18
Important Cannabis Issues
This chapter deals with some important questions surrounding the health risks and social issues associated with cannabis use. It should be the endeavor of every cannabis user to learn as much as they can about the plant, its immediate effects, and the long-term consequences of use. If you encourage yourself to learn more about these aspects of cannabis, you may eventually encourage other users to do the same. Try to stay up to date with the latest information and be sure to remain unbiased by checking alternative sources. Over the course of many years there have been numerous studies. Some of these studies were conducted with agendas. These same agendas (on both sides) continue today. However there has been much improvement in our understanding of how cannabis works.
There are a few pseudo-scientific claims that are commonly used to support the argument for cannabis prohibition due to the presence of stronger, more potent cannabis on the market:
• Cannabis is getting stronger
• The stronger the cannabis, the greater the health risks
• Hydroponics makes cannabis stronger
• New lighting technology means stronger cannabis
• Feeding products and growth hormones make cannabis stronger
• New extraction techniques make hashish stronger
• More crystals means more THC and stronger cannabis
In the pages that follow, we examine each of these claims, or myths. Growers will also learn something from this discussion.
Myth #1: Cannabis is Getting Stronger
The concept that “Today’s cannabis is stronger than the cannabis of the 60s or 70s” is unsubstantiated by fact. Open any seed bank catalogue that has strains from the 60s and 70s in stock. Order them, grow them, sample your results and you will learn why they are still some of the most expensive seed lines on the market. Strains developed in the 60s and 70s are arguably still the most potent cannabis strains around.
Not only are people more informed as to what constitutes bad cannabis nowadays, low potency plants are also less likely to be available and/or purchased. This does NOT imply a potency increase. What it does suggest is that people might need to USE LESS cannabis to get the SAME EFFECT as using a lot of bad cannabis. When you think about use in terms of smoking and its affects, it is easy to see that smoking less is far better than smoking more.
Consider this: If the cannabis of the 60s was weaker than the cannabis of the 21st Century, why would internationally known seed banks still advertise some of the oldest stabilized cannabis plants of the 60s and 70s as their most potent?
Haze strains, Thai and other Sativa (species of cannabis) strains of the 60s (imported largely from Asia) are landrace strains that were cultivated by locals for their high cannabinoid content and hemp material. They were bred for hundreds, maybe even thousands, of years.
The suggestion that hybridizing these plants in conjunction with breeding techniques has somehow made cannabis stronger is a false notion. What has happened is that a new species of cannabis has emerged on the market that was not previously widely available. This species is called Cannabis Indica and it is the reason why cannabis may seem different, but is not necessarily stronger or more potent.
Cannabis Indica and Cannabis Ruderalis were not common in 60s America and Europe, which was then mostly a Sativa market. Cannabis Sativa by its nature gives a head high effect. Cannabis Indica gives a body down effect. This has to do with the plants’ flowering times and cannabinoid contents. Cannabis Sativa and Cannabis Indica can be bred together to produce a hybrid plant that is a 50/50 mix, mostly Sativa or mostly Indica. However, this does not increase potency. Potency is genetically determined—you cannot GENERATE new genes that were NOT THERE in the first place.
G13 is a strain reputed to have been developed by the US Government in the mid-seventies.
Traditional Skunk#1.
New breeding techniques give growers and breeders more control over plant characteristics, but this does not lead to a potency increase. If seed banks could breed plants that were even double the potency of the strains of the 60s, they would be selling them. What we have gained over the years are strains that produce more flowers, and therefore higher yields, but this has nothing to do with the intoxicating properties of the plant.
Fact: Big plants do not equal more potent plants, quite simply because the traits for yield and potency are governed by different genes.
Myth # 2: The Stronger the Cannabis, the Greater the Health Risks
Long-term users experience something called tolerance. If you smoke cannabis every day, your tolerance level will increase within a few days. You will notice that you will need to take slightly more to get the same effect that you experienced when your tolerance level was at its lowest—when you first started using cannabis. This does not mean that you will have to keep increasing the amounts that you take in order to experience an effect. Your tolerance levels will eventually peak and the amount that you need to take in order to experience the effect will remain at this fixed level. Increasing the amounts that you take will no longer heighten the effects, but merely sustain them for longer. Usually, cessation of use for a week or two is enough to bring your tolerance back down to its initial level. When a user experiences a peak in tolerance this usually means that they are using the drug too much. Through experience you learn to respect your limits for cannabis. Other recreational drugs, like alcohol, can be pushed past your peak tolerance by consuming more. The effect of alcohol consumption increases vigorously with the amount taken and it is possible to exceed tolerance levels to the point at which users can even develop “alcohol poisoning.”

