7.4 Quality Planning
Quality planning helps users maintain master data to plan quality inspections. The quality planning component allows users to do the following:
- Manage quality information for materials, vendors, manufacturers, and customers.
- Monitor the QM systems of vendors and manufacturers.
- Plan inspections for goods receipt, stock transfers, production orders, predefined inspection points, shipping when deliveries are created, and recurring inspections.
- Plan inspection operations in work processes.
7.4.1 Master Data
Following are the key master data elements:
- Inspection methods
- Master Inspection Characteristics (MIC)
- Catalogs
- Selected sets
- Material master – QM view
- Inspection plan
7.4.2 Inspection Methods
Inspection methods provide details of how to carry out an inspection for an inspection characteristic. Inspection methods are created at the plant level and are assigned to Master Inspection Characteristics (MIC) or inspection plans to describe the inspection procedure.
Users can following these steps to create an inspection method:
- Navigate to Logistics • Quality Management • Quality Planning • Basic Data • Inspection Method • Create (QS31).
-
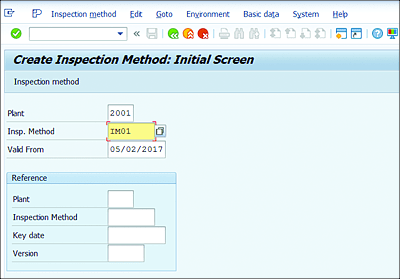
On the initial screen (see Figure 7.1), enter the following data:
-
Plant
Number of the plant. -
Insp. Method
Name of inspection method. -
Valid From
Date from which the inspection is valid. -
Reference
Optional reference data, including Plant, Inspection Method, Key date, and Version.
-
Plant
Figure 7.1 Inspection Method
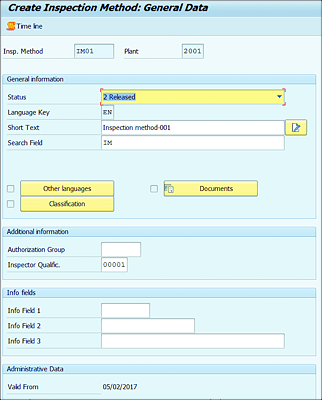
The following section of the screen provides details of the inspection method data elements such as inspection method number, description of inspection method, and inspector qualifications (see Figure 7.2). You can also use info fields to save additional details about the inspection method.
Figure 7.2 Inspection Menu, Continued
SAP S/4HANA allows you to attach documents such as diagrams in a Microsoft Word document format by using the Document Management System (DMS).
Save your data by clicking Save.
7.4.3 Master Inspection Characteristics
MIC describes the inspection criteria for materials, parts, and products. You can create MIC at the plant level. The MIC can be qualitative (attributive characteristics such as color, taste, visual inspection, etc.) or quantitative (for which values can be measured such as length, weight, etc.).
MIC contain general and control data. General data involves the name of characteristics and the name of the plant for which that MIC is applicable. In MIC, the following control data can be defined:
- Whether the master inspection characteristic is a qualitative or quantitative characteristic
- Sample details (e.g., sampling procedure, Statistical Process Control [SPC] characteristics)
- Information for results confirmation (e.g., summarized recording, recording by class, required or optional characteristic, and conditional characteristic, which means the inspection of this characteristic is dependent on either the acceptance or rejection of the previous required characteristic)
- Type of values to be inspected for quantitative characteristics (e.g., target value, lower specification limit, and upper specification limit)
- Inspection of characteristic attributes for qualitative characteristics
- Details of inspection scope
- Details of documentation in the results recording function
- Inspection methods
- Test equipment
Master Inspection Characteristics Models
There are three types of models available in MIC:
-
Reference characteristic
If you use the MIC in a task list or material specification, a reference is first created to this characteristic. You can, however, cancel this reference and change the data individually (e.g., tolerances). -
Complete copy model
If you use the MIC in a task list or material specification, the reference to this characteristic is canceled. You can therefore immediately change the data (e.g., tolerances). You can then only use this MIC as a copy model. -
Incomplete copy model
If you use the MIC in a task list, this can only be used as a copy model. This type of MIC can’t be used in a material specification.
7.4.4 Qualitative Master Inspection Characteristics
The example described in the following subsections provides details of the data parameters maintained for quantitative MIC. The General Data Section of Master Inspection Characteristics can be found by navigating to Logistics • Quality Management • Quality Planning • Basic Data • Inspection Characteristic • Create (QS21), or Transaction QS21.
