4.7
Zen Enlightenment
Kaiten Nukariya
1. Enlightenment Is beyond Description and Analysis.—In the foregoing chapters we have had several occasions to refer to the central problem of Zen or Enlightenment, whose content it is futile to explain or analyze. We must not explain or analyze it, because by doing so we cannot but mislead the reader. We can as well represent Enlightenment by means of explanation or analysis as we do personality by snapshots or by anatomical operations. As our inner life, directly experienced within us, is anything but the shape of the head, or the features of the face, or the posture of the body, so Enlightenment experienced by Zennists at the moment of their highest Samādhi1 is anything but the psychological analysis of mental process, or the epistemological explanation of cognition, or the philosophical generalization of concepts. Enlightenment can be realized only by the Enlightened, and baffles every attempt to describe it, even by the Enlightened themselves. The effort of the confused to guess at Enlightenment is often likened by the Zennists to the effort of the blind who feel an elephant to know what it looks like. Some of them who happen to feel the trunk would declare it is like a rope, but those who happen to feel the belly would declare it is like a huge drum; while those who happen to feel the feet would declare it is like the trunk of a tree. But none of these conjectures can approach the living elephant.
2. Enlightenment Implies an Insight into the Nature of Self.—We cannot pass over, however, this weighty problem without saying a word. We shall try in this chapter to present Enlightenment before the reader in a round-about way, just as the painter gives the fragmentary sketches of a beautiful city, being unable to give even a bird’s-eye view of it. Enlightenment, first of all, implies an insight into the nature of Self. It is an emancipation of mind from illusion concerning Self. All kinds of sin take root deep in the misconception of Self, and putting forth the branches of lust, anger, and folly, throw dark shadows on life. To extirpate this misconception Buddhism2 strongly denies the existence of the individual soul as conceived by common sense—that is, that unchanging spiritual entity provided with sight, hearing, touch, smell, feeling, thought, imagination, aspiration, etc., which survives the body. It teaches us that there is no such thing as soul, and that the notion of soul is a gross illusion. It treats of body as a temporal and material form of life doomed to be destroyed by death and reduced to its elements again. It maintains that mind is also a temporal spiritual form of life, behind which there is no immutable soul.
An illusory mind tends either to regard body as Self and to yearn after its material interests, or to believe mind dependent on soul as Ego. Those who are given to sensual pleasures, consciously or unconsciously, hold body to be the Self, and remain the lifelong slave to the objects of sense. Those who regard mind as dependent on soul as the Self, on the other hand, undervalue body as a mere tool with which the soul works, and are inclined to denounce life as if unworthy of living. We must not undervalue body, nor must we overestimate mind. There is no mind isolated from body, nor is there any body separated from mind. Every activity of mind produces chemical and physiological changes in the nerve-centers, in the organs, and eventually in the whole body; while every activity of body is sure to bring out the corresponding change in the mental function, and eventually in the whole personality. We have the inward experience of sorrow when we have simultaneously the outward appearance of tears and of pallor; when we have the outward appearance of the fiery eyes and short breath, we have simultaneously the inward feeling of anger. Thus body is mind observed outwardly in its relation to the senses; mind is body inwardly experienced in its relation to introspection. Who can draw a strict line of demarcation between mind and body? We should admit, so far as our present knowledge is concerned, that mind, the intangible, has been formed to don a garment of matter in order to become an intelligible existence at all; matter, the solid, has faded under examination into formlessness, as that of mind. Zen believes in the identification of mind and body, as Dōgen3 says: “Body is identical with mind; appearance and reality are one and the same thing.”
Bergson denies the identification of mind and body, saying:4 “It (experience) shows us the interdependence of the mental and the physical, the necessity of a certain cerebral substratum for the psychical state—nothing more. From the fact that the two things are mutually dependent, it does not follow that they are equivalent. Because a certain screw is necessary for a certain machine, because the machine works when the screw is there and stops when the screw is taken away, we do not say that the screw is the equivalent of the machine.” Bergson’s simile of a screw and a machine is quite inadequate to show the interdependence of mind and body, because the screw does cause the machine to work, but the machine does not cause the screw to work; so that their relation is not interdependence. On the contrary, body causes mind to work, and at the same time mind causes body to work; so that their relation is perfectly interdependent, and the relation is not that of an addition of mind to body, or of body to mind, as the screw is added to the machine. Bergson must have compared the workings of the machine with mind, and the machine itself with body, if he wanted to show the real fact. Moreover, he is not right in asserting that “from the fact that two things are mutually dependent, it does not follow that they are equivalent,” because there are several kinds of interdependence, in some of which two things can be equivalent. For instance, bricks, mutually dependent in their forming an arch, cannot be equivalent one with another; but water and waves, being mutually dependent, can be identified. In like manner fire and heat, air and wind, a machine and its working, mind and body.5
3. The Irrationality of the Belief of Immortality.—Occidental minds believe in a mysterious entity under the name of soul, just as Indian thinkers believe in the so-called subtle body entirely distinct from the gross body of flesh and blood. Soul, according to this belief, is an active principle that unites body and mind so as to form an harmonious whole of mental as well as bodily activities. And it acts through the instrumentality of the mind and body in the present life, and enjoys an eternal life beyond the grave. It is on this soul that individual immortality is based. It is immortal Self.
