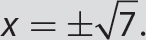Quadratic equations in the variable x can always be put in the standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0. This type of equation is always solvable for the variable x, and each result is a root of the quadratic equation. In one instance the solution will yield only complex number roots. This case will be singled out in the discussion that follows. You will get a feel for the several ways of solving quadratic equations by starting with simple equations and working up to the most general equations. The discussion will be restricted to real number solutions. When instructions are given to solve the system, then you are to find all real numbers x that will make the equation true. These values (if any) are the real roots of the quadratic equation.
Solving Quadratic Equations of the Form ax2 + c = 0
Normally, the first step in solving a quadratic equation is to put it in standard form. However, if there is no x term, that is, if the coefficient b is 0, then you have a simple way to solve such quadratic equations.
Problem Solve x2 = −4.
Solution

Step 1. Because the square of a real number is never negative, there is no real number solution to the system.
Problem Solve x2 = 7.
Solution

Step 1. Solve for x2.
x2 = 7
Step 2. Because both sides are nonnegative, take the square root of both sides.
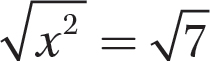
Step 3. Simplify and write the solution.
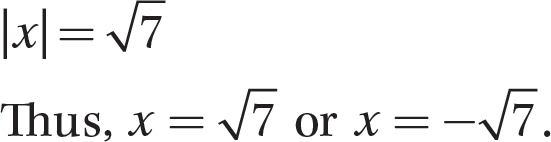
As you gain more experience, the solution of an equation such as 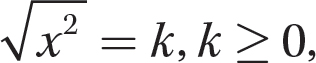 , can be considerably shortened if you remember that
, can be considerably shortened if you remember that 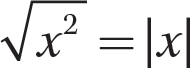 and apply that idea mentally. You can write the solution immediately as
and apply that idea mentally. You can write the solution immediately as 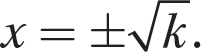
Problem Solve x2 −6 = 0.
Solution

Step 1. Solve for x2 to obtain the form for a quick solution.
x2 = 6
Step 2. Write the solution.
The solution is 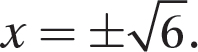
Problem Solve 3x2 = 48.
Solution

Step 1. Solve for x2 to obtain the form for a quick solution.
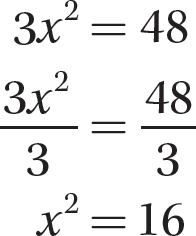
Step 2. Write the solution.
The solution is 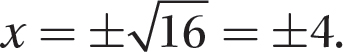 .
.
When the coefficient b of ax2 + bx + c = 0 is not 0, the quick solution method does not work. Instead, you have three common methods for solving the equation: (1) by factoring, (2) by completing the square, and (3) by using the quadratic formula.
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring
When you solve quadratic equations by factoring, you use the following property of 0.

Zero Factor Property
If the product of two numbers is 0, then at least one of the numbers is 0.
Problem Solve by factoring.
a. x2 + 2x = 0
b. x2 + x = 6
c. x2 – 4x = -4
Solution
a. x2 + 2x = 0

Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
x2 + 2x = 0 is in standard form because only a zero term is on the right side.
Step 2. Use the distributive property to factor the left side of the equation.
x(x + 2) = 0
Step 3. Use the zero factor property to separate the factors.
Thus, x = 0 or x + 2 = 0.
Step 4. Solve the resulting linear equations.
The solution is x = or x = −2.
b. x2 + x = 6

Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
x2 + x−6 = 0
Step 2. Factor.
(x−2)(x + 3) = 0
Step 3. Use the zero factor property to separate the factors.
Thus, x−2 = 0 or x + 3 = 0.
Step 4. Solve the resulting linear equations.
The solution is x = 2 or x = −3.
c. x2 – 4x = -4

Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
x2 −4x + 4 = 0
Step 2. Factor.
(x – 2) (x – 2) = 0
(x – 2)2 = 0
Step 3. Write the quick solution.
(x – 2)2 = 0
x – 2 = ±0 = 0
The solution is x = 2.
Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
You also can use the technique of completing the square to solve quadratic equations. This technique starts off differently in that you do not begin by putting the equation in standard form.
Problem Solve x2 −2x = 6 by completing the square.
Solution

