CHAPTER 13
Conic Sections
The circle is one member of a family of objects called conic sections. Each member of the family can be seen in the cross section of a cone, depending upon the angle of the cut. More importantly, for each conic section there is an equation which produces that conic when graphed. The equations also have similarities, so it makes sense to look at them as a group.
Circles
When a cone is sliced parallel to the base of the cone, the cross section is a circle. The radius of the circle is larger when the slice is closer to the base and smaller when the slice is closer to the tip.
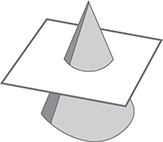
Just as you can find the equation that describes a graph that is a line, it is possible to find an equation that describes the graph of a circle. The equation comes from the definition of a circle: the set of all points at a fixed distance, called the radius, from a fixed point, called the center.
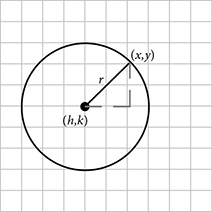
If the center is the point (h, k) and the radius is r, then every point (x, y) that sits on the circle is r units from (h, k). Apply the distance formula.
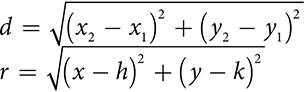
Square both sides to eliminate the radical and you have the equation of a circle.
(x − h)2 + (y − k)2 = r2
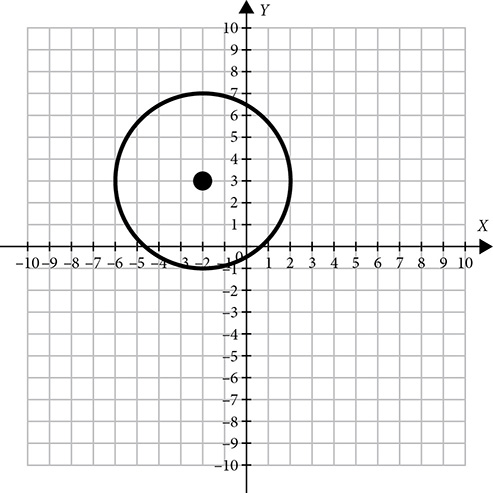
EXAMPLE
If the center of the circle is at the origin, the equation simplifies to x2 + y2 = r2.
EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE
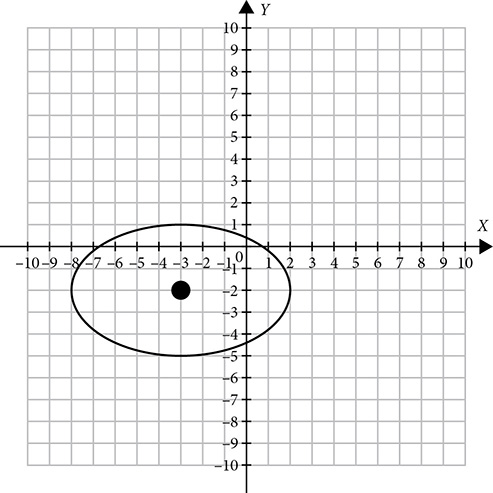
Ellipses
The ellipse, or oval, is another member of the family of conic sections, but it is created when the slice is not quite parallel to the base but on a slight tilt.

