work with, and copying and moving text.
Edit Document Text
Delete Characters
 Click immediately to the left of the first character you want to delete.
Click immediately to the left of the first character you want to delete.
A The cursor appears before the character.

 Press
Press  until you have deleted all the characters you want.
until you have deleted all the characters you want.
Note: An alternative method is to click immediately to the right of the last character you want to delete and then press  until you have deleted all the characters you want.
until you have deleted all the characters you want.
Note: If you make a mistake, immediately press  +
+ or click Undo (
or click Undo ( ). Alternatively, click Edit and then click Undo.
). Alternatively, click Edit and then click Undo.
Select Text for Editing

 Click and drag across the text you want to select.
Click and drag across the text you want to select.

 Release the mouse button.
Release the mouse button.
B The program highlights the selected text.
Edit Document Text (continued)
After you select some text, you can then copy or move the text to another location in your document. Copying text is often a useful way to save work instead of typing it from scratch. Likewise, if you need a similar passage in another part of the document, you can copy the original and then edit the copy as needed. If you enter a passage of text in the wrong position within the document, you can fix that by moving the text to the correct location.
Edit Document Text (continued)
Copy Text
 Select the text you want to copy.
Select the text you want to copy.
 Click Copy (
Click Copy ( )
)
A In WordPad, you display the Clipboard options by clicking the Home tab.
Note: In most programs, you can also press  +
+ or click the Edit menu and then click Copy.
or click the Edit menu and then click Copy.
 Click inside the document at the position where you want the copy of the text to appear.
Click inside the document at the position where you want the copy of the text to appear.
The cursor appears in the position you click.
 Click Paste (
Click Paste ( ).
).
Note: In most programs, you can also press  +
+ or click the Edit menu and then click Paste.
or click the Edit menu and then click Paste.
B The program inserts a copy of the selected text at the cursor position.
Move Text
 Select the text you want to move.
Select the text you want to move.
 Click Cut (
Click Cut ( )
)
C In WordPad, you display the Clipboard options by clicking the Home tab.
Note: In most programs, you can also press  +
+ or click the Edit menu and then click Cut.
or click the Edit menu and then click Cut.
The program removes the text from the document.
 Click inside the document at the position where you want to move the text.
Click inside the document at the position where you want to move the text.
The cursor appears at the position you clicked.
 Click Paste (
Click Paste ( ).
).
Note: In most programs, you can also press  +
+ , or click the Edit menu and then click Paste.
, or click the Edit menu and then click Paste.
D The program inserts the text at the cursor position.
Change the Text Font
When you work in a word processing document, you can add visual appeal by changing the font formatting. The font formatting includes attributes such as the typeface, style, size, or special effects. A typeface — also called a font — is a distinctive character design that you can apply to the selected text in a document. The type style refers to formatting applied to text, such as bold or italics. The type size refers to the height of each character, which is measured in points; 72 points equal one inch. Special effects are styles that change the appearance of the text. The most common examples are underline and strikethrough.
Change the Text Font
 Select the text you want to format.
Select the text you want to format.

 Display the font options.
Display the font options.
A In WordPad, you display the font options by clicking the Home tab.
Note: In many other programs, you display the font options by clicking Format in the menu bar and then clicking the Font command.
 In the Font list, click
In the Font list, click  and then click the typeface you want.
and then click the typeface you want.
 In the Size list, click the type size you want.
In the Size list, click the type size you want.

 For bold text, click Bold (
For bold text, click Bold ( ).
).
 For italics, click Italic (
For italics, click Italic ( ).
).
 For underlining, click Underline (
For underlining, click Underline ( ).
).
 For color, click the Font color
For color, click the Font color  and then click a color.
and then click a color.
B The program applies the font formatting to the selected text.
Note: Here are some shortcuts that work in most programs: For bold, press  +
+ ; for italics, press
; for italics, press  +
+ ; for underline, press
; for underline, press  +
+ .
.
Find Text
In large documents, when you need to find specific text, you can save a lot of time by using the program's Find feature. In short documents that contain only a few dozen or even a few hundred words, finding a specific word or phrase is usually not difficult. However, many documents contain hundreds or even thousands of words, so finding a word or phrase becomes much more difficult and time consuming. You can work around this problem by using the Find feature, which searches the entire document in the blink of an eye.
Find Text

