
Time: 60 Minutes
75 Questions
Directions: Each of the following questions is followed by five answer choices. Choose the one answer choice that best answers the question or completes the statement.
1. The distance north and south of the equator is the
(A) global grid system.
(B) Prime Meridian
(C) latitude.
(D) longitude.
(E) scale.
2. Which type of transportation system created the star-shaped city pattern?
(A) Highways to airports that link cities
(B) Interstate highways that link cities
(C) Beltways around cities
(D) Sidewalks in the CBD
(E) Streetcar and trolley lines extending from the CBD
3. The concentration of production activities and people spatially to benefit everyone is called
(A) the substitution principle.
(B) deglomeration.
(C) agglomeration.
(D) infrastructure.
(E) the multiplier effect.
4. Which form of migration below are farm workers from another country most likely to be practicing during the year?
(A) Chain migration
(B) Cluster migration
(C) Circular migration
(D) International migration
(E) International travel
5. Of these, the map using the smallest map scale would be the map of
(A) the world.
(B) Atlanta, Georgia.
(C) Main Street, Small Town, Ohio.
(D) Pennsylvania.
(E) South America.
6. All of the following are reasons major cities attract young people in Latin America EXCEPT
(A) the availability of jobs.
(B) the potential for decent housing.
(C) educational opportunities.
(D) their families live there already.
(E) the urban lifestyle.
7. The attempt by core countries to stimulate increased agricultural production in the periphery through use of technology, hybrid seed, and fertilizers is called the
(A) First Agricultural Revolution.
(B) Second Agricultural Revolution.
(C) Third Agricultural Revolution.
(D) Fourth Agricultural Revolution.
(E) Green Revolution.
8. Which country below is best represented by a population pyramid with a broad base that slopes quickly to a narrow top?
(A) France
(B) Russia
(C) Austria
(D) Uganda
(E) Italy
9. The use and spread of English in nineteenth-century India is an example of what type of diffusion?
(A) Stimulus
(B) Contagious
(C) Hierarchal
(D) Relocation
(E) Migratory
10. The outlying area serviced by a urban center is referred to as a
(A) redline area.
(B) threshold.
(C) range.
(D) hinterland.
(E) sphere of influence.
11. World population tends to be concentrated
(A) in continental interiors.
(B) on continental margins.
(C) in the desert.
(D) in the tropical lowlands and river valleys.
(E) at higher elevations.
12. Boundary problems along the United States–Mexico border are caused by which type of issue below?
(A) Ownership of fertile ground
(B) Land use
(C) Irredentism
(D) Document interpretation
(E) Immigration
13. Which of the following countries does NOT have a well-known example of a relict boundary?
(A) Vietnam
(B) United Kingdom
(C) Germany
(D) China
(E) Bolivia
14. What monotheistic religion is based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ of Nazareth?
(A) Islam
(B) Christianity
(C) Hinduism
(D) Buddhism
(E) Judaism
15. The “melting pot” theory of combining several immigrant groups into one mainstream culture is called
(A) amalgamation theory.
(B) acculturation.
(C) ethnic islands.
(D) ethnic clustering.
(E) cluster migration.
16. The birth of an urban industrial workforce in Europe contributed to the start of the
(A) First Agricultural Revolution.
(B) Second Agricultural Revolution.
(C) Third Agricultural Revolution.
(D) Fourth Agricultural Revolution.
(E) Green Revolution.
17. Which of the following world regions is NOT considered one of the world’s most densely populated regions?
(A) South Asia
(B) Europe
(C) South America
(D) Northeast United States
(E) East Asia
18. Which language family contains Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, and Romanian?
(A) European
(B) Slavic
(C) Germanic
(D) Romance
(E) Celtic
19. What is the most widespread primary economic activity in the world?
(A) Mining
(B) Hunting and gathering
(C) Fishing
(D) Agriculture
(E) Forestry
20. Which one of the following is NOT a centripetal force in a state?
(A) A high level of confidence in central government
(B) The existence of strong separatist groups
(C) The existence of national transportation networks
(D) The national anthem
(E) The national flag
21. The global lingua franca is
(A) Chinese.
(B) English.
(C) French.
(D) Arabic.
(E) Hindi.
22. Historically, the world’s major languages have spread by all of the following methods EXCEPT
(A) Sanskrit records.
(B) migration.
(C) trade.
(D) conquest.
(E) expanding populations.
23. Which urban model theorizes that high-rent residential areas grow outward from the center of the city along major highways with lower-rent inhabitants taking over sequentially?
(A) Concentric zone model
(B) Central place model
(C) Urban realms model
(D) Sector model
(E) Multiple-nuclei model
24. Which one of the following is NOT an advantage of urban agriculture?
(A) Helping to solve the problem of solid waste disposal
(B) Fresh produce for sale to others
(C) Beautification of a dingy urban area
(D) Low transportation and storage costs for food
(E) Renewed or purified water supplies
25. What is the most rapidly growing religion in the United States today?
(A) Islam
(B) Christianity
(C) Hinduism
(D) Buddhism
(E) Judaism
26. What is the population statistic that tells us the level of fertility at which a population will have just enough births to replace parents and compensate for early deaths?
(A) Crude birth rate
(B) Replacement level
(C) Mortality rate
(D) Total fertility rate
(E) Crude death rate
27. Which of the following statements regarding historical North American migration streams is NOT correct?
(A) Canada’s first major migration came from France.
(B) Canada’s second major migration stream originated in the British Isles.
(C) Canada’s third major migration stream came from Latin America.
(D) The first major migration wave to the United States originated in Europe.
(E) The last major wave of immigration to the United States from Latin America and Asia.
28. The main factor preventing subsistence economies from advancing economically is the lack of
(A) a currency.
(B) a well-connected transportation infrastructure.
(C) government activity.
(D) a banking service.
(E) a market surplus.
29. Ankara, Turkey and Islamabad, Pakistan are both examples of
(A) desert cities.
(B) forward-thrust capitals.
(C) old colonial capitals.
(D) rival cities.
(E) low-latitude capital cities.
30. What are the two major branches of Islam?
(A) Sunni and Shinto
(B) Shinto and Shiite
(C) Sunni and Shiite
(D) Shamanism and Shiite
(E) Shamanism and Sunni
31. Which type of economic activity is most closely tied to the physical environment?
(A) Primary
(B) Secondary
(C) Tertiary
(D) Quaternary
(E) Quinary
32. A map that presents a single class of statistics is called a
(A) general purpose map.
