

 18.01 Understanding Types of Assessments
18.01 Understanding Types of Assessments
 18.02 Performing a Security Assessment
18.02 Performing a Security Assessment
Periodic testing of computer systems and networks over time identifies security weaknesses. Security assessments are best conducted by a third party and may be required by government regulation or to acquire business contracts. As a Security+ professional, you must know when to use various tools and how to interpret their results.
1. As part of your security audit you would like to see what type of network traffic is being transmitted on the network. Which type of tool should you use?
A. Protocol analyzer
B. Port scanner
C. Vulnerability scanner
D. Password cracker
2. A network consists of 250 computers. You must determine which machines are secure and which are not. Which type of tool should you use?
A. Protocol analyzer
B. Port scanner
C. Vulnerability scanner
D. Password cracker
3. You would like to focus and track malicious activity to a particular host in your DMZ. What should you configure?
A. Honeynet
B. Honeypot
C. DMZ tracker
D. Web server
4. Which of the following would you employ to determine which TCP and UDP ports on a host are open?
A. Vulnerability scanner
B. Packet sniffer
C. Performance Monitor
D. Port scanner
5. Which procedure identifies assets, threats, and risks and also determines methods to minimize the impact of these threats?
A. Risk analysis
B. Vulnerability assessment
C. Port scanning
D. Network mapper
6. A technician must identify deviations from normal network activity. Which task must she first perform?
A. Trend analysis
B. Baseline analysis
C. Performance monitoring
D. Risk analysis
7. A developer analyzes source code to ensure there are no errors or potential security risks. Which term best identifies this activity?
A. Risk assessment
B. Patch management
C. Debugging
D. Code review
8. A Windows computer has not been patched nor have the unnecessary services been disabled. Which of the following statements is true regarding security?
A. The computer will perform faster.
B. The computer has a large attack surface.
C. The computer has a small attack surface.
D. The computer will perform slower.
9. A network security auditor simulates various network attacks against a corporate network. Which term best defines this procedure?
A. Vulnerability analysis
B. Network mapping
C. Penetration testing
D. Risk assessment
10. Your manager asks you to configure a collection of purposely vulnerable hosts in a DMZ for the purpose of tracking hacking attempts. What term best describes what you are configuring?
A. Honeynet
B. Honeypot
C. Firewall
D. Proxy server
11. You run a vulnerability scan on subnet 192.168.1.0/24. The results state TCP ports 135 through 139 are open on most hosts. What does this refer to?
A. File and Print Sharing
B. Web server
C. Mail server
D. Remote Desktop Protocol
12. You are a network consultant in charge of creating a wireless network infrastructure for a hotel. Toward the end of the implementation your team evaluates the project to ensure it meets the original stated requirements. What is this called?
A. Penetration testing
B. Risk assessment
C. Design review
D. Code review
13. After careful log examination you realize somebody has hacked into your WEP-secured home wireless network. What can you do to further secure wireless traffic?
A. Use WPA2 Enterprise.
B. Use WPA2 PSK.
C. Disable SSID broadcasting.
D. Change the SSID name.
14. What should be done to ensure your network security is effective?
A. Patch all operating systems.
B. Update the BIOS on all systems.
C. Periodically test network security controls.
D. Upgrade to the latest version of Microsoft Office.
15. Which of the following is considered passive security testing?
A. Capturing network traffic
B. Brute-force password attack
C. Dictionary-based disk decryption
D. OS fingerprinting
16. From the following list, identify the security misconfiguration:
A. A domain administrative account is used as a service account.
B. An Active Directory account is used as a service account.
C. Windows stations receive updates from a WSUS server instead of the Internet.
D. The Windows Guest account is disabled.
17. A security auditing team has been hired to conduct network penetration tests against a network. The team has not been given any data related to the network or its layout. What type of testing will the team perform?