The points of a circle are all the same distance from the center, but that is not true for the ellipse. An ellipse is longer in one direction than the other. The ellipse has a center, which will appear in the equation, and the definition talks about distance from two focal points. The focal points always sit on the major axis and the distance between them determines how close to or far from a circle the ellipse is.
The definition of an ellipse says that it is the set of all points for which the total distance from the first focal point and from the second focal point is equal to a fixed constant.
The equation of an ellipse is similar to the equation of a circle, but the ellipse does not have a single radius. It has a longer major axis and a shorter minor axis. Suppose you rewrite the equation of a circle by dividing each term by r2. It would look like this:
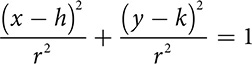 .
.
The r2 in the first denominator gives you information to help you sketch the graph. Move r units left and r units right from the center. The r2 in the second denominator says move r units up and r units down. That’s great for a circle, but for an ellipse, left-right movement will be different from up-down movement. Sometimes left-right will be larger; sometimes up-down will be larger. So the equation of the circle gets modified to produce the equation of an ellipse.
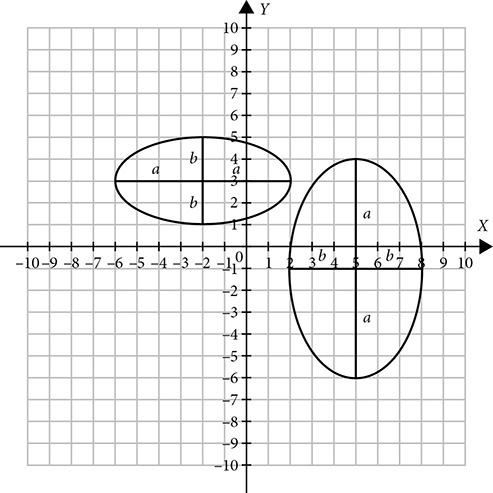
 Wider than it is tall:
Wider than it is tall: 
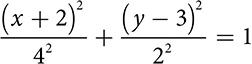
 Taller than it is wide:
Taller than it is wide: 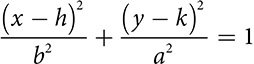

The letter a denotes half of the major axis and the letter b stands for half the minor axis, so the length of the major axis is 2a and the length of the minor axis is 2b. The number in the denominator under x tells you how far to move left and right, and the denominator under y tells you how to move up and down.
To graph an ellipse, you can follow the same basic steps as graphing a circle, but the left-right movement will be different from the up-down movement.
Parabolas
The conic section called a parabola is created when the cone is sliced at a steeper angle so that rather than entering on one side and exiting on the other, the plane slicing through enters on one side and exits at the base. It’s not vertical; that’s saved for the fourth conic.
The parabola is defined as the set of all points equidistant from a point called the focus and a line called the directrix. The vertex, or turning point, is midway between the focus and the directrix.
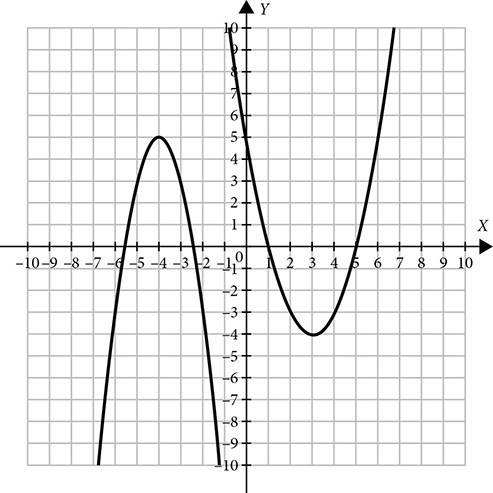
You may already be familiar with the parabola as the shape of the graph of a quadratic equation  . You can also look at what’s called the vertex form of the equation, which is easy to graph and in which you may see some similarity to the other conics. It describes a parabola whose vertex is the point (h, k). The sign of a shows the direction in which the parabola opens and the absolute value of a indicates the width of the parabola.
. You can also look at what’s called the vertex form of the equation, which is easy to graph and in which you may see some similarity to the other conics. It describes a parabola whose vertex is the point (h, k). The sign of a shows the direction in which the parabola opens and the absolute value of a indicates the width of the parabola.
Parabola that opens up or opens down: 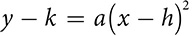
EXAMPLE
There is another possibility you may not have seen in algebra:
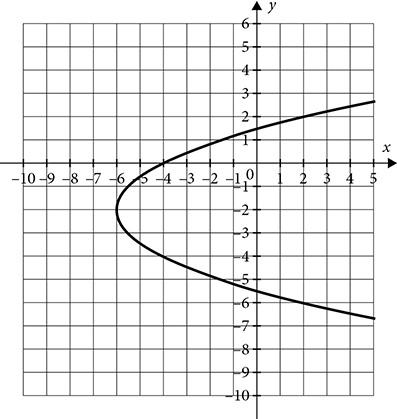
 Parabola that opens right or left
Parabola that opens right or left  .
.
EXAMPLE
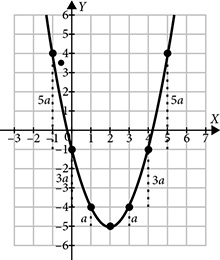
The larger the absolute value of a, the narrower the parabola will be. The actual value of a depends on the distance between the focus and the vertex. The bigger that distance is, the smaller a will be and the wider the parabola will be.
EXAMPLE
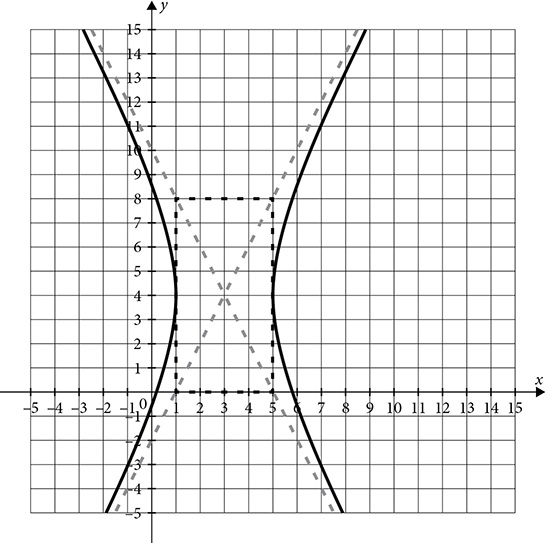
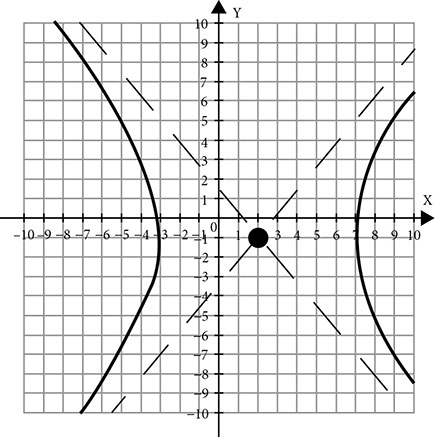
Hyperbolas
The final conic is the most dramatic shape. The hyperbola is created by slicing vertically through a double cone, creating two curves that open away from one another like wings.