 Click Find (
Click Find ( ).
).
A In WordPad, you display the Editing options by clicking the Home tab.
Note: In many programs, you run the Find command by clicking Edit in the menu bar and then clicking the Find command, or by pressing  +
+ .
.
 Click in the Find what text box and type the text you want to find.
Click in the Find what text box and type the text you want to find.
 Click Find Next.
Click Find Next.
B The program selects the next instance of the search text.
Note: If the search text does not exist in the document, the program displays a dialog box to let you know.
 If the selected instance is not the one you want, click Find Next until the program finds the correct instance.
If the selected instance is not the one you want, click Find Next until the program finds the correct instance.
 Click Close (
Click Close ( ) to close the Find dialog box.
) to close the Find dialog box.

C The program leaves the found text selected.
Replace Text
You can make it easier to replace multiple instances of one word with another by taking advantage of the program's Replace feature. Do you need to replace a word or part of a word with some other text? If you have several instances to replace, you can save time and do a more accurate job if you let the program's Replace feature replace the word for you. Most programs that work with text — including the Windows WordPad and Notepad programs — have the Replace feature.
Replace Text

 Click Replace
Click Replace 
A In WordPad, you display the Editing options by clicking the Home tab.
Note: In many programs, you run the Replace command by clicking Edit in the menu bar and then clicking the Replace command, or by pressing  +
+ .
.
The Replace dialog box appears.
 Click in the Find what text box, and type the text you want to find.
Click in the Find what text box, and type the text you want to find.
 Click in the Replace with text box, and type the text you want to use as the replacement.
Click in the Replace with text box, and type the text you want to use as the replacement.
 Click Find Next.
Click Find Next.
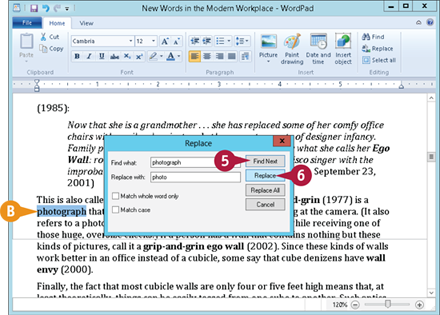
B The program selects the next instance of the search text.
Note: If the search text does not exist in the document, the program displays a dialog box to let you know.
 If the selected instance is not the one you want, click Find Next until the program finds the correct instance.
If the selected instance is not the one you want, click Find Next until the program finds the correct instance.
 Click Replace.
Click Replace.

C The program replaces the selected text with the replacement text.
D The program selects the next instance of the search text.
 Repeat steps 5 and 6 until you have replaced all the instances you want to replace.
Repeat steps 5 and 6 until you have replaced all the instances you want to replace.
 Click Close (
Click Close ( ) to close the Replace dialog box.
) to close the Replace dialog box.
Insert Special Symbols
You can make your documents more readable and more useful by inserting special symbols that are not available via your keyboard. The keyboard is home to a large number of letters, numbers, and symbols. However, the keyboard is missing some useful characters. For example, it is missing the foreign characters in words such as café and Köln. Similarly, your writing might require mathematical symbols such as ÷ and ½, financial symbols such as ¢ and ¥, or commercial symbols such as © and ®. These and many more symbols are available in Windows via the Character Map program.
Insert Special Symbols
 On the Start screen, type char.
On the Start screen, type char.
 Click Character Map.
Click Character Map.
The Character Map window appears.
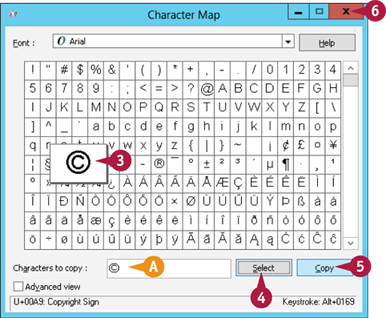
 Click the symbol you want.
Click the symbol you want.
 Click Select
Click Select
A Character Map adds the symbol to the Characters to Copy text box.
 Click Copy
Click Copy
 Click Close (
Click Close ( ) to shut down Character Map after you choose all the characters you want.
) to shut down Character Map after you choose all the characters you want.

