This chapter presents rules for multiplying polynomials. You use the properties of real numbers and the rules of exponents when you multiply polynomials.
Multiplying Monomials

Multiplying Monomials
To multiply monomials, (1) multiply the numerical coefficients, (2) multiply the variable factors using rules for exponents, and (3) use the product of the numerical coefficients as the coefficient of the product of the variable factors to obtain the answer.
Problem Find the product.
a. (5x5y3)(3x2y6)
b. (−2a3b4)(8ab2)
c. (6x)(−2x)
d. (−10x3)(4x2)
e. (4x2y5)(−2xy3)(−3xy)
f. (x)(2)
Solution
a. (5x5y3)(3x2y6)

Step 1. Multiply the numerical coefficients.
(5)(3) = 15
Step 2. Multiply the variable factors.
(x5y3)(x2y6) = x7y9
Step 3. Use the product in step 1 as the coefficient of x7y9.
(5x5y3)(3x2y6) = 15x7y9
b. (−2a3b4)(8ab2)

Step 1. Multiply the numerical coefficients.
(−2)(8) = −16
Step 2. Multiply the variable factors.
(a3b4)(ab2) = a4b6
Step 3. Use the product in step 1 as the coefficient of a4b6.
(−2a3b4)(8ab2) = − 16a4b6
c. (6x)(−2x)

Step 1. Multiply the numerical coefficients.
(6)(−2) = −12
Step 2. Multiply the variable factors.
(x)(x) = x2
Step 3. Use the product in step 1 as the coefficient of x2.
(6x)(−2x) = −12x2
d. (−10x3)(4x2)

Step 1. Multiply the numerical coefficients.
(−10)(4) = −40
Step 2. Multiply the variable factors.
(x3)(x2) = x5
Step 3. Use the product in step 1 as the coefficient of x5.
(−10x3)(4x2) = −40x5
e. (4x2y5)(−2xy3)(−3xy)

Step 1. Multiply the numerical coefficients.
(4)(−2)(−3) = 24
Step 2. Multiply the variable factors.
(x2y5)(xy3)(xy) = x4y9
Step 3. Use the product in step 1 as the coefficient of x4y9.
(4x2y5)(−2xy3)(−3xy) = 24x4y9
f. (x)(2)

Step 1. Multiply the numerical coefficients.
(1)(2) = 2
Step 2. Multiply the variable factors.
There is only one variable factor, x.
Step 3. Use the product in step 1 as the coefficient of x.
(x)(2) = 2x
Multiplying Polynomials by Monomials

Multiplying a Polynomial by a Monomial
To multiply a polynomial by a monomial, multiply each term of the polynomial by the monomial.
This rule is a direct application of the distributive property for real numbers.
Problem Find the product.
a. 2(x + 5)
b. x(3x − 2)
c. −8a3b5(2a2 −7ab2 −3)
d. x2(2x4 + 4x3 −3x + 6)
Solution
a. 2(x + 5)

Step 1. Multiply each term of the polynomial by the monomial.
2(x + 5)
= 2 ⋅ x + 2 ⋅ 5
= 2x + 10
b. x(3x − 2)

Step 1. Multiply each term of the polynomial by the monomial.
x(3x − 2)
= x ⋅ 3x − x ⋅ 2
= 3x2 − 2x
c. −8a3b5(2a2 −7ab2 −3)

Step 1. Multiply each term of the polynomial by the monomial.
−8a3b5(2a2−7ab2−3)
= (−8a3b5)(2a2)−(−8a3b5)(7ab2)−(−8a3b5)(3)
= −16a5b5 + 56a4b7 + 24a3b5
d. x2(2x4 + 4x3 −3x + 6)

Step 1. Multiply each term of the polynomial by the monomial.
x2(2x4 + 4x3−3x + 6)
= x2 · 2x4 + x2 · 4x3−x2 · 3x + x2 · 6
= 2x6 + 4x5−3x3 + 6x2
Multiplying Binomials

Multiplying Two Binomials
To multiply two binomials, multiply all the terms of the second binomial by each term of the first binomial and then simplify.
Problem Find the product.
a. (2x + 3)(x − 5)
b. (a + b)(c + d)
Solution
a. (2x + 3)(x − 5)