Step 1. Complete the square on the left side by adding the square of 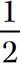 the coefficient of x, being sure to maintain the balance of the equation by adding the same quantity to the right side.
the coefficient of x, being sure to maintain the balance of the equation by adding the same quantity to the right side.
x2 −2x + = 6 +
x2−2x + 1 = 6 + 1
Step 2. Factor the left side.
(x + 1)(x + 1) = 7
(x + 1)2 = 7
Step 3. Solve using the quick solution method.
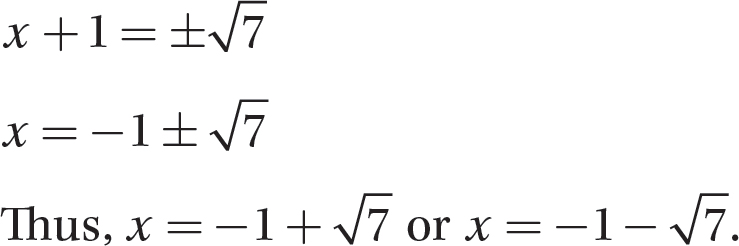
Solving Quadratic Equations by Using the Quadratic Formula
Having illustrated several useful approaches, it turns out there is one technique that will always solve any quadratic equation that is in standard form. This method is solving by using the quadratic formula.

Quadratic Formula
The solution of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 is given by the formula 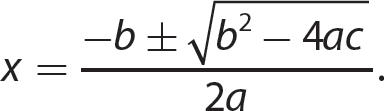 . The quantity under the radical, b2 −4ac, is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation.
. The quantity under the radical, b2 −4ac, is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation.
If b2 −4ac = 0, there is only one root for the equation. If b2 −4ac > 0, there are two real number roots. And if b2 −4ac < 0, there is no real number solution. In the latter case, both roots are complex numbers because this solution involves the square root of a negative number.
Problem Solve by using the quadratic formula.
a. 2x2 + 11x + 5 = 0
b. 3x2 −2x + 11 = 0
c. 2x2 + 2x−5 = 0
d. x2 −6x + 9 = 0
Solution
a. 2x2 + 11x + 5 = 0
Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
2x2 + 11x + 5 = 0 is in standard form.
Step 2. Identify the coefficients a, b, and c.
a = 2, b = 11, and c = 5
Step 3. Substitute the values of the coefficients into the quadratic formula and evaluate.
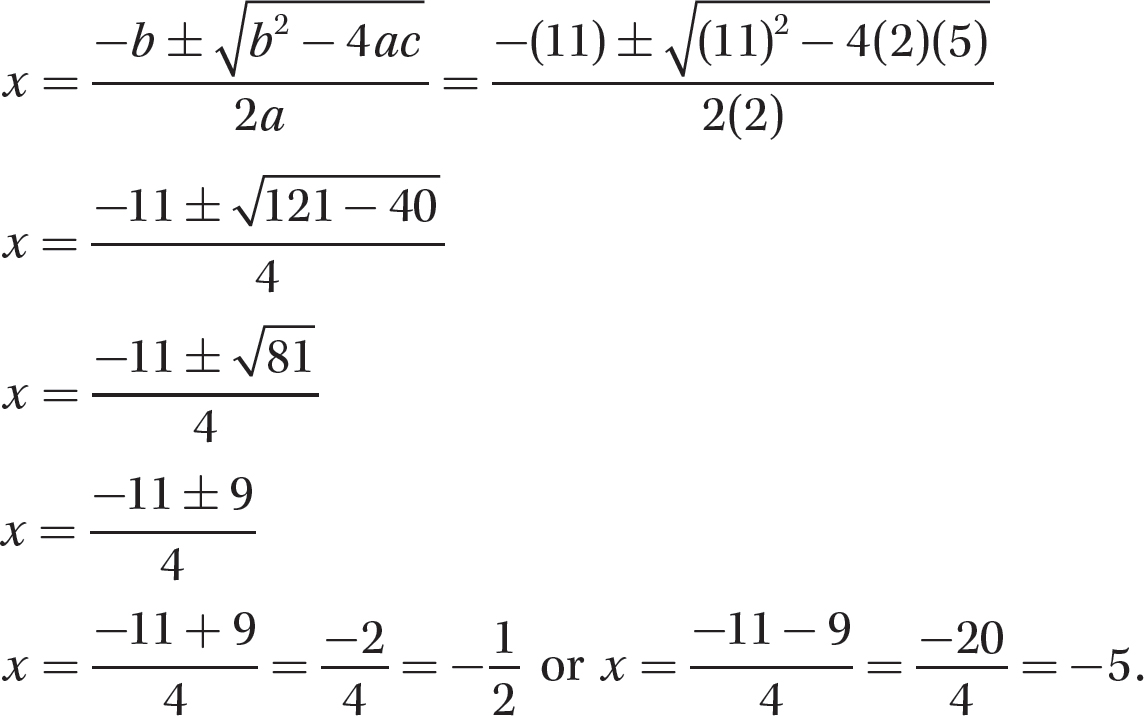
Step 4. State the solution.
The solution is 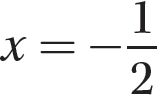 or x = −5.
or x = −5.
b. 3x2 −2x + 11 = 0
Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
3x2 −2x + 11 = 0 is in standard form.
Step 2. Identify the coefficients a, b, and c.
a= 3, b =− 2, and c=11
Step 3. Substitute the values of the coefficients into the quadratic formula and evaluate.

