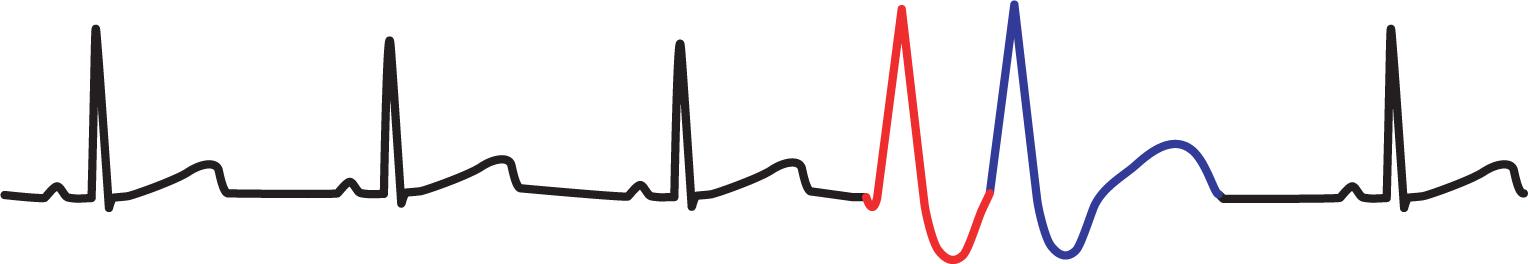
Figure 30-13 Unifocal couplet.
© Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Couplets, Triplets, and Salvos
Bigeminy, trigeminy, and the others in that group have normal complexes interspersed between single PVCs. In this section, we will look at what happens when PVCs occur in sequence. When two PVCs occur sequentially, they are known as a couplet (Figure 30-13). When three PVCs occur sequentially, they are known as a triplet (Figure 30-14). The term salvo refers to a group of three or more ectopic ventricular complexes occurring sequentially.

Figure 30-13 Unifocal couplet.
© Jones & Bartlett Learning.
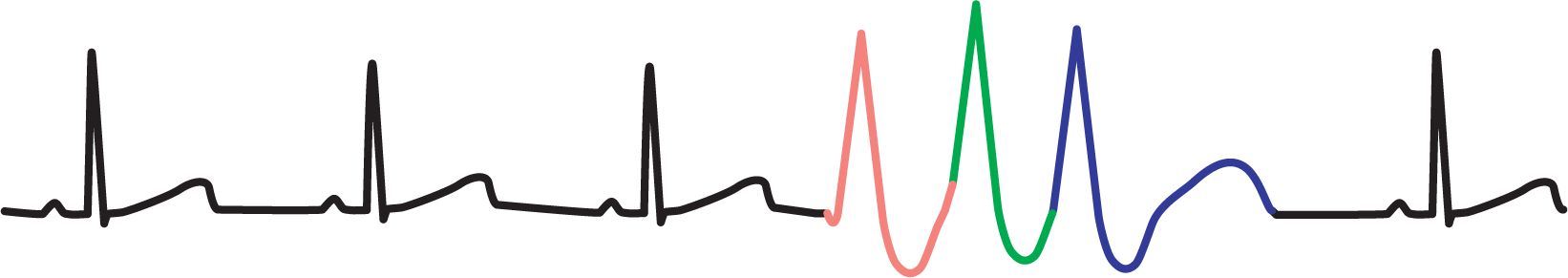
Figure 30-14 Unifocal triplet.
© Jones & Bartlett Learning.
NOTE
When there are three PVCs in a row, it starts to become difficult to tell if they are a run of PVCs or ventricular tachycardia. The term salvo is typically used when the clinical impression is leaning toward the presence of ventricular tachycardia. We will discuss this topic in much greater detail in Chapter 32, Ventricular Tachycardia.
Fusion of the various ventricular complexes and their associated waves is a very common occurrence when you are dealing with two or more sequential PVCs. The fusion can occur anywhere along the complexes and will affect the morphologic appearance of the various complexes.
Couplets and triplets can have PVCs that are either unifocal or multifocal. The morphologic appearance of unifocal couplets and triplets may be slightly altered because of fusion, but the general appearance of the complexes will be the same. Multifocal couplets and triplets will show a wide variation in morphologic appearance and timing (Figure 30-15).
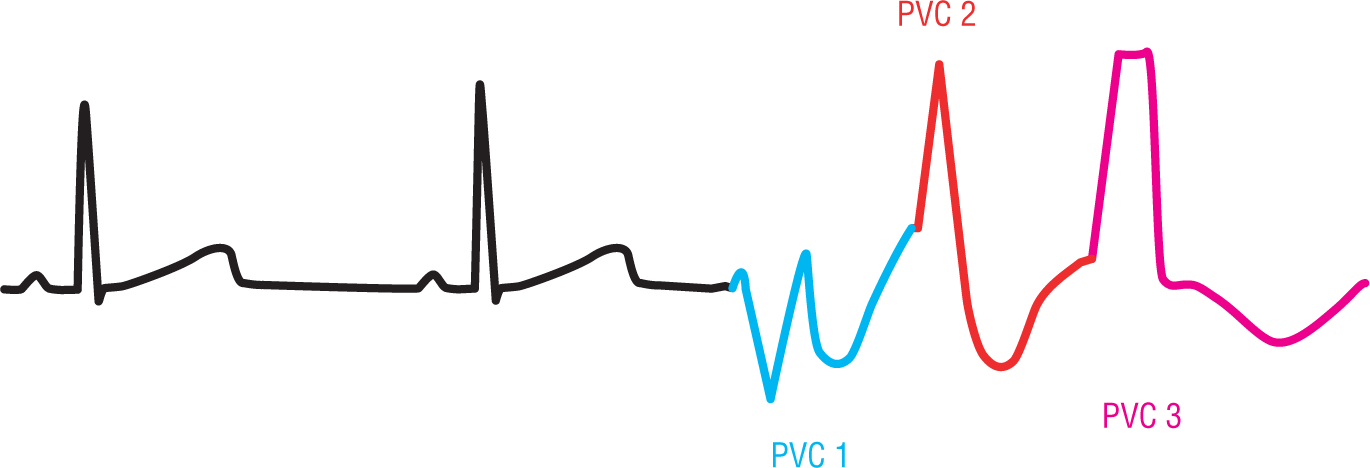
Figure 30-15 A multifocal triplet. Note the different appearance of the three ventricular beats and the varying degree of fusion between the waves.
© Jones & Bartlett Learning.
DescriptionClinically, unifocal couplets and triplets can be considered normal variants, but clinical correlation with your patient is definitely a good idea. Multifocal couplets and triplets are a bit more troubling and may be harbingers of further, more life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias to come. Observation and treatment may be clinically indicated for these patients.