Skunk hybrids are popular. This is Shiva Skunk.
A health-related misconception is that “high THC levels mean higher volumes of smoke being held in the lungs for longer, which is equivalent to smoking lots of cigarettes.” THC levels, percentages and concentrations do not equate to more smoke. In any given volume of smoke there is a ratio of THC-related compounds to other gases, such as carbon monoxide, that are released during the burning process. One ounce of poor quality cannabis will give off the same volume of smoke as one ounce of high-quality cannabis. Also, many people do not smoke cannabis in joints, but take the healthier, carbon-monoxide-and-tar-free route by using vaporization techniques. Smoke-free vaporization is discussed in detail later in this chapter.
Sensi Star. Photo Paradise Seeds
Myth #3: Hydroponics Makes Cannabis Stronger
Hydroponics is a method of cultivation whereby soil is replaced by a soilless substrate, such as rockwool, Oasis, perlite or vermiculite. The plant is placed in this soilless substrate and fed an aerated nutrient solution. This method allows the plant to receive the optimal levels of water, air and nutrients it needs in order to survive and thrive.
The very nature of hydroponics allows the plant to expend less energy in the pursuit of nutrients, air and water, and to divert more energy towards plant growth. This results in increased plant size, better health and bushiness (plants grown in hydroponics tend to produce more nodes because of the optimum growing conditions involved). This does not result in increased potency.
Why? Because potency is determined at a genetic level. The environment may influence the final expression of the gene but it certainly does not allow the gene to increase potency. Potency cannot increase past the gene’s threshold with any known type of growing method, growth hormone or stimulant.
A plant’s genotype (what is encoded as the plant’s DNA) is expressed in the plant’s phenotype (what you can see, smell, taste, etc.) when the plant is growing.
New light technology increases quantity, not potency.
Phenotypes are genetically governed but are also influenced by the environment. Even in optimum growing conditions the plant will never increase past the threshold for potency levels or size contained in its genotype.
It is also worth noting that hydroponic growing does not guarantee that you will automatically increase your overall yields. Many new soil-based methods can achieve the same or better results. The notion that hydroponics somehow increases cannabis potency is flawed.
Myth #4: New Lighting Technology Means Stronger Cannabis
HID lighting has indeed changed the world of indoor growing over the past twenty years. HID lighting like MH (Metal Halide) lights and HPS (High Pressure Sodium) are the choice of professional indoor cannabis growers the world over. However, all these lights do is provide the optimal lighting conditions plants require in order to live up to their full genetic potential. It does NOT improve potency, which, again, is genetically determined.
Also, HID lights may be a good replacement for natural light, but natural light is still the best light you can use for cannabis cultivation. Geographical and environmental conditions prevent growers from having complete access to this light for at least six months of the year. Some Sativa plants require up to six months flowering before they reach their full potential—which, after three months of vegetative growth, adds up to nine months growing time! Lighting is clearly important to achieving optimal growth, but the notion that new lighting technology led to stronger cannabis is flawed.
Myth #5: Feeding Products and Growth Hormones Make Cannabis Stronger
Most feeding products contain primary nutrients, secondary nutrients and micronutrients. None of these nutrients, in any combination, will increase a plant’s potency. They are simply elements that the plant needs in order to grow and thrive.
The only way in which a growth hormone can affect cannabis potency is if the hormone causes DNA repair malfunction, which can lead to a mutation of the plant’s DNA. However, this type of mutation is not controllable and the chances of it happening and resulting in increased potency are very slim. In addition, the plant may exhibit other side effects that could be negative. So, even if you did succeed in increasing the potency via a growth hormone or a DNA repair mutation, you could end up with a sickly or inferior plant that is hard to grow or reproduce. The notion that feeding products and growth hormones make cannabis stronger is flawed.
