From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.

From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 78 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regular with an event |
QRS width: Event is wide |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Normal, except in event Axis: Normal, except in event |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
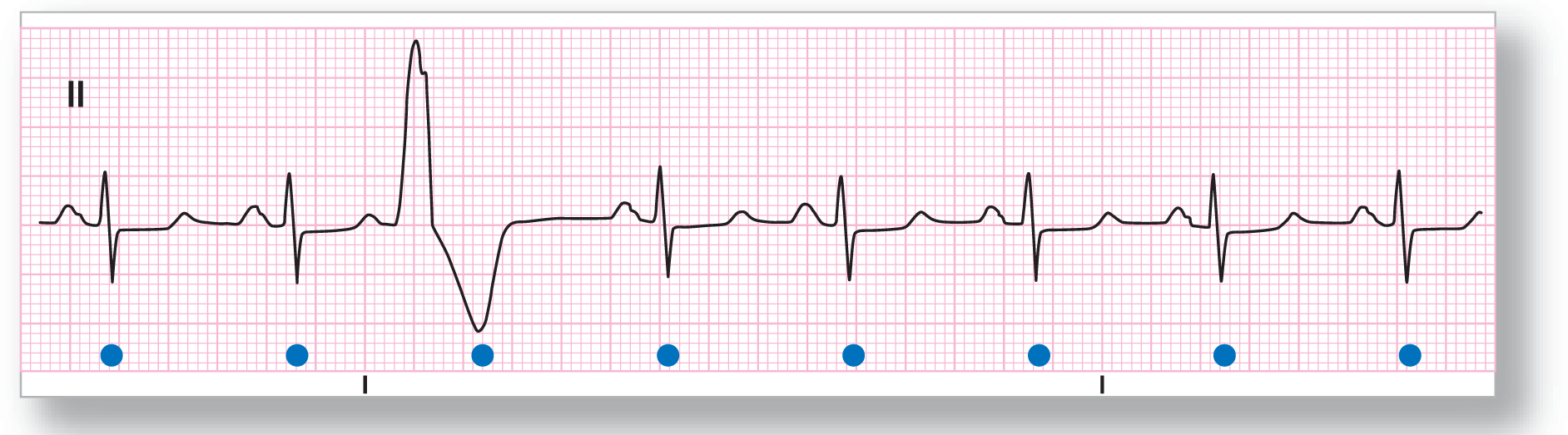
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with a PVC |
Discussion:
ECG 30-1 shows a sinus rhythm with a single PVC (third complex). Note that the PVC is wider than 0.12 seconds and is associated with ST-segment and T-wave abnormalities. The pause associated with the PVC is fully compensatory. Notice that the underlying cadence of the sinus rhythm is undisturbed by the PVC. The underlying sinus P wave is not visible because it is completely fused with the PVC.
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 104 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Event is wide |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Normal, except in event Axis: Normal, except in event |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
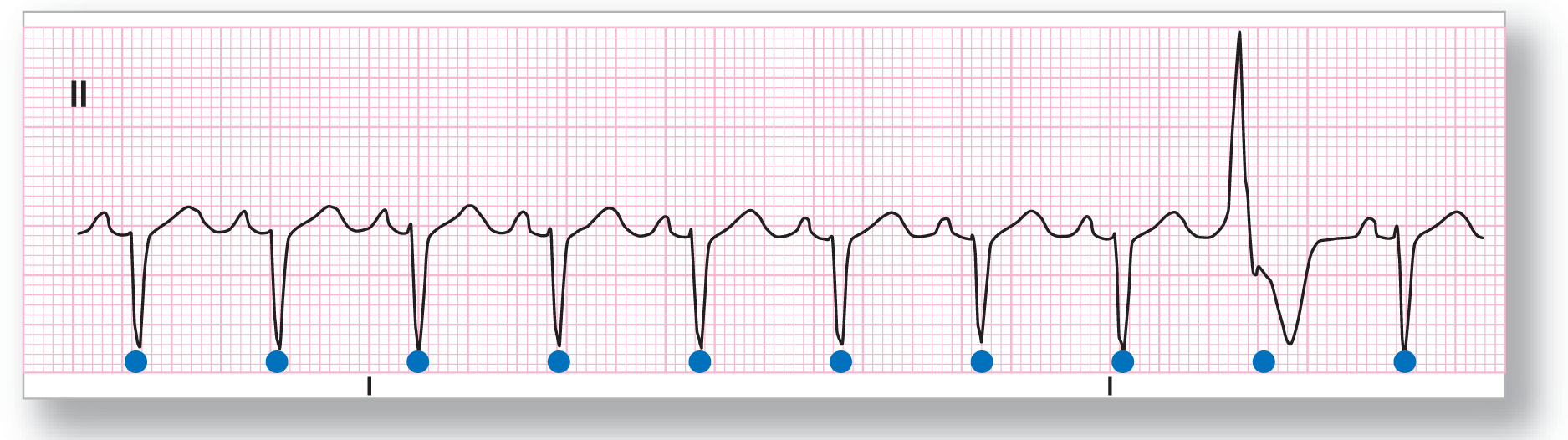
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with a PVC |
Discussion:
ECG 30-2 shows your typical PVC with a wide, bizarre complex with ST-segment and T-wave abnormalities. The pause is fully compensatory. The underlying rhythm, in this case, is sinus tachycardia.