A. Black box
B. White box
C. Gray box
D. Blue box
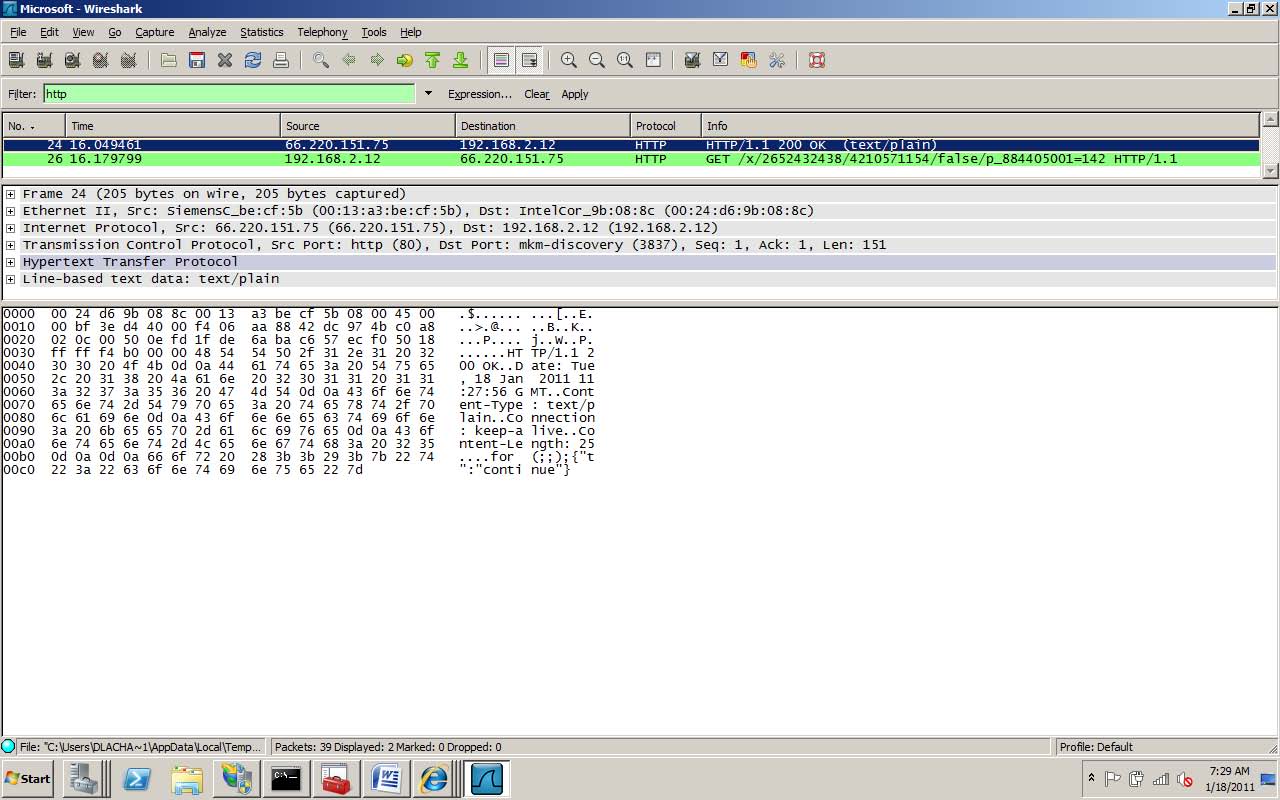
18. Refer to Figure 18-1. Which of the following statements are true? (Choose two.)
A. The web server IP address is 66.220.151.75.
B. The web server IP address is 192.168.2.12.
C. The web site is not using SSL.
D. Packet 24 is going to the web site.
FIGURE 18-1 Wireshark packet capture
19. You are having trouble pinging host 192.168.17.45; there are no replies. One of your users must use the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) against the host to run an application. You cannot test RDP for the user because you are currently logged on locally to a Linux server with only a command line. What can you use to quickly determine whether RDP is running on 192.168.17.45?
A. Packet sniffer
B. Virus scanner
C. Wireless scanner
D. Port scanner
20. After conducting a security audit, you inform the network owner that you discovered two unencrypted wireless networks. Your client asks how to best secure wireless traffic. Which of the following is the most secure wireless network encryption?
A. WEP
B. WPA
C. WPA2
D. WPA3
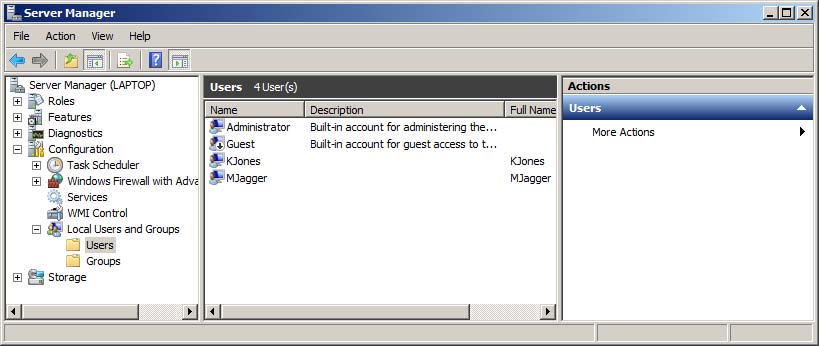
21. Refer to Figure 18-2. What configuration error would a security audit find?
A. The Administrator account should be deleted.
B. The Administrator account is enabled and has not been renamed.
C. The Guest account is enabled.
D. The Guest account should be deleted.
FIGURE 18-2 Local user accounts on a Windows server
22. A security auditor must determine what types of servers are running on a network. Which type of tool should be used?
A. Network mapper
B. Protocol analyzer
C. Port scanner
D. Virus scanner
23. A security auditor discovers open wireless networks. She must recommend a secure solution. Which of the following is the most secure wireless solution?
A. 802.1x
B. WEP
C. WPA PSK
D. Disable SSID broadcast
24. Which of the following would not be considered during a security audit?
A. Locked server rooms
B. Wireless encryption in use
C. Patch status of all hosts
D. Price of server licensing
25. While auditing a Windows Active Directory environment, you discover that administrative accounts do not have configured account lockout policies. Which of the following are security concerns? (Choose two.)
A. If account lockout is enabled, administrative accounts could be locked out as a result of repeated password attempts.
B. If account lockout is not enabled, administrative accounts could be subjected to password attacks.
C. If account lockout is enabled, administrative accounts could be subjected to password attacks.
D. If account lockout is not enabled, administrative accounts could be locked out as a result of repeated password attempts.
26. Which type of security testing provides network configuration information to testers?
A. White box
B. Black box
C. Gray box
D. Blue box
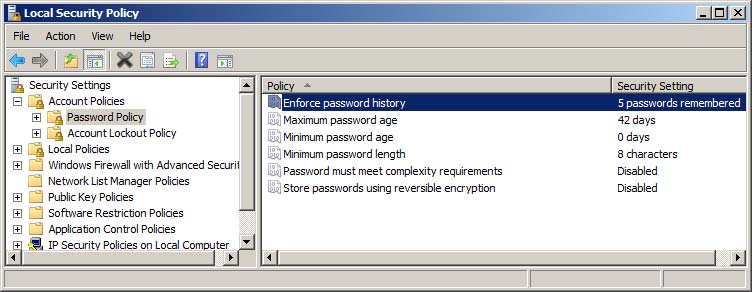
27. You are reviewing password policies during a security audit. Refer to Figure 18-3 and identify two security problems. (Choose two.)
A. The minimum password age is 0 days.
B. The password history is set only to 5.
C. The store passwords using reversible encryption option is disabled.
D. Passwords do not meet complexity requirements.
FIGURE 18-3 Local security policy password settings on a Windows computer
28. Which type of tool scans for known security threats on a group of computers?
A. Packet sniffer
B. Vulnerability scanner
C. Risk scanner
D. Port scanner
29. You would like an unused host to log zero-day exploit activity. What should you configure?
A. Patch server
B. Honeynet
C. Honeypot
D. Virus scanner
30. A large wireless network currently uses WPA PSK. As part of your network audit findings, you recommend a centralized wireless authentication option. What should you recommend?
