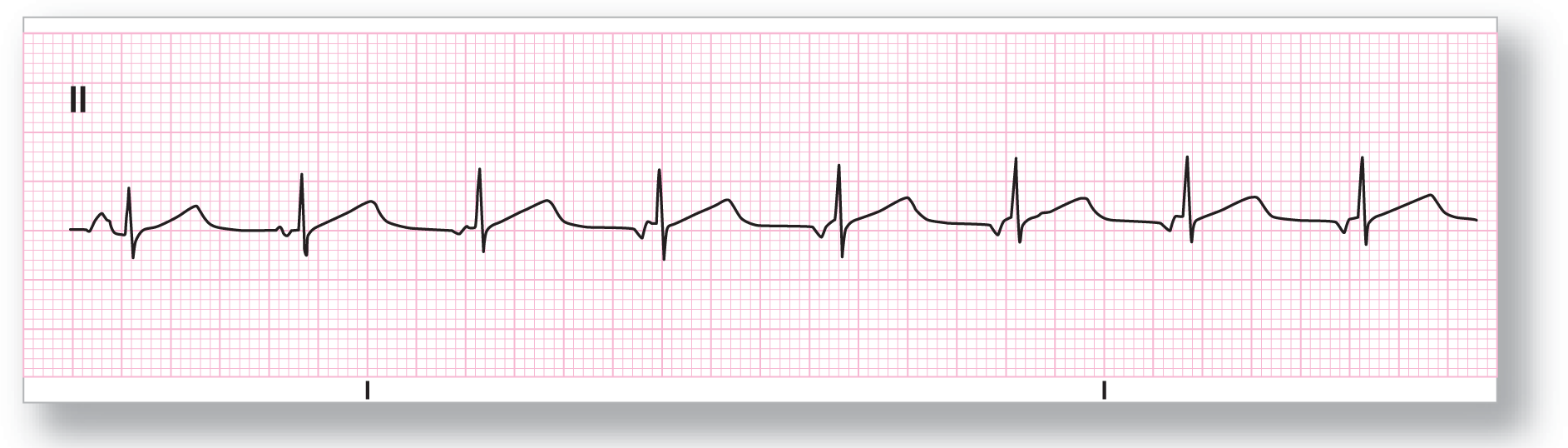
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.

From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: Around 85 BPM |
PR intervals: Variable |
|
Regularity: Irregularly irregular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present Morphology: Variable Axis: Variable |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Yes |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Wandering atrial pacemaker |
Discussion:
ECG 17-1 shows the classic changes of a WAP. Notice the slow, gradual transition of the P waves from upright to inverted. Longer strips show the transition occurring back and forth between the pacemakers. Notice that the QRS complexes and T waves are identical in this strip. There is no evidence of any aberrant conduction, as can sometimes occur with faster rates.
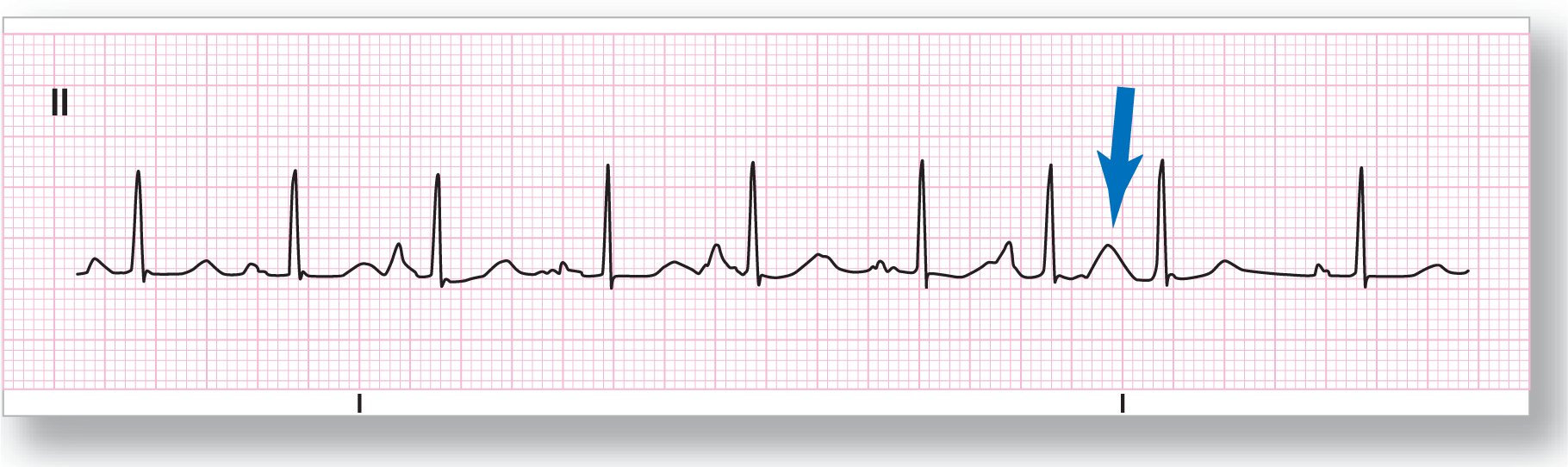
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: Upper 90s BPM |
PR intervals: Variable |
|
Regularity: Irregularly irregular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present Morphology: Variable Axis: Variable |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Wandering atrial pacemaker |