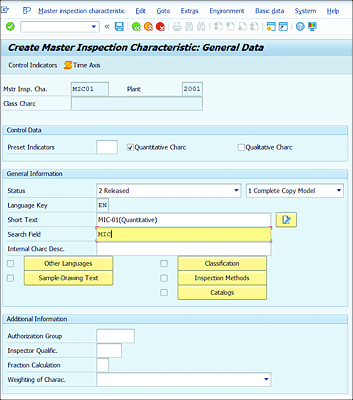
In the General Data screen, you can maintain the following information (see Figure 7.3):
-
Mstr Insp. Cha
MIC name. -
Plant
Plant number. -
Quantitative Char/ Qualitative Char
Characteristics type checkboxes. -
Status
Processing status (Released for business use or still in Created status). -
Short Text
Short description of MIC. -
Search Field
Search term for MIC. -
Complete Copy Model
Copy model details (can also choose Reference or Incomplete Copy Model). -
Inspection methods
Assignment of inspection methods.
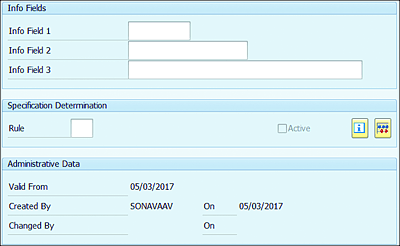
In the General Data screen, you can also enter additional text information in Info Field 1/2/3 and the Specification Determination Rule, as shown in Figure 7.4.
Figure 7.3 General Data Screen
Figure 7.4 General Data Screen Info Fields
Control Indicator Section
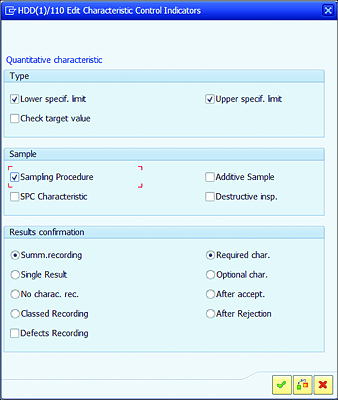
In this section of the screen, you can maintain the following indicators (see Figure 7.5):
-
Lower specif. limit
Maintain this indicator if there is a need to maintain a lower possible acceptable limit value of MIC. -
Upper specif. limit
Maintain this indicator if there is a need to maintain an upper possible acceptable limit value of MIC. -
Check target value
Maintain this indicator if there is a need to check the target value against the tolerance limit. -
Sampling Procedure
Sampling procedure is required for MIC. -
Additive Sample
Samples used in this characteristic can’t be used in any other characteristics. -
Destructive insp.
After testing of the MIC, the sample gets destroyed and can’t be used for any additional testing. -
SPC Characteristic
Control chart can be maintained for this MIC. -
Summ.recording
Summarized characteristic results can be performed in the results recording. -
Single Result
Characteristic results needs to be recorded as individual values in the results recording. -
No charac. rec.
This indicator won’t allow users to enter results recordings. -
Required char.
Recording of characteristics results is mandatory, and users won’t be allowed to perform usage decision and close lots if results aren’t maintained. -
Optional char.
System will allow users to perform usage decisions and close inspection lots without performing results recording. -
Classed recording
Results are recorded using a class data object. -
Defects recording
Defects need to be recorded if there is a failure during the results recording. -
After accept.
Inspection characteristics will be applicable only after previous characteristics from the inspection plan are accepted. -
After Rejection
Users need to record results for this MIC only after a previous MIC has failed.
Figure 7.5 Edit Characteristic Control Indicators
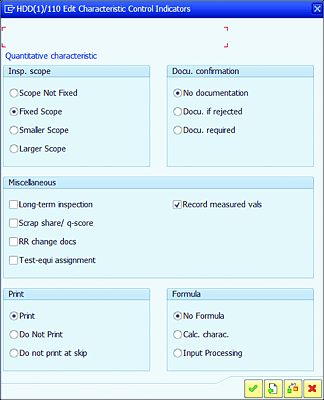
Following are some additional control indicators you can maintain (see Figure 7.6):
-
Scope Not Fixed
System won’t check the calculated inspection scope (sample size) during inspection lot processing. -
Fixed Scope
Inspection scope (sample size) must be the same as the system-calculated inspection scope during inspection lot processing. -
Smaller Scope
Inspection scope (sample size) can be changed to a smaller scope during results recording in inspection lot processing. -
Larger Scope
Inspection scope (sample size) can be increased during inspection lot processing. -
No documentation
No additional text information is needed to be entered during inspection lot processing. -
Docu. if rejected
If MIC results are rejected, then users have to enter text information regarding why it was rejected. -
Docu. required
For all results recordings, users have to enter additional text information. -
RR change docs
Historical change details will be maintained if users change the results. -
Test-equi assignment
Users can assign test equipment needed to perform testing. -
Confirm values
Users need to confirm values in the results recording before the usage decision. -
Calc. charac.
