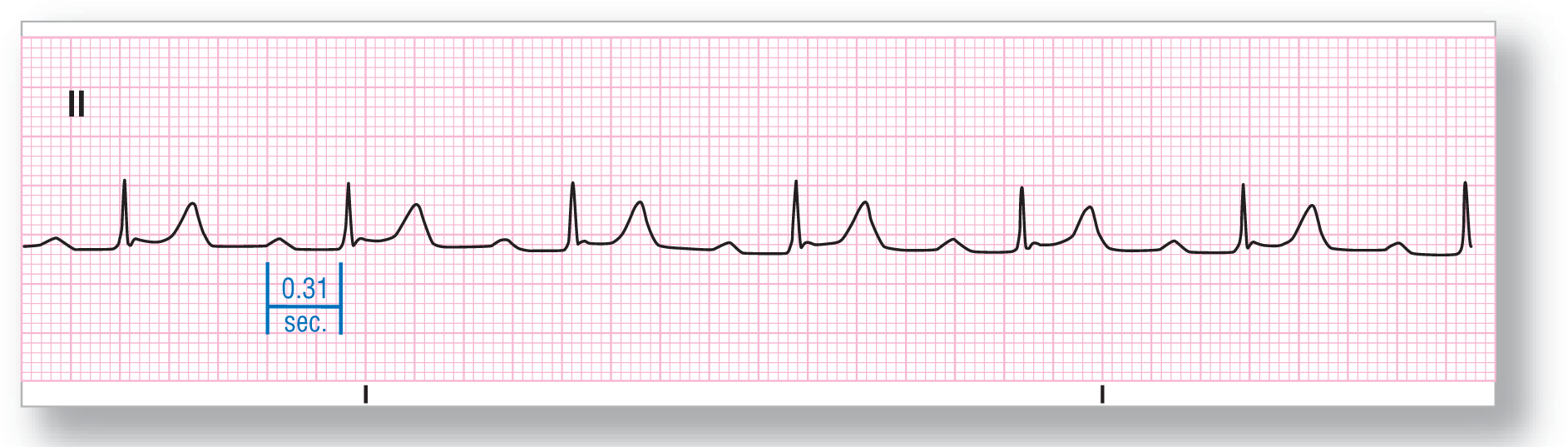
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.

From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 65 BPM |
PR intervals: Prolonged |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Normal Morphology: Normal Axis: Normal |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Absent |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with first-degree AV block |
Discussion:
ECG 28-1 shows a regular rhythm with upright P waves in lead II. This is consistent with a sinus rhythm. The PR interval is prolonged at 0.31 seconds, which is way above the upper limit of normal at 0.20 seconds. The P:QRS ratio is 1:1 with each P wave conducting to form one QRS complex. All of these findings are consistent with a sinus rhythm with a first-degree AV block.
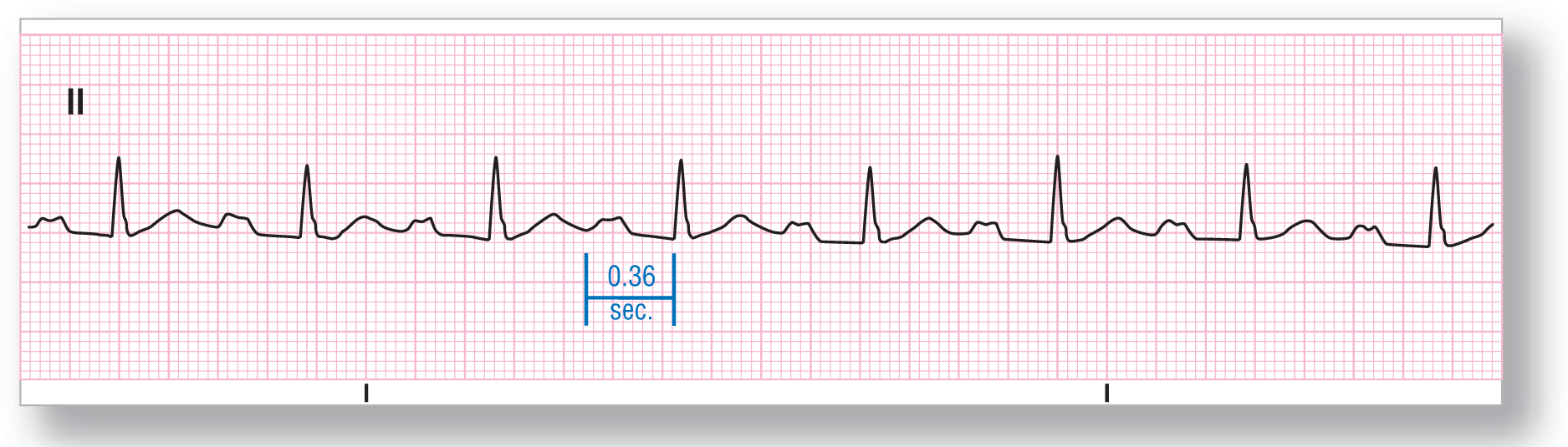
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 79 BPM |
PR intervals: Prolonged |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Wide Morphology: Wide Axis: Normal |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Absent |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with first-degree AV block |
Discussion:
ECG 28-2 shows upright P waves in lead II and normal-looking QRS complexes appearing at a rate of about 79 beats per minute (BPM). The P:QRS ratio is 1:1 with each P wave conducting to one QRS complex. The PR intervals are approximately 0.36 seconds and are, therefore, prolonged. This strip is consistent with a sinus rhythm with a first-degree AV block.