 In your document, position the cursor where you want to insert the symbol.
In your document, position the cursor where you want to insert the symbol.
B In WordPad, you can display the Clipboard options by clicking the Home tab.
 Click Paste (
Click Paste ( ).
).
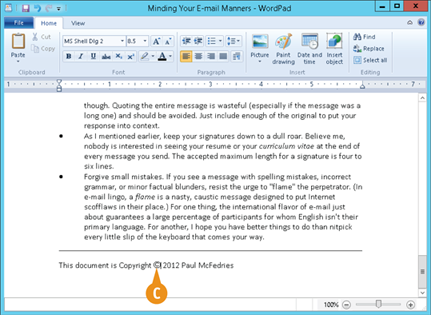
C The program inserts the symbol.
Make a Copy of a Document
When you need to create a document that is nearly identical to an existing document, instead of creating the new document from scratch, you can save time by making a copy of the existing document and then modifying the copy as needed. For example, you might have a résumé cover letter that you want to modify for a different job application. Similarly, this year's conference agenda is likely to be similar to last year's conference. Instead of creating these new documents from scratch, it is much faster to copy the original document and then edit the copy as needed.
Make a Copy of a Document

 Start the program you want to work with and open the original document.
Start the program you want to work with and open the original document.
 Click File.
Click File.
 Click Save as.
Click Save as.
The Save As dialog box appears.
 Click Documents.
Click Documents.
Note: In most programs, the Documents library is selected automatically when you run the Save As command.
A Windows opens the Documents library.
 Click in the File name text box and type the name you want to use for the copy.
Click in the File name text box and type the name you want to use for the copy.
Note: The name you type can be up to 255 characters long, but it cannot include the following characters: < > , ? : “ \ *.
 Click Save.
Click Save.
The program closes the original document and opens the copy you just created.

B The filename you typed appears in the program's title bar.
Print a Document
When you need a hard copy of your document to file or to distribute to someone else, you can obtain it by sending the document to your printer. Most applications that deal with documents also come with a Print command. When you run this command, the Print dialog box appears. You use the Print dialog box to choose the printer you want to use as well as to specify how many copies you want to print. Many Print dialog boxes also enable you to see a preview of your document before printing it.
Print a Document
 Turn on your printer.
Turn on your printer.
 Open the document you want to print.
Open the document you want to print.

 Click Print.
Click Print.
Note: In many programs, you can select the Print command by pressing  +
+ or by clicking Print (
or by clicking Print ( ).
).
The Print dialog box appears.
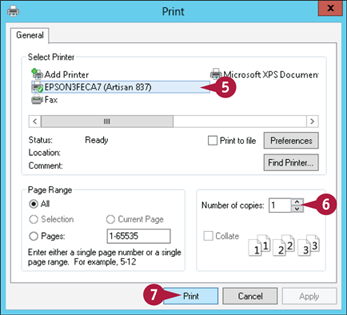
Note: The layout of the Print dialog box varies from program to program. The WordPad version shown here is a typical example.
 If you have more than one printer, click the printer you want to use.
If you have more than one printer, click the printer you want to use.
 Use the Number of copies spin button (
Use the Number of copies spin button ( ) to specify the number of copies to print.
) to specify the number of copies to print.
 Click Print.
Click Print.
A Windows prints the document. The print icon ( ) appears in the taskbar's notification area while the document prints.
) appears in the taskbar's notification area while the document prints.
 , double-click the new folder, and then follow steps
, double-click the new folder, and then follow steps  +
+ to select the entire document.
to select the entire document. , and then click to the right of the last character to select.
, and then click to the right of the last character to select. ) over the selection, and then click and drag the text to the new position within the document. To copy the selected text, position the mouse pointer (
) over the selection, and then click and drag the text to the new position within the document. To copy the selected text, position the mouse pointer ( changes to
changes to  ). This tells the program to match the search text only if it is a word on its own.
). This tells the program to match the search text only if it is a word on its own. +
+


 . When you type the numbers, be sure to use your keyboard's numeric keypad.
. When you type the numbers, be sure to use your keyboard's numeric keypad. changes to
changes to  ).
).