Now, to say nothing of the origin of soul, this long-entertained belief is hardly good for anything. In the first place, it throws no light upon the relation of mind and body, because soul is an empty name for the unity of mind and body, and serves to explain nothing. On the contrary, it adds another mystery to the already mysterious relationships between matter and spirit. Secondly, soul should be conceived as a psychical individual, subject to spacial determinations; but since it has to be deprived by death of its body which individualizes it, it will cease to be individuality after death, to the disappointment of the believer. How could you think anything purely spiritual and formless existing without blending together with other things? Thirdly, it fails to gratify the desire, cherished by the believer, of enjoying eternal life, because soul has to lose its body, the sole important medium through which it may enjoy life. Fourthly, soul is taken as a subject matter to receive in the future life the reward or the punishment from God for our actions in this life; but the very idea of eternal punishment is inconsistent with the boundless love of God. Fifthly, it is beyond all doubt that soul is conceived as an entity, which unifies various mental faculties and exists as the foundation of individual personality. But the existence of such soul is quite incompatible with the well-known pathological fact that it is possible for the individual to have double or treble or multiple personalities. Thus the belief in the existence of soul conceived by the common sense turns out not only to be irrational, but a useless encumbrance on the religious mind. Therefore Zen declares that there is no such thing as soul, and that mind and body are one. Hwui Chung (Ye-chu), a famous disciple of the Sixth Patriarch in China, to quote an example, one day asked a monk: “Where did you come from?” “I came, sir, from the South,” replied the man. “What doctrine do the masters of the South teach?” asked Hwui Chung again. “They teach, sir, that body is mortal, but mind is immortal,” was the answer. “That,” said the master, “is the heterodox doctrine of the Ātman!” “How do you, sir,” questioned the monk, “teach about that?” “I teach that the body and mind are one,” was the reply.6
Fiske7 in his argument against materialism, blames the denial of immortality, saying: “The materialistic assumption that there is no such state of things, and that the life of the soul ends accordingly with the life of the body, is perhaps the most colossal instance of baseless assumption that is known to the history of philosophy.” But we can say with equal force that the common-sense assumption that the life of the soul continues beyond the grave is, perhaps, the most colossal instance of baseless assumption that is known to the history of thought, because, there being no scientific evidences that give countenance to the assumption, even the spiritualists themselves hesitate to assert the existence of a ghost or soul. Again he says:8 “With this illegitimate hypothesis of annihilation the materialist transgresses the bounds of experience quite as widely as the poet who sings of the New Jerusalem with its river of life and its street of gold. Scientifically speaking, there is not a particle of evidence for either view.” This is as much as to say there is not a particle of evidence, scientifically speaking, for the common-sense view of soul, because the poet’s description of the New Jerusalem is nothing but the result of the common-sense belief of immortality.
4. The Examination of the Notion of Self.—The belief in immortality is based on the strong instinct of self-preservation that calls forth an insatiable longing for longevity. It is another form of egoism, one of the relics of our brute forefathers. We must bear in mind that this illusion of the individual Self is the foundation on which every form of immorality has its being. I challenge my readers to find in the whole history of mankind any crime not based on egoism. Evil-doers have been as a rule pleasure-hunters, money-seekers, seekers after self-interests, characterized by lust, folly, and cruelty. Has there been any one who committed theft that he might further the interests of his villagers? Has there been any paramour who disgraced himself that he might help his neighbors? Has there been any traitor who performed the ignoble conduct to promote the welfare of his own country or society at large?
To get Enlightened, therefore, we have to correct, first of all, our notions concerning Self. Individual body and mind are not the only important constituents of Self. There are many other indispensable elements in the notion of Self. For instance, I have come into existence as another form of my parents. I am theirs, and may justly be called the reincarnation of them. And again, my father is another form of his parents; my mother of hers; his and her parents of theirs; and ad infinitum. In brief, all my forefathers live and have their being in me. I cannot help, therefore, thinking that my physical state is the result of the sum total of my good and bad actions in the past lives I led in the persons of my forefathers, and of the influence I received therein;9 and that my psychical state is the result of that which I received, felt, imagined, conceived, experienced, and thought in my past existences in the persons of my ancestors.
Besides this, my brothers, my sisters, my neighbors—nay, all my fellow-men and fellow-women—are no other than the reincarnation of their parents and forefathers, who are also mine. The same blood invigorated the king as well as the beggar; the same nerve energized the white as well as the black men; the same consciousness vitalized the wise as well as the unwise. Impossible it is to conceive myself independent of my fellow-men and fellow-women, for they are mine and I am theirs—that is, I live and move in them, and they live and move in me.
It is bare nonsense to say that I go to school, not to be educated as a member of society, but simply to gratify my individual desire for knowledge; or that I make a fortune, not to lead the life of a well-to-do in society, but to satisfy my individual money-loving instinct; or that I seek after truth, neither to do good to my contemporaries nor to the future generations, but only for my individual curiosity; or that I live neither to live with my family nor with my friends nor with anyone else, but to live my individual life. It is as gross absurdity to say that I am an individual absolutely independent of society as to say that I am a husband with no wife, or I am a son to no parents. Whatever I do directly or indirectly I contribute to the common fortune of man; whatever anyone else does directly or indirectly determines my fate. Therefore we must realize that our Selves necessarily include other members of the community, while other members’ Selves necessarily comprehend us.
5. Nature Is the Mother of All Things.—Furthermore, man has come into existence out of Nature. He is her child. She provided him food, raiment, and shelter. She nourishes him, strengthens him, and vitalizes him. At the same time she disciplines, punishes, and instructs him. His body is of her own formation, his knowledge is of her own laws, and his activities are the responses to her own addresses to him. Modern civilization is said by some to be the conquest of man over Nature; but, in fact, it is his faithful obedience to her. “Bacon truly said,” says Eucken10 “that to rule nature man must first serve her. He forgot to add that, as her ruler, he is still destined to go on serving her.” She can never be attacked by any being unless he acts in strict conformity to her laws. To accomplish anything against her law is as impossible as to catch fishes in a forest, or to make bread of rock. How many species of animals have perished owing to their inability to follow her steps! How many immense fortunes have been lost in vain from man’s ignorance of her order! How many human beings disappeared on earth from their disobedience to her unbending will! She is, nevertheless, true to those who obey her rules. Has not science proved that she is truthful? Has not art found that she is beautiful? Has not philosophy announced that she is spiritual? Has not religion proclaimed that she is good? At all events, she is the mother of all beings. She lives in all things and they live in her. All that she possesses is theirs, and all that they want she supplies. Her life is the same vitality that stirs all sentient beings. Chwang Tsz11 (So-shi) is right when he says: “Heaven, Earth, and I were produced together, and all things and I are one.” And again: “If all things be regarded with love, Heaven and Earth are one with me.” Sang Chao (Sō-Jō) also says: “Heaven and Earth are of the same root as we. All things in the world are of one substance with me.”12
6. Real Self.—If there be no individual soul either in mind or body, where does personality lie? What is Real Self? How does it differ from soul? Self is living entity, not immutable like soul, but mutable and ever-changing life, which is body when observed by senses, and which is mind when experienced by introspection. It is not an entity lying behind mind and body, but life existent as the union of body and mind. It existed in our forefathers in the past, is existing in the present, and will exist in the future generations. It also discloses itself to some measure in vegetables and animals, and shadows itself forth in organic nature. It is Cosmic life and Cosmic spirit, and at the same time individual life and individual spirit. It is one and the same life which embraces men and nature. It is the self-existent, creative, universal principle that moves on from eternity to eternity. As such it is called Mind or Self by Zennists. Pan Shan (Ban-zan) says: “The moon of mind comprehends all the universe in its light.” A man asked Chang Sha (Chō-sha): “How can you turn the phenomenal universe into Self?” “How can you turn Self into the phenomenal universe?” returned the master.