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
|
Rate: About 82 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regular with multiple events |
QRS width: Event is wide |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Normal, except in event Axis: Normal, except in event |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
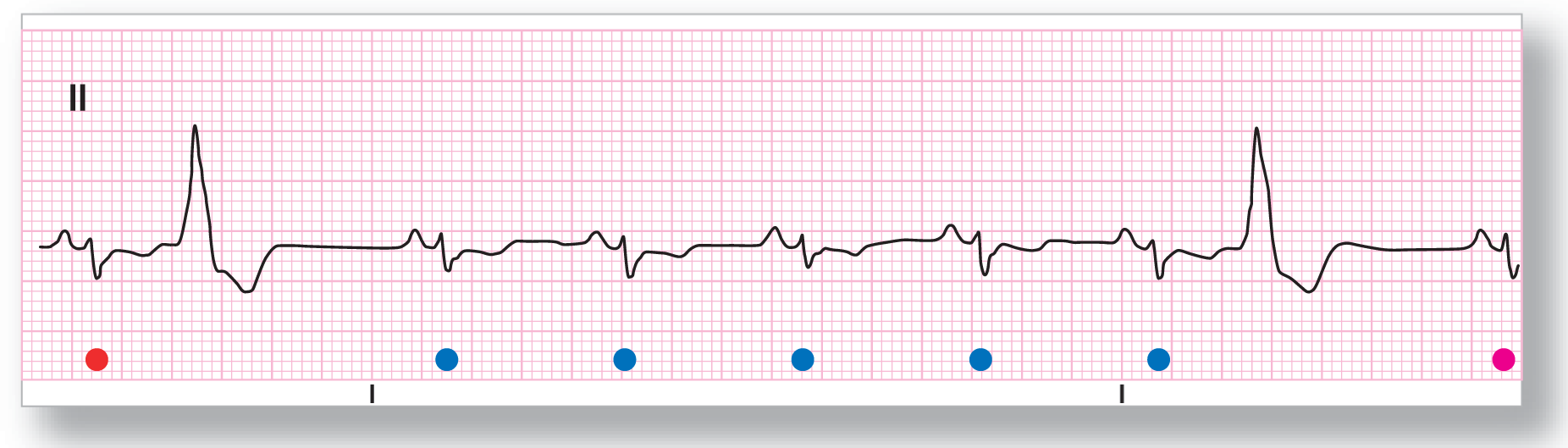
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with a PVC |
Discussion:
ECG 30-3 shows a sinus rhythm at about 82 to 84 BPM. The wide complexes (complexes 2 and 8) are PVCs. Note that the pauses associated with these PVCs are noncompensatory pauses. The retrograde V-A conduction of the ectopic depolarization wave causes a resetting of the sinus node. The reset node shows varying rates after each PVC. On a longer rhythm strip, the rate was constantly being reset throughout the strip.
