1 SAP S/4HANA for the Supply Chain
This chapter highlights the transition from the SAP Business Suite into the SAP S/4HANA product offering. It discusses the key concepts added via SAP HANA, such as the in-memory processing database architecture, the introduction of SAP Fiori apps for transactional processing, and on-premise versus cloud offerings.
The objective of this chapter is to outline how three key pillars—the database technology, business process improvements, and IT flexibility—come together in SAP S/4HANA to offer substantial business benefits.
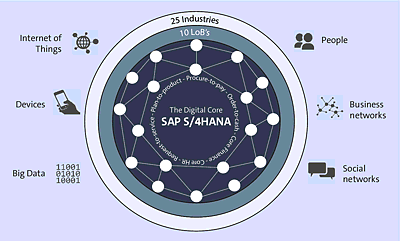
Within this chapter, we’ll discuss how SAP S/4HANA is evolving to meet the needs of future technology innovation. SAP S/4HANA has been built for the digital age to accommodate mobile processing and changes in the marketplace. SAP has modified the underlying technical architecture but has also changed the business process models that the technology supports. SAP has introduced the concept of Enterprise Management for business process definition. The SAP S/4HANA Enterprise Management model includes the mega processes supported by SAP S/4HANA, as well as the concept of value maps, which define the processes supported within a mega process (as seen in Figure 1.1).
The first section examines the SAP HANA foundation beneath SAP S/4HANA, the second section addresses simplifications delivered with SAP S/4HANA in the four main logistics workflows (and what functional groupings appear in each), and the third section explains the on-premise and cloud deployment options.
Figure 1.1 SAP S/4HANA Value Drivers
Following are some key terminology used throughout this chapter and in the general marketplace when discussing SAP S/4HANA:
-
SAP S/4HANA
This is SAP’s latest product offering and is the fourth generation of the business suite. SAP S/4HANA is the culmination of decades of experience in the enterprise software arena and is the future of SAP’s software offerings. SAP S/4HANA is a shift in SAP’s design as it’s not an incremental software offering but a platform built to support future technology innovations. The technology is also built to support end users with a new look and feel and a role-based approach to user interaction. -
Digital core
The SAP S/4HANA core is often referred to as the suite of technical solutions that make up the end solution, and they consist of the SAP S/4HANA platform and database, SAP Fiori app enablement, the simplifications list delivered, and the deployment option supporting SAP S/4HANA (on-premise or cloud). The SAP S/4HANA core allows you to scale your transformations across the entire enterprise (as seen in Figure 1.2).
-
SAP HANA platform
The in-memory database with faster access, parallel processing, and compressive data storage enables analytics on the fly and real-time data processing.Figure 1.2 SAP S/4HANA Core’s Integration Components
-
SAP Fiori applications
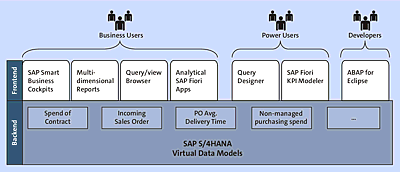
The “face” of SAP S/4HANA is the point of entry for the user. The new interface is focused only on relevant data. SAP Fiori apps provide a completely new user experience for interacting with SAP. They are web enabled to support multiple devices (as seen in Figure 1.3).
Figure 1.3 SAP Fiori Apps: Key Components
-
Simplifications
The simplifications, or simplifications list, is a document published by SAP that is SAP S/4HANA release dependent. It shows all of the changes being implemented with that release, compared to the SAP Business Suite products. The changes can be more technically based, functionality based, or a combination. This document is published to help those migrating from a legacy business suite product onto SAP S/4HANA. The business process- or functionality-based changes are published and should be considered during the upgrade because they could require changes to the existing business and should be planned in advance of the upgrade. The example provided by SAP in the 1610 simplification list is the classical SAP General Ledger (G/L) versus the new G/L. With SAP S/4HANA, the classical G/L isn’t supported, and businesses will have to migrate to the new G/L as part of the SAP S/4HANA upgrade. These decisions have been made by SAP strategically for the simplification and standardization of the product offering and are based on their many years of experience interacting with customers. Although conscious decisions have been made regarding what functionality not to propagate in the future releases, most traditional functionality is still supported so you can decide when to transition to the new functionality. -
Line of Business (LoB)
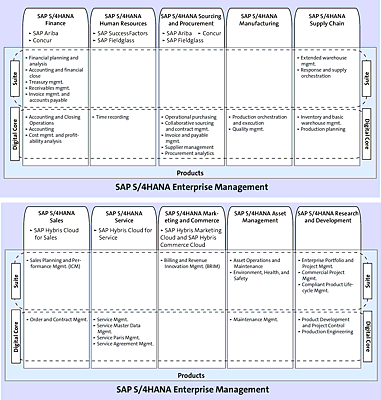
LoBs are the complementary functional solutions that are supported by the SAP HANA platform. SAP S/4HANA Finance, and SAP S/4HANA Supply Chain are examples of LoB offerings. There are a number of other offerings such as SAP S/4HANA Human Resources, SAP S/4HANA Sourcing and Procurement, and SAP S/4HANA Research and Development (as seen in Figure 1.4).