When we get the insight into this Self, we are able to have the open sesame to the mysteries of the universe, because to know the nature of a drop of water is to know the nature of the river, the lake, and the ocean—nay, even of vapor, mist, and cloud; in other words, to get an insight into individual life is the key to the secret of Universal Life. We must not confine Self within the poor little person called body. That is the root of the poorest and most miserable egoism. We should expand that egoism into family-egoism, then into nation-egoism, then into race-egoism, then into human-egoism, then into living-being-egoism, and lastly into universe-egoism, which is not egoism at all. Thus we deny the immortality of soul as conceived by common sense, but assume immortality of the Great Soul, which animates, vitalizes, and spiritualizes all sentient beings. It is Hīnayāna Buddhism that first denied the existence of Atman or Self so emphatically inculcated in the Upaniṣads, and paved the way for the general conception of Universal Self, with the eulogies of which almost every page of Mahāyāna books is filled.
7. The Awakening of the Innermost Wisdom.—Having set ourselves free from the misconception of Self, next we must awaken our innermost wisdom, pure and divine, called the Mind of Buddha,13 or Bodhi,14 or Prajñā15 by Zen masters. It is the divine light, the inner heaven, the key to all moral treasures, the center of thought and consciousness, the source of all influence and power, the seat of kindness, justice, sympathy, impartial love, humanity, and mercy, the measure of all things. When this innermost wisdom is fully awakened, we are able to realize that each and every one of us is identical in spirit, in essence, in nature with the universal life or Buddha, that each ever lives face to face with Buddha, that each is beset by the abundant grace of the Blessed One, that He arouses his moral nature, that He opens his spiritual eyes, that He unfolds his new capacity, that He appoints his mission, and that life is not an ocean of birth, disease, old age, and death, nor the vale of tears, but the holy temple of Buddha, the Pure Land,16 where he can enjoy the bliss of Nirvana.
Then our minds go through an entire revolution. We are no more troubled by anger and hatred, no more bitten by envy and ambition, no more stung by sorrow and chagrin, no more overwhelmed by melancholy and despair. Not that we become passionless or simply intellectual, but that we have purified passions, which instead of troubling us, inspire us with noble aspirations, such as anger and hatred against injustice, cruelty, and dishonesty, sorrow and lamentation for human frailty, mirth and joy for the welfare of fellow-beings, pity and sympathy for suffering creatures. The same change purifies our intellect. Scepticism and sophistry give way to firm conviction; criticism and hypothesis to right judgment; and inference and argument to realization.
What we merely observed before we now touch with heart as well. What we knew in relation of difference before we now understand in relation of unity as well. How things happen was our chief concern before, but now we consider as well how much value they have. What was outside us before now comes within us. What was dead and indifferent before grows now alive and lovable to us. What was insignificant and empty before now becomes important, and has profound meaning. Wherever we go we find beauty; whomever we meet we find good; whatever we get we receive with gratitude. This is the reason why the Zennists not only regarded all their fellow-beings as their benefactors, but felt gratitude even toward fuel and water. The present writer knows a contemporary Zennist who would not drink even a cup of water without first making a salutation to it. Such an attitude of Zen toward things may well be illustrated by the following example: Sueh Fung (Sep-pō) and Kin Shan (Kin-zan), once traveling through a mountainous district, saw a leaf of the rape floating down the stream. Thereon Kin Shan said: “Let us go up, dear brother, along the stream that we may find a sage living up on the mountain. I hope we shall find a good teacher in him.” “No,” replied Sueh Fung, “for he cannot be a sage who wastes even a leaf of the rape. He will be no good teacher for us.”
8. Zen Is Not Nihilistic.—Zen judged from ancient Zen masters’ aphorisms may seem, at the first sight, to be idealistic in an extreme form, as they say: “Mind is Buddha” or, “Buddha is Mind,” or, “There is nothing outside mind,” or, “Three worlds are of but one mind.” And it may also appear to be nihilistic, as they say: “There has been nothing since all eternity,” “By illusion you see the castle of the Three Worlds; by Enlightenment you see but emptiness in ten directions.”17 In reality, however, Zen18 is neither idealistic nor nihilistic. Zen makes use of the nihilistic idea of Hīnayāna Buddhism, and calls its students’ attention to the change and evanescence of life and of the world, first to destroy the error of immutation, next to dispel the attachment to the sensual objects.
