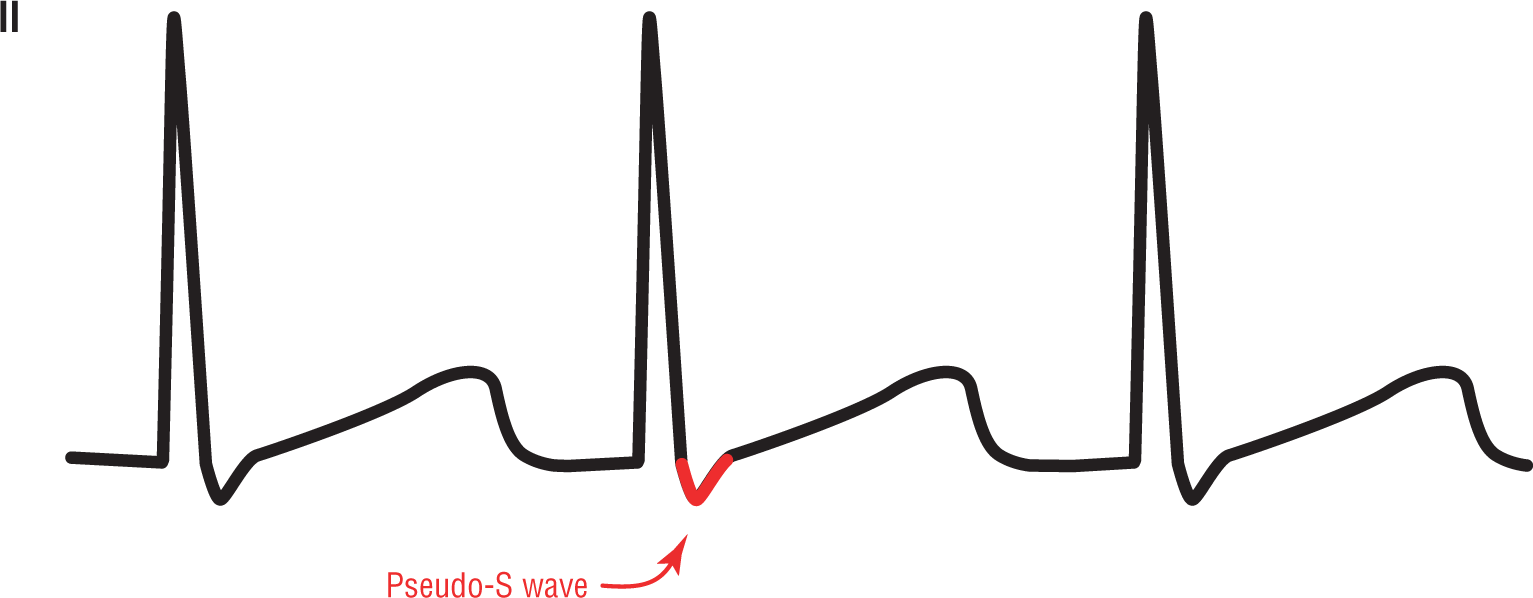
Figure 24-2 Pseudo-S wave in lead II, commonly found in junctional tachycardias.
© Jones & Bartlett Learning.
As we have seen, the P wave in the junctional rhythms can be inverted and can occur slightly after the QRS complex. In junctional tachycardias, that retrograde P wave can look just like a slurred S wave in leads II, III, and aVF and an R or R’ wave in lead V1. To differentiate these waves from “true” S and R’ waves, they are known as pseudo-S and pseudo-R (or pseudo-R’) waves (Figures 24-2 and 24-3). The “pseudo” part is added to reflect the fact that these appear to be S waves and R waves but are not true waves; rather, they are merely an electrocardiographic reflection caused by the retrograde P waves.

Figure 24-2 Pseudo-S wave in lead II, commonly found in junctional tachycardias.
© Jones & Bartlett Learning.