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: About 94 BPM |
PR intervals: Prolonged, see discussion below |
|
Regularity: Regular |
QRS width: Wide |
|
P waves: See discussion below Morphology: See discussion below Axis: See discussion below |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: See discussion below |
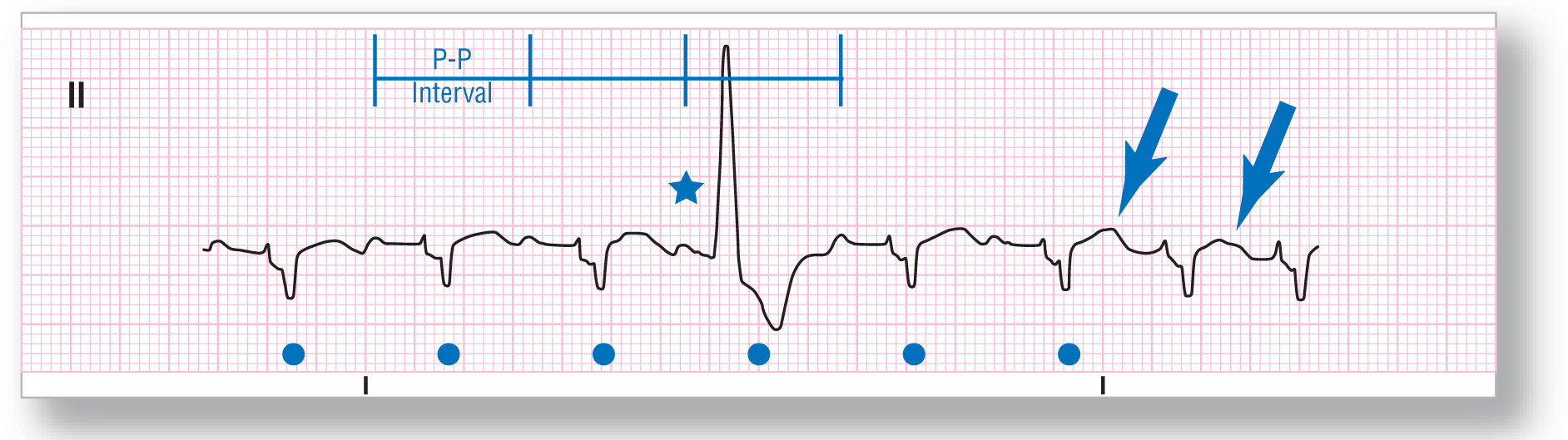
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with a PVC |
Discussion:
ECG 30-4 is much more complex than you would think at first. The underlying rhythm is sinus, but the last two complexes are premature. Note that the T waves of the complexes (labeled with the blue arrows) have a different morphology from the others. These are PACs with buried P waves. The PVC has a P wave in front of it (see blue star), but the PR interval is different. Could this be an aberrantly conducted PAC? No, it is not premature (see P-P interval brackets) and the underlying cadence is not interrupted. Finally, the pause is fully compensatory (see blue dots). This is an end-diastolic PVC.
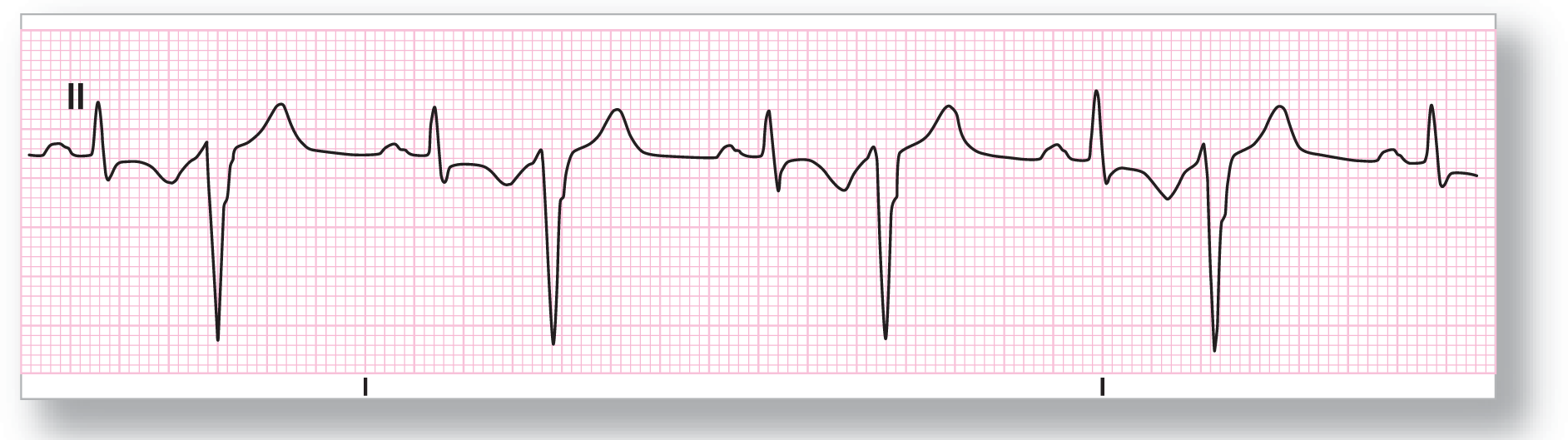
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: See discussion below |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regularly irregular |
QRS width: Events are wide |
|
P waves: Present, except in events Morphology: Normal, except in event Axis: Normal, except in event |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with ventricular bigeminy |
Discussion:
The rate on ECG 30-5 is hard to state electrocardiographically. The reason is that every other beat is a PVC, making this a sinus rhythm with ventricular bigeminy. The best guess is that it is 90 BPM (nine complexes in a 6-second strip). The best thing to do is to go to the patient and actually take a manual pulse for accuracy. It is impossible in bigeminy to state if the pauses are compensatory or noncompensatory pauses because there is no clear underlying P-P interval.