A. RADIUS
B. WEP
C. WPA2 PSK
D. TKIP
31. You are performing a network penetration test for a client. From a command prompt you issue the command telnet smtp1.acme.com 25 to see what information is returned. Which term refers to what you have done?
A. Denial of service
B. Port scan
C. Banner grab
D. Mail grab
32. Your company hired a consultant to implement a secure VPN solution using PKI certificates and smartcard authentication. Mark, your boss, has asked you to evaluate the implementation to ensure that the solution addresses the original need. Which term best describes what you will be doing?
A. Design review
B. Application security architecture review
C. VPN review
D. Network review
33. Tribbles Inc. recently hired a security consulting firm to perform a security audit of its network at its Vulcan, Alberta, location. An excerpt of the audit findings is listed here:

What is wrong with the audit findings?
A. The subnet mask is incorrect.
B. The IP address range is incorrect.
C. The consultant ran a noncredentialed scan.
D. The consultant ran a credentialed scan.
34. A user complains that legitimate e-mail messages from some customers are incorrectly flagged as spam by the corporate mail server. How might you explain what is happening to your user?
A. The e-mail messages in question are generating false positives.
B. The false positives are generating e-mail messages.
C. The e-mail message in question are generating false negatives.
D. The false negatives are generating e-mail messages.
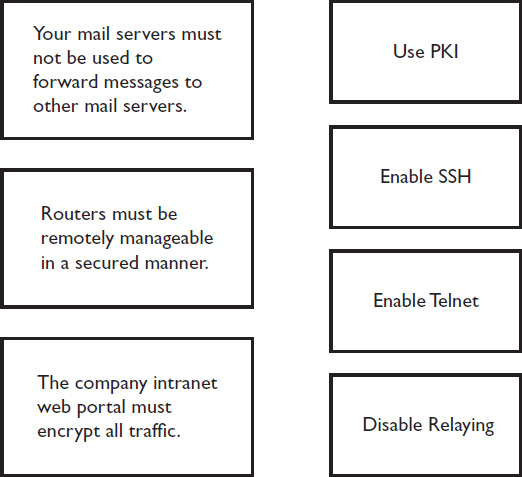
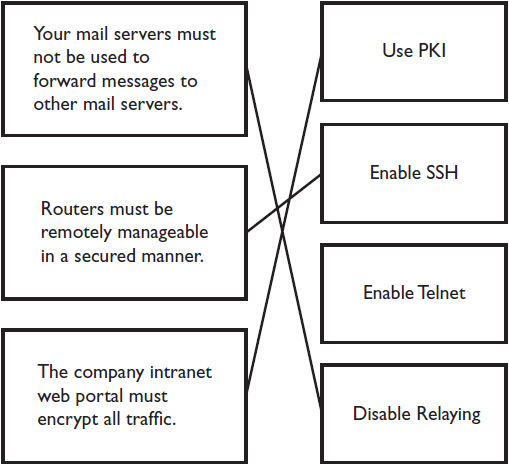
35. You are a security consultant. After performing a threat assessment on a client network, you recommend actions that should be taken. In Figure 18-4, draw a line linking the requirements on the left to the correct solution on the right.
FIGURE 18-4 Security requirements and solutions
36. You are the newly hired security officer for Jokers Inc. An existing network diagram for the Halifax location has been provided, as shown in Figure 18-5. Which recommendations should you make to secure the network infrastructure? (Choose two.)
A. Do not allow all outbound traffic through the firewalls.
B. Allow DNS replication traffic only between specific DNS hosts.
C. Do not place DNS servers in a DMZ.
D. Do not allow outbound TCP 443 traffic.
37. Acme Inc. uses the 199.126.129.0/24 network address range in its DMZ. You are configuring the firewall separating the DMZ from the private network so that traffic from DMZ hosts is allowed into the private network. You issue the command router(config)#access-list 45 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255. What is the problem with this configuration?
A. Access-list 55 must be used.
B. 192.168.1.0 is a reserved private network address.
C. The subnet mask in the router command is incorrect.
D. The router needs to be rebooted.
38. Employee laptops must be secured when employees travel for business purposes. What can you do to harden user laptops?
A. Set a CMOS password.
B. Configure disk mirroring.
C. Generate file hashes for all hard disk files.
D. Enable verbose logging.
39. When is baseline reporting useful?
A. When conducting a penetration test
B. When hardening DNS servers
C. When hardening HTTPS servers
D. When comparing normal activity with current activity
40. Why are penetration tests sometimes not recommended?
A. They can identify security threats.
B. They could degrade network performance.
C. They could generate too much logging data.
D. They are expensive.
1. A
2. C
3. B
4. D
5. A
6. B
7. D
8. B
9. C
10. A
11. A
12. C
13. B
14. C
15. A
16. A
17. A
18. A, C
19. D
20. C
21. B
22. A
23. A
24. D
25. A, B
26. A
27. A, D
28. B
29. C
30. A
31. C
32. A
33. D
34. A
35. See Figure 18-6.
FIGURE 18-6 Security requirements and solutions—the answer
36. A, B
37. B
38. A
39. D
40. B
1.  A. Protocol analyzers use a promiscuous mode network card driver that allows the capture of all network traffic. Each switch port is a collision domain that prevents capturing unicast traffic related to other hosts; however, some switches allow mirroring of all switch traffic to a specific port.