Potency is related to genes, not growth hormones or nutrients.
Myth #6: New Extraction Techniques Make Hashish Stronger
This myth may contain an element of truth but it is worth discussing anyway. The reason why hash may seem stronger is because it is not always pure on the black market. In fact, most mass-produced hash contains traces of adulterates like tranquillizers, opium, heroin and even commonly-purchased medicines to help add spice to the product. This is very common with imported cannabis products, but does not mean that cannabis produced in your home country is not adulterated too.
The black-market creates an incentive to produce and sell adulterated cannabis products. Remember that there are absolutely no content restrictions on illegal cannabis and most people have no way of knowing what it is they are taking. Hashish can be cut just like other drugs during production so that the drug manufacturer can sell their product for more money. Cannabis prohibition fuels that!
New hashish extraction methods, like cold water bubble hash extraction (the best of methods), do not increase potency; they simply reduce the amount of foreign bodies (leaf, stem, dirt) in the hash. The objective of the extraction method is to produce almost pure THC. This does not make the product stronger, or more potent, per se. It makes it more concentrated and pure, so that smaller doses are needed to achieve an effect. At the same time, consuming more of a purer substance does make the effects stronger.
The only way to create stronger cannabis outside of breeding for potency is to prepare high quality extraction.
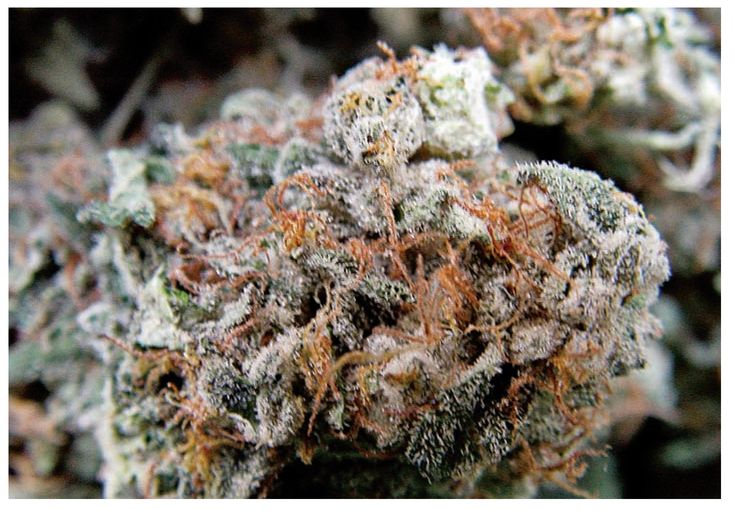
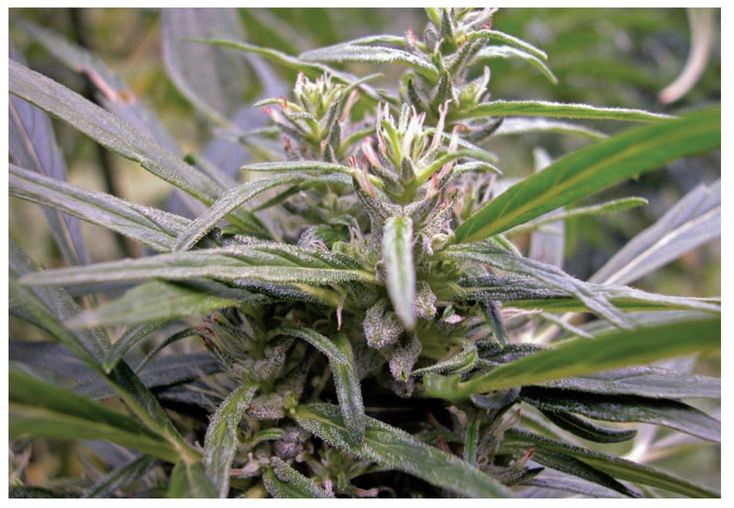
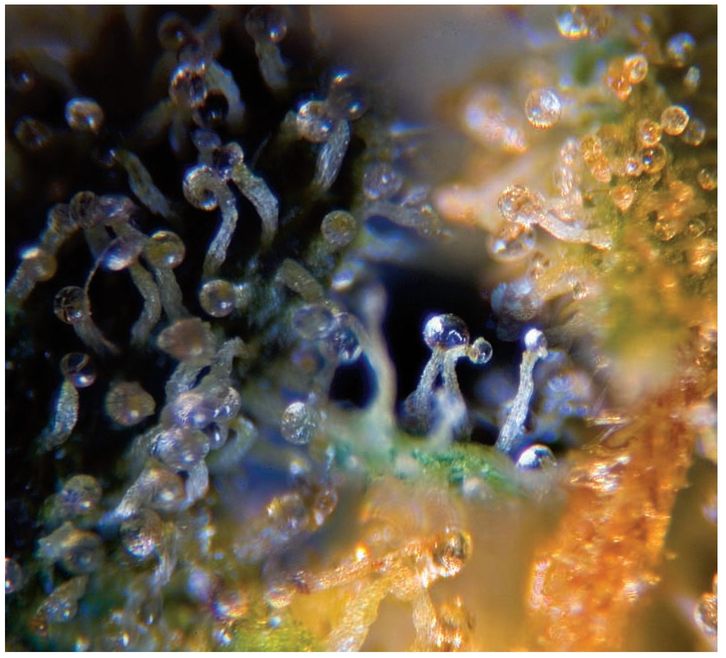
Lots of trichomes does not mean lots of potency. This plant with minimal trichomes could be more potent than strains with lots of trichomes.
Myth #7: More Crystals Means More THC and Stronger Cannabis
Crystals are simply indicators of trichome development on the flowering pistils and the surrounding leaves and stems of the female cannabis plant. Under close observation, these crystals look like mushroom heads on a long stalk. That is why they are also known as stalked capitate resin glands. The head of the trichome and stalk contain the highly prized cannabinoids.
Trichomes containing cannabinoids in quantities and levels that relate to potency. The potency of the trichome is genetically inherited. Photo Paradise Seeds.
Trichome growth and potency levels are two very different traits. You could have an extremely frosty plant with low cannabinoid content in the trichomes or you could have a plant with hardly any trichomes that are extremely high in cannabinoid content.
