4.4 Delivery Processing in Extended Warehouse Management
This section details the specific changes in EWM processing when leveraging the embedded offering. Because data now resides in the central instance documents, data that was traditionally required to transfer from SAP ERP to SAP SCM is no longer needed. Generally, these changes reduce the number of transactions and documents created in EWM and leverage the documents and data that reside in the SAP S/4HANA core database.
4.4.1 Inbound Processing
Inbound processing includes all process steps that are relevant for receiving material into the facility: unloading, goods receipt posting, deconsolidation, quality inspection, VAS (e.g., labeling for putaway preparation), and putaway execution to the final destination bin. In this section, we’ll highlight the key changes in data flow in embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA.
Skip Inbound Delivery Requests in Inbound Processes
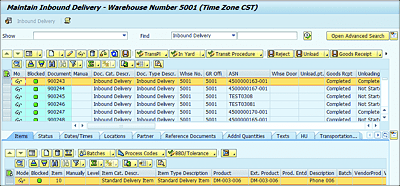
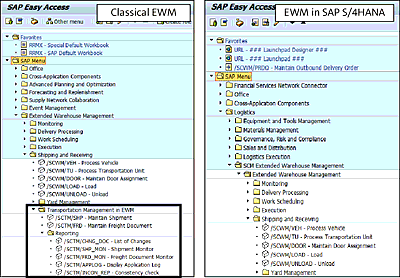
In the decentralized EWM environment, inbound delivery is distributed to EWM, which creates an inbound delivery notification (IDN) in EWM. This ensures the delivery document is complete and can be further used for processing in EWM. However, in EWM embedded in SAP S/4HANA, IDN isn’t required and is replaced with the standard inbound delivery for incompletion and consistency checks. As shown in Figure 4.14, the inbound delivery notification option is missing in the embedded version of EWM.
Figure 4.14 Inbound Delivery in EWM in SAP S/4HANA
Skip Expected Goods Receipt Document in Inbound Processes
In classic EWM (decentralized EWM), using the expected goods receipt (EGR) allows you to receive and save data transferred from open purchase orders, scheduling agreements, or production orders and to generate EGR documents from them. The EGR documents can then be used as a template to create inbound delivery documents. This is particularly useful if you don’t receive or create ASNs or inbound deliveries for purchase orders.
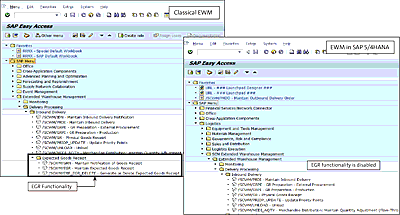
In EWM in SAP S/4HANA, this process is simplified and enables usage of up-to-date data. EWM will directly read purchase orders or production orders to create the inbound delivery. In embedded EWM the transaction codes for expected goods receipt functionality have been removed, as shown in Figure 4.15.
Figure 4.15 Transaction for Expected Goods Receipt Removed from EWM in SAP S/4HANA
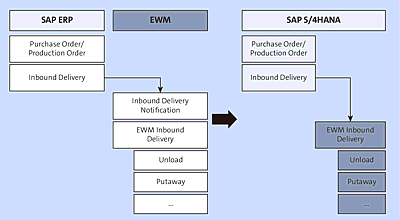
Figure 4.16 shows the nonembedded traditional inbound document flow and the updated embedded document flow. The key consideration is that the IDN isn’t needed in the embedded EWM offering because the preceding documents now exist in the same database.
Figure 4.16 Inbound Document Flow of Decentralized EWM versus Embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA
4.4.2 Outbound Processing
One of the primary goals of a warehouse is to deliver the right products to the right place at the right time; therefore, the outbound processing (picking, packing, staging, loading, and other related activities) plays an important role in EWM.