A. Protocol analyzers use a promiscuous mode network card driver that allows the capture of all network traffic. Each switch port is a collision domain that prevents capturing unicast traffic related to other hosts; however, some switches allow mirroring of all switch traffic to a specific port.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Port scanners identify running services on a host. For example, a running web server might show TCP port 80 as being open. Vulnerability scanners assess computers for weaknesses and will often generate reports. Password cracking refers to repeated attempts to guess a password and is often automated.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Port scanners identify running services on a host. For example, a running web server might show TCP port 80 as being open. Vulnerability scanners assess computers for weaknesses and will often generate reports. Password cracking refers to repeated attempts to guess a password and is often automated.
2.  C. Vulnerability scanners scan computers for known security violations and weaknesses.
C. Vulnerability scanners scan computers for known security violations and weaknesses.
 A, B, and D are incorrect. Protocol analyzers capture network traffic. Port scanners list some or all open ports on one or more hosts. Password crackers repeatedly attempt to determine a password. Although port scanners and password cracking could be utilized to test system security, a vulnerability scanner provides much more data about computer security including open ports and vulnerable password settings.
A, B, and D are incorrect. Protocol analyzers capture network traffic. Port scanners list some or all open ports on one or more hosts. Password crackers repeatedly attempt to determine a password. Although port scanners and password cracking could be utilized to test system security, a vulnerability scanner provides much more data about computer security including open ports and vulnerable password settings.
3.  B. A honeypot is an intentionally vulnerable host used to attract and track malicious activity.
B. A honeypot is an intentionally vulnerable host used to attract and track malicious activity.
 A, C, and D are incorrect. The question stated activity tracking on a single host, not a network of hosts. There is no such thing as a DMZ tracker. Web sites are not a tool to track malicious activity; web sites deliver content to web browsers.
A, C, and D are incorrect. The question stated activity tracking on a single host, not a network of hosts. There is no such thing as a DMZ tracker. Web sites are not a tool to track malicious activity; web sites deliver content to web browsers.
4.  D. Port scanners identify open ports on hosts. Personal firewall software may impede the success of port scanners. It should also be noted that port scanning can be detected.
D. Port scanners identify open ports on hosts. Personal firewall software may impede the success of port scanners. It should also be noted that port scanning can be detected.
 A, B, and C are incorrect. Vulnerability scanners can detect open ports as well as many more items; if all that is required is a list of open TCP and UDP ports, a port scanner is a better (and faster) choice. Packet sniffers capture network traffic, and from that captured traffic you can see port numbers in the TCP and UDP packet headers, but you cannot identify exactly which ports are open on a host. Performance Monitor is a Windows tool used to measure and monitor performance metrics of a Windows computer; it does not scan for open ports.
A, B, and C are incorrect. Vulnerability scanners can detect open ports as well as many more items; if all that is required is a list of open TCP and UDP ports, a port scanner is a better (and faster) choice. Packet sniffers capture network traffic, and from that captured traffic you can see port numbers in the TCP and UDP packet headers, but you cannot identify exactly which ports are open on a host. Performance Monitor is a Windows tool used to measure and monitor performance metrics of a Windows computer; it does not scan for open ports.
5.  A. Risk analysis identifies and prioritizes threats while determining how to minimize their effect on business operations.
A. Risk analysis identifies and prioritizes threats while determining how to minimize their effect on business operations.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Vulnerability assessments identify and prioritize potential threats and are performed during a risk analysis. Port scanning identifies open TCP and UDP ports; the impact of the open ports is not determined. Network mapping refers to the process of creating a map of the network layout, its configuration, and its computer systems. Threats are not identified.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Vulnerability assessments identify and prioritize potential threats and are performed during a risk analysis. Port scanning identifies open TCP and UDP ports; the impact of the open ports is not determined. Network mapping refers to the process of creating a map of the network layout, its configuration, and its computer systems. Threats are not identified.
6.  B. A baseline analysis establishes what is normal on a given network. Without this data, it is difficult to determine deviations from the norm.
B. A baseline analysis establishes what is normal on a given network. Without this data, it is difficult to determine deviations from the norm.
 A, C, and D are incorrect. Trend analysis refers to the collection of data in hopes of identifying a pattern. Performance Monitor is a tool for Windows computers that measures performance metrics such as CPU and memory utilization. Risk analysis identifies assets and related risks along with methods to minimize business disruption.
A, C, and D are incorrect. Trend analysis refers to the collection of data in hopes of identifying a pattern. Performance Monitor is a tool for Windows computers that measures performance metrics such as CPU and memory utilization. Risk analysis identifies assets and related risks along with methods to minimize business disruption.
7.  D. Code review is an examination of source code in order to uncover errors or security risks.
D. Code review is an examination of source code in order to uncover errors or security risks.
 A, B, and C are incorrect. Although risk assessment might involve code review, risk management also includes identifying assets and threat mitigation. Patch management involves the orderly application of software updates to hosts. Debugging implies the developer is aware of a specific problem with the code; analyzing code for errors would occur before debugging.
A, B, and C are incorrect. Although risk assessment might involve code review, risk management also includes identifying assets and threat mitigation. Patch management involves the orderly application of software updates to hosts. Debugging implies the developer is aware of a specific problem with the code; analyzing code for errors would occur before debugging.
8.  B. Computers with many potential vulnerabilities (software, physical) are said to have a larger attack surface than patched machines that only run software that is required. A larger attack surface means a higher degree of possibility of a machine becoming compromised.
B. Computers with many potential vulnerabilities (software, physical) are said to have a larger attack surface than patched machines that only run software that is required. A larger attack surface means a higher degree of possibility of a machine becoming compromised.
 A, C, and D are incorrect. The question asks about security, not performing faster. Computers generally run faster with patches applied and fewer services running. Because unnecessary services have not been disabled, the machine has a larger attack surface than it otherwise should. The question refers to security, not performance; the computer might very well be performing slower since extra unnecessary services may be running.
A, C, and D are incorrect. The question asks about security, not performing faster. Computers generally run faster with patches applied and fewer services running. Because unnecessary services have not been disabled, the machine has a larger attack surface than it otherwise should. The question refers to security, not performance; the computer might very well be performing slower since extra unnecessary services may be running.