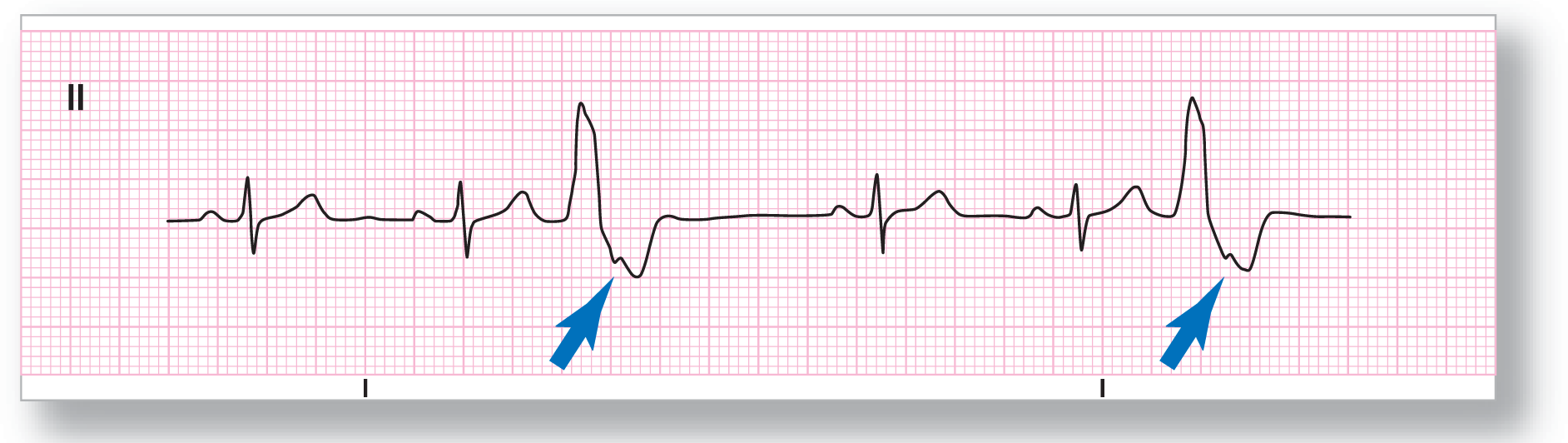
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: About 70 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regular with frequent events |
QRS width: Event is wide |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Normal, except in event Axis: Normal, except in event |
Grouping: Yes |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with ventricular trigeminy |
Discussion:
ECG 30-6 has a PVC for every third complex. This is an example of ventricular trigeminy. In this strip, the rate is a little over 70 BPM and slightly irregular. It would be a good idea to go and manually check the pulse on the patient to evaluate for effective mechanical contractions by the PVCs. The blue arrows are there to show the underlying P waves fusing with the PVCs.