It is a misleading tendency of our intellect to conceive things as if they were immutable and constant. It often leaves changing and concrete individual objects out of consideration, and lays stress on the general, abstract, unchanging aspect of things. It is inclined to be given to generalization and abstraction. It often looks not at this thing or at that thing, but at things in general. It loves to think not of a good thing nor of a bad thing, but of bad and good in the abstract. This intellectual tendency hardens and petrifies the living and growing world, and leads us to take the universe as a thing dead, inert, and standing still. This error of immutation can be corrected by the doctrine of Transience taught by Hīnayāna Buddhism. But as medicine taken in an undue quantity turns into poison, so the doctrine of Transience drove the Hīnayānists to the suicidal conclusion of nihilism. A well-known scholar and believer of Zen, Kwei Fung (Kei-hō) says in his refutation of nihilism:19
“If mind as well as external objects be unreal, who is it that knows they are so? Again, if there be nothing real in the universe, what is it that causes unreal objects to appear? We stand witness to the fact that there is no one of the unreal things on earth that is not made to appear by something real. If there be no water of unchanging fluidity, how can there be the unreal and temporary forms of waves? If there be no unchanging mirror, bright and clean, how can there be the various images, unreal and temporary, reflected in it? If mind as well as external objects be nothing at all, no one can tell what it is that causes these unreal appearances. Therefore this doctrine (of the unreality of all things) can never clearly disclose spiritual Reality. So that Mahābheri-hārakaparivarta-sūtra says: “All the sutras that teach the unreality of things belong to the imperfect doctrine” (of the Shakya Muni). Mahāprajñā-pāramitā-sūtra says: “The doctrine of unreality is the entrance-gate of Mahāyāna.”
9. Zen and Idealism.—Next Zen makes use of Idealism as explained by the Dharmalaksana School of Mahāyāna Buddhism.20 For instance, the Fourth Patriarch says: “Hundreds and thousands of laws originate with mind. Innumerable mysterious virtues proceed from the mental source.” Niu Teu (Go-zu) also says: “When mind arises, various things arise; when mind ceases to exist, various things cease to exist.” Tsao Shan (Sō-zan) carried the point so far that he cried out, on hearing the bell: “It hurts, it pains.” Then an attendant of his asked: “What is the matter?” “It is my mind,” said he, “that is struck.”21
We acknowledge the truth of the following considerations: There exists no color, nor sound, nor odor in the objective world, but there are the vibrations of ether, or the undulations of the air, or the stimuli of the sensory nerves of smell. Color is nothing but the translation of the stimuli into sensation by the optical nerves, so also sounds by the auditory, and odors by the smelling. Therefore nothing exists objectively exactly as it is perceived by the senses, but all are subjective. Take electricity, for example: it appears as light when perceived through the eye; it appears as sound when perceived through the ear; it appears as taste when perceived through the tongue; but electricity in reality is not light, nor sound, nor taste. Similarly, the mountain is not high nor low; the river is not deep nor shallow; the house is not large nor small; the day is not long nor short; but they seem so through comparison. It is not objective reality that displays the phenomenal universe before us, but it is our mind that plays an important part. Suppose that we have but one sense organ, the eye, then the whole universe should consist of colors only. If we suppose we were endowed with the sixth sense, which entirely contradicts our five senses, then the whole world would be otherwise. Besides, it is our reason that finds the law of cause and effect in the objective world, that discovered the law of uniformity in Nature, and that discloses scientific laws in the universe so as to form a cosmos. Some scholars maintain that we cannot think of non-existence of space, even if we can leave out all objects in it; nor can we doubt the existence of time, for the existence of mind itself presupposes time. Their very argument, however, proves the subjectivity of time and space, because, if they were objective, we should be able to think them non-existent, as we do with other external objects. Even space and time, therefore, are no more than subjective.
10. Idealism Is a Potent Medicine for Self-Created Mental Disease.—Insofar as Buddhist idealism refers to the world of sense, insofar as it does not assume that to be known is identical with to be, insofar as it does not assert that the phenomenal universe is a dream and a vision, we may admit it as true. On the one hand, it serves us as a purifier of our hearts polluted with materialistic desires, and uplifts us above the plain of sensualism; on the other hand, it destroys superstitions which as a rule arise from ignorance and want of the idealistic conception of things.
It is a lamentable fact that every country is full of such superstitious people as described by one of the New Thought writers: “Tens of thousands of women in this country believe that if two people look in a mirror at the same time, or if one thanks the other for a pin, or if one gives a knife or a sharp instrument to a friend, it will break up friendship. If a young lady is presented with a thimble, she will be an old maid. Some people think that after leaving a house it is unlucky to go back after any article which has been forgotten, and if one is obliged to do so, one should sit down in a chair before going out again; that if a broom touches a person while someone is sweeping, bad luck will follow; and that it is unlucky to change one’s place at a table. A man took an opal to a New York jeweler and asked him to buy it. He said that it had brought him nothing but bad luck, that since it had come into his possession he had failed in business, that there had been much sickness in his family, and all sorts of misfortune had befallen him. He refused to keep the cursed thing any longer. The jeweler examined the stone, and found that it was not an opal after all, but an imitation.”
Idealism is a most potent medicine for these self-created mental diseases. It will successfully drive away devils and spirits that frequent ignorant minds, just as Jesus did in the old days. Zen makes use of moral idealism to extirpate, root and branch, all such idle dreams and phantasmagoria of illusion and opens the way to Enlightenment.
11. Idealistic Scepticism Concerning Objective Reality.—But extreme Idealism identifies “to be” with “to be known,” and assumes all phenomena to be ideas as illustrated in Mahāyāna-vidyāmātra-siddhi-tridasa-śāstra22 and Vidy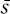 mātra-vincati-śāstra23 by Vasubandhu. Then it necessarily parts company with Zen, which believes in Universal Life existing in everything instead of behind it. Idealism shows us its dark side in three sceptic views: (1) scepticism respecting objective reality; (2) scepticism respecting religion; (3) scepticism respecting morality. First it assumes that things exist insofar as they are known by us. It is as a matter of course that if a tree exists at all, it is known as having a trunk long or short, branches large or small, leaves green or yellow, flowers yellow or purple, etc., all of which are ideas. But it does not imply in the least that “to be known” is equivalent to “to be existent.” Rather we should say that to be known presupposes to be existent, for we cannot know anything non-existent, even if we admit that the axioms of logic subsist. Again, a tree may stand as ideas to a knower, but it can stand at the same time as a shelter in relation to some birds, as food in relation to some insects, as a world in relation to some minute worms, as a kindred organism to other vegetables. How could you say that its relation to a knower is the only and fundamental relation for the existence of the tree? The disappearance of its knower no more affects the tree than of its feeder; nor the appearance of its knower affects the tree any more than that of kindred vegetables.