9.  C. Penetration testing (pen testing) involves simulating malicious activity against hosts or entire networks in order to assess how secure they are and to identify threats. Proper written consent must be obtained prior to performing this type of testing.
C. Penetration testing (pen testing) involves simulating malicious activity against hosts or entire networks in order to assess how secure they are and to identify threats. Proper written consent must be obtained prior to performing this type of testing.
 A, B, and D are incorrect. Vulnerability analysis identifies and classifies potential threats. Network mapping plots the network layout using a discovery tool. Risk assessment does not simulate network attacks; it is used to identify business threats and how to mitigate them.
A, B, and D are incorrect. Vulnerability analysis identifies and classifies potential threats. Network mapping plots the network layout using a discovery tool. Risk assessment does not simulate network attacks; it is used to identify business threats and how to mitigate them.
10.  A. A honeynet is composed of two or more honeypots. These are intentionally vulnerable hosts used to track malicious activity.
A. A honeynet is composed of two or more honeypots. These are intentionally vulnerable hosts used to track malicious activity.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. The question stated a collection of hosts, not a single (honeypot) host. Firewalls and proxy servers should never be left intentionally vulnerable.
B, C, and D are incorrect. The question stated a collection of hosts, not a single (honeypot) host. Firewalls and proxy servers should never be left intentionally vulnerable.
11.  A. Windows File and Print Sharing generally uses TCP ports 135 to 139.
A. Windows File and Print Sharing generally uses TCP ports 135 to 139.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Web servers typically use TCP port 80 (clear text) or 443 (SSL). Mail servers use a variety of ports depending on their type and role. For example, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) servers listen on TCP port 25. Remote Desktop Protocol uses TCP port 3389.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Web servers typically use TCP port 80 (clear text) or 443 (SSL). Mail servers use a variety of ports depending on their type and role. For example, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) servers listen on TCP port 25. Remote Desktop Protocol uses TCP port 3389.
12.  C. Design review is a process whereby the original project objectives are compared against current progress to ensure the objectives are being met.
C. Design review is a process whereby the original project objectives are compared against current progress to ensure the objectives are being met.
 A, B, and D are incorrect. Penetration testing simulates attacks against hosts or networks to test their security. Risk assessment determines which assets need protection from risks and how to minimize the threat impact. A code review refers to the analysis of computer source code to ensure it functions as intended and does not contain errors or security holes.
A, B, and D are incorrect. Penetration testing simulates attacks against hosts or networks to test their security. Risk assessment determines which assets need protection from risks and how to minimize the threat impact. A code review refers to the analysis of computer source code to ensure it functions as intended and does not contain errors or security holes.
13.  B. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA2) PreShared Key (PSK) is considered more secure than Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP).
B. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA2) PreShared Key (PSK) is considered more secure than Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP).
 A, C, and D are incorrect. WPA2 Enterprise requires a central authentication server; the average user will not have one at home. Disabling Station Set Identifier (SSID) suppresses the WLAN name from appearing in Wi-Fi beacon packets, but this is easily circumvented with freely available tools. Changing the SSID name may make it difficult for a hacker to identify what they are breaking into, but WPA2 is a much more secure solution.
A, C, and D are incorrect. WPA2 Enterprise requires a central authentication server; the average user will not have one at home. Disabling Station Set Identifier (SSID) suppresses the WLAN name from appearing in Wi-Fi beacon packets, but this is easily circumvented with freely available tools. Changing the SSID name may make it difficult for a hacker to identify what they are breaking into, but WPA2 is a much more secure solution.
14.  C. Period network testing, perhaps even penetration testing, is valuable to ensure your network security controls remain valid over time.
C. Period network testing, perhaps even penetration testing, is valuable to ensure your network security controls remain valid over time.
 A, B, and D are incorrect. Patching an operating system, updating the BIOS, and upgrading Microsoft Office are all important for a single host’s security, but the question asks about network security; therefore, C is the best answer.
A, B, and D are incorrect. Patching an operating system, updating the BIOS, and upgrading Microsoft Office are all important for a single host’s security, but the question asks about network security; therefore, C is the best answer.
15.  A. Passive security testing techniques do not interfere with the normal operation of a computer system or network. Capturing network traffic simply takes a copy of network packets already being transmitted.
A. Passive security testing techniques do not interfere with the normal operation of a computer system or network. Capturing network traffic simply takes a copy of network packets already being transmitted.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Brute-force password attacks, disk decryption, and OS fingerprinting all must interact directly with a computer system and might affect the performance or normal operation of that host.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Brute-force password attacks, disk decryption, and OS fingerprinting all must interact directly with a computer system and might affect the performance or normal operation of that host.
16.  A. Windows services (and Unix and Linux daemons) must run under the context of a user account. Assigning a powerful domain administrative account presents a major threat in the event that the service is compromised; the hacker would then have domain administrative privileges. Service accounts should have only the rights and permissions required to function—nothing more. Many administrators do not force periodic password changes for service accounts, which presents yet another security risk.
A. Windows services (and Unix and Linux daemons) must run under the context of a user account. Assigning a powerful domain administrative account presents a major threat in the event that the service is compromised; the hacker would then have domain administrative privileges. Service accounts should have only the rights and permissions required to function—nothing more. Many administrators do not force periodic password changes for service accounts, which presents yet another security risk.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Some services run on Windows domain controller computers and must use an Active Directory account. Using Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to update client workstations is considered ideal; this is not a security misconfiguration. The Windows Guest account is disabled by default in newer Windows versions. It should not be enabled in the interest of security and user auditing.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Some services run on Windows domain controller computers and must use an Active Directory account. Using Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to update client workstations is considered ideal; this is not a security misconfiguration. The Windows Guest account is disabled by default in newer Windows versions. It should not be enabled in the interest of security and user auditing.
