You’ll now create a program that combines many of the programming techniques you’ve learned throughout this book. I’ve introduced each programming technique and block previously with short example programs, but now you’ll see how to combine them in a larger, more sophisticated program.
In this chapter, you’ll create a program that lets you play an Etch-A-Sketch-like game on the EV3. You’ll create drawings on the EV3 screen using the Large Motors as input knobs, and you’ll use the Touch Sensor and Color Sensor as additional input controls (see Figure 17-1).
An Etch-A-Sketch device draws lines on its screen as you turn the knobs, as if moving a pencil across a piece of paper. The left knob controls the horizontal position of the pencil (X), while the right knob controls the vertical position (Y). This behavior is surprisingly easy to re-create in an EV3 program, as shown in Figure 17-2.
The program repeatedly displays a new dot (small circle) on the EV3 screen at a location specified by an X-and-Y coordinate. The program determines these coordinates using the Rotation Sensors in the Large Motors. The white dial (motor B) controls the X position, while the red dial (motor C) controls the Y position. As the program adds dots to the screen, you can create drawings by “moving the pencil” using SK3TCHBOT’s dials.
To begin, create a new project called SK3TCHBOT-Games with a program called Etch-A-Sketch. To display the dot, you’ll simply use a Display block in Shapes – Circle mode, but you’ll need to create two My Blocks to clear the screen and to calculate the coordinates where the dot must be displayed.
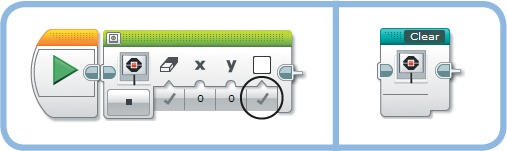
The Display block doesn’t have an option to clear the screen without displaying something new, but you can mimic this action by displaying a single white pixel while clearing the rest of the screen. Configure a Display block as shown in Figure 17-3, and turn it into a My Block called Clear.
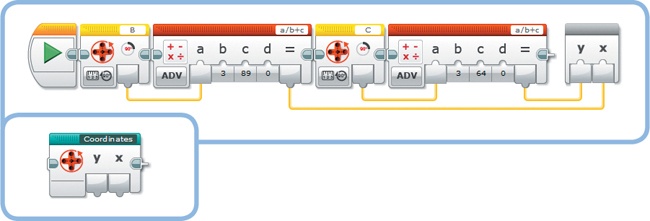
You’ll now create a My Block called Coordinates, as shown in Figure 17-4. It has two Numeric output values (X and Y) that you’ll use to control the position of each new dot. Let’s have a look at how this block calculates the X coordinate.
Recall that a Rotation Sensor gives you the number of degrees a motor has turned since the start of the program. In principle, you could use the sensor value from motor B to control the X coordinate directly. However, this would make the pencil move a bit too fast: Turning the white dial for only 180 degrees would move the pencil across the entire screen. (The screen has 178 pixels in the X direction.)
To make more precise movements, divide the number of degrees by 3 so that turning the white dial for 180 degrees draws a line across only a third of the screen. Add 89 (half of 178) to the result of this division so that the dot is displayed in the middle of the screen when the degrees value is 0 at the start of the program.
The procedure for the Y coordinate is similar, except that you’ll use motor C and you’ll add 64 to the division (there are 128 pixels in the Y direction). Because motor C is mounted upside down, you get a negative degrees value if you turn it in the direction of the red arrow in Figure 17-1. Consequently, the pencil moves upward (vertical red arrow), which is opposite to the positive Y direction (vertical blue arrow).
To create the My Block, place two Motor Rotation blocks and two Math blocks on the canvas, and turn them into a My Block with two Numeric outputs called Coordinates, as shown in Figure 17-4.
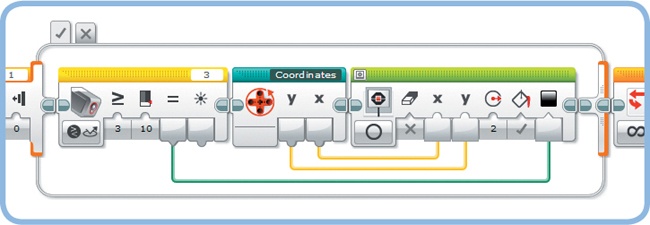
Now that you’ve created the essential components of the flow diagram in Figure 17-2, finish the program as shown in Figure 17-5. Besides the two My Blocks, the program contains a Display block configured to display the dot (small circle) at the required coordinates and a Loop block to repeat the program. Download the program to your robot and test it before expanding the program in the next section.