Step 4. State the solution.
Because the discriminant is negative, there is no real number solution for 3x2 −2x + 11 = 0.
c. 2x2 + 2x−5 = 0
Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
2x2 + 2x−5 = 0 is in standard form.
Step 2. Identify the coefficients a, b, and c.
a= 2, b= 2, and c =− 5
Step 3. Substitute the values of the coefficients into the quadratic formula and evaluate.
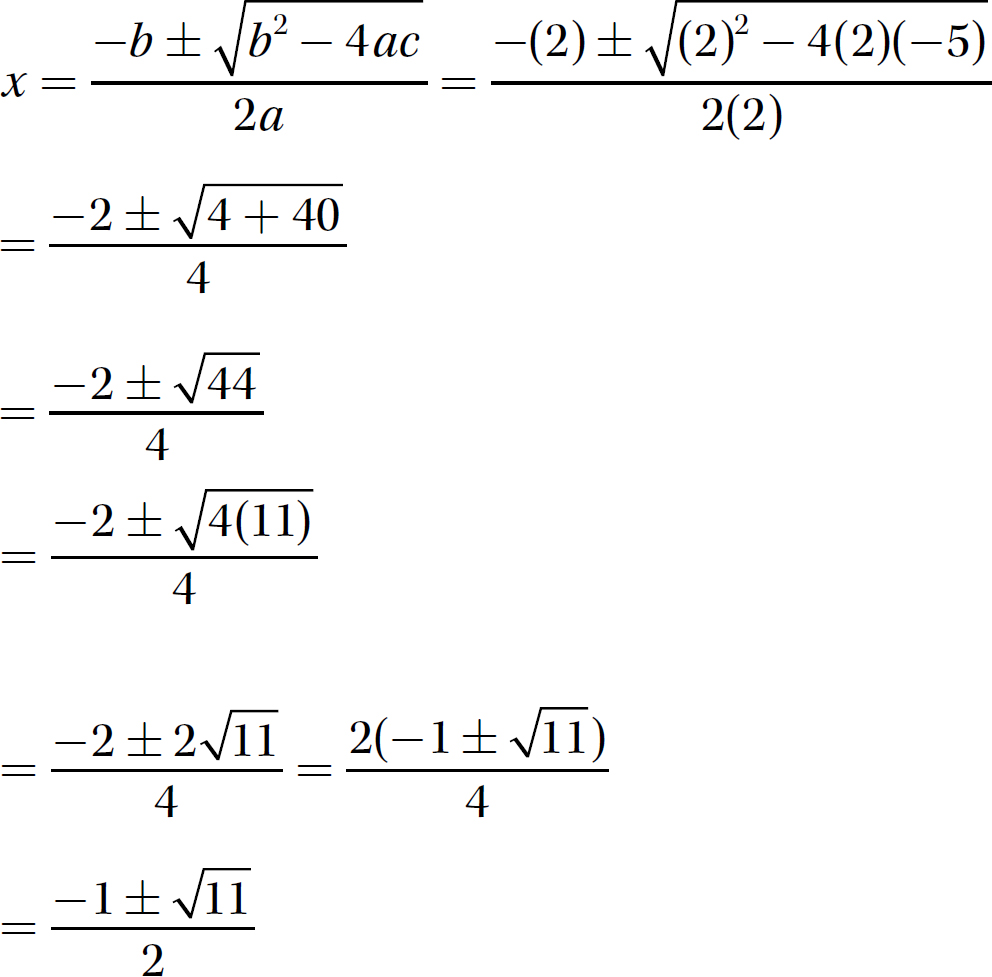
Note: Writing 44 as 4(11) allows you to take the square root of 4, which is 2, and place it in front of the square root radical as a coefficient.
Step 4. State the solution.
The solution is 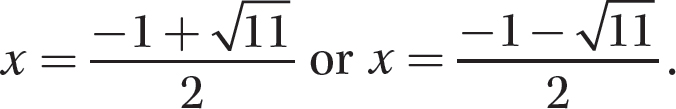
d. x2 −6x + 9 = 0
Step 1. Put the equation in standard form.
x2 −6x + 9 = 0 is in standard form.