The hyperbola has an equation very similar to the ellipse, but rather than adding the terms, it subtracts. There are a lot of variations on the equation, because of the length of axes and the direction of opening.
 Opening left and right
Opening left and right  or
or 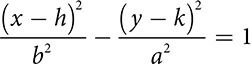
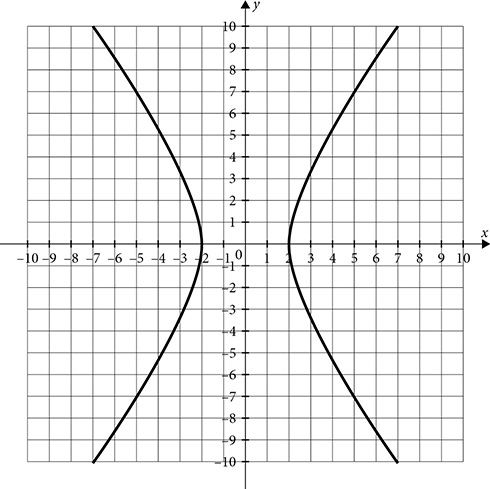
 Opening up and down
Opening up and down 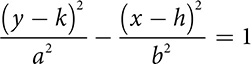 or
or 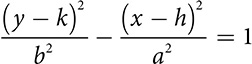


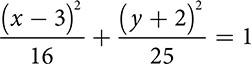 ?
? ?
?
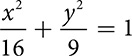 and
and  .
. .
.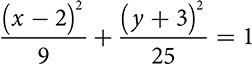 .
.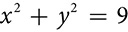 ,
,  , and
, and  .
.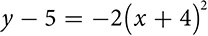 and on the right
and on the right 
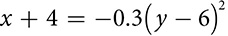 . On the lower right is
. On the lower right is 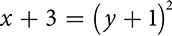 .
.
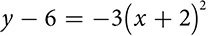
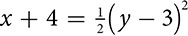
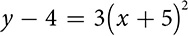

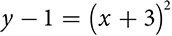
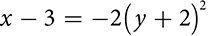
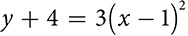
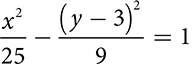

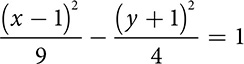


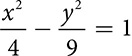 .
. .
.