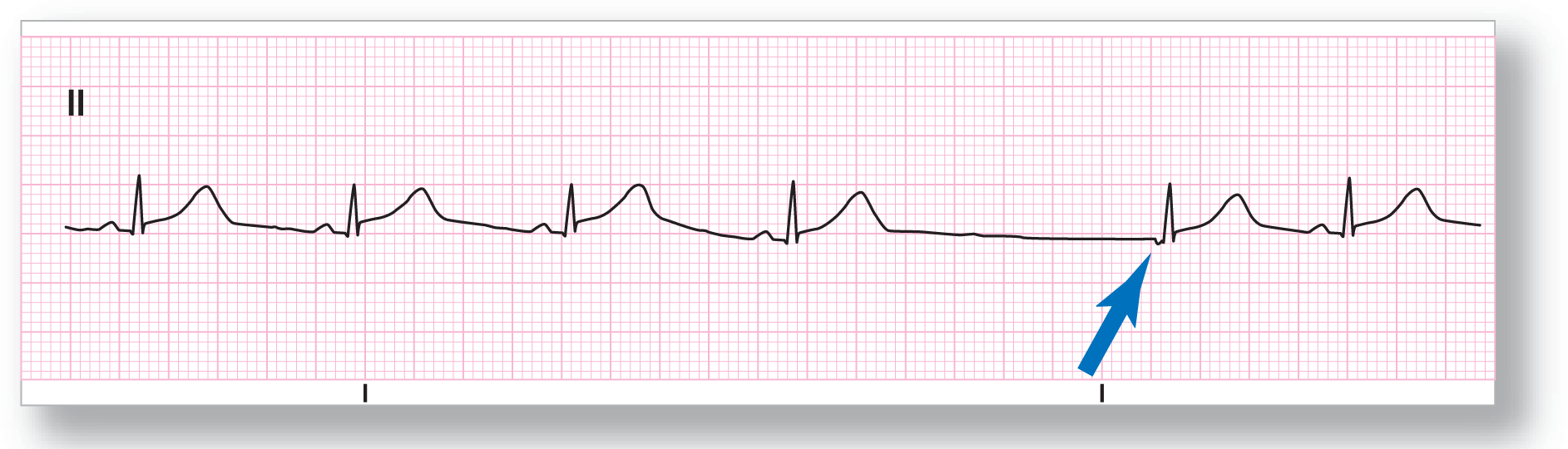
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: About 67 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regular with an event |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Inverted in event Axis: Abnormal in event |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with a junctional escape complex |
Discussion:
The underlying rhythm in ECG 23-1 is sinus rhythm. The SA node then fails to pace and there is a prolonged pause leading to a junctional escape complex. Notice that the P wave for the junctional escape complex is inverted and found before the QRS complex (see blue arrow). This signifies retrograde conduction of the junctional impulse backward to the atria.
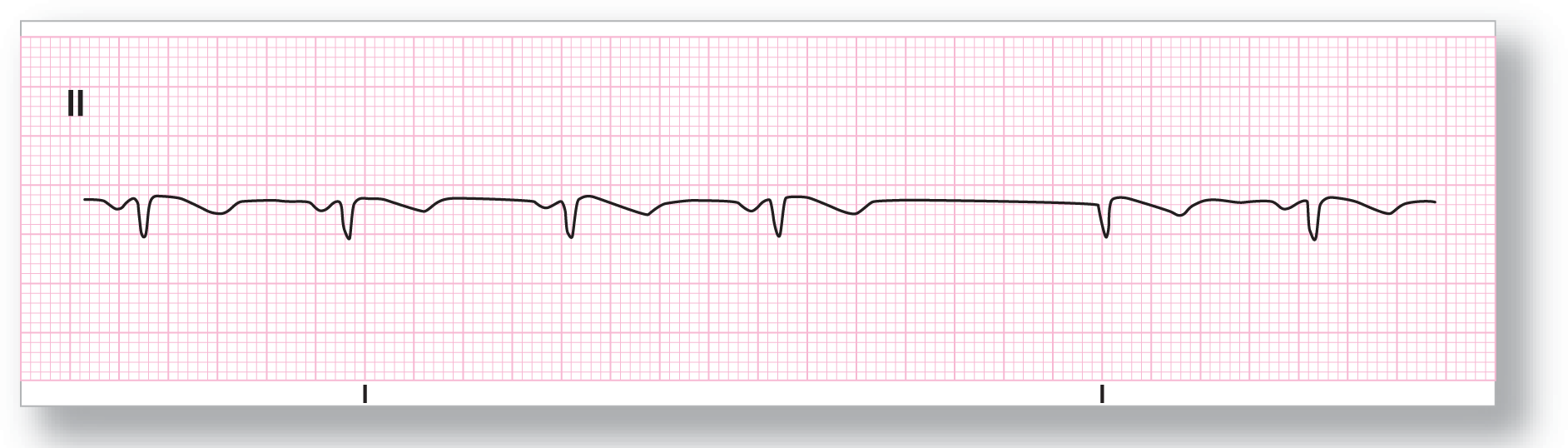
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 68 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regular with an event |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Inverted; none in event Axis: Abnormal; none in event |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
Rhythm: Ectopic atrial rhythm with a junctional escape complex |
Discussion:
ECG 23-2 shows inverted P waves with normal PR intervals all throughout the rhythm. Therefore, the underlying rhythm is an ectopic atrial rhythm. The event that occurs is related to the prolonged pause leading to the formation of a junctional escape complex. Note that the P wave is not visible in the junctional escape complex because it is either missing or buried in the QRS complex.