Figure 17-4. The Coordinates My Block calculates the X and Y coordinates of the dot that will be displayed on the EV3 screen. The completed My Block is shown to the left.
Figure 17-5. The basic Etch-A-Sketch program. Note that the Display block is configured not to clear the screen; this ensures that previously printed dots remain visible when another dot is added to the screen.
Note
If you’re experiencing problems while creating this program, download the finished program from http://ev3.robotsquare.com/ and compare it to your own program.
The basic Etch-A-Sketch program is fun, but you can give it more functionality by expanding it, as shown in Figure 17-6. You’ll use the Touch Sensor to temporarily stop drawing, the Color Sensor to turn the pencil into an eraser, the Center EV3 button to clear the screen, and the Up and Down buttons to change the pencil size.
To make it easier to spot potential problems, be sure to test your program each time you add a new feature. When you’re ready, you’ll be challenged to further expand the program with new Discoveries.
While drawing, you’ll sometimes want to lift the pencil in order to move to a new position without creating any lines. To accomplish this, make the program draw new dots only if the Touch Sensor is released (see Figure 17-7). If the Touch Sensor is pressed, nothing happens. (The false tab of the Switch block doesn’t contain any blocks.)
Now you’ll add an eraser tool to your program by making it draw white dots when you trigger the Color Sensor, as shown in Figure 17-8. By drawing white dots, you can effectively erase parts of your drawing, which is helpful in case you make mistakes.
When you cover the Color Sensor with your finger, the reflected light intensity measurement increases beyond 10%, and the Compare Result of the Color Sensor block becomes true, causing the Display block’s Color setting to become white. When you remove your finger from the sensor, the output becomes false, and the Display block continues to add black circles to the screen.
To clear the screen when you press the Center button, add a Switch block and a Clear block (see Figure 17-9). If none of the EV3 buttons are pressed, nothing happens. (The No Buttons case, which is also the default case, does not contain any blocks.)
Finally, you’ll expand the program to set the pencil size with the Up and Down buttons on the EV3 brick. To do so, you’ll use a variable called Size to control the value of the Radius setting on the Display block. Then, you’ll add blocks that allow you to modify the Size variable using the EV3 buttons.
To begin, define a Numeric variable called Size and add two Variable blocks to your current program, as shown in Figure 17-10. The first Variable block initializes the value to 1. The second block sends the Size value to the Radius setting of the Display block. Consequently, the Radius is 1 as long as you don’t change the variable’s value.
Next, add two cases (tabs) to the Switch block that you’ve configured previously. Add one case for the Up button and another for the Down button.
If you press the Up button, the Size variable should be incremented, as shown in Figure 17-11. Because the screen is quite small, you’ll limit the Size value to 25. In other words, you’ll increment the variable only if its current value is less than 25, as determined by a Compare block. If the Size value is 25 and you try to increase it further, the Compare block outputs false, you’ll hear a beep, and the value isn’t changed. Finally, a Wait block pauses the program until you release the Up button. (If you do not wait for a release, the program continues to repeat, incrementing the variable each time it goes through the loop.)
The variable should be decremented (lowered by 1) if you press the Down button, but only if the current Size value is greater than 1 so you don’t end up displaying a circle with a negative or 0 radius (which wouldn’t work). If the Size value is 1 and you try to decrease it further, the Compare block outputs false, you’ll hear a beep, and the variable’s value isn’t changed (see Figure 17-12).
Congratulations! You’ve finished the Etch-A-Sketch program. Once you’ve verified that your program works, see whether you can further expand the program using Discoveries #112 through #114.
In this chapter, you created a program that combines many of the programming techniques you’ve learned throughout this book. If you enjoyed creating this program, I recommend you explore Discoveries #115 and #116. In the next part of this book, you’ll learn how to build and program two more cool robots.