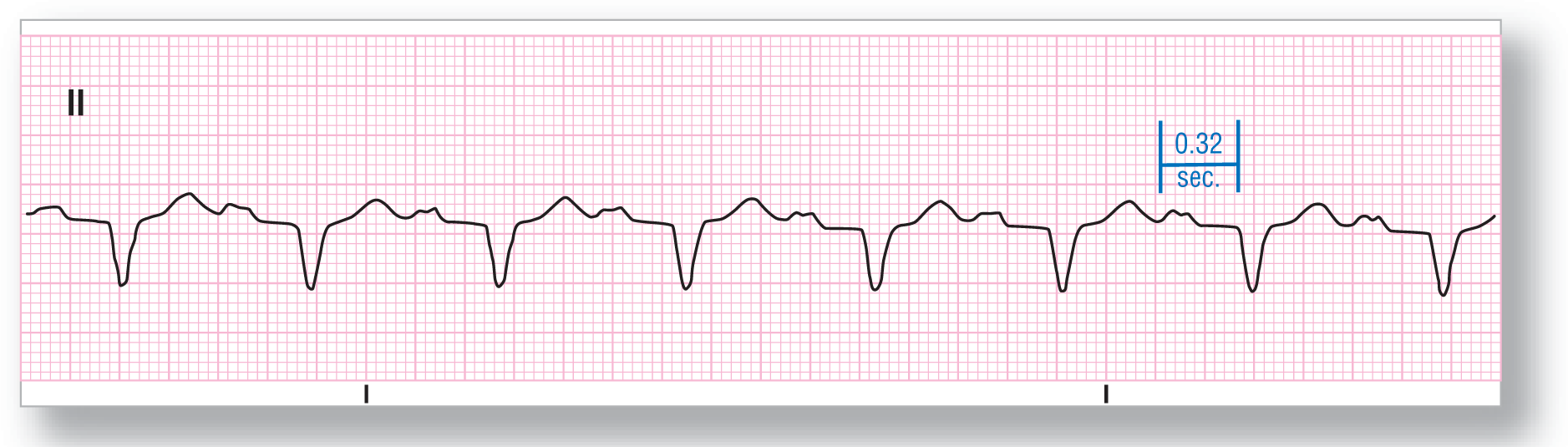
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 77 BPM |
PR intervals: Prolonged |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Wide |
|
P waves: Normal Morphology: Normal Axis: Normal |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Absent |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with first-degree AV block |
Discussion:
No, this is not the same patient as in ECG 28-2. In ECG 28-3, the P waves and the rates are similar, but that is where the similarities end. This patient shows upright P waves in lead II that are also humped, but the PR interval is prolonged at 0.32 seconds. Also note that these QRS complexes are exactly 0.12 seconds due to a preexisting left bundle branch block. The final diagnosis is a sinus rhythm with a first-degree AV block in a patient with a preexisting left bundle branch block.