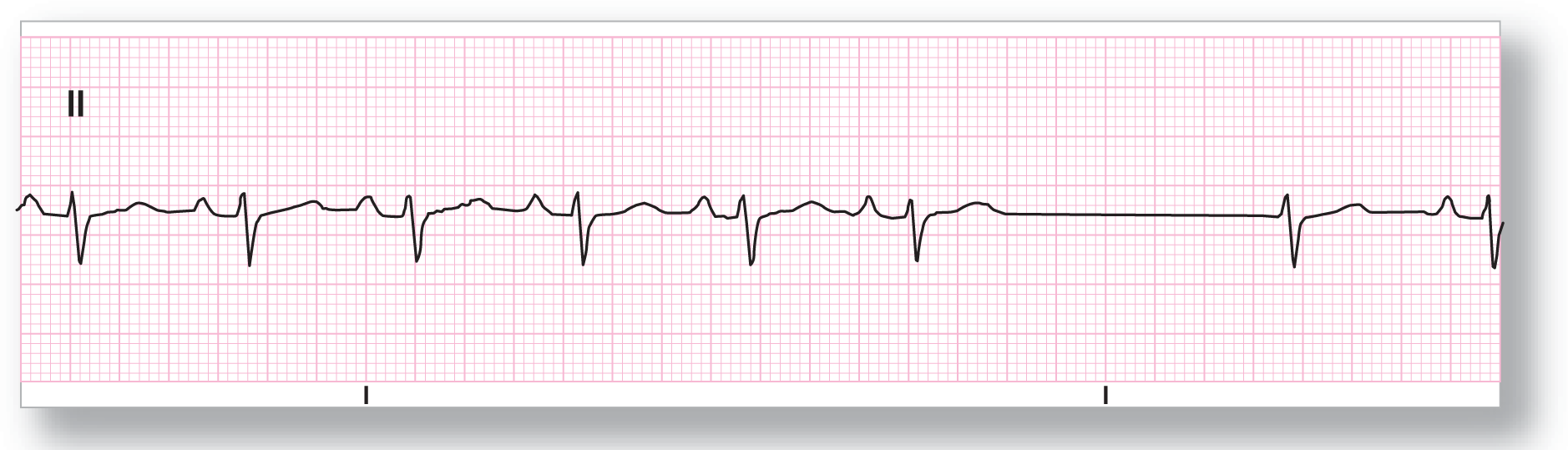
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 90 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regular with an event |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Normal; none in event Axis: Normal; none in event |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with a junctional escape complex |
Discussion:
ECG 23-3 shows a normal sinus rhythm with a sinus pause leading to a junctional escape complex. The normal sinus pacemaker appears to take over the pacing functions again after the junctional escape complex. The P wave is either missing or buried within the QRS complex of the junctional escape beat.