Although high trichome numbers do not mean high potency levels, breeders generally try to stabilize high trichome numbers with high cannabinoid levels for aesthetic and manicuring purposes intended for the final product’s presentation. The notion that more crystals mean more THC and therefore stronger cannabis is also flawed.
The Truth About Hyper-Potent Cannabis
Random mating of plants may eventually lead to the emergence of a plant with the right genetics to contribute to a breeding program for hyper-increased potency.
• Most new traits are discovered accidentally, and not always by people with breeding knowledge who can harness the trait and continue it.
• If you did discover this trait, you would have to grow extremely large selections of test offspring to breed such a plant. You would have to test each and every plant to find the trait and stabilize it, so that all of its offspring would produce the same hyper-potent trait. This could take a matter of months or a number of lifetimes to achieve.
• Sometimes the authorities get to it first, bringing your hyper-cannabinoid breeding program to an abrupt halt.
• The strains of the 60s and 70s still have not been beaten for cannabinoid levels because these old strains have been selected by generations of local growers; this is compared to our mere 40 years of cannabis cultivation and breeding agendas.
• It is less common to find poor strains being produced by breeders these days. This means that nearly all commercial cannabis is potent in some way.
• Only a handful of cuttings (clones) in the world exist which have proven to be hyper-potent—Cali O, MTF, Champagne, Chemo and G13, to name a few.
• Clones are not sold by internationally known seed banks, perhaps because clones are difficult to ship around the world.
• Only good (not to mention lucky) breeding techniques or GM (genetically modified) crops can make cannabis genetically stronger, or more potent.
• The only group that claims to have truly hyper-potent cannabis plants is the U.S. government, which conducts experiments into genetically modifying cannabis. They have never released them to the public.
So, What Has Actually Changed?
Maybe now would be a good time to list some actual changes that have taken place over the years.
Original Cheese—named for it’s deep pungent odor. Photo Dr. Greenthumb
1. The introduction of Cannabis Indica species has led to the development of hybrid plants that combine the head high effect with the body down effect.