(B) thematic map.
(C) reference map.
(D) mental map.
(E) location map.
33. Which of the following is a centrifugal force in a country?
(A) Religious differences
(B) A national holiday
(C) An attack by another country
(D) A charismatic national leader
(E) Effective national government
34. In which country does language pose a centrifugal force?
(A) Canada
(B) United States
(C) Brazil
(D) Norway
(E) Thailand
(F)
35. According to the map above showing US farmland, which grouping of states has roughly half its land area in farms?
(A) Pennsylvania, West Virginia, New York
(B) Louisiana, Mississippi, Georgia
(C) Illinois, Indiana, Ohio
(D) Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont
(E) Nevada, Utah, Oregon
36. Which one of the following North American associations is NOT correct?
(A) Southeast—African Americans
(B) Oklahoma and the Southwest—Native Americans
(C) Quebec and northern Maine—French Americans and French Canadians
(D) Southern California—Hispanic Americans
(E) Southern prairie provinces—African Americans
37. Which one of the following groups is excluded from the caste system of Hinduism?
(A) Scholar-priests
(B) Warrior-landowners
(C) Businessmen and farmers
(D) Servants
(E) Untouchables
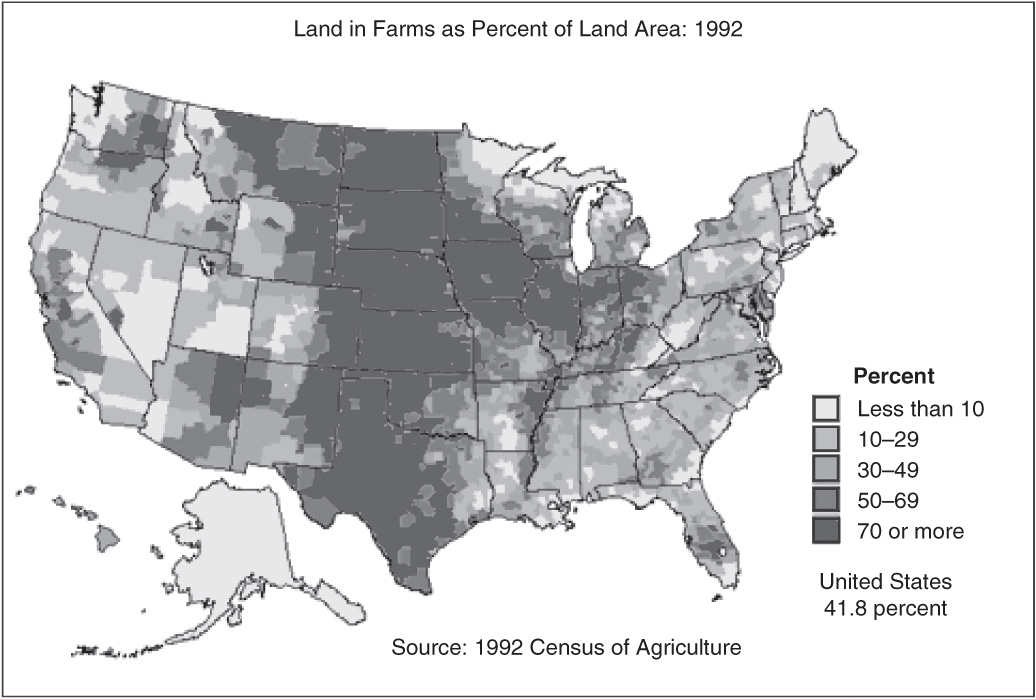
Source: United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
United States Population, 2000. Source: US Census Bureau.
38. Which one of the following is NOT a factor in creating the Third Agricultural Revolution?
(A) Use of chemical fertilizers
(B) Use of chemical pesticides and herbicides
(C) Mechanization
(D) The processing and packaging of agricultural products
(E) The use of field drainage systems
39. In which urban US setting below would you expect to find planned communities?
(A) Ghettos
(B) Suburbs
(C) CBDs
(D) Transition zones
(E) Barrios
40. Which of the following factors has little or no impact on mortality rates in the developing countries?
(A) New medicines
(B) Improved birth control methods
(C) Pesticides
(D) Famine relief
(E) Improved vaccines
41. The Rhine River is an example of which type of boundary?
(A) Geometric
(B) Artificial
(C) Natural
(D) Relic
(E) Subsequent
42. According to the population pyramid above, which one of the following statements is correct?
(A) The death rate exceeds the birth rate.
(B) The economically active and productive population is too small to support the youth and old-age population.
(C) Gender numbers are nearly identical until the older-age cohort is reached.
(D) The population is experiencing a rapid growth rate.
(E) The population is experiencing a high mortality rate.
43. Which one of the following items is an example of nonmaterial culture?
(A) Dove soap
(B) Dove candy bar
(C) Dove symbol
(D) A dove (bird)
(E) Dove stew
44. Which of the following statements does NOT describe a factor that contributed to suburbanization in the United States?
(A) A shorter workweek made time for a commute possible.
(B) Changes in the housing mortgage regulations made home ownership easier.
(C) Fixed-route public transit routes increased in importance.
(D) Improved automobiles made transportation easier and less limited.
(E) Increased demands for housing occurred after World War II ended.
45. Which factor in the last quarter century greatly destabilized Eastern Europe and led to ethnic conflict?
(A) The introduction of new languages
(B) The end of the Cold War
(C) The invasion by the Soviets
(D) The acceptance of many Eastern European countries into the EU
(E) The adoption of the euro
46. The sacred book of the Hindu is called the
(A) Talmud.
(B) Bible.
(C) Torah.
(D) Veda.
(E) Koran.
47. Urban agriculture can benefit urban society in all of the following ways EXCEPT
(A) create sustainable food systems in urban areas.
(B) provide jobs for women and children.
(C) turn urban waste into a resource when utilized in safe manner.
(D) strengthen food security for urban families.
(E) replace agribusiness as the main focus of global food production.
48. Which theory below was used as justification for US involvement in Vietnam in the 1960s and 1970s?
(A) Devolution
(B) Colonialism
(C) Heartland theory
(D) Rimland theory
(E) Containment theory
49. The Basques, Bretons, Kashmiris, and Tamils are all examples of
(A) regionalist groups.