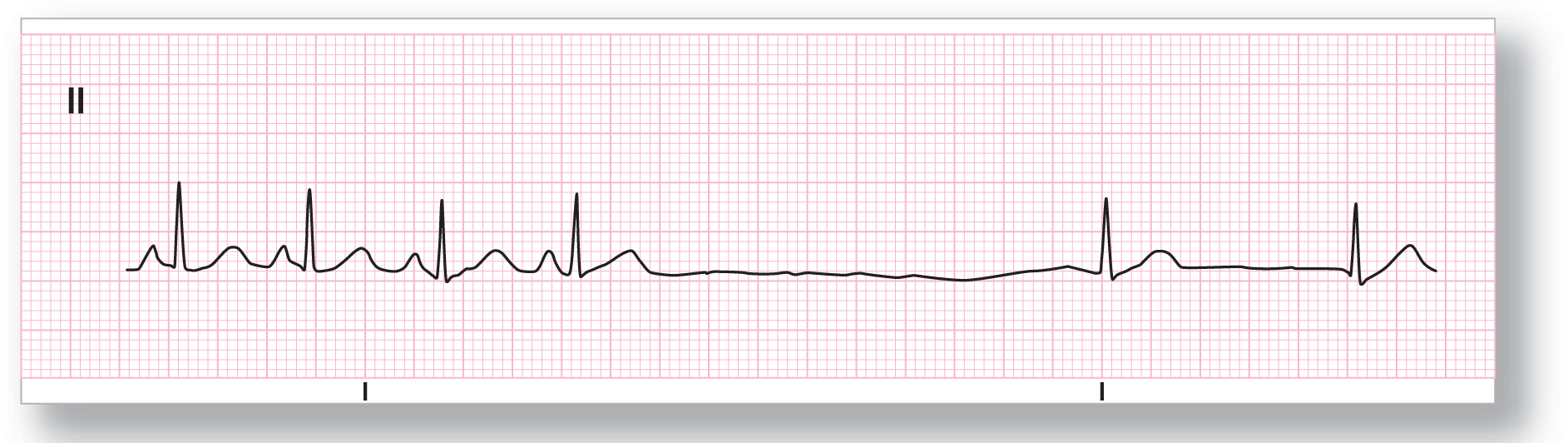
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 110 BPM |
PR intervals: See discussion below |
|
Regularity: Regularly irregular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: See discussion below Morphology: See discussion below Axis: See discussion below |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: See discussion below |
Rhythm: Sinus tachycardia, sinus arrest, and a junctional escape rhythm |
Discussion:
ECG 23-4 starts off with what appears to be a sinus tachycardia. Then it shows a fairly long interval with no electrical activity. This is compatible with a sinus arrest followed by a rescue junctional escape rhythm occurring at a rate of about 58 BPM. The P waves are not visible in the junctional rhythm, signifying either the absence of P waves or buried P waves.
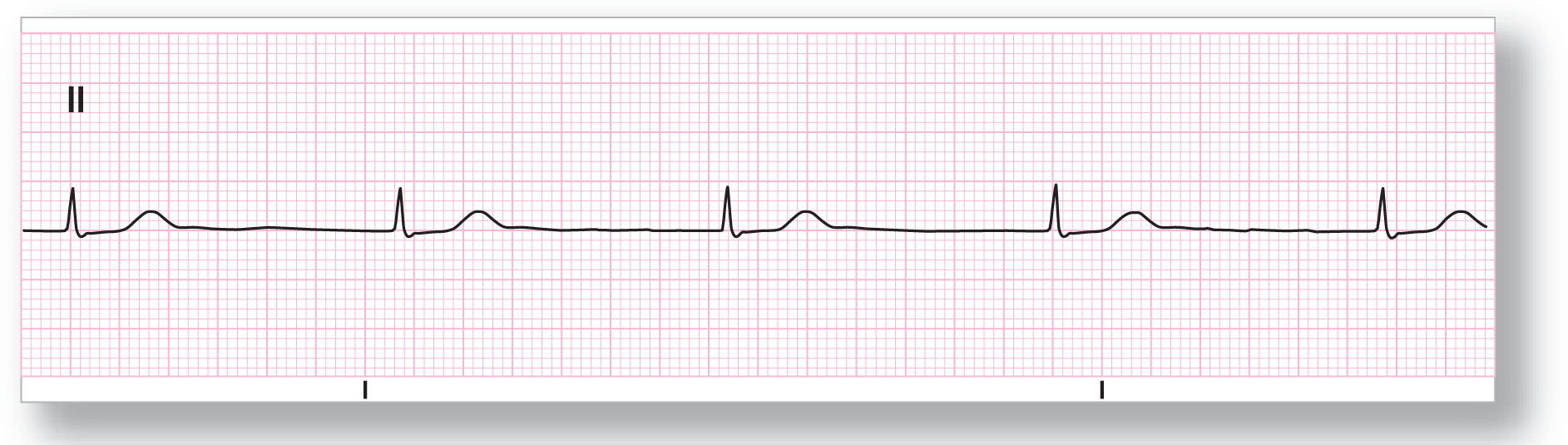
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 45 BPM |
PR intervals: Not applicable |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: None Morphology: None Axis: None |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: Not applicable |
Rhythm: Junctional rhythm |
Discussion:
ECG 23-5 shows a junctional rhythm at a rate of about 45 BPM. Notice the absence of P waves, the regularity of the rhythm, and the normal-looking supraventricular complexes.