mātra-vincati-śāstra23 by Vasubandhu. Then it necessarily parts company with Zen, which believes in Universal Life existing in everything instead of behind it. Idealism shows us its dark side in three sceptic views: (1) scepticism respecting objective reality; (2) scepticism respecting religion; (3) scepticism respecting morality. First it assumes that things exist insofar as they are known by us. It is as a matter of course that if a tree exists at all, it is known as having a trunk long or short, branches large or small, leaves green or yellow, flowers yellow or purple, etc., all of which are ideas. But it does not imply in the least that “to be known” is equivalent to “to be existent.” Rather we should say that to be known presupposes to be existent, for we cannot know anything non-existent, even if we admit that the axioms of logic subsist. Again, a tree may stand as ideas to a knower, but it can stand at the same time as a shelter in relation to some birds, as food in relation to some insects, as a world in relation to some minute worms, as a kindred organism to other vegetables. How could you say that its relation to a knower is the only and fundamental relation for the existence of the tree? The disappearance of its knower no more affects the tree than of its feeder; nor the appearance of its knower affects the tree any more than that of kindred vegetables.
Extreme idealism erroneously concludes that what is really existent, or what is directly proved to be existent, is only our sensations, ideas, thoughts; that the external world is nothing but the images reflected on the mirror of the mind, and that therefore objective reality of things is doubtful—nay, more, they are unreal, illusory, and dreams. If so, we can no longer distinguish the real from the visionary; the waking from the dreaming; the sane from the insane; the true from the untrue. Whether life is real or an empty dream, we are at a loss to understand.
12. Idealistic Scepticism Concerning Religion and Morality.—Similarly, it is the case with religion and morality. If we admit extreme idealism as true, there can be nothing objectively real. God is little more than a mental image. He must be a creature of mind instead of a Creator. He has no objective reality. He is when we think He is. He is not when we think He is not. He is at the mercy of our thought. How much more unreal the world must be, which is supposed to have been created by an unreal God! Providence, salvation, and divine grace—what are they? A bare dream dreamed in a dream!
What is morality, then? It is subjective. It has no objective validity. A moral conduct highly valued by our fathers is now held to be immoral by us. Immoral acts now strongly denounced by us may be regarded as moral by our posterity. Good deeds of the savage are not necessarily good in the eyes of the civilized, nor are evil acts of the Orientals necessarily evil before the face of the Occidentals. It follows, then, that there is no definite standard of morality in any place at any time.
If morality be merely subjective, and there be no objective standard, how can you distinguish evil from good? How can you single out angels from among devils? Was not Socrates a criminal? Was not Jesus also a criminal? How could you know Him to be a Divine man different from other criminals who were crucified with Him? What you honor may I not denounce as disgrace? What you hold as duty may I not condemn as sin? Every form of idealism is doomed, after all, to end in such confusion and scepticism. We cannot embrace radical idealism, which holds these threefold sceptical views in her womb.
13. An Illusion Concerning Appearance and Reality.—To get Enlightened we must next dispel an illusion respecting appearance and reality. According to certain religionists, all the phenomena of the universe are to succumb to change. Worldly things one and all are evanescent. They are nought in the long run. Snow-capped mountains may sink into the bottom of the deep, while the sands in the fathomless ocean may soar into the azure sky at some time or other. Blooming flowers are destined to fade and to bloom again in the next year. So destined are growing trees, rising generations, prospering nations, glowing suns, moons, and stars. This, they would say, is only the case with phenomena or appearances, but not with reality. Growth and decay, birth and death, rise and fall, all these are the ebb and flow of appearances in the ocean of reality, which is always the same. Flowers may fade and be reduced to dust, yet out of that dust come flowers. Trees may die out, yet they are reproduced somewhere else. The time may come when the earth will become a dead sphere quite unsuitable for human habitation, and the whole of mankind will perish; yet who knows whether another earth may not be produced as man’s home? The sun might have its beginning and end, stars, moon, theirs as well; yet an infinite universe would have no beginning nor end.
Again, they say, mutation is of the world of sense or phenomenal appearances, but not of reality. The former are the phases of the latter shown to our senses. Accordingly they are always limited and modified by the mirror in which they are reflected. On this account appearances are subject to limitations, while reality is limitless. And it follows that the former are imperfect, while the latter is perfect; that the former is transient, while the latter is eternal; that the former is relative, while the latter is absolute; that the former is worldly, while the latter is holy; that the former is knowable, while the latter is unknowable.
These considerations naturally lead us to an assertion that the world of appearances is valueless, as it is limited, short-lived, imperfect, painful, sinful, hopeless, and miserable; while the realm of reality is to be aspired for, as it is eternal, perfect, comfortable, full of hope, joy, and peace—hence the eternal divorce of appearance and reality. Such a view of life tends to make one minimize the value of man, to neglect the present existence, and to yearn after the future.
Some religionists tell us that we men are helpless, sinful, hopeless, and miserable creatures. Worldly riches, temporal honors, and social positions—nay, even sublimities and beauties of the present existence, are to be ignored and despised. We have no need of caring for those things that pass away in a twinkling moment. We must prepare for the future life which is eternal. We must accumulate wealth for that existence. We must endeavor to hold rank in it. We must aspire for the sublimity and beauty and glory of that realm.
14. Where Does the Root of the Illusion Lie?—Now let us examine where illusion lies hidden from the view of these religionists. It lies deeply rooted in the misconstruction of reality, grows up in the illusive ideas of appearances, and throws its dark shadow on life. The most fundamental error lies in their construing reality as something unknowable existing behind appearances.