(B) separatist groups.
(C) terrorist groups.
(D) interventionist groups.
(E) religious groups.
50. The process whereby an immigrant learns the values, language, and customs of their new country is called
(A) assimilation.
(B) acculturation.
(C) adaptation.
(D) amalgamation.
(E) dispersion.
51. Which of the following jobs is in the non-basic employment sector?
(A) Software engineer
(B) F-10 pickup truck assembly-line worker
(C) Oil refinery worker
(D) Warehouse guard
(E) Parking lot attendant
52. Variations in vocabulary, pronunciation, and rhythm in a spoken language are called
(A) syntax.
(B) isoglosses.
(C) lingua francas.
(D) creoles.
(E) dialects.
53. The map shown above is the following type of map:
(A) statistical map.
(B) topographic map.
(C) general-purpose map.
(D) dot-distribution map.
(E) graduated circle map.
54. The intensive agricultural practice of planting and harvesting the same crop more than once a year is called
(A) swidden.
(B) double cropping.
(C) pastorialism.
(D) intertillage.
(E) shifting agriculture.
55. A large node of office and commercial land use outside the central city with more jobs than residents is a(n)
(A) suburb.
(B) primate city.
(C) town.
(D) edge city.
(E) gated community.
56. Which one of the following statements does NOT correctly describe the Green Revolution?
(A) It changed centuries-old methods of farming.
(B) It was an attempt to feed a growing world population.
(C) It centered on increased rice, wheat, and maize yields.
(D) It greatly improved crop yields in Subsaharan Africa.
(E) It required use of new seeds and lots of fertilizer, pesticides, and water.
57. The theory that whoever controlled the landmass of Europe would rule the world is called the
(A) devolution theory.
(B) domino theory.
(C) heartland theory.
(D) rimland theory.
(E) containment theory.
58. Which of the following is a distinct characteristic of an East European city?
(A) A central park
(B) Prominent religious buildings
(C) A large central square surrounded by government and administrative buildings
(D) Luxury apartment buildings
(E) A well-developed retail sector
59. Which religion below is a universalizing religion?
(A) Taoism
(B) Islam
(C) Shintoism
(D) Confucianism
(E) Judaism
60. What is the most abundant fossil fuel?
(A) Phosphate
(B) Oil
(C) Petroleum
(D) Natural gas
(E) Coal
61. The majority of Kurds are found in which country?
(A) Iran
(B) Iraq
(C) Turkey
(D) Egypt
(E) Pakistan
62. According to Alfred Weber’s least-cost theory, which one of the following costs of production is the most important factor in locating an industry?
(A) Labor
(B) Transport
(C) Raw materials
(D) Agglomeration costs
(E) Rent
63. Which one of the following demographic factors characterizes stages 4 and 5 in the demographic transition model?
(A) Zero population growth
(B) High mortality rates
(C) High birth rates
(D) High sex ratios
(E) Overpopulation
64. The purpose for the creation of NATO was to
(A) defend North America and Western Europe against the threat of communism.
(B) form an economic alliance for trade between Europe and North America.
(C) defend Europe against a second Nazi invasion.
(D) defend northern Europe against Chinese missiles.
(E) form a binding peace treaty for all Europe.
65. The way of life based on breeding and herding of animals that are used as a source of food, shelter, and clothing is called
(A) swidden.
(B) subsistence farming.
(C) pastorialism.
(D) hunting and gathering.
(E) domestication.
66. State-sponsored terrorism has occurred recently in which of the following countries?
(A) Rwanda
(B) United States
(C) Canada
(D) Spain
(E) Bahrain
67. Which type of city model contains a distinct residential spine proceeding outward from center city along the main boulevard?
(A) European
(B) Muslim
(C) Sub-Saharan African
(D) Asian
(E) Latin American
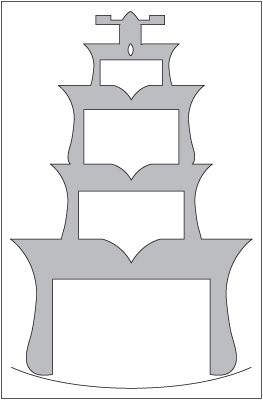
68. With what religion is the architecture shown above associated?
(A) Roman Catholicism
(B) Russian Orthodox
(C) Hinduism
(D) Judaism
(E) Buddhism
69. Which of the following is a major concern in countries with a large and rapidly aging population?
(A) Immunization
(B) Adequate schools
(C) Daycare facilities
(D) Birth control
(E) Health care
70. Which of the following capital cities is located OUTSIDE the central core area of the country?
(A) Abuja, Nigeria
(B) Paris, France
(C) London, United Kingdom
(D) Cairo, Egypt
(E) Moscow, Russia
71. The language with the largest number of “speakers” is
(A) English.
(B) Russian.
(C) Spanish.
(D) Mandarin Chinese.
(E) Hindi/Urdu.
72. An earlier boundary formed before meticulous geographic knowledge and mapping was available is known as
(A) an antecedent boundary.
(B) a geometric boundary.
(C) a relict boundary.
(D) a subsequent boundary.
(E) a natural boundary.
73. Which of the following religions developed first?
(A) Buddhism
(B) Christianity
(C) Islam
(D) Judaism
(E) Hinduism
74. If you wanted to find the global distribution of coal, you would use a
(A) reference map.
(B) topographic map.
(C) thematic map.
(D) location map.
(E) general-purpose map.
75. The practice of drawing the boundaries of voting districts to give an unfair advantage to one political party is called
(A) separatism.
(B) gerrymandering.
(C) containment.
(D) domino theory.
(E) redistricting.
END OF SECTION I
Time: 75 minutes
Section II Comprises 50 Percent of Total AP Score
Directions: Answer each of the three questions below in the allotted time of 75 minutes. You should spend approximately 25 minutes on each question. Answers must be in essay form, not a list of facts or thoughts, although a formal essay (with an introduction and conclusion) is not required. Use substantive examples where appropriate. Make sure you answer all parts of each question and label each part of your answer to correspond with the part of the question you are answering. Feel free to make a short outline first to capture your thoughts but only the essay will be scored.
1. Folk culture and pop culture are both important defining elements of American society today.
(A) Define folk culture and pop culture in the United States today.
(B) Give one example of folk culture and one example of pop culture in the United States today.
(C) Explain how folk culture and pop culture can both unify and divide a society.