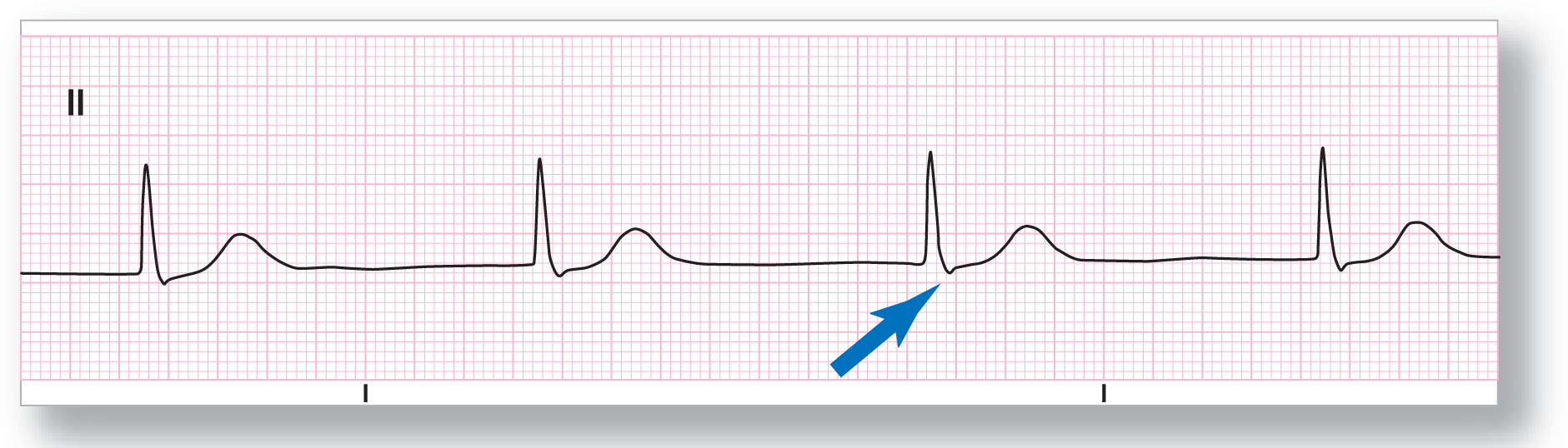
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 38 BPM |
PR intervals: Not applicable |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: None Morphology: None Axis: None |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: Not applicable |
Rhythm: Junctional rhythm |
Discussion:
ECG 23-6 shows a junctional rhythm with a rate that is slightly lower than expected for the AV nodal area. Drugs, ischemia, or a CNS event may be the culprit behind the slower rate. Notice the slight depression immediately after the QRS complex. This negative wave could represent a retrograde P wave occurring immediately after the QRS complex. An old ECG strip would be helpful to see if this finding was present during a period of normal sinus rhythm.
