Glossary*
| amir | ‘commander’; an army leader and/or governor of a province |
| amir al-mu’minin | ‘Commander of th e Believers’; a title of the caliph |
| ashraf | leading members of the leading families among the Arab tribesmen |
| barid | the system of communications between the provinces and the caliphal court |
| bay‘a | the pledge of allegiance given to a caliph, heir apparent, or contender for power |
| dar al-islam | the regions under Muslim government in contrast to the dar al-harb (‘house of war’) |
| da‘wa | ‘call’, ‘propaganda’; the movement which prepared the way for the ‘Abbasid takeover of the caliphate |
| dinar | the gold coin |
| dirham | the silver coin |
| diwan | the register of individuals entitled to pay or pension from the government; a government department |
| fils | the copper coin |
| fiqh | the theory of Islamic law (not the law itself, the shari‘a) |
| fitna | conflict within the Muslim community, especially that between ‘Ali and Mu‘awiya |
| hajj | the pilgrimage to Mecca in the month of Dhu’l-Hijja |
| imam | a) the supreme head of the Muslims, particularly used in this sense by the Shi‘ites b) a prayer leader in a mosque c) an honorific title applied to a religious scholar |
| jizya | a tax, in the classical system a poll tax (tax on individual persons) |
| jund | ‘army’; a military district |
| khalifa | ‘deputy’; the caliph |
| kharaj | a tax, in the classical system a land tax |
| khutba | a speech; in the early period any speech of importance delivered by a figure of authority, especially the caliph or governor; eventually developing into the sermon delivered at the mid-day prayer service in the mosque on Fridays |
| majus | ‘Magian’; in the strict sense Zoroastrians but used more widely for followers of religions other than Judaism or Christianity to whom the Muslims wished to grant some toleration |
| mawla | ‘client’; a non-Arab who has accepted Islam; a follower of an important individual |
| salat | the ritual, five times daily, prayer service of Islam |
| shurta | a small force used by the governor or other authority to keep order |
| sunna | ‘accepted usage or practice’; eventually identified with the Sunna of the Prophet, the usage of Muhammad which Sunni Islam accepted as being, together with the Koran, the main source of authority for its law |
| ‘ulama’ | the religious scholars of Islam |
| wali’l-‘ahd | the heir apparent |
* The meanings given are those usually applicable in this book. In other contexts the words may have other meanings.
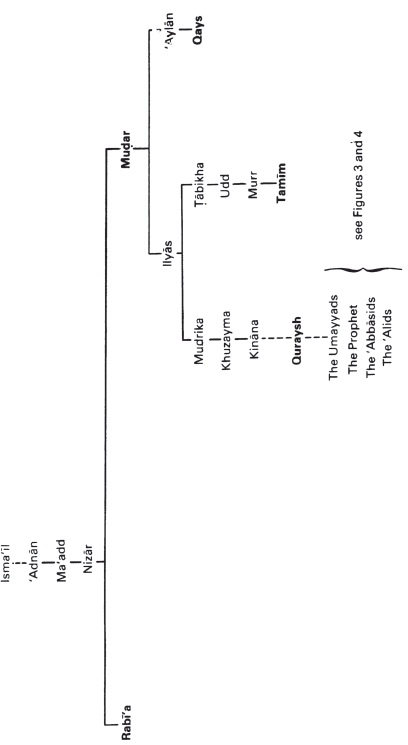
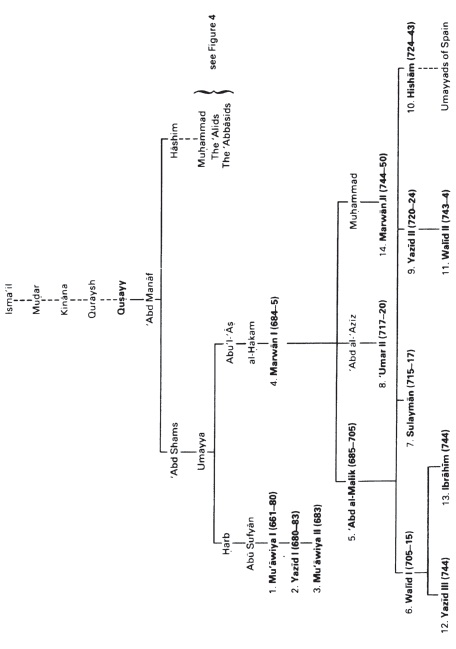
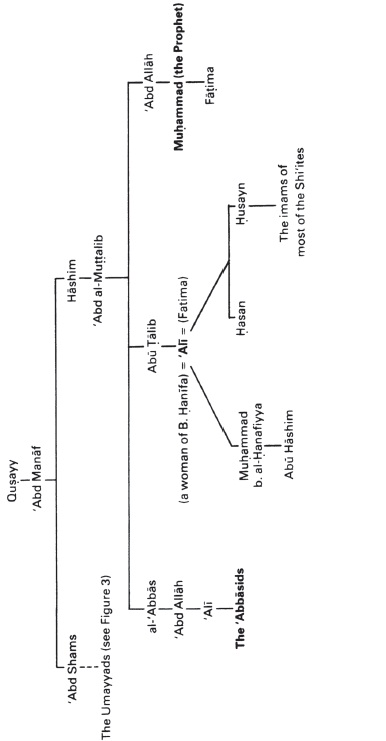
Figure 4: The Other Descendants of ‘Abd Manaf