In this chapter, you apply your skills in multiplying polynomials to the process of simplifying polynomial expressions.
Identifying Polynomial Expressions
A polynomial expression is composed of polynomials only and can contain grouping symbols, multiplication, addition, subtraction, and raising to nonzero powers only.
Problem Specify whether the expression is a polynomial expression.
a. 5 + 2(a − 5)
b. 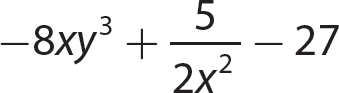
c. (2x − 1)(3x − 4) + (x − 1)2
d. 4(x −3 − y2) + 5(x + y −1)
e. 
f. 2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5(x − 4)]
Solution
a. 5 + 2(a − 5)

Step 1. Check whether the expression meets the criteria for a polynomial expression.
5 + 2(a − 5) is composed of polynomials and contains permissible components, so it is a polynomial expression.
b. 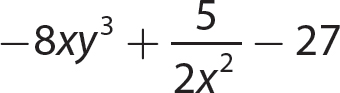

Step 1. Check whether the expression meets the criteria for a polynomial expression.
 is not a polynomial expression because it contains division by x2.
is not a polynomial expression because it contains division by x2.
c. (2x − 1)(3x − 4) + (x − 1)2

Step 1. Check whether the expression meets the criteria for a polynomial expression.
(2x − 1)(3x − 4) + (x − 1)2 is composed of polynomials and contains permissible components, so it is a polynomial expression.
d. 4(x−3 − y2) + 5(x + y−1)

Step 1. Check whether the expression meets the criteria for a polynomial expression.
4(x −3 − y2) + 5(x + y −1) is not a polynomial expression because it is not composed of polynomials due to negative exponents.
e. 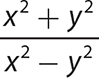

Step 1. Check whether the expression meets the criteria for a polynomial expression.
 is not a polynomial expression because it contains division by a non-constant polynomial.
is not a polynomial expression because it contains division by a non-constant polynomial.
f. 2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5(x − 4)]

Step 1. Check whether the expression meets the criteria for a polynomial expression.
2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5(x − 4)] is composed of polynomials and contains permissible components, so it is a polynomial expression.
Simplifying Polynomial Expressions
When you simplify polynomial expressions, you proceed in an orderly fashion so that you do not violate the order of operations for real numbers. After all, the variables in polynomials are simply stand-ins for real numbers, so it is important that what you do is consistent with the rules for working with real numbers.

Simplifying Polynomial Expressions
To simplify a polynomial expression:
1. Simplify within grouping symbols, if any. Start with the innermost grouping symbol and work outward.
2. Do powers, if indicated.
3. Do multiplication, if indicated.
4. Simplify the result.
Problem Simplify.
a. 5 + 2(a − 5)
b. − 3(y + 4) + 8y
c. 9xy − x(3y − 5x) − 2x2
d. (2x − 1)(3x − 4) + (x − 1)2
e. 2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5(x − 4)]
f. 2(x + 1)2
Solution
a. 5 + 2(a − 5)

Step 1. Do multiplication: 2(a − 5).
5 + 2(a − 5)
= 5 + 2a − 10
Step 2. Simplify the result.
= 2a − 5
Step 3. Review the main steps.
5 + 2(a − 5) = 5 + 2a − 10 = 2a − 5
b. − 3(y + 4) + 8y

Step 1. Do multiplication: − 3(y + 4).
− 3(y + 4) + 8y
= − 3y − 12 + 8y
Step 2. Simplify the result.
= 5y − 12
Step 3. Review the main steps.
− 3(y + 4) + 8y = − 3y − 12 + 8y = 5y − 12
c. 9xy − x(3y − 5x) − 2x2

Step 1. Do multiplication: − x(3y − 5x).
9xy − x(3y − 5x) − 2x2
= 9xy − 3xy + 5x2 − 2x2
Step 2. Simplify the result.
= 3x2 + 6xy Write answer in descending powers of x.
Step 3. Review the main steps.
9xy − x(3y − 5x) − 2x2 = 9xy − 3xy + 5x2 − 2x2 = 3x2 + 6xy
d. (2x − 1)(3x − 4) + (x − 1)2

Step 1. Do the power: (x − 1)2.
(2x − 1)(3x − 4) + (x − 1)2
(2x − 1)(3x − 4) + x2 − 2x + 1
Step 2. Do multiplication: (2x − 1)(3x − 4).
= 6x2 − 11x + 4 + x2 − 2x + 1
Step 3. Simplify the results.
= 7x2 − 13x + 5
Step 4. Review the main steps.
(2x − 1)(3x − 4) + (x − 1)2 = 6x2 − 11x + 4 + x2 − 2x + 1 = 7x2 − 13x + 5
e. 2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5(x − 4)]

Step 1. Simplify within the brackets. First, do multiplication: 5(x − 4).
2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5(x − 4)]
2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5x − 20]
Step 2. Simplify 3x + 5x − 20 within the brackets.
= 2x2 − x − 4[8x − 20]
Step 3. Do multiplication: − 4[8x − 20].
= 2x2 − x − 32x + 80
Step 4. Simplify the result.
= 2x2 − 33x + 80
Step 5. Review the main steps.
2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5(x − 4)] = 2x2 − x − 4[3x + 5x − 20]
2x2 − x − 4[8x − 20]
2x2 − x − 32x + 80 = 2x2 − 33x + 80
f. 2(x + 1)2

Step 1. Do the power: (x + 1)2.
= 2(x2 + 2x + 1)
Step 2. Do multiplication: 2(x2 + 2x + 1).
= 2x2 + 4x + 2
Step 3. Review the main steps.
2(x + 1)2 = 2(x2 + 2x + 1) = 2x2 + 4x + 2
Exercise 10

Simplify.
1. 8 +2(x − 5)
2. −7(y − 4)+ 9y
3. 10xy − x(5y − 3x) − 4x2
4. (3x − 1)(2x − 5)+(x +1)2
5. 3x2 − 4x − 5[x − 2(x − 8)]
6. − x(x + 4)+5(x − 2)
7. (a − 5)(a +2) − (a − 6)(a − 4)
8. 5x2 − (− 3xy − 2y2)
9. x2 − [2x − x(3x − 1)]+ 6x
10. (4x2y5)(− 2xy3)(− 3xy) − 15x2 y3(2x2 y6 + 2)