2. Good cannabis breeders have eradicated poorer forms of cannabis from the gene pool in their breeding programs. This includes hermaphrodite plants that can never produce sinsemilla crops. The net effect is that there are less poor cannabis plants on the market so nearly every type of home grown cannabis is good to some degree, as long as it has been grown, flowered, harvested and cured correctly.
3. Sinsemilla crops are flowering female plants that do not bear seeds because the males have been removed before pollination occurs. This does not increase potency. It does however increase yield, because the plants can divert energy from seed production towards flower production.
4. There are many variations of cannabis on the market with different tastes, smells and high types. The Sativas of the 60s and 70s are very strong and are not really suitable for the novice smoker.
5. Imported hashish usually contains adulterates. It is rarely, if ever, just cannabis.
Most strains are bred for higher yields rather than higher potency levels.
The bottom line is that since the cannabis plant first started being used by humans, the gene pool has not undergone any form of a major potency increase. What has changed is our ability to stabilize traits in a plant population and to ensure that traits are continued in the offspring.
How to Avoid Taking Cancer-Causing Agents
Is cannabis a carcinogen? The answer is yes, if you smoke it using a flame directly in contact with the cannabis, which causes a process called combustion. This is because carbon monoxide is released during combustion and carbon monoxide can be deadly to humans.
Whatever way you look at it, regular inhalation of carbon monoxide will eventually destroy your lungs. If there is a history of cancer in your family, then chances are that constant, prolonged inhalation of carbon monoxide will cause cancer to develop in you. The risks are staggering if you think about it. Most people who breathe in a lot of carbon monoxide die from carbon monoxide-related diseases. Of course, pollution from modern society (cars, industry, etc.) has produced much more carbon monoxide than cannabis smokers ever have or will.
Nicotine was also recently discovered to be a carcinogen. It was thought for a long time that it was just the tar and carbon monoxide that were carcinogens, but the more we look at less suspicious substances, the more we find that they are indeed carcinogens as well.
At the moment, it is not known if cannabis is a carcinogen because cannabis is made up of so many different types of materials, including cannabinoids and their thousands of related gases that are released during combustion. The number of compounds we need to analyze to be able to say for sure probably runs in to the ten of thousands.
Before anyone discovers carcinogens in these compounds, we might as well assume that some of them are bad, and are actually the result of the combustion process. It makes good sense to remove the risk of contact with carbon monoxide from the equation. This is easy to do: you can either cook with cannabis or use a process known as vaporization.
Cooking with Cannabis
Non-smokers can enjoy marijuana without the effects of carbon monoxide. The Marijuana Chef Cookbook, by S. T. Oner, is a great cannabis cooking guide for all marijuana lovers. It covers the basics of cooking, cannabis drinks, desserts, vegetarian marijuana meals, main marijuana courses, starters and soups. It contains quite a number of recipes for you to choose from.
Cooking with cannabis is a healthy way to enjoy cannabis. Many cannabis users have found that cannabis foods are just as delightful as smoking a joint or using a vaporizer. If you like cannabis you should give cooking a try.
Save the cows. Go with the green or just have fun.
Hash butter a.k.a cannabutter.
Vaporization
Vaporization is the key to the future of smoking cannabis. The vaporization technique simply uses heat instead of a flame to convert your cannabis matter into a fume rather than smoke that contains carbon monoxide.
Imagine placing a small amount cannabis on a knife and gradually heating the knife over a stove. As the knife heats up, the cannabis begins to heat up as well, but it does not burn or catch fire right away. As the knife heats up, a vapor drifts out from the bud. After a while, the knife will become very hot and the cannabis will catch fire (if there is still some matter left) and give off a plume of gray and blue smoke.
There is a point at which the cannabis is converted into fumes without releasing carbon monoxide. It will only start to release the cancer-causing agent when the temperature of the knife increases to the point at which cannabis reaches its combustion threshold and starts to burn. In other words, you do not need to burn cannabis in order to smoke it. All you need to do is heat the knife to the point at which THC vaporizes. This is what a vaporizer does.
You don’t need to burn this to enjoy it.
This is a commercial vaporizer. You can get a very enjoyable experience from this.
