6.7 Claims, Returns, and Refund Management
SAP S/4HANA provides a number of tools to manage rebates, settlements, and complaints. Let’s start by exploring the rebates process.
6.7.1 Rebates Process
The rebates process is used to offer targeted price discounts to customers, which are often created as part of an overall trade promotions plan or marketing effort. With the introduction of SAP S/4HANA, the traditional SAP ERP SD rebates processing is being replaced by Settlement Management, except in two specific instances:
- There are active, valid rebate agreements that were created in the previous SAP ERP system. These rebate agreements are only able to be processed until the end of the validity period. At the end of the validity period, one final settlement is made for the rebate agreement. Afterward, the Settlement Management module is used to create and manage new agreements.
- SAP S/4HANA has been integrated with SAP CRM, and the SAP Trade Promotion Management functionality is used to create rebate agreements. Rebate agreements will continue to be created using the SAP Trade Promotion Management functionality in SAP CRM and will continue to be processed in the same way.
6.7.2 Settlement Management
The Settlement Management module in SAP S/4HANA is used to manage all types of settlement processes, including purchase rebates, chargebacks, sales rebates, commissions, and royalties. From an order management perspective, the Settlement Management module is used to create and maintain condition contracts, integrate settlement agreements with sales orders and invoices, and settle the conditions agreements based on settlement calendars. It integrates seamlessly with master data, SAP ERP SD, SAP ERP Materials Management (SAP ERP MM), and SAP ERP Financials (SAP ERP FI). There are a number of SAP Fiori apps available to support Settlement Management (see Figure 6.12).
Figure 6.12 SAP Fiori Apps Available to Support the Settlement Management Processes
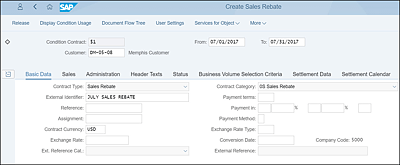
The Maintain Contracts app is used to create and maintain conditions contracts based on agreements made with customers. When creating a condition contract, the contract type must be chosen. The contract type determines how the contract will interact with the system, including the types of conditions that can be applied to the contract. The following contract header information should be maintained:
-
Basic Data
This tab includes contract owner (customer), validity dates, external reference information (used to identify a contract), and payment method. -
Sales
This tab contains the area to which the contract applies. -
Business Volume Selection Criteria
The business data on this tab is used by the system to determine the invoices that will apply to the contract. -
Settlement Data
This tab includes the settlement type and contract extension information. -
Settlement Calendar
This tab outlines the settlement dates that will apply to the contract. There can be a number of partial settlements defined throughout the life of the contract, and a final settlement date is also defined.
The contract header will also contain administrative data, contract status, and header text information (see Figure 6.13).
Figure 6.13 Creating Settlement Contracts
After the header information is maintained, the eligible partners and condition types are maintained. The conditions contracts provide flexibility for multiple eligible partners to be assigned to the contract. These partners are allowed to partake in the condition contract, so that if a group of customers can all partake in the same contract, a new contract doesn’t need to be maintained for each. Multiple condition types can be maintained for the contract based on the agreements made with the customer. For example, rebates can be maintained for multiple materials, different calculation types can be applied to a contract, and varying validity dates for each condition can be maintained, as long as the start and end dates fall within the validity period of the overall contract.
The condition contract must be released before it will be applied to the sales orders. The status of the contract will be updated after it’s released. If a sales order is created after the contract is released, the condition information will be calculated using SAP pricing procedures and displayed in the sales order and invoice condition screens, as long as the customer/material data aligns with the data maintained in the condition contract. If a sales order was created before the contract, but the invoice falls within the validity period of the contract, the contract condition may not be displayed in the conditions screens; however, the invoice will be included in the settlements process. Therefore, existing sales order prices don’t need to be updated if a new contract is created. Along with the condition records, the Compensation Management tab will display the contract information that applies to the document. The accounting document created from the invoice will also show entries for accrued rebates and sales deductions accounts.
Settlement of the condition contracts can be completed in one of two ways. The first is to have the settlement document automatically created for each invoice created in the system. The second is to create collective settlement documents based on the settlement calendar outlined in the contract header. Settlement documents are run against the condition contract and will be created for all invoices eligible for the contract. The outcome of settlement management is that a credit memo is issued to the customer. To facilitate settlement, the following SAP Fiori apps can be used:
- Settle Condition Contracts
- Collect Settlement Documents
- Display Settlement Calendars
- Release Documents—Settlement Documents
- Schedule Job for Contract Settlement
- Schedule Job to Collect Documents—Settlement Document
- Schedule Job to Release Settlement Management Documents
6.7.3 Complaint Management
The complaint management functionality allows a business to register customer complaints, issue returns, and even trigger quality checks on products. From a Sales and Distribution perspective, some of the key features of complaint management in SAP S/4HANA include the ability to create and process warranties for products. If a company has activated Biller Direct capabilities for customers to directly view invoices, bill recipients are able to file complaints and make inquiries directly through the Biller Direct app. These are then reviewed by the company, and action is taken to resolve the complaint. Returns management functionality allows a business to link a return document directly to a customer’s original sales order or invoice, create a Returns Management Authorization form that the customer will return with their goods, process the inbound delivery, and either credit the customer or trigger a new delivery of goods to replace the returned quantity. If a complaint is related to product quality, the complaint notification can trigger a quality review.
The complaint management process begins with the creation of a general notification in the system after a company has been contacted by a customer. Information is stored in the notification such as customer name, contact information, and details of the notification. If the notification isn’t related to a complaint, it can be closed; however, if it’s related to a complaint, it will be converted into a customer complaint notification. After the sales order or delivery document numbers are updated in the complaint, the material information will be copied into the notification. The created customer complaint notification can be accessed from the notification worklist.
The QA process is then initiated from the complaint notification. First, items are created for each defect outlined in the complaint. If the complaint includes materials sourced from multiple locations, multiple items can be created from a single defect. Tasks and activities are listed in the notification and are assigned to internal resources responsible for completing the activities. Tasks and activities can include confirming receipt of return, inspecting returned stock, inspecting stock from a specific storage location, emailing the customer, and so on. The complaint notification is released to the system, and users can begin processing the complaint and completing their tasks. As tasks are completed, the status is updated, and comments are stored in the notification to document progress, findings, and next steps. Documents can be attached to the notification as a backup on findings. After all tasks and activities are completed, and a root-cause analysis is done, the notification can be closed.
SAP S/4HANA provides a number of SAP Fiori apps to support the complaints management process.
SAP ERP System Upgrade to SAP S/4HANA
If your company uses industry-specific SAP ERP SD complaints handling, this functionality won’t be available in SAP S/4HANA. Instead, the standard SAP ERP SD complaints handling processes will need to be used. Transactions WCMP_PROCESSING, WCMP_MASS, and WCMP_RESULT won’t be available in the SAP S/4HANA system, so a review of all custom code is required to identify whether changes need to be made before converting to the new system.