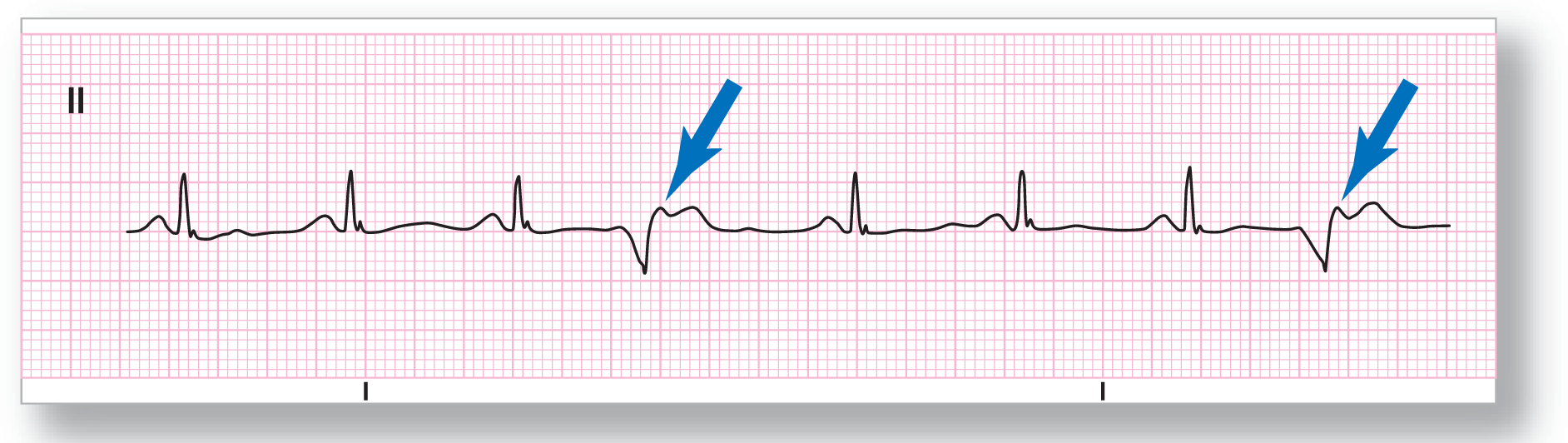
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: About 88 BPM |
PR intervals: 1:1, except in events |
|
Regularity: Regular with frequent events |
QRS width: Events are wide |
|
P waves: Present, except in events Morphology: Normal, except in events Axis: Normal, except in events |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 11:1, except in events |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with ventricular quadrigeminy |
Discussion:
ECG 30-7 shows an underlying sinus rhythm with a PVC occurring every fourth complex. This pattern for PVCs is known as ventricular quadrigeminy. The PVCs are unifocal and the coupling intervals are identical. The pauses are fully compensatory. It is interesting to note that the hump at the end of the QRS complex of the PVCs is actually the fusion of the P wave of the underlying rhythm with the PVCs.
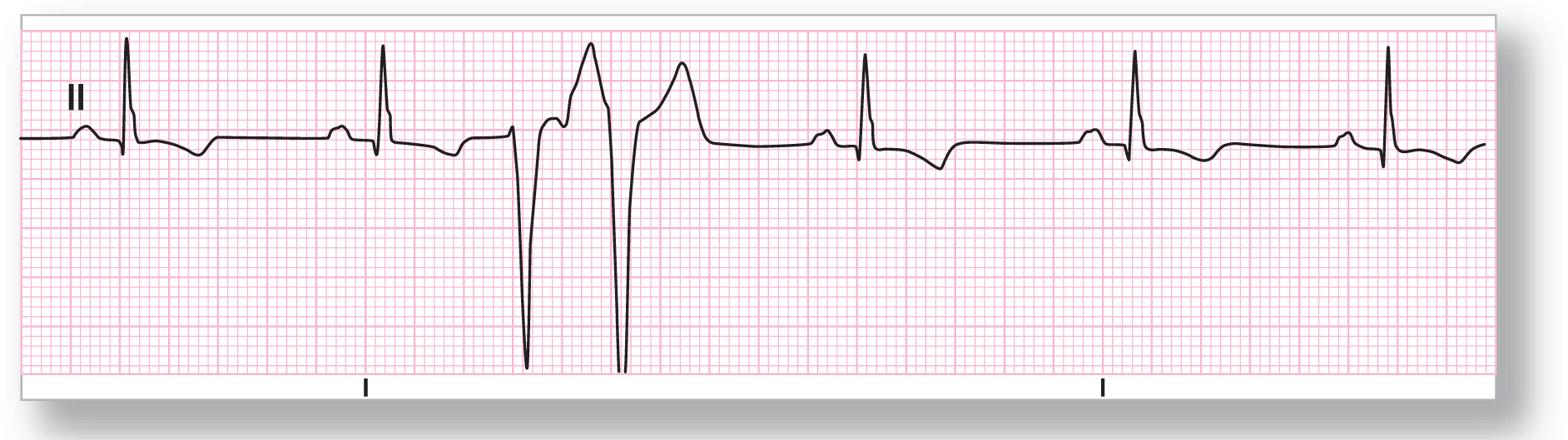
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: About 57 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in event |
|
Regularity: Regular with an event |
QRS width: Events are wide |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Normal, except in event Axis: Normal, except in event |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in event |
Rhythm: Sinus bradycardia with a unifocal couplet |
Discussion:
ECG 30-8 shows a sinus bradycardia with a unifocal couplet. Note the slight morphologic differences between the two ventricular complexes. This morphologic difference is due to fusion of the two complexes with each other or by a slight alteration in a reentry circuit.