Discussion:
ECG 17-2 shows an irregularly irregular rhythm with at least three P-wave morphologies. As a matter of fact, just the first three complexes show differing P-wave morphologies and PR intervals. This is a typical example of a wandering atrial pacer. Note the area highlighted by the blue arrow. This is a fusion between the T wave of the preceding complex with the P wave of the complex that follows, the buried P-wave phenomenon we discussed before.
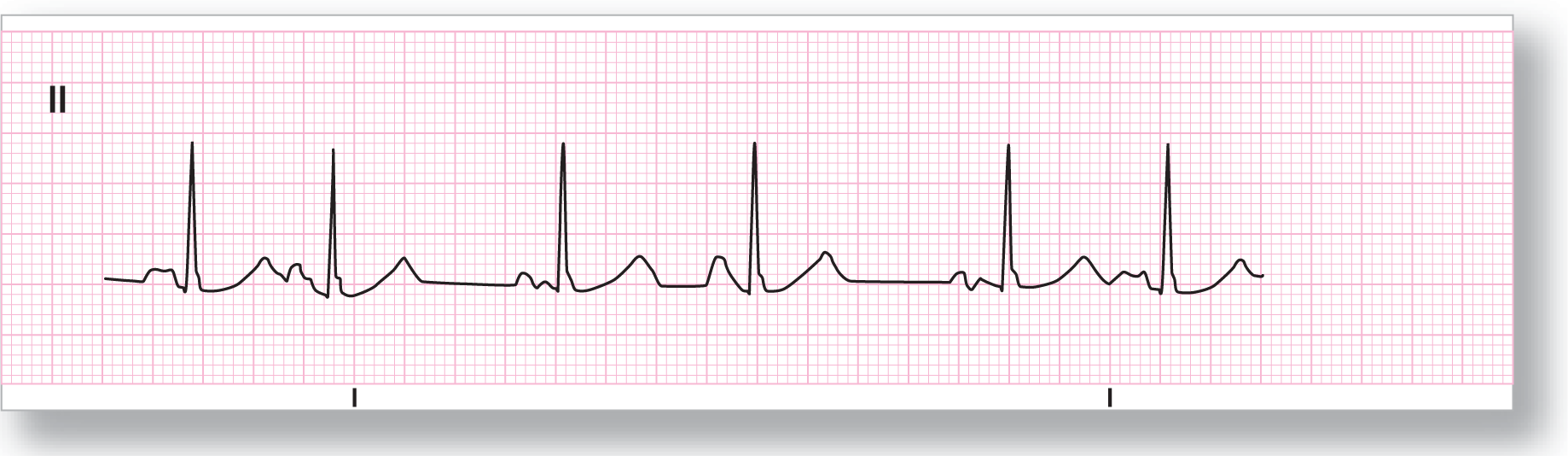
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: Around 70 to 80 BPM |
PR intervals: Variable |
|
Regularity: Irregularly irregular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present Morphology: Variable Axis: Variable |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Wandering atrial pacemaker |
Discussion:
It is very easy to identify the different P-wave morphologies and PR intervals in ECG 17-3. The irregularly irregular rhythm, along with at least three different P-wave morphologies that are present, clinch the diagnosis as WAP.