17.  A. Black-box testing refers to the process by which computer software or networks are tested where the testers have no information on how the software or networks are designed.
A. Black-box testing refers to the process by which computer software or networks are tested where the testers have no information on how the software or networks are designed.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. White-box testing means the testers have been given details regarding the item they are testing, for example, software source code or network diagrams. Testers have a minimal knowledge of the internals of software or network configuration when conducting gray-box testing. This allows testers to make better informed testing decisions. Blue-box testing does not exist; in the past, a blue box was a device used to make free long-distance telephone calls.
B, C, and D are incorrect. White-box testing means the testers have been given details regarding the item they are testing, for example, software source code or network diagrams. Testers have a minimal knowledge of the internals of software or network configuration when conducting gray-box testing. This allows testers to make better informed testing decisions. Blue-box testing does not exist; in the past, a blue box was a device used to make free long-distance telephone calls.
18.  A and C. Packet 24 shows the packet coming from 66.220.151.75 with a source port of 80 (look at the middle of the figure at the Transmission Control Protocol, Src Port area). Since web servers use port 80, we now know the IP address of the web server. Because the packet payload (bottom-right panel) contains readable text, we know the packet is not encrypted with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). We could determine this another way as well; SSL web servers normally use TCP port 443, not 80.
A and C. Packet 24 shows the packet coming from 66.220.151.75 with a source port of 80 (look at the middle of the figure at the Transmission Control Protocol, Src Port area). Since web servers use port 80, we now know the IP address of the web server. Because the packet payload (bottom-right panel) contains readable text, we know the packet is not encrypted with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). We could determine this another way as well; SSL web servers normally use TCP port 443, not 80.
 B and D are incorrect. The client station IP address is 192.168.2.12 (look at the Transmission Control Protocol destination port of 3837 in packet 24). If this were the web server, traffic would be going to either port 80 or 443. Web browsing clients are assigned a dynamic port value above 1024 (such as 3837) that is used when receiving data from the web server.
B and D are incorrect. The client station IP address is 192.168.2.12 (look at the Transmission Control Protocol destination port of 3837 in packet 24). If this were the web server, traffic would be going to either port 80 or 443. Web browsing clients are assigned a dynamic port value above 1024 (such as 3837) that is used when receiving data from the web server.
19.  D. A port scanner is a quick, simple way to determine which ports are open on a host. Even though ping packets may be blocked, RDP packets may not be.
D. A port scanner is a quick, simple way to determine which ports are open on a host. Even though ping packets may be blocked, RDP packets may not be.
 A, B, and C are incorrect. A packet sniffer captures transmitted network traffic, but it cannot determine whether RDP is available on 192.168.17.45. Virus scanners look for malicious code; they do not test for open ports on remote hosts. Wireless scanners list wireless networks within range; they do not perform port scans.
A, B, and C are incorrect. A packet sniffer captures transmitted network traffic, but it cannot determine whether RDP is available on 192.168.17.45. Virus scanners look for malicious code; they do not test for open ports on remote hosts. Wireless scanners list wireless networks within range; they do not perform port scans.
20.  C. WPA2 is the most secure option from the presented list. Unlike WPA, WPA2 must be tested and certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance. WPA2 also uses a stronger encryption implementation.
C. WPA2 is the most secure option from the presented list. Unlike WPA, WPA2 must be tested and certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance. WPA2 also uses a stronger encryption implementation.
 A, B, and D are incorrect. WEP encryption is easily broken sometimes within seconds with freely available tools. WPA supersedes WEP, but WPA2 is superior to WPA. WPA3 does not exist (yet).
A, B, and D are incorrect. WEP encryption is easily broken sometimes within seconds with freely available tools. WPA supersedes WEP, but WPA2 is superior to WPA. WPA3 does not exist (yet).
21.  B. Default administrative accounts must be renamed or disabled. Malicious users will try default admin accounts before moving on. Consider renaming the default admin account and creating a new administrator named account (as a regular user) with no rights or permissions. Always have more than one inconspicuous administrative account.
B. Default administrative accounts must be renamed or disabled. Malicious users will try default admin accounts before moving on. Consider renaming the default admin account and creating a new administrator named account (as a regular user) with no rights or permissions. Always have more than one inconspicuous administrative account.
 A, C, and D are incorrect. The Windows Administrator and Guest accounts cannot be deleted because they are built-in accounts, but they can be renamed or disabled.
A, C, and D are incorrect. The Windows Administrator and Guest accounts cannot be deleted because they are built-in accounts, but they can be renamed or disabled.
22.  A. Network mapping utilities such as the open source Cheops tool can map out a network’s layout and identify operating systems running on hosts.
A. Network mapping utilities such as the open source Cheops tool can map out a network’s layout and identify operating systems running on hosts.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Protocol analyzers capture only transmitted network traffic; they do not scan for network hosts or network configuration. Port scanners identify listening ports. Virus scanners protect against malicious software on a host; they do not scan entire networks.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Protocol analyzers capture only transmitted network traffic; they do not scan for network hosts or network configuration. Port scanners identify listening ports. Virus scanners protect against malicious software on a host; they do not scan entire networks.
23.  A. 802.1x requires that connecting hosts or users first authenticate with a central authentication server before even gaining access to the network. This is considered the most secure of the listed choices since WEP and WPA PSK do not require authentication to get on the network; only a passphrase is required. Neither of the two uses a centralized authentication server.
A. 802.1x requires that connecting hosts or users first authenticate with a central authentication server before even gaining access to the network. This is considered the most secure of the listed choices since WEP and WPA PSK do not require authentication to get on the network; only a passphrase is required. Neither of the two uses a centralized authentication server.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. WEP encryption is easily defeated with freely available tools, so it is not a secure choice. WPA PSK is more secure than WEP, but WPA2 PSK would be a more secure choice if it were listed. Disabling the SSID broadcast will stop only very inexperienced wireless hackers. 802.1x is the most secure option from the presented list.