From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: About 98 BPM |
PR intervals: Normal, except in events |
|
Regularity: Regular with an events |
QRS width: Wide |
|
P waves: Present, except in events Morphology: Normal, except in events Axis: Normal, except in events |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in events |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with a unifocal couplet and a PVC |
Discussion:
ECG 30-9 shows an underlying sinus rhythm that is undisturbed by the extra events occurring in the ventricles (P waves timing is represented by the pink dots, QRS timing by the blue dots). Notice that the pauses are fully compensatory. The P waves show through and fuse with the morphology of the PVCs at the start of the complexes. The underlying ventricular depolarizations during the sinus complexes demonstrate a varying degree of aberrancy in ventricular conduction.
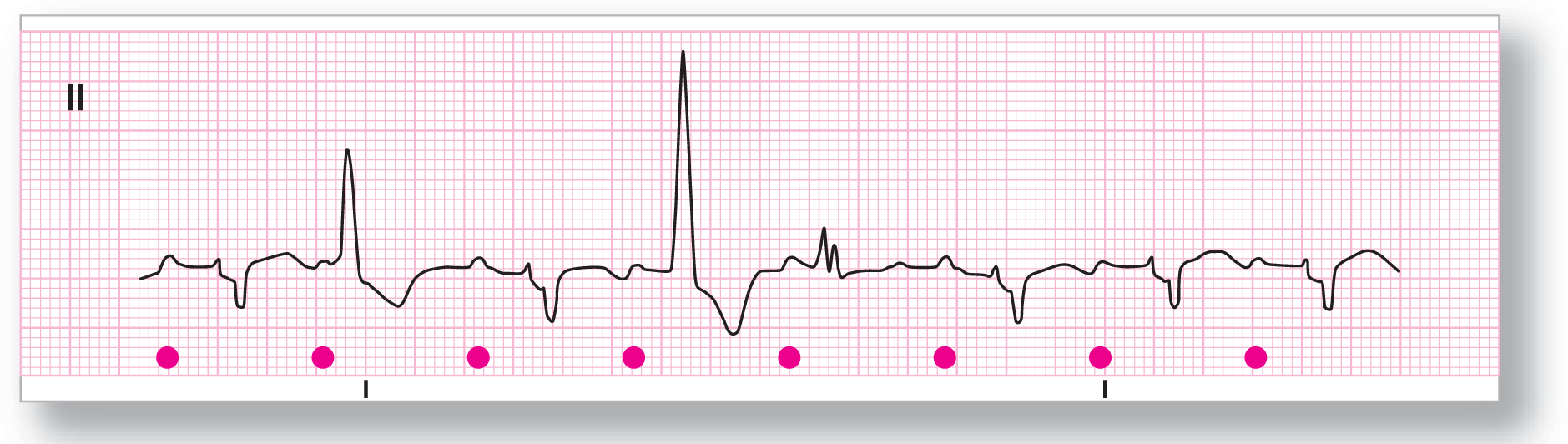
From Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD.
Description|
Rate: About 94 BPM |
PR intervals: Prolonged, except in events |
|
Regularity: Regular with an events |
QRS width: Wide in events |
|
P waves: Present, except in event Morphology: Normal, except in events Axis: Normal, except in events |
Grouping: None |
|
Dropped beats: Present |
|
|
P:QRS ratio: 1:1, except in events |
Rhythm: Sinus rhythm with frequent multifocal PVCs |
Discussion:
ECG 30-10 shows an underlying sinus rhythm with a very prolonged PR interval. There are at least two different morphologies to the ventricular complexes (complexes 2, 4, and 5), making them multifocal PVCs. (To be completely correct, complexes 4 and 5 should be considered a multifocal couplet.) The PVCs are also end-diastolic PVCs with the normal P waves occurring right before them. The pauses are fully compensatory.