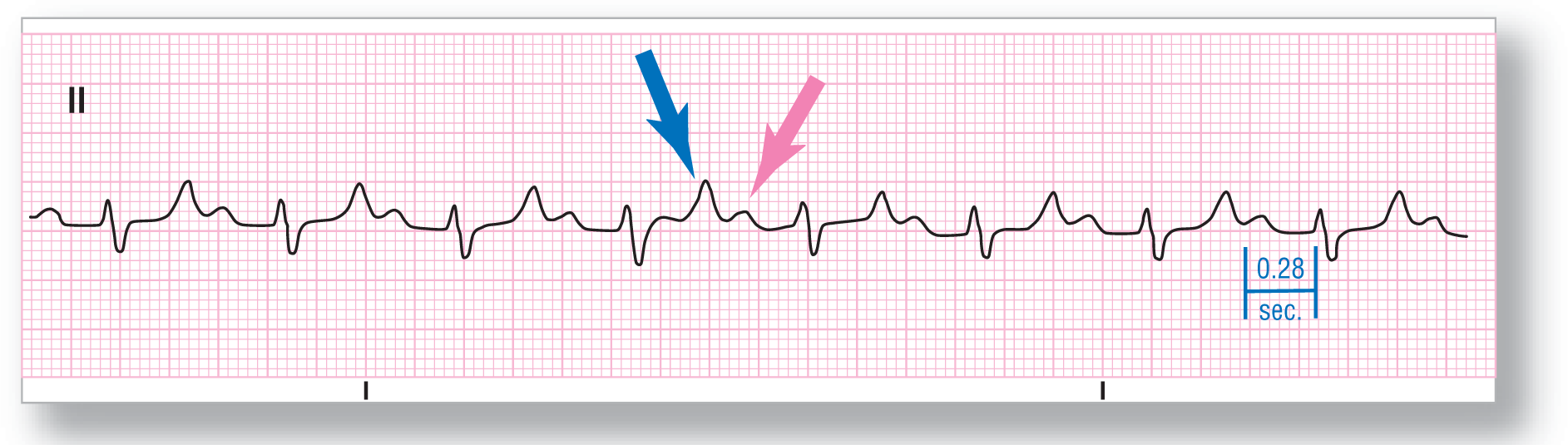
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 85 BPM |
PR intervals: Prolonged |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Normal Morphology: Normal Axis: Normal |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Absent |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with first-degree AV block |
Discussion:
ECG 28-4 shows prolonged PR intervals at about 0.28 seconds. The QRS complexes are small and relatively isoelectric, whereas the T waves are very prominent. The blue arrow is pointing at the T waves, and the pink arrow is pointing at the P waves. Note that the true PR interval may be slightly longer than 0.28 seconds because the P waves are partly buried in the previous T wave. This means that the early onset of the P waves, and the additional width of the PR interval, cannot be seen clearly.
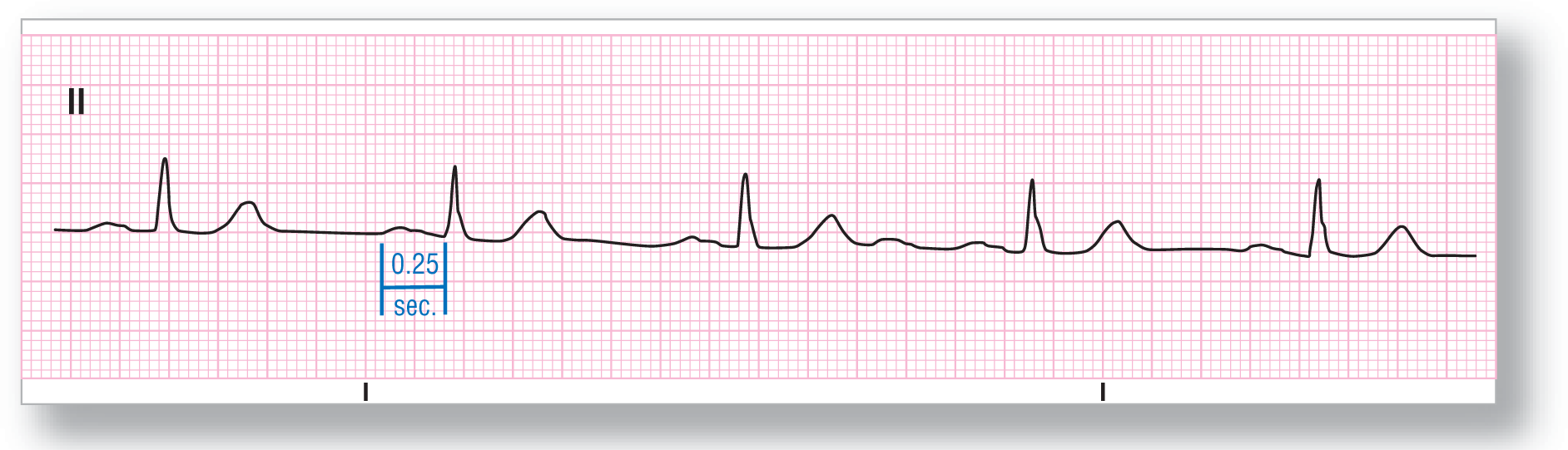
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 52 BPM |
PR intervals: Prolonged |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Normal |
|
P waves: Wide Morphology: Wide Axis: Normal |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Absent |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1 |
Rhythm: Sinus bradycardia with first-degree AV block |
Discussion:
ECG 28-5 shows a sinus bradycardia with narrow ventricular complexes. The P-waves are upright in lead II, which is a normal P-wave axis. The PR intervals are prolonged at 0.25 seconds, giving this patient a first-degree AV block. Notice that in this case, the PR interval is mostly made up of a very wide P wave (P-mitrale due to left atrial enlargement). Remember, it doesn’t matter what component of the PR interval is prolonged to make the call of a first-degree AV block—it just has to be prolonged.