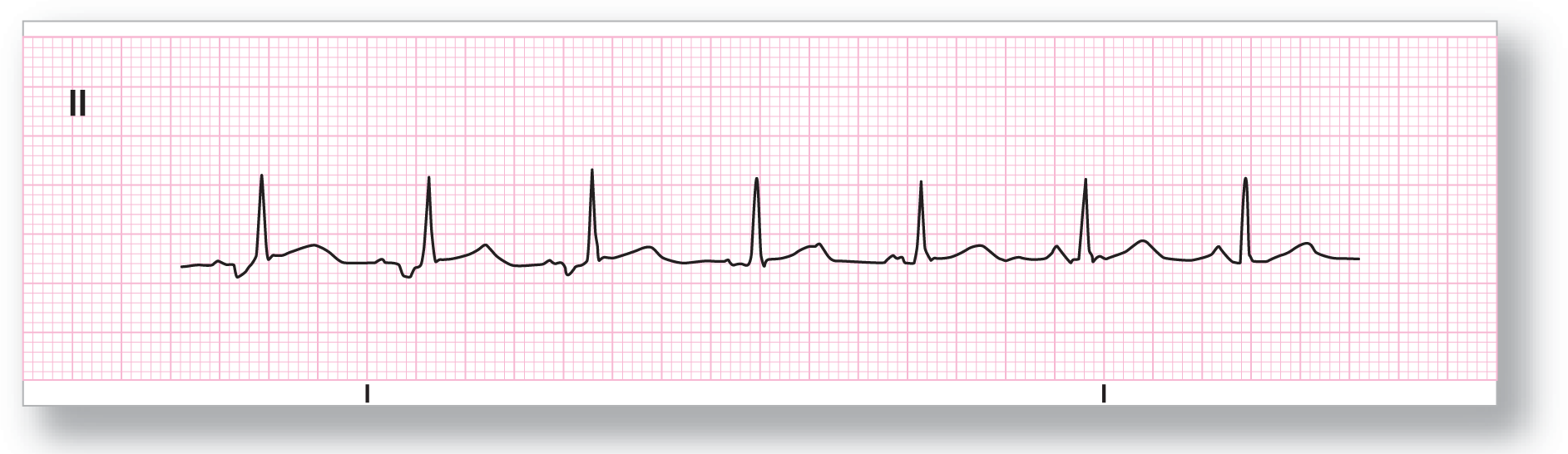
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: Around 90 BPM |
PR intervals: Variable |
|
Regularity: Irregularly irregular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present Morphology: Variable Axis: Variable |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Wandering atrial pacemaker |
Discussion:
ECG 17-4 shows the classic changes of a WAP. Note the slow transition from the negative P-wave morphologies at the onset of the strip to the more normal-appearing P waves found at the end of the strip. Be careful though; you cannot state that any of the P waves above resemble sinus P waves unless you have old strips to compare, in which the patient was in normal sinus rhythm.