2. (A) Define a central place.
(B) Identify and discuss one function of a central place.
(C) Explain why towns of the same size that perform the same function in a central place system will be the same distance from each other.
3. (A) Define the term “world city.”
(B) Identify two examples of a world city and explain how each of these cities fits your definition.
(C) Discuss the role of a world city in the international scene and explain why a world city is not just a very large city.
END OF SECTION II
1. C
2. E
3. C
4. C
5. A
6. D
7. E
8. D
9. C
10. D
11. B
12. E
13. E
14. B
15. A
16. B
17. C
18. D
19. D
20. B
21. B
22. A
23. D
24. E
25. A
26. B
27. C
28. B
29. B
30. C
31. A
32. B
33. A
34. A
35. C
36. E
37. E
38. E
39. B
40. B
41. C
42. C
43. C
44. C
45. B
46. D
47. E
48. E
49. B
50. B
51. E
52. B
53. B
54. D
55. D
56. C
57. C
58. C
59. B
60. E
61. C
62. B
63. A
64. A
65. C
66. A
67. E
68. E
69. E
70. A
71. D
72. A
73. E
74. C
75. B
1. C—Latitude is measured in degrees north and south of the equator (0 degrees). The global grid system (A) is the global reference system using both latitude and longitude. Longitude (D) refers to distance east and west of the Prime Meridian (B), which is the 0 degrees line that passes through the North and South Poles and Greenwich, England.
2. E—Horse-drawn streetcars in the 1860s and electric ones starting in 1890 encouraged city residents to live along the trolley lines in a star-shaped pattern that radiated out from the CBD like spokes on a wheel.
3. C—Agglomeration refers to the grouping of activities and people to gain economic advantage by sharing services and resources. The substitution principle (A) is the replacement of one economic input with another. Deglomeration (B) refers to the locating of an industry away from an agglomeration to avoid higher costs of traffic congestion or competition. Infrastructure (D) refers to all the facilities and services required to support economic development.
4. C—Circular migration is a type of temporary migration associated with agricultural work where the migrant follows the harvest of various crops, moving from one place to another each time. This is common in agriculture in the United States (Mexican farm workers) and in Western Europe (Eastern European farm workers). Chain migration (A) is the practice of relatives and friends moving to a location based on the good reports of already established family members. Cluster migration (B) is seen in regions dominated by one particular ethnic group. International migration (D) is the permanent movement and relocation of people from one country to another country. International travel (E) is the temporary travel between countries for work or vacation.
5. A—The smaller the map scale, the larger the area being represented on the map. A map of the entire world represents the largest area from these choices.
6. D—In Latin America, most young people migrating to the city leave their families behind; the families do not already live in the city. The other answer choices all list factors why young people in Latin America are drawn to the city. The availability of jobs (A) and the potential for decent housing (B), educational opportunities (C), and urban lifestyle, including its nightlife (E) are all reasons for the in-migration of many persons to the large cities of this region.
7. E—The Green Revolution started in the late 1960s as the core countries exported new hybrid seeds and fertilizers to periphery countries to help stimulate greater food harvests. The other answer choices refer to earlier agricultural revolutions that occurred at different times in different regions of the world.
8. D—Uganda (D) as well as the majority of Sub-Saharan African states, have very young populations with roughly 50 percent of the population 15 years of age or younger. European states such as France (A), Austria (C), and Italy (E), along with Russia, (B) have population pyramids that reflect lower birth and total fertility rates.
9. C—During the British colonial period in nineteenth-century India, language was a very important part of the administrative and judicial systems of the country. English was required in schools, trade, commerce, and government and it became the language of power and a higher station in life. Its use gradually diffused downward into Indian society. Stimulus diffusion (A) occurs when a cultural trait from one culture causes a change in the culture of another society. Contagious diffusion (B) is the spread of a cultural trait from one person to another like catching a cold. Relocation diffusion (D) is the process of taking a cultural trait or innovation from one geographic location to another by immigrants or traders. There is no diffusion type called migratory (E).
10. D—The hinterland is the outlying region served by an urban center. Redline (A) refers to the illegal practice of refusing mortgage loans to persons buying houses in a minority-dominated neighborhood on the excuse they would likely default on their loans. Threshold (B) is the minimum number of people needed for a particular economic function to be performed in a central place according to Christaller’s central place model. The more unique and specialized the economic function, the higher the threshold for it to exist and the more common and mundane its function, the lower the threshold or number of customers it would need in order to operate. Range (C) is the maximum distance a customer is willing to travel to purchase a good or service in Christaller’s central place model. The sphere of influence (E) of an urban center is the area it serves for a particular economic function. The larger an urban center is the greater its sphere of influence is likely to be because it has a wider range of services and functions to draw people to go there.
11. B—Continental margins have always drawn the largest settlement of people. Approximately 60 percent of the world’s population lives within 60 miles of the ocean. Continental interiors (A) are not generally much more sparsely settled than seacoasts. Aridity (deserts) (C) and high elevation (mountains) (E) usually create harsher living conditions that limit human habitation. Population is more concentrated in lowlands and river valleys (D), but not particularly in tropical river valleys and lowlands.
12. E—Illegal aliens crossing the United States–Mexico border has been an ongoing source of conflict and a continuing boundary problem between the two countries. The other answer choices list types of boundary disputes that do not apply to the United States–Mexico border. Ownership of fertile ground (A) and land use (B) are resources issues. Irredentism (C) involves a territorial conflict and document interpretation (D) is a boundary disagreement based differing interpretations of how the boundary was defined in writing.
13. E—Bolivia does not have a well-known example of a relict boundary. Since Vietnam’s reunification in 1976 (A), the old boundary between North and South Vietnam has been a relict boundary. The United Kingdom (B) contains the relict boundary between England and Wales as evidenced by the abandoned castles on the old frontier. The old border between East and West Germany, now within a reunited Germany (C), is an example of a relict boundary. The Great Wall of China, now within China, served at one time as a boundary between China (D) and the warring nomadic tribes from the north.
14. B—Christianity is the monotheistic religion based on the teachings of Jesus Christ and the Bible is its main document of faith. Islam (A) and Judaism (E) regard Jesus Christ as a prophet. Hinduism (C) and Buddhism (D) are polytheistic religions that worship a pantheon of gods.