Skip Outbound Delivery Requests in Outbound Process
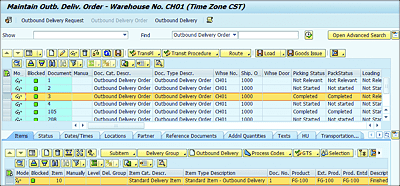
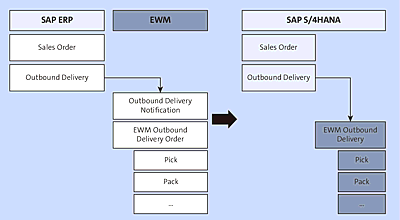
In the decentralized EWM environment, the outbound process starts with the creation of an outbound delivery in SAP ERP and is replicated to EWM. In EWM an outbound delivery request (ODR) is created, which is just a copy of the SAP ERP delivery. Subsequently, an outbound delivery order (ODO) is created (see Figure 4.17). Warehouse users use the ODO for subsequent warehouse operations, such as pick, pack and ship, and so on.
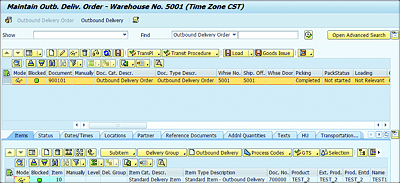
In embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA, the ODR isn’t required. After the outbound delivery is created the relevant ODO is created in EWM (see Figure 4.18).
Figure 4.17 Outbound Delivery Order in Decentralized EWM
Figure 4.18 Outbound Delivery in Embedded EWM with SAP S/4HANA
Figure 4.19 shows the non-embedded traditional outbound document flow and the updated embedded document flow. The key consideration is that the ODR isn’t needed in the embedded EWM offering because the preceding documents now exist in the same database.
Figure 4.19 Outbound Document Flow in Decentralized EWM versus Embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA
SAP Supply Chain Management Routes Unavailable in SAP S/4HANA EWM
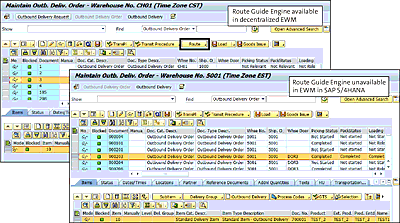
The functionality provided in EWM in SAP SCM by the Routing Guide Engine is disabled in embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA (see Figure 4.20). The functional recommendation is to leverage the route determination functionality offered in SAP S/4HANA.
Figure 4.20 Availability and Unavailability of the Routing Guide Engine in SAP S/4HANA Embedded EWM
In addition, there are some other functions based on IDN and ODR that aren’t available, for example, new split delivery in case of quantity reduction and delivery split in case of different route determination.
As shown in Figure 4.21, the transactions related to the Route Guide Engine aren’t included in EWM in SAP S/4HANA. The recommendation is to leverage the route determination functionality offered in SAP S/4HANA. Since the embedded EWM solution is leveraging data in SAP S/4HANA, it needs to rely on the routing functionality offered in the logistics execution functionality as opposed to the routing functionality that was offered in the decentralized EWM offering.
Figure 4.21 Removal of Routing Guide Engine Transactions in Embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA
Disable Freight Order Management in Extended Warehouse Management
The Freight Order Management (FOM) module is disabled in EWM in SAP S/4HANA (see Figure 4.22). The SAP Transportation Management (SAP TM) solution offers enhanced functionality for freight orders. SAP TM can be connected as a sidecar solution and is also planned to move into SAP S/4HANA in the near future.
Figure 4.22 Removal of Freight Order Management Transactions in Embedded EWM SAP S/4HANA
Skip Posting Change Request Document
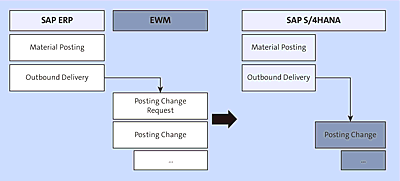
Keeping the reduced database footprint and simplified processing theme in mind, changes similar to the inbound and outbound process have also been made to the posting change request process.
As shown in Figure 4.23, EWM in SAP S/4HANA will directly read posting change data from the outbound delivery, which eliminates the need for a posting change request document created in EWM.
Figure 4.23 Posting Change Document Flow in Decentralized EWM versus Embedded EWM in SAP S/4HANA