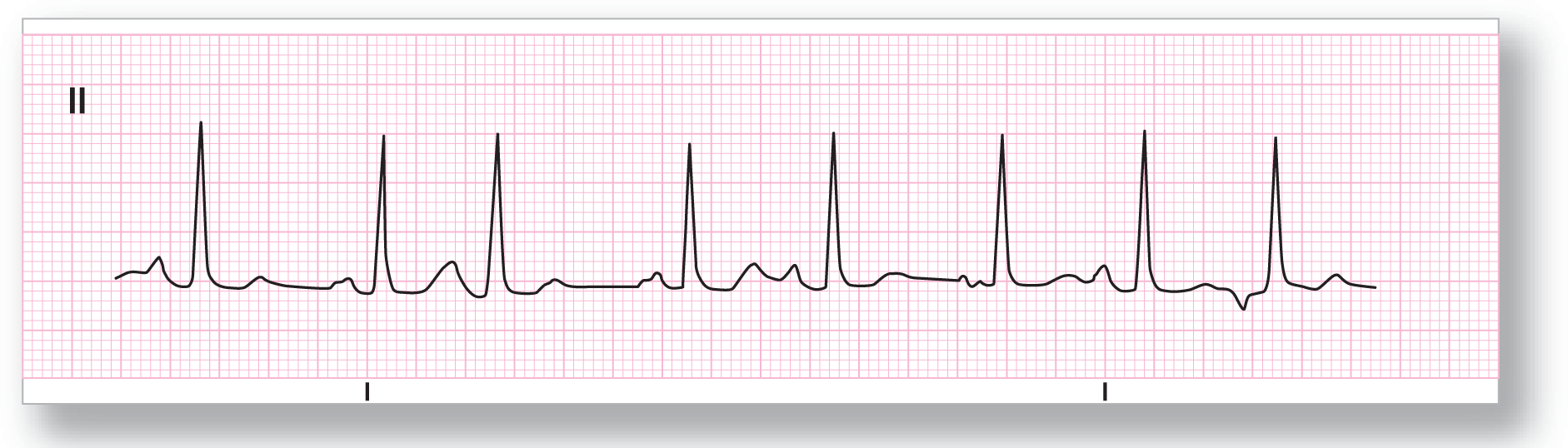
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: Around 90 BPM |
PR intervals: Variable |
|
Regularity: Irregularly irregular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present Morphology: Variable Axis: Variable |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Wandering atrial pacemaker |
Discussion:
In ECG 17-5, once again note the irregularly irregular rhythm with the differing P-wave morphologies and PR intervals. There are at least three differing P-wave morphologies, which makes the diagnosis a WAP. There is a fusion of the T wave of the second complex with the P wave of the third complex. Always think about a buried P wave when you see a single abnormal T wave on a strip.
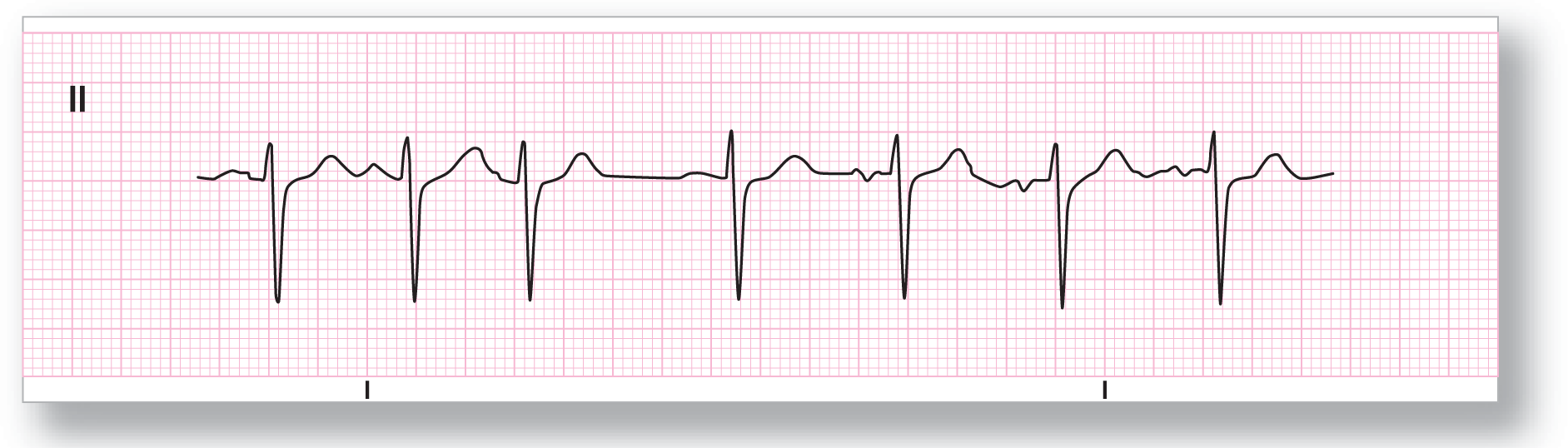
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: Around 90 BPM |
PR intervals: Variable |
|
Regularity: Irregularly irregular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present Morphology: Variable Axis: Variable |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Wandering atrial pacemaker |
Discussion:
ECG 17-6 shows a WAP rhythm very clearly. Once again, the third P wave is buried in the T wave of the second complex.