Like a bong, hookah or any glass pipe, the vaporizer holds the vapor or fumes in an enclosure before you inhale. Most vaporizers are electric and require charging before the heating element is ready for the application of cannabis. Since the temperature of the heating element never rises above the threshold of THC combustion, you do not release carbon monoxide.The boiling point of THC is 200°C (392°F). Between 200°C and 300°C will release THC more quickly. Between 300°C and 400°C carbon monoxide may be released along with THC. Between 400°C and 500°C carbon monoxide will be released along with THC. Temperatures of 500°C and above result in complete combustion with maximum carbon monoxide emissions; everything burns up, leaving very little ash. Vaporizer users stick with 200°C (392°F) to achieve the desired effect of keeping carbon monoxide levels either at zero or to natural levels present in air.
Vaporizers can be bought in all sizes, shapes and forms. Pharmaceutical companies spend hundreds of thousands on industrial vaporizers in order to reduce carbon monoxide emissions from their factories. Make sure that your vaporizer has an adjustable temperature function so that you can choose how hot you want the element to get.
Before you buy a vaporizer you may want to check out the low-cost, do-it-yourself method described below. Remember, though, that you are much better off buying a professional vaporizer to ensure that no carbon monoxide is released.
Cannabis Legalization and Social Issues
Cannabis and Young Adults
Many parents and teachers are opposed to cannabis decriminalization and legalization because of concerns about risks to the health, wellbeing and future of children. This is very understandable.
All parents agree that children should not use drugs. Never promote cannabis among children.
If you have seen the Academy Award-winning film Traffic, then you will probably understand that there is also a need for closer parent/child communication with regards to drug education. The concept that cannabis decriminalization or legalization will lead to more (or less) children using cannabis is flawed. But then, the illegality of cannabis doesn’t seem to stop them from using it either. Cannabis is a very popular recreational drug.
Ask yourself this basic question: if my child is determined to get hold of cannabis, would he or she be better off procuring it from the black market or from a controlled, regulated manufacturer or retailer where other drugs, such as alcohol, are purchased from?
A cannabis activist is the new caped crusader.
A cannabis enthusiast in his native habitat.
Some people suggest that cannabis is only taken for euphoria. However, there are many other reasons why people take cannabis. Some take it for medical use. Others take it to feel more relaxed and not for its euphoric properties. Cannabis is a substance that has many more uses than getting you high.
The Alcohol vs. Cannabis Debate
Even though alcohol is water-soluble and is cleared from the body at the rate of one unit per hour (the amount in half a pint of beer, a single whisky or a glass of wine) it can still kill you. A drop of pure alcohol is enough to send any grown man to the local ER ward; some will even die if the problem is not treated quickly enough. That is why there is a legal limit on how much percentage of alcohol is allowed per bottle. Go above this limit and you can seriously hurt people, if not kill them outright.
Alcohol poisoning is common. Upwards of 5,000 people die from alcohol overdoses every year in the United States alone.
50 percent of THC is still present in the body five days after use, and 10 percent after a month. Traces can be detected in hair and urine for months after that. However, this does not mean that the psychoactive effects of cannabis are still active in the brain. It simply means that the body is disposing of THC in its own way, over time.
Cannabis does not directly kill people. Unlike alcohol, pure, concentrated THC will not kill you unless you have some rare allergy to it. There are more deaths associated directly with alcohol than there are indirectly with cannabis. The only deaths associated with cannabis are either indirect (cancer from smoking) or avoidable (car crashes or other accidents).
Animal testing has shown that extremely high doses of cannabinoids are needed to have a lethal effect on the animals. At this moment, the hypothetical toxicity amount needed to cause death derived from these studies is 1:40,000 for cannabis. That means that you would have to consume 40,000 times as much cannabis as you normally would in order to reach the hypothetical toxicity amount that causes death.
In the annals of medical history no one is ever reported to have died from a cannabis overdose, while hundreds of thousands have died from alcohol overdose or alcohol poisoning. Alcohol abuse will also damage more vital organs in the body than cannabis use. In most cases, cannabis-related damage (mainly lung disease) can be reversed by discontinuing the use of the drug or taking it in another form (unless cancer is contracted, in which chemotherapy is usually the treatment option).