15. A—Amalgamation theory refers to the traditional theory of blending diverse immigrant groups into the host country’s mainstream culture. In today’s climate of ethnic conflicts, this theory is no longer a realistic expectation. Acculturation (B) refers to the embracing of the host country’s culture and values by the immigrant. Ethnic islands (C) are regions of ethnic concentration scattered among the dominant cultural realm. Ethnic clustering (D) is the process of immigrants grouping in communities in the host country. Cluster migration (E) refers to the process of immigrants of a certain ethnicity grouping in a particular region.
16. B—The demands for more food by a swelling urban workforce combined with the ability to produce larger harvests due to the use of horse-drawn farm equipment birthed the Second Agricultural Revolution. The other answer choices refer to more recent changes in agricultural methods and technologies.
17. C—South America is not one of the top four regions of population density in the world while South Asia (A), Europe (B), Northeast United States (D), and East Asia (E) are the most densely populated regions of the world.
18. D—The Romance language family is part of the large Indo-European language tree and traces its beginnings to the Latin protolanguage. European languages (A) are not a valid linguistic classification. Slavic languages (B) are part of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European language tree. The Germanic languages (C) are also part of the IndoEuropean family tree but trace back to a northern European Germanic proto-language. The Celtic languages (E) are Welsh, Irish, Gaelic, and Breton and form a separate branch of the Indo-European language tree.
19. D—Agriculture (raising crops and livestock) is the most widespread economic activity in the world today. One-third of all land area is now used for some form of agricultural activity. The other primary economic activities—mining (A), hunting and gathering (B), fishing (C), and forestry (E) are important, too, but are based on the uneven distribution of natural resources. This means they are not practiced as universally as agriculture throughout the world.
20. B—Separatists groups are not a unifying, or centripetal force, in a country. They usually lead to division and strife. The other answer choices are generally all unifying, centripetal forces that serve to bind a country together.
21. B—English is the global lingua franca or language of global trade, commerce, and communication. Although some of the other languages listed serve as regional lingua francas, none of them has the global dominance that English has.
22. A—Sanskrit records have not contributed to the spread of world languages. All the other answer choices indicate ways languages have spread. For example, migration (A) carried Spanish to the Americas and trade (C) carried Hindi/Urdu to the countries of Southeast and East Asia. The Roman conquests (D) spread Latin into Europe and replaced the widespread use of the Celtic languages there. Driven by a growing Bantu population, the Bantu language spread southward, replacing traditional languages.
23. D—The sector model views urban housing like spokes radiating from a central hub on a wheel. It states that new housing for the wealthy extends outward on its original axes from the city as it grows, middle-income housing extends in the same way to higher-income sector, and lower-income housing fills in the gaps. The concentric zone model (A) depicts the city as a set of rings radiating out from the CBD and was developed to explain the social patterns of American cities in the 1920s. The central place model (B) was developed by German geographer, Walter Christaller in 1933 to explain the patterns and distributions of settlements as they are interconnected with their surrounding hinterlands. The urban realms model (C) is an economic model that states an urban resident’s life is mainly lived in one realm within the urban environment. The multiple-nuclei model (E) states that large cities spread out from several nodes of growth rather than just one.
24. E—Urban agriculture often diverts valuable urban water supplies and animal waste, pesticides, and fertilizer can leak into and contaminate a city’s drinking water supplies. All the other answer choices are positive factors when urban agriculture is practiced in the world’s cities.
25. A—Islam is the fastest growing religion in the United States today. Over six million Muslims live in the United States. The increase is the result of Americans converting to Islam, as well as from immigration.
26. B—The replacement level of 2.1 is the fertility level that allows a population to replace itself. The crude birth rate (A) is the number of live births per 1000 every year. The mortality rate (C) and the crude death rate (E) both refer to the number of deaths per 1000 of a population. The total fertility rate (D) refers to the average number of children a woman of childbearing age is expected to produce.
27. C—Canada’s third major wave of migration came from Europe, not Latin America. All the other answer choices correctly describe migration streams to the United States and Canada.
28. B—Subsistence economies usually lack adequate transportation infrastructure. Currency (A), government activity (C), banking services (D), and market surplus (E) are all nice to have, but transportation is the key to economic advancement.
29. B—Ankara and Islamabad are both forward-thrust capital cities built to encourage more even development and move the seat of government away from the coastal margin and into a more inland and central position within the country. (A) They are not desert cities nor are they rival cities (D). Both cities are newer cities and not old colonial capitals and both are located in the mid-latitudes (between 23 and 66 degrees north or south of the equator)(E).
30. C—The two major branches of Islam are Sunni and Shiite. Shintoism is the historic Japanese worship of gods in shrines and combines elements of animism or shamanism with later-arriving elements of Buddhism. Shamanism is part of many traditional native religions found in the Americas, Asia, and Africa. A shaman is a spiritual healer or person who is thought to be able to make the connection between the spiritual world and the “real” world to get guidance, healing, etc. for others in the group.
31. A—Primary economic activities are dependent on natural resources that are randomly distributed in the natural environment. All the other economic activities can occur in almost any location and are not as dependent on the physical environment.
32. B—Thematic maps show a particular category of information such as persons per square mile or annual corn production in the United States. General-purpose maps (A), reference maps (C), and location maps (E) are maps which show both natural and man-made features without any analysis. A mental map (D) is the map-like image a person carries in his mind of an area.
33. A—Religious differences often divide a country, creating a centrifugal force. All the other choices are centripetal forces that serve to promote unity and strength in a country.
34. A—Canada has had a continuing centrifugal force at work—language. Quebec, a large French-speaking province in chiefly English-speaking Canada, periodically seeks independence from Canada through public referendums. All the other answer choices are countries unified by one, clearly dominant national language.
35. C—All three of these states—Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio—have far more than half their land area in farms. The other choices all show combined land use categories that total less than half in farms.
36. E—The southern prairie provinces of Canada (Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba) have large ethnic distributions of Native Americans (called First Nation people in Canada). African Americans (A) are found in large numbers in the Southeast, Native Americans (B) are located in the Southwest and in Oklahoma, and Franco Americans and French Canadians (C) are well distributed in Quebec Province and northern Maine. (E) Hispanic Americans are found in concentrations along the United States–Mexico border from southern California through Texas.
37. E—The untouchables of India are outside the Hindu caste system and considered to be of such low status in Hindu society that the nastiest, dirtiest jobs are reserved for them. The other answer choices list occupations, each of which has a separate caste in the Hindu caste system.