Step 1. Multiply all the terms of the second binomial by each term of the first binomial.
(2x + 3)(x−5)
= 2x · x + 2x · −5 + 3 · x + 3 · −5 Note: Mentally do this step.
= 2x2 −10x + 3x−15
Step 2. Simplify.
= 2x2 −7x−15
Step 3. Review your main result.
(2x + 3)(x−5) = 2x2 −7x−15
b. (a + b)(c + d)

Step 1. Multiply all the terms of the second binomial by each term of the first binomial.
(a + b)(c + d)
= a · c + a · d + b · c + b · d Note: Mentally do this step.
= ac + ad + bc + bd
Step 2. Simplify.
There are no like terms, so ac + ad + bc + bd is simplified.
Step 3. Review your main result.
(a + b)(c + d) = ac + ad + bc + bd
The FOIL Method
From the last problem, you can see that to find the product of two binomials, you compute four products, called partial products, using the terms of the two binomials. The FOIL method is a quick way to get those four partial products. Here is how FOIL works for finding the four partial products for (a + b)(c + d).
1. Multiply the two First terms: a ⋅ c.
2. Multiply the two Outer terms: a ⋅ d.
3. Multiply the two Inner terms: b ⋅ c.
4. Multiply the two Last terms: b ⋅ d.
Notice that FOIL is an acronym for first, outer, inner, and last. The inner and outer partial products are the middle terms.
Here is an example.
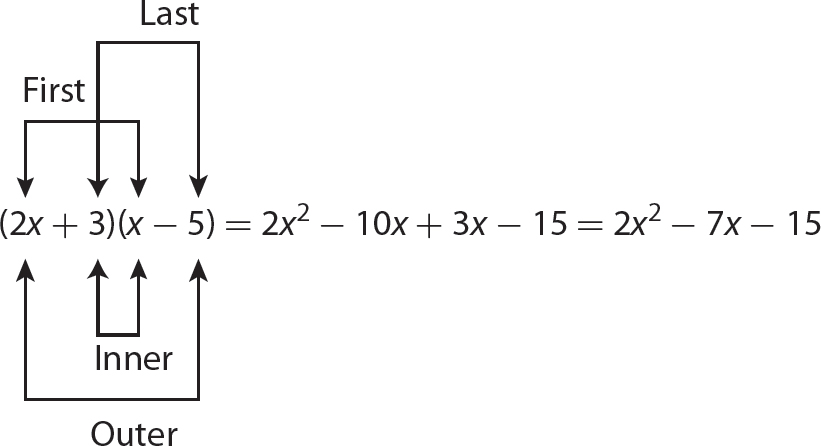
Problem Find the product using the FOIL method.
a. (5x + 4)(2x − 3)
b. (x − 2)(x − 5)
c. (x − 2)(x + 5)
d. (x + y)2
Solution
a. (5x + 4)(2x − 3)

Step 1. Find the partial products using the acronym FOIL.
(5x + 4)(2x−3)
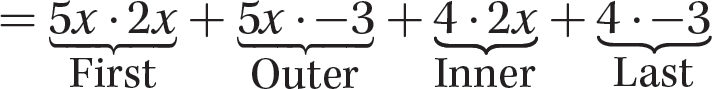 Note: Mentally do this step.
Note: Mentally do this step.
= 10x2 − 15x + 8x − 12
Step 2. Simplify.
= 10x2 − 7x − 12
Step 3. Review your main result.
(5x + 4)(2x−3) = 10x2 −7x−12
b. (x − 2)(x − 5)

Step 1. Find the partial products using the acronym FOIL.
(x−2)(x−5)

x2 − 5x − 2x + 10
Step 2. Simplify.
= x2−7x + 10
Step 3. Review your main result.
(x−2)(x + 5) = x2−7x + 10
c. (x−2)(x + 5)

Step 1. Find the partial products using the acronym FOIL.
(x−2)(x + 5)
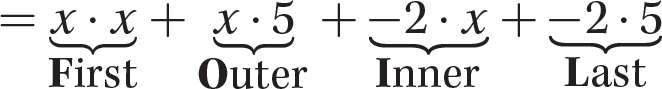
= x2 + 5x −2x − 10
Step 2. Simplify.
= x2 + 3x−10
Step 3. Review your main result.
(x−2)(x + 5) = x2 + 3x−10
d. (x + y)2