Characteristics results are calculated based on values entered on another MIC’s predefined formula. -
Print
Users can print MIC details on inspection instructions. -
Do not print
MIC details won’t be printed on inspection instructions. -
Do not print at skip
MIC details won’t be printed for skip inspection lots.
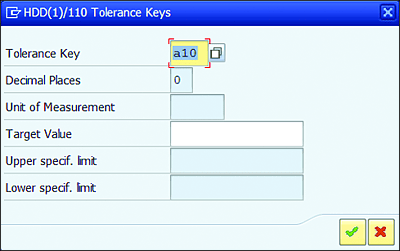
You can maintain tolerance key values relevant for MIC, as displayed in Figure 7.7.
Figure 7.6 Additional Editable Characteristic Control Indicators
Figure 7.7 Maintaining the Tolerance Key
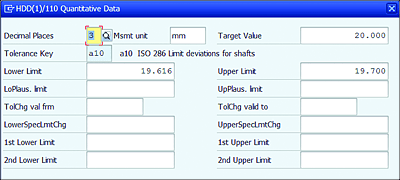
You can maintain quantitative data such as upper limit/lower limit values for MIC, unit of measure, and upper/lower plausible limits based on predefined control indicators, as shown in Figure 7.8.
Figure 7.8 Maintaining Limits
7.4.5 Catalog
The catalog contains unique, nonnumerical data that is used to define, manage, and standardize information such as inspection parameters, defects, and decisions for the inspections. This data can help to record and subsequently evaluate qualitative data, as well as describe problems.
Catalog Types
Table 7.1 lists the standard catalog types available in SAP S/4HANA for QM.
| Catalog | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Characteristic attributes | For qualitative characteristics |
| 2 | Tasks | For notifications |
| 3 | Usage decisions | For giving usage decisions |
| 5 | Causes | For notifications |
| 8 | Activities(QM) | For notifications |
| 9 | Defect types | For notifications |
| E | Defect locations | For notifications |
Table 7.1 Standard Catalog Types in QM
7.4.6 Code Group
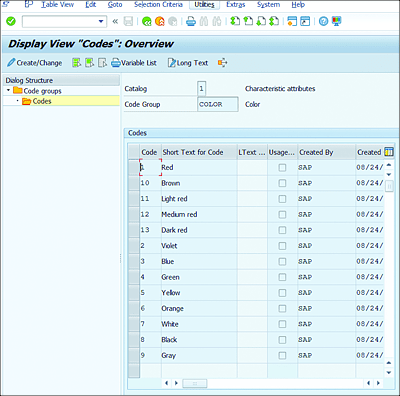
Code groups are used to combine and structure codes within a catalog type. You can use code groups at the client level to group codes that have the same content or relate to one another within a catalog type. Codes that are assigned to a code group are also known as group codes. You can group together codes for different colors (see Table 7.2), surface characteristics, or usage options.
| Code Group | Overview of Codes |
|---|---|
| Color | Red |
| Brown | |
| Blue |
Table 7.2 Code Group Example
Codes describe qualitative contents in machine form that can be easily processed. Codes make up the lowest level of a catalog and can describe, for example, a characteristic attribute, a defect type, a defect location, or a usage decision. The code is distinctive in conjunction with the catalog and code group.
Figure 7.9 displays how code group COLOR is assigned to the characteristics attribute catalog with various codes such as Red, Brown, Light red, and so on. To get there, navigate to Logistics • Quality Management • Quality Planning • Basic Data • Catalog • Code Group • Edit (QS41), or Transaction QS41.
Figure 7.9 Catalog Types with Code Group and Codes
7.4.7 Selected Sets
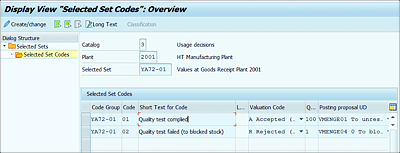
A selected set contains a combination of different catalog codes, for example, coded descriptions of characteristic attributes (e.g., color, shape, and surface characteristics), defect causes, or usage decisions from different code groups. Selected sets are maintained only for catalog types 1 and 3. The following example is displayed for a selected set (usage decision).
As shown in Figure 7.10, you can define selected sets for each plant and assign a code group and codes with valuation decision (Accepted/Rejected), quality scores, and suggested stock posting. Navigate to Logistics • Quality Management • Quality Planning • Basic Data • Catalog • Selected Set • Edit (QS51), or Transaction QS51.