-
Release history and naming conversion
SAP has been rolling out SAP S/4HANA solutions for a number of years now (as seen in Figure 1.5). The most notable releases being the 1511 and 1610 releases. The 1709 release is scheduled for September 2017. The release names are based on a naming convention of YYMM when the releases are made public.Figure 1.4 SAP S/4HANA 1610 LoB Scope and SAP S/4HANA Core
Figure 1.5 SAP Evolution to SAP S/4HANA
1.1 Architecture and SAP S/4HANA
The core architecture of SAP S/4HANA has been built as an enabling architecture. The SAP HANA in-memory database remains the foundation for SAP S/4HANA, serving as a powerful data engine for real-time transactions and insights, with data structures further simplified in the 1610 release. Meanwhile, SAP has expanded the core, more tightly integrating solutions such as SAP S/4HANA Finance and SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM). SAP also has brought a number of enhancements and innovations to the core, including enhancements to streamline inventory management and accelerate material requirements planning (MRP). Based on an open architecture, SAP S/4HANA allows you to connect with other cloud or on-premise solutions, which is a critical capability if you plan on having other sales and marketing solutions in the mix.
In the following subsections, we’ll describe the in-memory architecture and the resulting performance improvements. In addition, we’ll highlight the changes to the SAP Business Suite data structures and the removal of aggregation tables. Finally, we’ll talk about improvements in analytics facilitated by the architectural changes and the enablement of analytics from the introduction of the SAP Fiori apps.
1.1.1 In-Memory Processing and Performance Improvements
Within SAP S/4HANA, the in-memory processing allows for faster processing speeds. All of the transactional data is stored in main memory, which avoids the need to post to disk and saves the roundtrip processing time. The in-memory database significantly improves data processing functions.
1.1.2 Real-Time Analytics
SAP S/4HANA provides a number of analytics tools. Most of the analytics are embedded in the functional offering either via the GUI or more frequently enabled via new SAP Fiori apps. The new SAP Fiori apps provide information in numerous lists and reports. These lists and reports are highlighted in the functional chapters, and the ad hoc reporting and analytics functionality is detailed in Chapter 9.
The reporting offered via the SAP Fiori apps includes new tools such as enhanced search capabilities and the ability to report based on multiple search criteria. In addition, the report displays are modifiable by user and role.
The reporting functionality is also enhanced based on the core architectural changes in SAP S/4HANA that allow for much faster reporting performance. Reports can now be run numerous times and incorporated into business processes versus the traditional business suite that relied on batch jobs and long-running reporting execution. In addition, new reporting tools are created that help move analytics from historical data analysis into predictive analysis to move businesses from reactive to proactive (as seen in Figure 1.6).
Figure 1.6 SAP S/4HANA Embedded Analytics
1.1.3 Improved Data Quality
The world of data is changing based on new technology, and the people and machines creating, capturing, and processing data are evolving. Data in today’s environment must include Internet of Things (IoT), radio-frequency identification (RFID), Quick Response codes (QR codes), and so on. The SAP S/4HANA core is built to support and excel in these technologies.
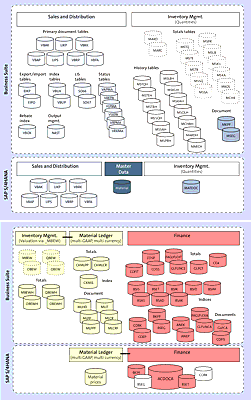
Data model simplifications are also a major part of the conversion into the SAP S/4HANA model (as seen in Figure 1.7). SAP S/4HANA has removed a number of traditional database tables from the SAP Business Suite, including the aggregation tables and any redundant data structures. All aggregations will be calculated in real time, which will also reduce locking issues. These changes will also provide more precision and improved speed in transactions to allow for more simulation and predictive functionality.
Figure 1.7 Simplified Data Model in SAP S/4HANA