38. E—Field drainage systems are most closely associated with the Second Agricultural Revolution when it became common to drain fields and add fertilizers. All the other answer choices describe activities associated with the Third Agricultural Revolution.
39. B—Planned communities (American suburbs are a general example) are neighborhoods that are typically built at the same time by a developer according to a master plan. The modern planned community has evolved to include shopping, parks, similar architecture throughout, and includes other well-chosen amenities. Planned cities take this concept to a larger scale and include Canberra, Australia; Abuja, Nigeria; Ottawa, Canada; and New Delhi, India to name a few. Ghettos (A) are poverty zones in urban areas. CBDs (central business districts) (C) are the original cores of economic activity in cities. Transition zones (D) are areas on the outskirts of the CBD that are always in a state of change because of invasion and succession patterns that keep it destabilized for development and settlement. In the United States, barrios (E) are Spanish-speaking enclaves in a city.
40. B—Birth control methods (B) have very little, if any, impact on mortality rates in developing countries. New and better medicines (A), vaccines (E), pesticides (C), and famine relief in the form of adequate food supplies (D) have all led historically to reduced mortality rates in developing countries.
41. C—The Rhine River is an example of a natural, or physical, boundary. Mountains, deserts, lakes, and rivers are all types of natural boundaries that are often used as political boundaries. A geometric boundary (A) is an artificial boundary, often a parallel of latitude or a meridian of longitude. An artificial boundary (B) is the same as a geometric boundary and often used when precise geographic information is lacking. A relict boundary (D) is an old boundary that is no longer used. Examples of relict boundaries are the Berlin Wall, the Great Wall of China, and the abandoned castles on the old border between England and Wales. A subsequent border (E) is one put into place after the people and settlement have already modified the cultural landscape. The imposed political borders of the Berlin Conference on the cultural landscape of Africa are an example of a subsequent border.
42. C—There are fairly equal numbers of males and females in all cohorts until 80 years of age and older, then women outlive men in the United States. In the United States, the birth rate actually exceeds the death rate (A). In regards to choice B, the working-age-population middle cohort consisting of ages 15 to 64 is large enough to comfortably provide the goods and services required by the dependent sectors of the population (the very young and the older folks). The problem lies in the future when the huge middle cohort of Baby Boomers advances into their “golden years” when it will be required that their needs and services to be met by a much smaller middle cohort. The country is not experiencing a rapid growth rate (D) or a high mortality (death) rate (E).
43. C—The symbol of a dove is used in several cultures and is an example of nonmaterial culture. The Dove soap, Dove candy, and dove stew are all tangible articles that are examples of material culture. The bird itself is not a creation of human culture but a part of nature.
44. C—Streetcar and trolley lines decreased in importance as the automobile was perfected and came into wider use, freeing residents from the necessity of only shopping, working, and living along public transit routes. The other choices all describe changes that contributed to suburbanization in the United States.
45. B—The Cold War ended in 1991 when the Soviet Union collapsed. Communism was a strong centripetal force holding people of many ethnicities together; when it collapsed, ethnic conflicts naturally arose that destabilized or split many countries of Eastern Europe. No new languages were introduced (A) and there was no Soviet invasion (C). The acceptance of many formerly communist countries into the EU (D) was a stabilizing force rather than a destabilizing force. The euro (E) has not yet become the currency of any formerly communist countries other than tiny Slovenia.
46. D—The Veda is the sacred book of Hinduism. The Talmud (A) is the ultimate book of Jewish law. The Bible (B) is the sacred book of Christianity. The Torah (C) consists of the books of Jewish scriptures and holy writings. The Koran (E) is the teachings of the Muslim prophet Mohammad.
47. E—Urban agriculture is a secondary system of food production that enhances, but cannot take the place of, modern commercial agriculture in the world. The other answer choices all describe ways that urban agriculture helps urban residents.
48. E—The containment theory, from which was derived the US foreign policy of blocking the expansion of the Soviet Union’s area of control, was used as a basis for US involvement in Vietnam in the 1960s and 1970s. Devolution (A) refers to the transfer of powers from a central authority to a regional one. Colonialism (B) is a system in which a country declares control over a territory or people outside its own boundaries, usually for economic purposes. The English geographer Halford Mackinder theorized that the greatest world power would be situated in Eurasia, in the “heartland” of the landmass with Eastern Europe at its core (C). Nicholas Spykman theorized that the densest populations, richest resources, and best strategic position overall lay in the peripheries of continents so his “rimland” theory (D) claimed the coastal areas of Eurasia would have more power and wealth.
49. B—These groups are all separatists groups fighting for greater autonomy or total separation from the country in which they live. The Basques of Spain, the Bretons of France, the Kashmiris in India, and the Tamils in Sri Lanka all identify more closely with their regional ethnic group than with their political state, a fact which often causes great conflict and tension.
50. B—Acculturation describes the process through which new immigrants adopt the cultural traits of their new host country. Assimilation (A) occurs when the newcomers blend into the host culture, completely losing their own original culture. Adaptation (C) is the process of adapting one’s culture to a new environment. Amalgamation (D) refers to the theory that societies characterized by diversity form a fusion of the cultural traits of their separate ethnic groups. Dispersion (E) is the spread of something over a spatial area.
51. E—Non-basic jobs provide services to the city dwellers and do not usually generate “new” income for the city. The other answer choices are all basic jobs that produce goods for “export” out of the city and generate an inflow of revenue.
52. E—Dialects are different spoken regional versions of the same language. They usually vary in pronunciation, rhythm, and speed. Syntax (A) refers to how words are arranged in a sentence. An isogloss (B) is the geographic boundary of a linguistic feature such as the sound given to a vowel. A lingua franca (C) is the language of business and trade among groups of people who normally speak different languages. A creole (D) is a language that began as a pidgin language and graduated to a permanent language.
53. B—A topographical map gives a detailed representation of the shape and elevation of an area by using contour lines. A statistical map (A) is a map that shows the actual number of an item per unit or location. A general-purpose map (C) shows both natural and manmade features without analysis. A dot-distribution map (D) shows the distribution, dispersion, and spatial pattern of a feature. A graduated circle map (E) is a map that uses circles of increasing size to show the frequency of occurrence of something.
