IMPORTANT FORMULAS AND CONDITIONS
Chapter 5
1. Optimal Decision Making: MB = MC
2. Opportunity Cost from a Production Possibility Curve (PPC):
Good X: The slope of the PPC
Good Y: The inverse of the slope of the PPC
Chapter 6
1. Market Equilibrium:
Qd = Qs
2. Shortage:
Qd – Qs
3. Surplus:
Qs – Qd
4. Total Welfare:
= Consumer surplus + Producer surplus
Chapter 7
1. Price Elasticity of Demand:
Ed = (%D in quantity demanded of good X)/(%D in the price of good X)
2. Percentage Change:
%D = 100 × (New value – Old value)/ Old value
3. Total Revenue:
= Price × Quantity demanded
4. Income Elasticity:
EI = (%D Qd good X)/(%D income)
5. Cross-Price Elasticity:
Ex,y = (%D Qd good X)/(%D price good Y)
6. Price Elasticity of Supply:
Es = (%D in quantity supplied of good X)/(%D in the price of good X)
7. Marginal Utility:
MU = DTU/DQ
8. Utility Maximizing Rule:
MUx/Px = MUy/Py or MUx/MUy = Px/Py
9. Revenue from a Tariff:
= Per-Unit Tariff × Units Imported
Chapter 8
1. Accounting Profit:
TR – Explicit costs
2. Economic Profit:
TR – Explicit costs – Implicit costs
3. Marginal Product of Labor:
MPL = D in TPL/D in L
4. Average Product of Labor:
APL = TPL/L
5. Total Costs:
TC = TVC + TFC
6. Marginal Costs:
MC = DTVC/DQ
7. Average Fixed Cost:
AFC = TFC/Q
8. Average Variable Cost:
AVC = TVC/Q
9. Average Total Cost:
ATC = TC/Q = AFC + AVC
10. Marginal Cost and Marginal Product of Labor:
MC = w/MPL
11. Average Variable Cost and Average Product of Labor:
AVC = w/APL
Chapter 9
1. Profit Maximization Point:
MR = MC
2. Demand for Firm’s Product (Perfectly Competitive Market):
P = MR = AR
3. Profit:
P = TR - TC = P × qe - TC = qe × (P - ATC)
4. Breakeven Point:
P = ATC
5. Shutdown Point:
P < AVC or TR < TVC
6. Allocative Efficiency:
Produce output q where Pc = MR = MC
7. Excess Capacity in Monopolistic Competition:
Qatc – Qmc
8. Perfectly Competitive Long-Run Equilibrium:
P = MR = AR = MC = ATC
9. Monopoly Long-Run Equilibrium:
Pm > MR = MC
Chapter 10
1. Marginal Revenue Product:
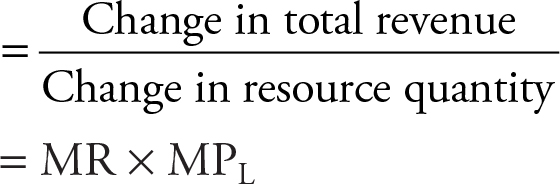
a. Under perfectly competitive price-taking conditions:
MRPc = MR × MPL = P × MPL
b. Under conditions of market power, MR < P:
MRPm = MR × MPL < MRPc
2. Marginal Resource Cost:

3. Least-Cost Hiring Rule:
MPL/PL = MPK/PK or equivalently,
MPL/MPK = PL/PK
4. Profit Maximizing Resource Employment:
MRP = MRC
5. Monopsony Hiring Decision:
MFC = MRP > W
Chapter 11
1. Socially Optimal Output:
MSB = MSC
2. Marginal Tax Rate:
= (D taxes due)/(D taxable income)
3. Average Tax Rate:
= (Total taxes due)/(Total taxable income)