Name
URL Access Scripting
Synopsis
The following descriptions detail the available URL Access commands (download and upload ) available for scripting.
Dictionary commands
- download
The download command downloads a file using either FTP or HTTP to the disk of the machine running the script. The web file can then be viewed with a browser locally. Any images, however, are not downloaded with the web page using HTTP, so you would have to download the images separately using the download command. download takes two required parameters: a
stringURL (as in http://www.parkerriver.com) and afile specificationobject to which the script downloads the file. Afile specificationis an AppleScript data type that represents the name and location of a file before it is actually saved to the hard disk. In other words, you can create a new file with the new file scripting addition, which will have the operating system reserve a unique path for the new file. The new file osax displays a dialog box requesting that the user choose a location and name for the new file. Figure 18-2 shows this new file dialog window.The return value for new file is a
file specificationobject. You can then download a file to this reserved file path and an actual file is saved to the hard disk with the prior specified location and name. You have to enclose the download command in atellblock targeting the URL Access Scripting application, as in:tell app "URL Access Scripting" to download¬ "http://129.69.59.34/index.html" to filespec
The rest of the download command’s parameters are optional. The return value of the download command is a reference to the file after it is downloaded:
file "Macintosh HD:Desktop Folder:parkerriver.com"
The following example encloses the download script in a
try/on error/endtryblock to catch any errors that are associated with the download, including the user clicking the Cancel button on the new file dialog window. The script also uses awithtimeoutstatement to give the download command two minutes to complete its task, before AppleScript raises an “Apple event timed out” error. By default, AppleScript gives an application 60 seconds to respond to an Apple event before the script times out. See Chapter 7 , for more details onwith timeout.The following are
downloadproperties:-
tofile specification This property is a required labeled parameter that identifies the
filespecificationobject to which the web page will be downloaded. For example:download "ftp://www.parkerriver.com/resources.html" to filespec
-
replacing yes/no If a file already exists at this location, then
replacing yesreplaces that file with the new one, as in:download "http://my.yahoo.com" to filespec with progress¬ replacing yes
-
unpacking boolean If you are downloading a BinHexed and/or stuffed file, then this labeled parameter (e.g.,
unpacking true) attempts to decode and/or decompress the file. AppleScript uses the Stuffit Engine extension, which is inside the System Folder's Extensions folder, to decode and decompress files. An example of a file that would have to be decoded and unstuffed would be a file that has been encoded using the BinHex protocol and compressed using Aladdin Stuffit. These files sometimes have suffixes such as “afile.sit.hqx.”-
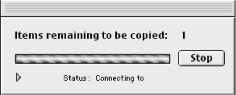
progress boolean We all know that downloading web files with FTP or HTTP, particularly those that involve some server-side processing, can be a tricky and lengthy process. This parameter requests the display of a progress bar during the web-file download, which is a good idea. A progress bar is a horizontal cylinder shape that gradually fills with solid color as a task is executed. Figure 18-3 shows the progress bar. Just add a
with progressto your download command:download "http://www.highendDesign.com/index.html" to filespec¬ with progress
The progress bar includes a Stop button that causes AppleScript to quit the script (with error number -128) containing the download command if the user clicks the button.