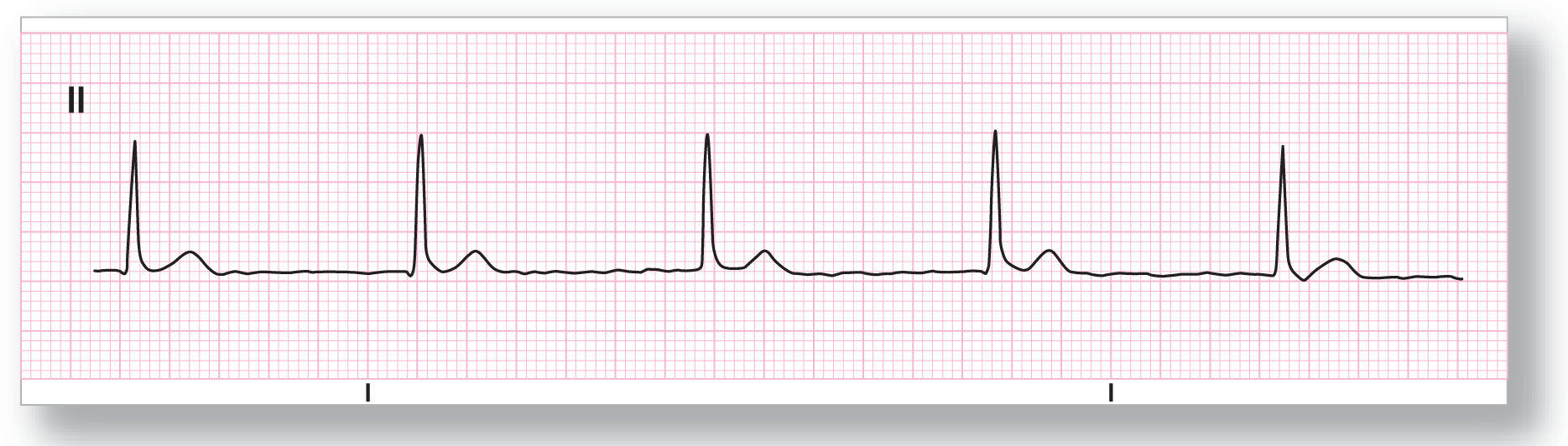
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 52 BPM |
PR intervals: Not applicable |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: None Morphology: None Axis: None |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: Not applicable |
Rhythm: Junctional rhythm |
Discussion:
ECG 23-7 is also a textbook example of a junctional rhythm. There are no discernible P waves anywhere along the strip. The QRS complexes are narrow and obviously of supraventricular origin. Finally, the rate of 52 BPM is definitely consistent with a junctional rhythm.
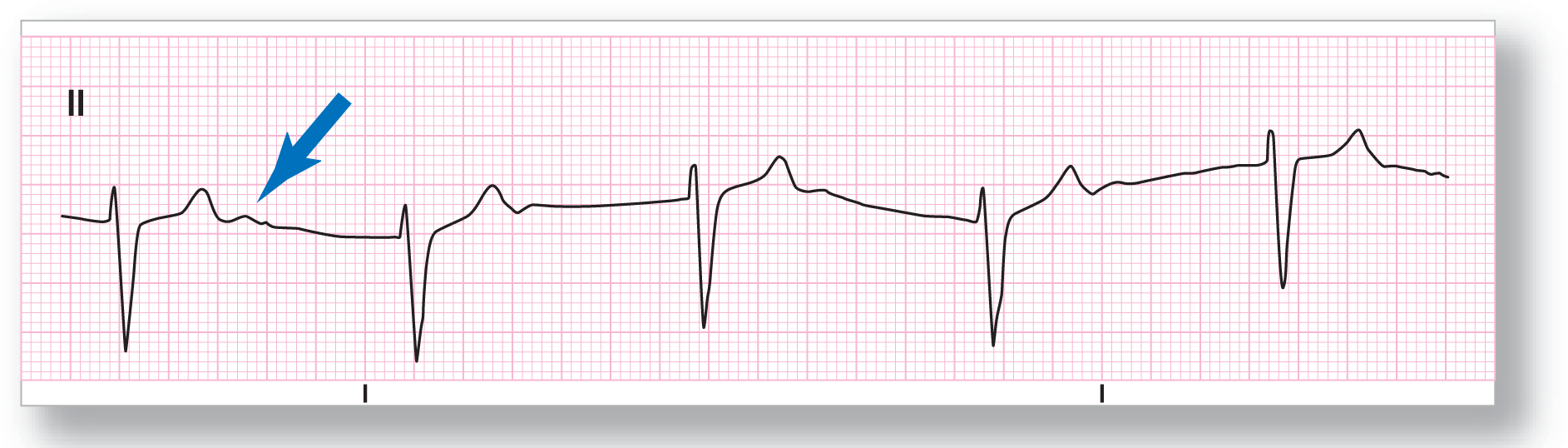
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 51 BPM |
PR intervals: Not applicable |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: None Morphology: None Axis: None |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: None |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: Not applicable |
Rhythm: Junctional rhythm |
Discussion:
ECG 23-8 is also a great example of a junctional rhythm. The wandering baseline is due to movement of the patient or one of the leads. The blue arrow is pointing toward a positive wave immediately after the T wave. This deflection is not a P wave but an example of a typical U wave. The U wave has no special clinical significance in the evaluation of this arrhythmia, except that it could raise the possibility of a pathologic process, especially an electrolyte abnormality (hypokalemia). Typically, however, U waves are seen in the absence of pathology.