Step 2. Identify the coefficients a, b, and c.
a = 1, b = −6, and c = 9
Step 3. Substitute the values of the coefficients into the quadratic formula and evaluate.
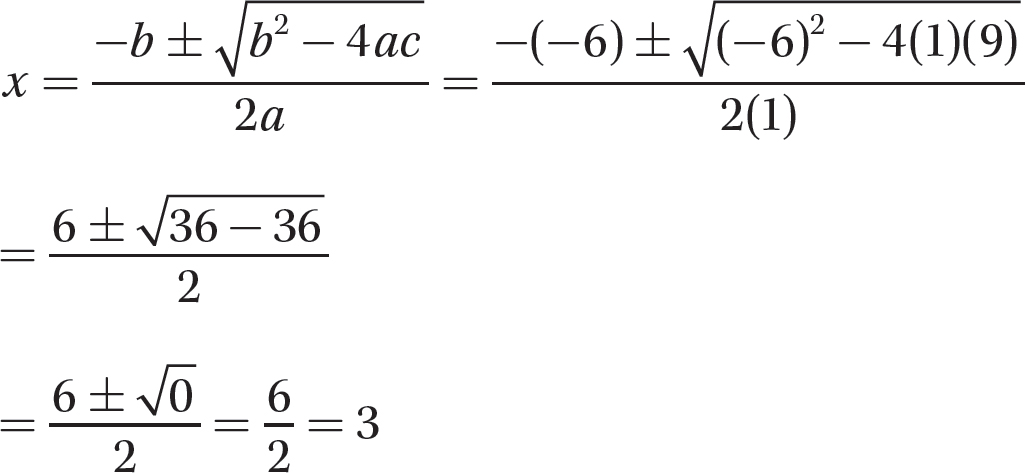
Step 4. State the solution.
The solution is x = 3.

Exercise 15
1. Solve x2 −x−6 = 0 by factoring.
2. Solve x2 + 6x = −5 by completing the square.
3. Solve 3x2 −5x + 1 = 0 by using the quadratic formula.
For 4–10, solve by any method.
4. x2 – 6 = 8
5. x2 – 3x + 2 = 0
6. 9x2 + 18 x – 17 = 0
7. 6x2 – 12x + 7 = 0
8. x2 – 10 x = -25
9. – x2 = – 9
10. 6x2 = x +2
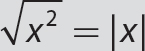 was discussed at length in
was discussed at length in 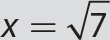 or
or 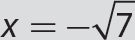 is usually written
is usually written