1 With alcohol, most damage cannot be reversed and damaged organs can only be replaced via a transplant operation (if you can afford one or can afford to wait for one).
Cannabis is natural. It is not synthetic.
Deaths recorded in the United States in any typical year are as follows:
2
| Tobacco deaths | 400,000 |
| Alcohol deaths | 80,000 |
| Workplace accidents that result in death | 60,000 |
| Automobile accidents that result in death | 40,000 |
| Cocaine deaths | 2,200 |
| Heroin deaths | 2,000 |
| Aspirin deaths | 2,000 |
| Cannabis deaths | 0 |
The Califano Report from The National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse (CASA) at Columbia University is also worth noting.
Far more people are hospitalized for alcohol-related illness than cannabis-related illness even though cannabis is the third most commonly used drug in the Western world. Also, there are more types of alcohol-related illness than cannabis-related illness to deal with. The burden on taxpayers to solve alcohol-related illness is significantly higher than cannabis-related abuses, even in countries that have decriminalized or tolerate cannabis use.
Tobacco legalization in light of cannabis criminalization is irrational.
For goodness sake, it’s just a plant!
Any type of drug abuse can cause a different personality to emerge. Abusers cannot manage themselves properly and can become stubborn,find it hard to deal with disapproval and feel misinterpreted. This is common to all types of drug abuses and should not be singled out with cannabis alone. Mobile phone addiction, internet addiction, computer game addiction and television addiction can also cause these types of personality disorders to emerge and yet mobile phones, computer games, the internet and television are not illegal. All these things have suspected or proven health risks associated with them, too—that is why there are warnings included with the instructions!
Driving While Under the Influence
Cannabis has been brought into the intoxicating driving debate. The bottom line to any debate is that you should not do drugs and drive, period. Even though some people have suggested that cannabis causes more road accidents than alcohol there does not appear to be any data to support this.
The Federal Bureau of Prisons estimates that they have roughly 170,000 inmates for any given month. Out of these, roughly 84,000 (55 percent) are in on drug-related offenses. These figures indicate more drug-related incarceration per capita than any other nation in the world. Since 1965, America has arrested more than ten million people for marijuana-related offences.
3The church. Photo Greenhouse Seed Co.
In 2002, the annual report on the state of the drug problem in the European Union and Norway concluded that “Use of illegal substances is concentrated among young adults and particularly males in urban areas, although some spreading to smaller towns and rural areas may be taking place.”
4
Recent cannabis use (last 12 months) was reported by 5 to 15 percent of young adults in most countries. Recent amphetamine use was reported by 0.5 to 6 percent, cocaine use by 0.5 to 3.5 percent and ecstasy use by 0.5 to 5 percent.
Lifetime experience of cannabis is reported by 10 to 30 percent of European adults, while amphetamines, cocaine and ecstasy have been tried by about 1 to 5 percent.
Cannabis use increased markedly during the 1990s in most EU countries, particularly among young people, although in recent years its use seems to be leveling off in some countries. Cocaine use may have increased in recent years in some countries, although this trend is less clear.
If you have not read George Orwell’s 1984 or Animal Farm, then do.
There is an incentive for individuals who are subjected to drug tests to choose harder drugs as their form of recreational drug because these substances disappear from the system more quickly. This is another indication that drug testing does not help the cannabis problem in any way.
Cannabis remains one of the most confiscated drugs in the world and makes up almost a whopping 80 percent of all illegal confiscations, even though it is considered a less problematic drug than alcohol or harder drugs. If cannabis were legalized tomorrow, drug enforcement agencies would automatically lose 80 percent of their figures, which are used as a basis for government budgeting on drug enforcement programs. On many levels, cannabis prohibition could be more about money than most government officials would care to admit.
5
Cannabis and Brain Damage
There is no scientific evidence to suggest that THC damages the brain in any way. Animal asphyxiation experiments, using monkeys, were conducted in the 70s and subsequently used to prove that cannabis kills brain cells. Monkeys were gassed to death with cannabis smoke over a long period of time. The monkeys had electrodes implanted in their brains to monitor the effects of the exposure to cannabis smoke. The animals died and the brain cells were counted. A healthy monkey was also killed as a control experiment and its brain cells were counted. The U.S. government was brought to court on this issue to reveal the experiment under the “Freedom of Information” act. When the hoax was exposed (along with the unnecessary animal deaths), the U.S. government never used these findings again. The study was harshly condemned for its inadequate sample size of only four monkeys, its complete failure to manage experimental prejudice and the misidentification of the monkeys’brains as “damaged.”