-
form datastring You can post some data to a Common Gateway Interface script on the Web with the optional parameter
form data. This would be the equivalent of a web user filling out a form and submitting it to a CGI script on a web server. A CGI script intercepts web data on a server and processes it in some way (such as storing the user data in a database) before sending back a response page to the user. The following is an example use of the download command with thewith dataparameter:tell application "URL Access Scripting" to download URLstr to¬ filespec form data "username=adminenter&password=mypass#$"¬ with progress
The
with dataparameter is a URL-encoded string, in other words, one or more name/value pairs (e.g.,firstname=Bruce) separated by a “&” character.-
directory listing boolean This
true/falsevalue is designed to download a directory listing using FTP. The result is a text file in which each line is of the form “-rw-rw-rw- 1 owner group 17 Oct 29 1998 myfile.txt.” An example of using this labeled parameter is:download "ftp://www.parkerriver.com" to filespec with¬ directory listing, authentication and progress
-
download directoryboolean This
true/falsevalue is designed to download a directory of files using FTP. With this parameter, the script should download the files to afolder alias:alias "Macintosh HD:Desktop Folder:WebFiles"
An example of using this labeled parameter is:
download "ftp://www.parkerriver.com" to folder_alias with¬ download directory, authentication and progress
-
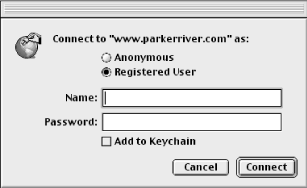
authentication boolean This optional parameter displays a dialog box asking for a username and password, if the web server requires authentication for FTP and HTTP requests. Figure 18-4 shows this authentication window. An example of using this parameter is:
tell app "URL Access Scripting" to download¬ "ftp://my.yahoo.com" to filespec with authentication try -- catch any errors caused during the download (* get a file specification first, and optionally give the new file a default name *) set filespec to new file with prompt¬ "Choose a location for the Web file" default name¬ "resources.html" with timeout of 120 seconds (* give the download command two minutes before the Apple Event times out *) tell application "URL Access Scripting" to download¬ "ftp://www.parkerriver.com/resources.html" to¬ filespec with progress and authentication end timeout on error errmesg number errNum if errNum is -128 then (* if the user cancels the file dialog or the progress dialog *) display dialog "You quit before downloading a file: the applet " &¬ "will quit now." else display dialog (errNum as text) & ": " & errmesg &¬ return & return & "An error occurred during the " &¬ "download. Try running the applet again." end if end try
-
- upload
Use this command if you want your script to upload a file or a directory of files with FTP. Like the download command, you can optionally provide a username and password for authentication (usually required for FTP uploads) and display a progress-bar window. If your script is uploading an entire directory of files, you can use the choose folder scripting addition to allow the script user to choose the directory to upload. choose folder returns an
aliasto the folder that the user chooses. You can then use thisaliasas a parameter to the upload command:tell app "URL Access Scripting" to upload folder_alias to¬ "ftp:// www. mysite.org" with authentication
You have to enclose the upload command in a
tellstatement targeting the URL Access Scripting application. Chapter 7 describes thetellstatement.-
to string Provide the receiving server with this URL
string, as in “ftp://www.parkerriver.com”. You have to include the protocol (“ftp://”) part of the URL. An example is:upload myfile to "ftp://www.mysite.org"
-
replacing yes/no If a version of the uploaded file already exists on the server, then the upload-command default is
replacing no. If you want to replace any existing files, use:upload myfile to "ftp://www.mysite.org" replacing yes
-
progress boolean Display a progress bar for longer tasks such as uploading a directory of files. For example:
upload myfolder to "ftp://www.mysite.org/newfiles/" with¬ authentication and progress
The default value for this parameter is
false.-
binhexingboolean The default value for the binhexing parameter is
true. This encodes the uploaded files for safer transfer across the network. If you do not want to binhex the files, usebinhexing falsein your upload command:upload myfile to "ftp://www.mysite.org" replacing yes¬ binhexing false
-
upload directoryboolean This
true/falseparameter uploads an entire directory of files. An example of using the upload directory parameter is:tell application "URL Access Scripting" to (upload fol_alias¬ to "ftp://www.parkerriver.com/" with progress,¬ upload directory and authentication)
This parameter is
falseby default.-
authenticationboolean Many FTP sites require the user to be authenticated with the username and password before they are allowed to upload any files or directories. If you use
authentication trueorwith authenticationwith your upload command, then the script will display an authentication dialog window that looks like Figure 18-4. This parameter isfalseby default. For example:tell application "URL Access Scripting" try -- catch any upload errors set fil to (choose file with prompt¬ "Choose a file to upload") set bool to (upload fil to¬ "ftp://www.parkerriver.com/" with authentication and¬ progress) on error errmesg number errnum if errnum is not -128 then display dialog (errnum as text) & ": " & errmesg &¬ return & return & "Applet quitting." return end if end try end tell
-