According to their opinion, all that we know, or perceive, or feel, or imagine about the world, is appearances or phenomena, but not reality itself. Appearances are “things known as,” but not “things as they are.” Thing-in-itself, or reality, lies behind appearances permanently beyond our ken. This is probably the most profound metaphysical pit into which philosophical minds have ever fallen in their way of speculation. Things appear, they would say, as we see them through our limited Senses; but they must present entirely different aspects to those that differ from ours, just as the vibration of ether appears to us as colors, yet it presents quite different aspects to the color-blind or to the pur-blind. The phenomenal universe is what appears to the human mind, and in case our mental constitution undergoes change, it would be completely otherwise.
This argument, however, is far from proving that the reality is unknowable, or that it lies hidden behind appearances or presentations. Take, for instance, a reality which appears as a ray of the sun. When it goes through a pane of glass it appears to be colorless, but it exhibits a beautiful spectrum when it passes through a prism. Therefore you assume that a reality appearing as the rays of the sun is neither colorless nor colored in itself, since these appearances are wholly due to the difference that obtains between the pane of glass and the prism.
We contend, however, that the fact does not prove the existence of the reality named the sun’s ray beyond or behind the white light, nor its existence beyond or behind the spectrum. It is evident that the reality exists in white light, and that it is known as the white light when it goes through a pane of glass; and that the same reality exists in the spectrum, and is known as the spectrum when it goes through the prism. The reality is known as the white light on the one hand, and as the spectrum on the other. It is not unknowable, but knowable.
Suppose that one and the same reality exhibits one aspect when it stands in relation to another object; two aspects when it stands in relation to two different objects; three aspects when it stands in relation to three different objects. The reality of one aspect never proves the unreality of another aspect, for all these three aspects can be equally real. A tree appears to us as a vegetable; it appears to some birds as a shelter; and it appears to some worms as a food. The reality of its aspect as a vegetable never proves the unreality of its aspect as food, nor does the reality of its aspect as food disprove the reality of its aspect as shelter. The real tree does not exist beyond or behind the vegetable. We can rely upon its reality, and make use of it to a fruitful result. At the same time, the birds can rely on its reality as a shelter, and build their nests in it; the worms, too, can rely on its reality as food, and eat it to their satisfaction. A reality which appears to me as my wife must appear to my son as his mother, and never as his wife. But the same real woman is in the wife and in the mother; neither is unreal.
15. Thing-in-Itself Means Thing-Knowerless.—How, then, did philosophers come to consider reality to be unknowable and hidden behind or beyond appearances? They investigated all the possible presentations in different relationships, and put them all aside as appearances, and brooded on the thing-in-itself, shut out from all possible relationship, and declared it unknowable. Thing-in-itself means thing cut off from all possible relationships. To put it in another way: thing-in-itself means thing deprived of its relation to its knower—that is to say, thing knowerless. So that to declare thing-in-itself unknowable is as much as to declare thing-unknowable unknowable; there is no doubt about it, but what does it prove?
Deprive yourself of all the possible relationships, and see what you are. Suppose you are not a son to your parents, nor the husband to your wife, nor the father to your children, nor a relative to your kindred, nor a friend to your acquaintances, nor a teacher to your students, nor a citizen to your country, nor an individual member to your society, nor a creature to your God, then you get you-in-yourself. Now ask yourself, what is you-in-yourself? You can never answer the question. It is unknowable, just because it is cut off from all knowable relations. Can you thus prove that you-in-yourself exists beyond or behind you?
In like manner our universe appears to us human beings as the phenomenal world or presentation. It might appear to other creatures of a different mental constitution as something else. We cannot ascertain how it might seem to Devas, to Asuras, to angels, and to the Almighty, if there be such beings. However different it might seem to these beings, it does not imply that the phenomenal world is unreal, nor that the realm of reality is unknowable.
“Water,” the Indian tradition has it, “seems to man as a drink, as emerald to Devas, as bloody pus to Pretas, as houses to fishes.” Water is not a whit less real because of its seeming as houses to fishes, and fishes’ houses are not less real because of its seeming as emerald to Devas. There is nothing that proves the unreality of it. It is a gross illusion to conceive reality as transcendental to appearances. Reality exists as appearances, and appearances are reality known to human beings. You cannot separate appearances from reality, and hold out the latter as the object of aspiration at the cost of the former. You must acknowledge that the so-called realm of reality which you aspire after, and which you seek for outside or behind the phenomenal universe, exists here on earth. Let Zen teachers tell you that “the world of birth and death is the realm of Nirvāṇa”; “the earth is the pure land of Buddha.”
• • •
18. All the Worlds in Ten Directions Are Buddha’s Holy Land.—Suffice it to say for the present it is the law of Universal Life that manifoldness is in unity, and unity is in manifoldness; difference is in agreement, and agreement in difference; confliction is in harmony, and harmony in confliction; parts are in the whole, and the whole is in parts; constancy is in change, and change in constancy; good is in bad, and bad in good; integration is in disintegration, and disintegration is in integration; peace is in disturbance, and disturbance in peace. We can find something celestial among the earthly. We can notice something glorious in the midst of the base and degenerated.
“There are nettles everywhere, but are not smooth, green grasses more common still?” Can you recognize something awe-inspiring in the rise and fall of nations? Can you not recognize something undisturbed and peaceful among disturbance and trouble? Has not even grass some meaning? Does not even a stone tell the mystery of Life? Does not the immutable Jaw of good hold sway over human affairs after all, as Tennyson says—
I can but trust that good shall fall
At last—far off—at last, to all.
Has not each of us a light within him, whatever degrees of luster there may be? Was Washington in the wrong when he said: “Labor to keep alive in your heart that little spark of celestial fire called conscience.”
We are sure that we can realize the celestial bliss in this very world, if we keep alive the Enlightened Consciousness, of which Bodhidharma and his followers showed the example. “All the worlds in ten directions are Buddha’s Holy Lands!” That Land of Bliss and Glory exists above us, under us, around us, within us, without us, if we open our eyes to see. “Nirvāṇa is in life itself,” if we enjoy it with admiration and love. “Life and death are the life of Buddha,” says Dōgen. Everywhere the Elysian gates stand open, if we do not shut them up by ourselves. Shall we starve ourselves refusing to accept the rich bounty which the Blessed Life offers to us? Shall we perish in the darkness of scepticism, shutting our eyes to the light of Tathāgata? Shall we suffer from innumerable pains in the self-created hell where remorse, jealousy, and hatred feed the fire of anger? Let us pray to Buddha, not in word only, but in the deed of generosity and tolerance, in the character noble and loving, and in the personality sublime and good. Let us pray to Buddha to save us from the hell of greed and folly, to deliver us from the thralldom of temptation. Let us “enter the Holy of Holies in admiration and wonder.”