B, C, and D are incorrect. WEP encryption is easily defeated with freely available tools, so it is not a secure choice. WPA PSK is more secure than WEP, but WPA2 PSK would be a more secure choice if it were listed. Disabling the SSID broadcast will stop only very inexperienced wireless hackers. 802.1x is the most secure option from the presented list.
24.  D. The cost of licensing software is not considered during a security audit. Ensuring license compliance might be considered but not the cost of the licenses.
D. The cost of licensing software is not considered during a security audit. Ensuring license compliance might be considered but not the cost of the licenses.
 A, B, and C are incorrect. Locked server rooms, wireless encryption, and patching status are all valid considerations during a security audit because they directly impact how secure data systems are.
A, B, and C are incorrect. Locked server rooms, wireless encryption, and patching status are all valid considerations during a security audit because they directly impact how secure data systems are.
25.  A and B. These answers present a catch-22 scenario. The best solution is to authenticate admin accounts with a smartcard. This would eliminate remote attacks on admin accounts because of the requirement of possessing a physical smartcard.
A and B. These answers present a catch-22 scenario. The best solution is to authenticate admin accounts with a smartcard. This would eliminate remote attacks on admin accounts because of the requirement of possessing a physical smartcard.
 C and D are incorrect. Account lockout impedes the success of password attacks by locking the account for a time after a small number of successive incorrect passwords. Not configuring account lockout means password attacks could run against admin accounts incessantly.
C and D are incorrect. Account lockout impedes the success of password attacks by locking the account for a time after a small number of successive incorrect passwords. Not configuring account lockout means password attacks could run against admin accounts incessantly.
26.  A. A white-box test provides testers with detailed configuration information regarding the software or network they are testing.
A. A white-box test provides testers with detailed configuration information regarding the software or network they are testing.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Black-box testing provides no information at all to system testers. Gray-box testing provides some, but not detailed, information to testers, which allows a more informed testing environment. Blue-box testing does not exist in this context.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Black-box testing provides no information at all to system testers. Gray-box testing provides some, but not detailed, information to testers, which allows a more informed testing environment. Blue-box testing does not exist in this context.
27.  A and D. The minimum password age prevents users from immediately changing their password a number of times (password history) to return to one they have already used that is easy to remember. Complexity requirements on Windows systems means the password cannot contain any variation of the username, it must be at least six characters long, it must contain an uppercase/lowercase character and number, and so on.
A and D. The minimum password age prevents users from immediately changing their password a number of times (password history) to return to one they have already used that is easy to remember. Complexity requirements on Windows systems means the password cannot contain any variation of the username, it must be at least six characters long, it must contain an uppercase/lowercase character and number, and so on.
 B and C are incorrect. Compared to answers A and D, a password history of 5 is not a security issue. Storing passwords using reversible encryption is meant to be used by specific software needing the user password. Enabling this option does not store the passwords in a secure manner.
B and C are incorrect. Compared to answers A and D, a password history of 5 is not a security issue. Storing passwords using reversible encryption is meant to be used by specific software needing the user password. Enabling this option does not store the passwords in a secure manner.
28.  B. Vulnerability scanners normally use an updated database of known security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations for various operating systems and network devices. This database is compared against a single host or a network scan to determine whether any hosts or devices are vulnerable. Reports can then be generated from the scan.
B. Vulnerability scanners normally use an updated database of known security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations for various operating systems and network devices. This database is compared against a single host or a network scan to determine whether any hosts or devices are vulnerable. Reports can then be generated from the scan.
 A, C, and D are incorrect. Packet sniffers are not designed to look for vulnerabilities; they simply capture transmitted network packets. There is no such thing as a risk scanner. Port scanners do not identify security threats; port scanners list open TCP and UDP ports.
A, C, and D are incorrect. Packet sniffers are not designed to look for vulnerabilities; they simply capture transmitted network packets. There is no such thing as a risk scanner. Port scanners do not identify security threats; port scanners list open TCP and UDP ports.
29.  C. Honeypots are intentionally exposed systems used to attract the attention of hackers or malicious code for further study.
C. Honeypots are intentionally exposed systems used to attract the attention of hackers or malicious code for further study.
 A, B, and D are incorrect. Patch servers ensure software on network hosts is kept up to date. Honeynets are a collection of two or more honeypots; the question specifically states a single host. Virus scanners would not detect zero-day exploits. A zero-day exploit is a vulnerability that has not yet been made known to the software author or virus scanner.
A, B, and D are incorrect. Patch servers ensure software on network hosts is kept up to date. Honeynets are a collection of two or more honeypots; the question specifically states a single host. Virus scanners would not detect zero-day exploits. A zero-day exploit is a vulnerability that has not yet been made known to the software author or virus scanner.
30.  A. Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) is a central server that authenticates users connecting to a network. Failure to authenticate to the RADIUS server means access to the network is denied.
A. Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) is a central server that authenticates users connecting to a network. Failure to authenticate to the RADIUS server means access to the network is denied.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. WEP is not a centralized authentication mechanism; it must be configured on each access point and client station. WPA2 PSK must also be configured on each access point and client. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) uses key mixing and packets sequence counters to enhance security. TKIP is used with WPA to address the lack of security offered by WEP.
B, C, and D are incorrect. WEP is not a centralized authentication mechanism; it must be configured on each access point and client station. WPA2 PSK must also be configured on each access point and client. Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) uses key mixing and packets sequence counters to enhance security. TKIP is used with WPA to address the lack of security offered by WEP.
31.  C. A banner grab is used to probe the listening port of a network service with the intent of learning more, such as what version of software is running.
C. A banner grab is used to probe the listening port of a network service with the intent of learning more, such as what version of software is running.
 A, B, and D are incorrect. Denial-of-service attacks render a network service unavailable for legitimate use; in this case, we have nothing more than information gathering. Port scanning returns ports in use on a host; in this example, we already know that port 25 is in a listening state. There is no such term as mail grab.