54. B—Double cropping is an intensive land use widely practiced in milder climates where it is possible to plant and harvest two crops in one year. Swidden (A) is land that has been cleared off and burned to prepare it for planting. Pastoralism (C) is a subsistence lifestyle revolving around breeding and herding animals for livelihood. Intertillage (D) is the practice of planting several different plants in the swidden to minimize the impact of crop failure and enhance the farmer’s diet. Shifting agriculture (E) is based on growing crops in different fields on a rotating basis.
55. D—An edge city is a large collection of office and retail activities on the outskirts of an urban center. A suburb (A) is a residential and retail area outside of the central city. A primate city (B) is a city that is far more than twice as large as any other city in the country. A town (C) is an urban center that is larger than a village but smaller than a city. A gated community (E) is a planned residential community that is surrounded by walls or fences with a security guard and limited access.
56. D—Poor soils and insufficient water supplies in Sub-Saharan Africa combined with lack of research in the main food grains of the region—millet and sorghum—made the Green Revolution a poor fit for this region. Crop yields were not measurably increased. All the other statements correctly describe the Green Revolution.
57. C—The English geographer Halford Mackinder theorized that the greatest world power would be situated in Eurasia, in the “heartland” of the landmass with Eastern Europe at its core. Devolution (A) refers to the transfer of powers from a central authority to a regional one. The domino theory (B) was the theory that if one country in a region became communist, communism would then easily spread to neighboring countries. Nicholas Spykman theorized that the densest populations, richest resources, and best strategic position overall lay in the peripheries of continents so his “rimland” theory (D) claimed the coastal areas of Eurasia would have more power and wealth. Containment theory (E) refers to the US foreign policy of surrounding the Soviet Union with military alliances to hold communism in check—a position based on the rimland theory.
58. C—Eastern European cities generally contain reminders of the Soviet communist era in East Europe in a large central square lined with government and administrative buildings. Due to the historical communist influence, the cities are not generally characterized by prominent religious structures (B), luxury apartment buildings (D), or commercial buildings (E).
59. B—Islam is a universalizing religion since its adherents believe their religion is applicable to all people. The other answer choices are ethnic religions that do not actively try to gain new members or converts.
60. E—Coal, the first important fossil fuel to be exploited is still the most abundant, although it is unevenly distributed. Phosphate (A) is not a fossil fuel formed from hydrocarbon compounds in sedimentary rocks. It is a mineral widely used to produce fertilizer. Oil or petroleum (C) and natural gas (D) are also unevenly distributed. Although their reserves are not as easily predicted, it is apparent that they are less abundant than coal.
61. C—Approximately 55 percent of the world’s Kurdish population lives in Turkey. Kurds constitute the largest ethnic minority in both Turkey and Iraq (B), and there are smaller Kurdish minorities in Iran (A), Egypt (D), and Pakistan (E).
62. B—Weber’s theory stated that the best location for a manufacturing business would be where the costs of transporting raw materials to the factory and the finished product to the market are the lowest. Labor (A), the cost of raw materials (C), agglomeration costs (D), and rent (E) are all important costs to any industry making location decisions, but transportation is the most important cost consideration.
63. A—In stages 4 and 5 of the demographic model, there is zero growth in a population. New births are equal to deaths, and the population experiences no growth. There is a low birth rate (C) and a low mortality rate (B). In regard to choice D, there is no way to predict the sex ratio without knowing more demographic characteristics and economic characteristics of the population. Overpopulation (E) is highly unlikely in this scenario as there is no population growth at all.
64. A—NATO was created to defend North America and Western Europe against the threat of communism, particularly an attack by the Soviet Union. The other answer choices are not reasons for the formation of NATO.
65. C—Pastoralism is a subsistence lifestyle based on the breeding and herding of animals used as a source of food, shelter, and clothing. It is practiced in marginal lands such as deserts, steppes, and savannas where the climate is generally unfavorable for farming. Swidden (A) is land cleared for planting by slash-and-burn methods. In subsistence farming (B), produce is consumed by the farmer and his family rather than sold for consumption by others. Hunting and gathering (D) is a way of life that involves a diet of meat obtained by hunting and killing wild animals and of roots, nuts, berries, and fruits that are gathered. (E) Domestication is the transforming of a plant or animal species into a tame condition that is dependent on humans.
66. A—Rwanda’s government carried out genocidal state-sponsored terrorist acts against its own citizens, the Tutsi minority in 1994. None of the other countries listed have engaged in state-sponsored terrorism.
67. E—Latin American cities generally have a spine that begins in the center city and proceeds outward along a wide boulevard. High- and middle-income residential housing in the form of apartments and town houses is situated along this spine.
68. E—This is the temple (pagoda) used in Buddhist worship. This temple holds an image or relic of Buddha, the Enlightened One and founder of Buddhism.
69. E—Health care and social security support systems are a major need in country’s with a large number of older adults (E). Immunizations (A), adequate schools (B), daycare facilities (C), and birth control (D) are things needed in countries with a younger population.
70. A—Abuja, Nigeria is located in the center of the country and away from the core economic area of the Niger River delta and the coast. All of the other capital cities are located in the national cores of their respective countries.
71. D—Mandarin Chinese is spoken by well over a billion people (as native and second-language speakers). English (A) is the second most-spoken language. Hindi/Urdu (E), or Hindustani, is the third most spoken. Spanish (D) is fourth on the list and Russian (C) is fifth.
72. A—An antecedent boundary is an earlier boundary put in place before the region was mapped and populated. A geometric boundary (B) is an artificial boundary, often a parallel of latitude or a meridian of longitude. An example of this is the 49th parallel separating the United States and Canada. A relict boundary (C) is an old boundary that is no longer used. A subsequent border (D) is one put into place after the people and settlement have already modified the cultural landscape. A natural boundary (E) is one formed by a feature of the physical landscape such as a mountain range or a river.
73. E—Hinduism emerged about 4000 B.C. in the lowlands of the Indian subcontinent as the first of the Indo-Gangetic religions. Buddhism (A) evolved from Hinduism in 500 B.C. Judaism (D), Christianity (B), and Islam (C) emerged in the Middle East and are all related. Judaism is the oldest of these and was the first monotheistic religion. Christianity followed and Islam is the most recent.
74. C—A thematic map shows a specific spatial allocation of something such as coal, Democrats, or people who grow sweet potatoes for a living. Reference maps (A), location maps (D), and general-purpose maps (E) are maps that simply display an assortment of both natural and man-made features without providing any analysis or explanation. A topographical map (B) is a map that gives a detailed representation of the shape and elevation of an area by using contour lines.