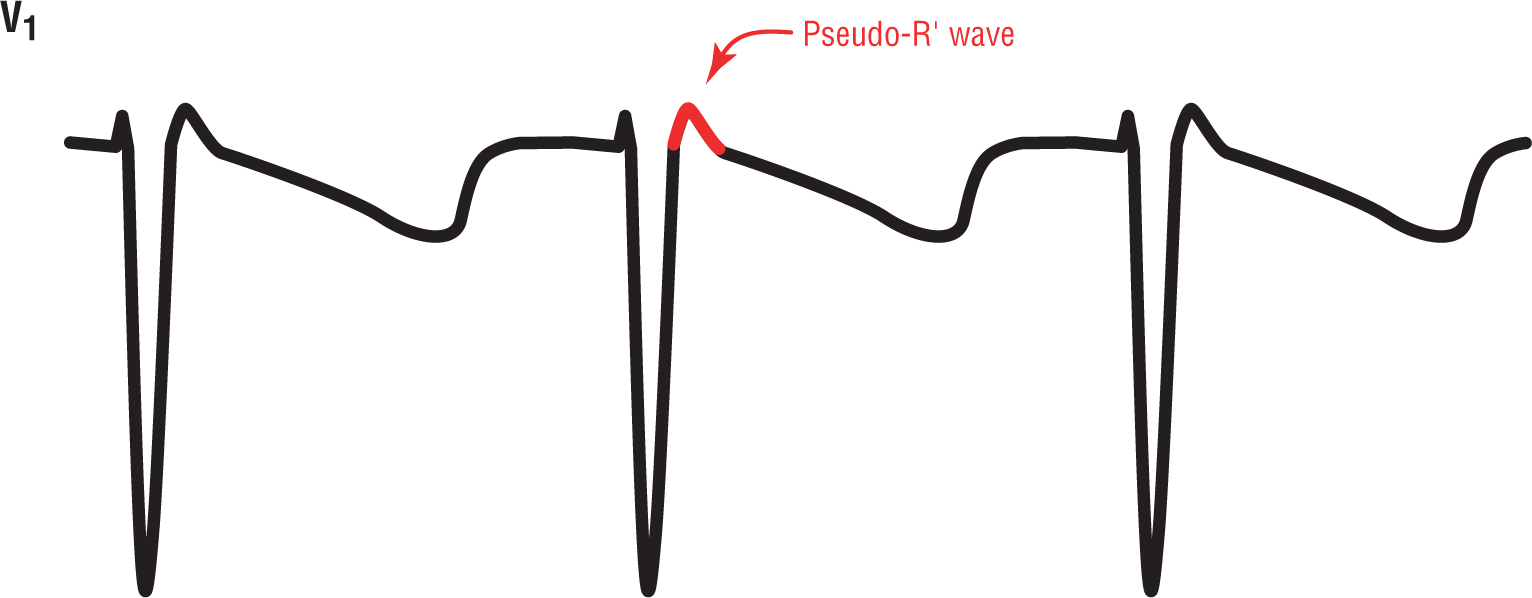
Figure 24-3 Pseudo-R’ wave in lead V1, commonly found in junctional tachycardias.
© Jones & Bartlett Learning.
These pseudo waves sometimes cause confusion when interpreting an ECG. But, they can also add a great clue to the correct arrhythmic diagnosis. Whenever you see a narrow-complex tachycardia with no obvious P waves but an s wave in the inferior leads and a small r’ in lead V1, think of an accelerated junctional rhythm, a junctional tachycardia, or AV nodal reentry tachycardia (which we will discuss in the next chapter).
ARRHYTHMIA RECOGNITION
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
| Rate: | > 60 to 100 BPM |
| Regularity: | Regular |
| P wave:
Morphology: Upright in II, III, and aVF: |
Variable
Different, if present No |
| P:QRS ratio: | Variable |
| PR interval: | Variable |
| QRS width: | Normal |
| Grouping: | None |
| Dropped beats: | None |
ARRHYTHMIA RECOGNITION
Junctional Tachycardia
| Rate: | > 100 to 200 BPM |
| Regularity: | Regular |
| P wave:
Morphology: Upright in II, III, and aVF: |
Variable
Different, if present No |
| P:QRS ratio: | Variable |
| PR interval: | Variable |
| QRS width: | Normal |
| Grouping: | None |
| Dropped beats: | None |
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm and Junctional Tachycardia
This list is not all-inclusive.