Figure 7.10 Selected Sets
7.4.8 Sampling Scheme
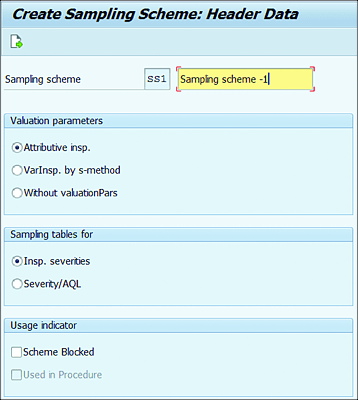
A sampling scheme is the group of sampling plans that provides information about the sample sizes and criteria used to valuate the results in the sampling inspection. Navigate to Logistics • Quality Management • Quality Planning • Basic Data • Sample • Sampling Scheme • Create (QDP1), or Transaction QDP1. As shown in Figure 7.11, you can define a sampling scheme based on the following valuation parameters:
-
Attributive insp.
Users can define sample size for various lot sizes with various inspection levels (e.g., normal inspection, reduced inspection). This parameter also requires users to define a maximum number of defective units allowed to accept the inspection lot and a minimum number of defective units that will result in rejection of the inspection lot. -
VarInsp. by s-method
Users can define sample sizes for various lot sizes and assign a k-factor to calculate the acceptance number. -
Without valuationpars
Users can define sample sizes for various lot size valuation parameters such as acceptance number.
Figure 7.11 Sampling Scheme
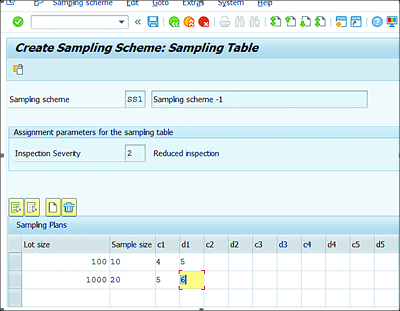
In sampling schemes, users can define sampling tables to calculate the sample size either based on inspection severity (Insp. severities) or based on the Severity/AQL (acceptance quality level) combination.
Figure 7.12 shows the lot size details and reduced inspection details with acceptance and rejection numbers.
Figure 7.12 Sampling Scheme Lot Size and Inspection Details
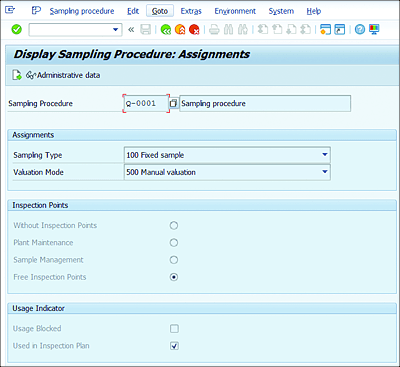
7.4.9 Sampling Procedure
A sampling procedure defines the rules that specify how the system calculates the sample size, and it contains information about the valuation of an inspection characteristic during results recording (e.g., attributive, variable, manual, etc.). Navigate to Logistics • Quality Management • Quality Planning • Basic Data and then Sample • Sampling Procedure • Create (QDV1), or Transaction QDV1.
In the sampling procedure, you can define the following key parameters (see Figure 7.13):
-
Sampling Type
Choose how the system should determine sample size (e.g., 100% sample size, fixed sample size, % of total lot size, based on sampling scheme). -
Valuation Mode
Define rules for accepting or rejecting samples or characteristics (e.g., characteristics to be accepted or rejected based on number of nonconforming units, number of defects, or manual valuation). -
Inspection Points
Required in a scenario where there is a need to record results with a predefined frequency of time or quantity. Use the following options based on your business needs:- Without Inspection Points: Use this option for inspection plans.
- Plant Maintenance: Use for calibration inspections (calibration inspection plans).
- Sample Management: Use if there is a need for a sampling procedure along with inspection points.
- Free Inspection Points: Use mainly for in-house production routings where there might be a need to record results based on a predefined time interval (e.g., every 30 minutes).
Figure 7.13 Sampling Procedure
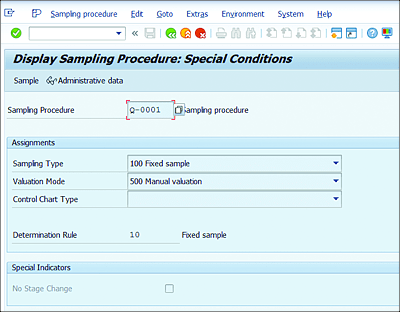
Lot size (Determination Rule) can be maintained in the screen shown in Figure 7.14.
Figure 7.14 Sampling Procedure Special Conditions