75. B—Gerrymandering is a practice of drawing voting district boundaries to give an unfair advantage to one political party over another. Separatism (A) refers to the attempt of a minority group to govern themselves or obtain greater autonomy. Containment theory (C) refers to the US foreign policy of surrounding the Soviet Union with military alliances to hold communism in check. The domino theory (D) is the theory that if one country in a region becomes communist, communism would then easily spread to neighboring countries too. Redistricting (E) is the process in the United States of redrawing the boundaries of voting districts based on the latest census results.
Question 1 (6 points total)
1A. (2 points)
Folk culture is the sum total of institutions, customs, traditions, dress, music, etc. of a fairly isolated, homogenous ethnic group that is self-sufficient and not reliant on mainstream society. Pop culture is the constantly changing material and nonmaterial cultural elements that influence mainstream society via the mass media.
Folk culture example: any cultural element relating to the Amish, Mennonite, Hutterite, aborigine, Appalachian, or other rural, isolated group. Correct answers would include Amish clothing, Appalachian medicinal healing herbs, aboriginal artwork, etc.
Pop culture example: anything pertaining to the culture of the mainstream society as promoted by mass media. Correct answers would include types of clothing, fast food, housing, sports, social customs, etc.
1C. (2 points)
Folk culture can unify a society by proving that distinct cultural groups can hold onto their unique cultural identities while living peacefully within a larger society of people who hold a different set of beliefs. This has happened in the United States with the Amish and Mennonite folk cultures. They peacefully coexist within the larger mainstream culture without giving up their cultural practices.
Pop culture unifies a society by providing cultural artifacts that are widely accepted and used by the majority of the population. For example, McDonald’s, Michael Jackson, and Levi’s jeans are elements of pop culture that the majority recognize and hold in common.
Folk and pop cultures can also divide a society. The aborigines of Australia had to fight for their culture when mainstream settlers tried to wrest their land away from them and force them to conform with their cultural ways. Some societies cannot accept cultural differences and constantly try to force the minority folk culture to assimilate into their culture. Pop culture has a subtler divisive influence. Television shows, movies, and books that depict the Amish as old-fashioned and strange or the Appalachian mountain folk as inbred hillbillies serve to propagate negative stereotypes that are divisive.
Question 2 (6 points total)
2A. (2 points)
A central place is an urban center or settlement that serves as a distribution center for the supply of goods and services to the surrounding area. Central places can be large cities, small towns, or tiny villages—wherever residents go to obtain goods and services. A central place is much more than just a distribution point; it involves a pattern of similar-sized distribution areas that provide basically the same functions to their surrounding areas. Central places are not grouped together with each other but are distributed in a regular pattern with central places spaced equal distances from each other.
2B. (2 points—1 for identifying one function and 1 point for the discussion of it.)
The functions of a central place are to provide goods to local market area (pizza, groceries, gasoline, birdseed, specialty goods like Harley-Davidson motorcycles, designer clothing, jewelry, exotic plants, etc.) or to provide services to a local market area (dental, pharmacy, doctor, medical, school or education, firefighting, ambulance, police, water and sanitation, etc.).
The discussion can include examples such as:
• Pizza shops are found in every small neighborhood strip mall or as free-standing stores.
• Grocery stores are found in every small neighborhood and service small noncompeting market areas.
• Specialty stores, such as Harley-Davidson motorcycles, floral shops specializing in exotic plants, high-priced designer clothing stores like Burberry’s and Tommy Hilfiger, etc. are spaced farther apart, usually in retail malls.
• Big-box retail—Walmart, Kmart, Target, etc.—are found on the outer perimeter of the local market areas and often service more than one central place.
Customers generally buy their good or service from the nearest supplier, which would usually be the store or supplier of the service in their central place. If a person wanted pizza for supper, they would drive to the nearest pizza place to purchase the pizza, usually a neighborhood pizza shop. If they need to get their winter coats cleaned, they would drop them off at a neighborhood drycleaner. In central place theory, customers go to the closest central place to obtain everyday items such as milk and bread. For luxury items like Mercedes-Benz automobiles or fur coats, they would be willing to travel further. These market areas of demand each contain a central place in the center and form a system of hexagonal patterns that gives us a hierarchy of central places with cities and towns of similar size grouped into several classes.
Question 3 (6 points total)
3A. (2 points)
A world city is a large urban center that is a command-and-control center in the global economy. It is also called a world center or alpha city and serves as a node in the world’s economic system. It is a hub for banking, finance, and trade.
3B. (2 points—1 point for identifying two cities and 1 point for the explanation)
New York City, London, and Tokyo are the top three world cities. Also acceptable are Hong Kong, Paris, Singapore, Sydney, Milan, Shanghai, etc. from the secondary tier of world cities.
An explanation for New York City could include the following information: New York City is the top international air passenger gateway to the United States. The area is served by three major airports, John F. Kennedy International, Newark Liberty International and LaGuardia, with plans for a fourth airport. It is the headquarters of the United Nations. New York is the only global city that has a subway system running 24/7.
An explanation for London could include the following information: London has five international airports that offer numerous direct flights to every conceivable international destination. The London Internet Exchange (LINX) is the world’s largest Internet hub and it is the transit point for much of Europe’s Internet traffic. The London Stock Exchange is the world’s largest international exchange with a $1470 billion yearly turnover of foreign equities—more than New York and Tokyo combined. It was once the head of a vast empire and has kept the vitality and power of that connection with the world.
An explanation for Tokyo could include the following information: Tokyo has the largest metropolitan economy in the world. According to a study conducted by PricewaterhouseCoopers, the Tokyo urban area (35.2 million people) had a total GDP of US $1.479 trillion in 2008 (at purchasing power parity). Tokyo is a major international finance center and houses the headquarters of several of the world’s largest investment banks and insurance companies.
3C. (2 points)
A world city is much more than just a large international city. Some cities count as world-class not just because of their size but because of their importance in business, finance and government, or all three. World-class business cities are those where strategic and tactical decisions are made on everything from new plant investment to developing new markets and products. They are the cities others watch and react to. World-class business cities are not guaranteed exclusivity in producing the next wave of influential products, technologies, or companies, but they are a likely incubator for them. And those products, technologies and companies are where new jobs come from.