A, B, and D are incorrect. Denial-of-service attacks render a network service unavailable for legitimate use; in this case, we have nothing more than information gathering. Port scanning returns ports in use on a host; in this example, we already know that port 25 is in a listening state. There is no such term as mail grab.
32.  A. A design review ensures a solution meets stated security requirements.
A. A design review ensures a solution meets stated security requirements.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Application security architecture review is focused on a particular application and not a network VPN implementation. VPN and network review do not describe the scenario as well as design review.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Application security architecture review is focused on a particular application and not a network VPN implementation. VPN and network review do not describe the scenario as well as design review.
33.  D. The consultant ran the vulnerability scan with administrative credentials. While this is fine, a noncredentialed scan should have also been run.
D. The consultant ran the vulnerability scan with administrative credentials. While this is fine, a noncredentialed scan should have also been run.
 A, B, and C are incorrect. The subnet mask and IP address are correct. The consultant did not run a noncredential scan; they ran a credentialed scan.
A, B, and C are incorrect. The subnet mask and IP address are correct. The consultant did not run a noncredential scan; they ran a credentialed scan.
34.  A. A false positive occurs when a harmless item or event occurs but is flagged as problematic.
A. A false positive occurs when a harmless item or event occurs but is flagged as problematic.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. False positives and negatives do not generate e-mail messages, but the opposite is possible. False negatives are described as problematic security occurrences that did not generate some type of alert.
B, C, and D are incorrect. False positives and negatives do not generate e-mail messages, but the opposite is possible. False negatives are described as problematic security occurrences that did not generate some type of alert.
35.  See Figure 18-6.
See Figure 18-6.
FIGURE 18-6 Security requirements and solutions—the answer

36.  A and B. Firewalls should scrutinize not only incoming network traffic but also traffic leaving a network. This can prevent SMTP relaying, spam, DDoS attacks, and many more attacks initiated from your network to a victim host or network. DNS servers must replicate only with other known DNS servers to prevent replicating DNS records to rogue DNS hosts.
A and B. Firewalls should scrutinize not only incoming network traffic but also traffic leaving a network. This can prevent SMTP relaying, spam, DDoS attacks, and many more attacks initiated from your network to a victim host or network. DNS servers must replicate only with other known DNS servers to prevent replicating DNS records to rogue DNS hosts.
 C and D are incorrect. DNS servers can be placed in a DMZ as long as the appropriate firewall rules are in place and as long as private network DNS records are not replicated to the DMZ DNS host. HTTPS uses TCP 443, and in most cases this type of traffic should be allowed to leave a private network so users can connect to secured web sites.
C and D are incorrect. DNS servers can be placed in a DMZ as long as the appropriate firewall rules are in place and as long as private network DNS records are not replicated to the DMZ DNS host. HTTPS uses TCP 443, and in most cases this type of traffic should be allowed to leave a private network so users can connect to secured web sites.
37.  B. Reserved private network addresses such as 192.168.1.0 are not routed by Internet routers and therefore should be used only on internal networks, not on a DMZ.
B. Reserved private network addresses such as 192.168.1.0 are not routed by Internet routers and therefore should be used only on internal networks, not on a DMZ.
 A, C, and D are incorrect. The access-list value does not have to be 55. Cisco routers use the binary reverse subnet mask, so a /24 bit subnet mask (255.255.255.0) is expressed as 0.0.0.255; this is correct in this scenario. Rebooting a router after configuring access lists is not required.
A, C, and D are incorrect. The access-list value does not have to be 55. Cisco routers use the binary reverse subnet mask, so a /24 bit subnet mask (255.255.255.0) is expressed as 0.0.0.255; this is correct in this scenario. Rebooting a router after configuring access lists is not required.
38.  A. CMOS passwords prevent unauthorized persons from booting from USB or CD to bypass operating system security.
A. CMOS passwords prevent unauthorized persons from booting from USB or CD to bypass operating system security.
 B, C, and D are incorrect. Disk mirroring duplicates all disk writes to a separate disk; this is considered high availability, not hardening. File hashes are unique values for files that change in any way. This is useful for ensuring a file has not changed or been tampered with, but it does not make sense for traveling user laptops. Verbose logging is helpful when troubleshooting, but it does not secure a laptop.
B, C, and D are incorrect. Disk mirroring duplicates all disk writes to a separate disk; this is considered high availability, not hardening. File hashes are unique values for files that change in any way. This is useful for ensuring a file has not changed or been tampered with, but it does not make sense for traveling user laptops. Verbose logging is helpful when troubleshooting, but it does not secure a laptop.
39.  D. A baseline establishes what system performance looks like under normal conditions. This can be compared to current conditions to determine whether anything is out of the norm.
D. A baseline establishes what system performance looks like under normal conditions. This can be compared to current conditions to determine whether anything is out of the norm.
 A, B, and C are incorrect. Penetration testing involves security technicians issuing common attacks against networks and hosts to identify threats. Hardening hosts is unrelated to baseline reporting.
A, B, and C are incorrect. Penetration testing involves security technicians issuing common attacks against networks and hosts to identify threats. Hardening hosts is unrelated to baseline reporting.
40.  B. Penetration testing can be risky. Many techniques are involved, but the possibility of degrading network performance or crashing hosts is a distinct possibility.
B. Penetration testing can be risky. Many techniques are involved, but the possibility of degrading network performance or crashing hosts is a distinct possibility.
 A, C, and D are incorrect. Penetration tests are supposed to identify security threats; this is a good thing. Generating excessive logging and pen test costs are not as good a reason to skip a penetration test as the danger involved.
A, C, and D are incorrect. Penetration tests are supposed to identify security threats; this is a good thing. Generating excessive logging and pen test costs are not as good a reason to skip a penetration test as the danger involved.