NOTES
1. Abstract Contemplation, which the Zennists distinguish from Samādhi, practised by the Brahmins. The author of ‘An Outline of Buddhist Sects’ points out the distinction, saying: “ ‘Contemplation of outside religionists is practised with the heterodox view that the lower worlds (the worlds for men, beasts, etc.) are disgusting, but the upper worlds (the worlds for Devas) are desirable; Contemplation of common people (ordinary lay believers of Buddhism) is practised with the belief in the law of Karma, and also with disgust (for the lower worlds) and desire (for the upper worlds); Contemplation of Hīnayāna is practised with an insight into the truth of Anātman (non-soul); Contemplation of Mahāyāna is practised with an insight of Unreality of Ātman (soul) as well as of Dharma (thing); Contemplation of the highest perfection is practised with the view that Mind is pure in its nature, it is endowed with unpolluted wisdom, free from passion, and it is no other than Buddha himself.”
2. Both Mahāyāna and Hīnayāna Buddhism teach the doctrine of Anātman, or Non-self. It is the denial of soul as conceived by common-sense, and of Ātman as conceived by Indian heterodox thinkers. Some Mahāyānists believe in the existence of real Self instead of individual self, as we see in Mahāparinirvāṇa-sūtra, whose author says: “There is real self in non-self.” It is worthy of note that the Hīnayānists set forth Purity, Pleasure, Ātman, and Eternity, as the four great misconceptions about life, while the same author regards them as the four great attributes of Nirvāṇa itself.
3. The master strongly condemns the immortality of the soul as the heterodox doctrine in his Shō-bō-gen-zō. The same argument is found in Mu-chū-mon-dō, by Koku-hi.
4. Creative Evolution, pp. 354, 355.
5. Bergson, arguing against the dependence of the mind on brain, says: “That there is a close connection between a state of consciousness and the brain we do not dispute. But there is also a close connection between a coat and the nail on which it hangs, for if the nail is pulled out, the coat will fall to the ground. Shall we say, then, that the shape of the nail gave the shape of the coat, or in any way corresponds to it? No more are we entitled to conclude, because the psychical fact is hung on to a cerebral state, that there is any parallelism between the two series, psychical and physiological.” We have to ask, in what respects does the interrelation between mind and body resemble the relation between a coat and a nail?
6. For further explanation, see Shō-bō-gen-zō and Mu-chū-mon-dō.
7. The Destiny of Man, p. 110.
8. The Destiny of Man, pp. 110, 111.
9. This is the law of Karma.
10. Eucken’s Philosophy of Life, by W. II. Royce Gibbon, p. 51.
11. Chwang Tsz, vol. i, p. 20.
12. This is a favorite subject of discussion by Zennists.
13. Zen is often called the Sect of Buddha-mind, as it lays stress on the awakening of the Mind of Buddha. The words ‘the Mind of Buddha’ were taken from a passage in Lankāvatāra-sūtra.
14. That knowledge by which one becomes enlightened.
15. Supreme wisdom.
16. Sukhavātū, or the land of bliss.
17. These words were repeatedly uttered by Chinese and Japanese Zennists in all ages. Chwen Hih (Fu-dai-shi) expressed this very idea in his Sin Wang Ming (Shin-ō-mei) at the time of Bodhidharma.
18. The Rin-zai teachers mostly make use of the doctrine of unreality of all things, as taught in Prajñā-pāramitā-sūtras. We have to note that there are some differences between the Mahāyāna doctrine of unreality and the Hānayāna doctrine of unreality.
19. See the appendix, chap. ii, “The Mahāyāna Doctrine of Nihilism.”
20. Appendix, chap. ii, “The Mahāyāna Doctrine of Dharmalaksana.”
21. Zen-rin-rui-shū.
22. A philosophical work on Buddhist Idealism by Vasubandhu, translated into Chinese by Hiuen Tsang in A.D. 648. There exists a famous commentary on it, compiled by Dharmapāla, translated into Chinese by Hiuen Tsang in A.D. 659. See Nanjā’s Catalogue, Nos. 1197 and 1125.
23. A simpler work on Idealism, translated into Chinese by Hiuen Tsang in A.D. 661. See Nanjā’s Catalogue, Nos. 1238, 1239, and 1240.
STUDY QUESTIONS
1. Discuss the ontological argument for the existence of God. Do you agree with Anselm that it proves the existence of God?
2. What is Gaunilo’s criticism of the argument? Do you agree with Gaunilo? Argue pro or con.
3. Is it possible for us to distinguish in thought between (i) a being that exists only in our concept, and (ii) a being that exists in our concept and reality? Do you agree or disagree? Defend your position.
4. Is a being that exists in our concept and in reality superior to an otherwise identical being existing in concept only? Argue pro or con.
5. In your opinion, is the ontological argument a sound argument? If so, why so? If not, why not?
6. What are the five ways in which Aquinas claims that the existence of God can be proven?
7. Has Aquinas proved the existence of God? Why or why not? Do you see the value of these arguments? Argue for your position.
8. Out of the five ways that Aquinas discusses, which way seems most defensible and why?
9. Compare and contrast ontological and cosmological arguments. Which argument appeals to you more and why?
10. Select a proof for the existence of God and outline it clearly. Does the proof you have selected prove the existence of God? If it does, discuss some of the strongest objections to the proof and why they do not constitute good reasons for rejecting the proof. If it does not, discuss some of the strongest reasons for accepting the proof and why they do not constitute good reasons for the acceptance of the proof.