It has never been demonstrated that cannabis can kill.
Cannabis and the Immune System
Cannabis use may affect the immune system. For some illnesses, it is advised that you discontinue cannabis use until the illness has passed. Consult your doctor for further information. This is because cannabis may cause fewer white blood cells to be produced, which are used in the fight against some diseases. Discontinuing cannabis use will restore the immune system to its previous condition.
Cannabis and Sexual Dysfunction
Sperm production may be decreased with cannabis use; discontinue cannabis use and sperm production should return to normal levels again. There is no scientific evidence to suggest that young men will develop breasts if they use cannabis. This is a red herring associated with a testosterone decrease in some individuals who use cannabis. There is absolutely no evidence to support a case that this decrease is permanent. Cannabis tolerance can also occur, bringing testosterone levels back to normal again, even though cannabis use has not been discontinued. If you want to reproduce, stop using cannabis.
Cannabis and Pregnancy
The bottom line here is the same advice that has always been administered to pregnant women: when pregnant, only take drugs that your doctor recommends. It is your duty to discontinue cannabis use if you are pregnant.
Cannabis and Human DNA Repair Malfunction
There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that cannabis directly causes DNA repair malfunction in human beings. DNA repair malfunction results in a mutation at the cellular reproduction level. A DNA repair malfunction is usually random and can result in anything. There are no specific conclusions to random D.N.A repair malfunction, although scientists can cause certain types of malfunctions to appear using specific techniques. However, these techniques may result in other types of uncontrollable mutations occurring alongside the controllable one. The notion that cannabis can cause a certain type of, or any type of, DNA repair malfunction in human beings is not scientifically proven.
These political and legal problems over an herb do not make sense.
Even medical users find themselves persecuted for reasons that have never been established scientifically.
Some sanity has been recovered in places where it is now recognized that cannabis is medicine.
Medicinal Use
In March 1999, the U.S. government-sponsored Institute of Medicine (IOM) Report concluded that:
Until a nonsmoked rapid-onset cannabinoid drug delivery system becomes available, we acknowledge that there is no clear alternative for people suffering from chronic conditions that might be relieved by smoking marijuana, such as pain or AIDS wasting.
The U.S. DEA ignored this and has said:
Any determination of a drug’s valid medical use must be based on the best available science undertaken by medical professionals. The Institute of Medicine (under the National Academy of Sciences) conducted a comprehensive study in 1999 to assess the potential health benefits of marijuana and its constituent cannabinoids. The study concluded that smoking marijuana is not recommended for the treatment of any disease condition.
Becoming a part of the cannabis community can be rewarding. . .
. . . but if for any reason you feel that it is negatively affecting your life, you can always stop.
Cannabis and Harder Drugs: The Gateway Theory
The suggestion that marijuana use leads to the use of hard drugs is based on the belief that once the person breaks the law they will be susceptible to breaking the law again. Most hard drug users have taken cannabis; however, out of the hundreds of millions of people worldwide who have tried cannabis, we do not find hundreds of millions of hard drug users. In fact, one in 100 cannabis users will likely try a harder drug, but this is not because of cannabis use. How many bicycle riders grow up to become motorcycle drivers?
That said, if a cannabis user cannot get cannabis, then they may take a harder drug that is more readably available from a dealer. This is why drug dealers are also called drug pushers. The cannabis user may be pushed to buy something else because the dealer does not have cannabis available. This is very important, and we find that most cannabis users come in contact with hard drugs as a result of contact with the same source who does not have any cannabis available. Drug dealers can also use this tactic to sell the user stronger and more expensive drugs. This is a major reason why cannabis should be disassociated with other forms of harder drugs. It is a problem that springs from prohibition.
Cannabis and Memory
Cannabis does affect short-term memory until you terminate its use. There is no evidence that cannabis can affect the memory permanently.