Step 1. Write as a product.
(x + y)2 = (x + y)(x + y)
Step 2. Find the partial products using the acronym FOIL.
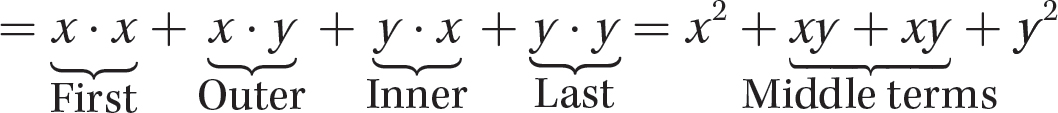
Step 3. Simplify.
= x2 + 2xy + y2
Step 4. Review the main steps.
(x + y)2 = (x + y)(x + y) = x2 + 2xy + y2
Multiplying Polynomials

Multiplying Two Polynomials
To multiply two polynomials, multiply all the terms of the second polynomial by each term of the first polynomial and then simplify.
Problem Find the product.
a. (2x−1)(3x2−5x + 4)
b. (4x2 + 2x−5)(2x2−x−3)
c. (x−2)(x2 + 2x + 4)
Solution
a. (2x−1)(3x2−5x + 4)

Step 1. Multiply all the terms of the second polynomial by each term of the first polynomial.
(2x−1)(3x2−5x + 4)
= 2x · 3x2 + 2x · −5x + 2x · 4 + −1 · 3x2 + −1 · −5x + −5x + 1 · 4 Note: Mentally do this step.
= 6x3 −10x2 + 8x−3x2 + 5x−4
Step 2. Simplify.
= 6x3 −13x2 + 13x−4
b. (4x2 + 2x−5)(2x2−x−3)

Step 1. Multiply all the terms of the second polynomial by each term of the first polynomial.
(4x2 + 2x−5)(2x2−x−3)
= 4x2 · 2x2 + 4x2 · −x + 4x2 · −3 + 2x · 2x2 + 2x · −x + 2x · −3 + −5 · 2x2 + −5 · −x + −5 · −3
= 8x4 −4x3 −12x2 + 4x3 −2x2 −6x−10x2 + 5x + 15
Step 2. Simplify.
= 8x4 −24x2 −x + 15
c. (x−2)(x2 + 2x + 4)

Step 1. Multiply all the terms of the second polynomial by each term of the first polynomial.
(x−2)(x2 + 2x + 4)
= x · x2 + x · 2x + x · 4 + −2 · x2 + −2 · 2x + −2 · 4
= x3 + 2x2 + 4x−2x2 −4x−8
Step 2. Simplify.
= x3 − 8
Special Products
The answer to part c of the last problem is an example of the “difference of two cubes.” It is a special product. Here is a list of special products that you need to know for algebra.

Special Products
Perfect Squares
(x + y)2 = x2 + 2xy + y2
(x−y)2 = x2−2xy + y2
Difference of Two Squares
(x + y)(x−y) = x2−y2
Perfect Cubes
(x + y)3 = x3 + 3x2y + 3xy2 + y3
(x−y)3 = x3−3x2y + 3xy2−y3
Sum of Two Cubes
(x + y)(x2−xy + y2) = x3 + y3
Difference of Two Cubes
(x−y)(x2 + xy + y2) = x3−y3
Exercise 9

Find the product.
1. (4x5y3)(−3x2y3)
2. (−8a4b3)(5ab2)
3. (−10x3)(−2x2)
4. (−3x2y5)(6xy4)(−2xy)
5. 3(x − 5)
6. x(3x2 − 4)
7. −2a2b3(3a2 − 5ab2 − 10)
8. (2x − 3)(x + 4)
9. (x + 4)(x + 5)
10. (x − 4)(x − 5)
11. (x + 4)(x − 5)
12. (x − 4)(x + 5)
13. (x − 1)(2x2 − 5x + 3)
14. (2x2 + x − 3)(5x2 − x − 2)
15. (x − y)2
16. (x + y)(x − y)
17. (x + y)3
18. (x − y)3
19. (x + y)(x2 − xy + y2)
20. (x − y)(x2 + xy + y2)