11. Discuss the main tenets of the Islāmic conception of God.
12. Discuss key ideas of Aurobindo’s “Omnipresent Reality.”
13. Do you agree with Aurobindo that both being and non-being are different states of one omnipresent reality? Give reasons for your answer.
14. Sri Aurobindo characterizes the reality as conscious existence, supreme intelligence, and self-existent bliss. Explain what Aurobindo means by these characterizations.
15. Compare and contrast western, Islāmic, and Hindu conceptions of God. Discuss the unique feature of each of these religions.
16. Discuss the Zennist conception of enlightenment.
17. Both the Zennists and the Hindus maintain that enlightenment implies an insight into the self. Compare and contrast the two.
18. Summarize the main points of Wang Ch’ung’s thesis that the soul after death does not assume any conscious form.
19. Discuss Wang Ch’ung’s notion of the spontaneity of the natural order. Outline the method of reasoning he uses to substantiate his naturalism.
20. Do you agree with Wang Ch’ung’s thesis that natural is without any consciousness or purpose? Argue for or against.
SUGGESTIONS FOR FURTHER READING
The Mind of Light by Sri Aurobindo, introduction by Robert A. McDermott (New York: E. P. Dutton & Co., 1971), is an excellent, though brief, introduction to Aurobindo’s thought.
The Life Divine, The Synthesis of Yoga, and The Human Cycle are Aurobindo’s most important writings. They are available in various editions.
The Ontological Argument by Jonathan Barnes (London: Macmillan, 1972) is a good general discussion of the argument.
Sounds of Valley Streams: Enlightenment in Dōgen’s Zen: Translation of Nine Essays from Shōbōgenzō edited by Francis H. Cook (Albany: State University of New York Press, 1988), is an excellent collection of translations.
Thomas Aquinas by F.C. Copleston (New York: Barnes & Noble, 1977) is an excellent introduction to the philosophy of Aquinas.
The Cosmological Argument from Plato to Leibnitz by William Craig (New York: Barnes & Noble, 1980) is a good survey of the history of the argument.
Islam: The Straight Faith by J.L. Esposito (New York: Oxford University Press, 1990) is a clear and lively account of Islamic religion.
Classical and Contemporary Readings in the Philosophy of Religion, 4th edition, edited by John Hick, is an excellent anthology with introductory remarks on major issues in philosophy of religion.
Arguments for the Existence of God by John Hick (London: Macmillan, 1971) is a clearly written and insightful examination of the traditional arguments for the existence of God.
Islam: Muhammed and His Religion edited by Arthur Jeffery (Indianapolis: The Bobbs-Merrill Company, Inc., 1958), contains a good selection of writings from traditional Islam.
An Introduction to the Philosophy of Sri Aurobindo, 2nd ed., by S.K. Maitra (Benares: Benares Hindu University, 1945) is a brief and concise introduction to Sri Aurobindo’s philosophy.
Students interested in comparative philosophy might wish to consult The Meeting of the East and the West in Sri Aurobindo’s Philosophy, by S.K. Maitra (Pondicherry: Sri Aurobindo Ashram, 1956).
The Existence of God by Wallace Matson (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1965) is a cogently argued attack on the traditional arguments.
The Ontological Argument from St. Anselm to Contemporary Philosophers by Alvin Plantinga (Garden City, NY: Doubleday, 1965) contains a good survey of the history of the argument.
The Cosmological Argument by William Rowe (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1975) is a thorough and penetrating study of the classic formulations of the argument.
The Existence of God by Richard Swinburne (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1979) is perhaps the most sustained defense of the traditional arguments.
A Short History of Chinese Philosophy by Fung Yu-lan (New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., 1960), is an excellent account of the development of Chinese philosophy. It is a shorter version of the two-volume work by Fung entitled A History of Chinese Philosophy (Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1959–60), a comprehensive and authoritative survey of Chinese philosophy.
_____________
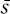 mātra-vincati-śāstra23 by Vasubandhu. Then it necessarily parts company with Zen, which believes in Universal Life existing in everything instead of behind it. Idealism shows us its dark side in three sceptic views: (1) scepticism respecting objective reality; (2) scepticism respecting religion; (3) scepticism respecting morality. First it assumes that things exist insofar as they are known by us. It is as a matter of course that if a tree exists at all, it is known as having a trunk long or short, branches large or small, leaves green or yellow, flowers yellow or purple, etc., all of which are ideas. But it does not imply in the least that “to be known” is equivalent to “to be existent.” Rather we should say that to be known presupposes to be existent, for we cannot know anything non-existent, even if we admit that the axioms of logic subsist. Again, a tree may stand as ideas to a knower, but it can stand at the same time as a shelter in relation to some birds, as food in relation to some insects, as a world in relation to some minute worms, as a kindred organism to other vegetables. How could you say that its relation to a knower is the only and fundamental relation for the existence of the tree? The disappearance of its knower no more affects the tree than of its feeder; nor the appearance of its knower affects the tree any more than that of kindred vegetables.
mātra-vincati-śāstra23 by Vasubandhu. Then it necessarily parts company with Zen, which believes in Universal Life existing in everything instead of behind it. Idealism shows us its dark side in three sceptic views: (1) scepticism respecting objective reality; (2) scepticism respecting religion; (3) scepticism respecting morality. First it assumes that things exist insofar as they are known by us. It is as a matter of course that if a tree exists at all, it is known as having a trunk long or short, branches large or small, leaves green or yellow, flowers yellow or purple, etc., all of which are ideas. But it does not imply in the least that “to be known” is equivalent to “to be existent.” Rather we should say that to be known presupposes to be existent, for we cannot know anything non-existent, even if we admit that the axioms of logic subsist. Again, a tree may stand as ideas to a knower, but it can stand at the same time as a shelter in relation to some birds, as food in relation to some insects, as a world in relation to some minute worms, as a kindred organism to other vegetables. How could you say that its relation to a knower is the only and fundamental relation for the existence of the tree? The disappearance of its knower no more affects the tree than of its feeder; nor the appearance of its knower affects the tree any more than that of kindred vegetables.