An Example Program
Let’s look at how a real-life PHP program integrates with an HTML form by creating the program convert.php, listed in Example 11-10. Type it in as shown and try it for yourself.
<?php // convert.php
$f = $c = "";
if (isset($_POST['f'])) $f = sanitizeString($_POST['f']);
if (isset($_POST['c'])) $c = sanitizeString($_POST['c']);
if ($f != '')
{
$c = intval((5 / 9) * ($f - 32));
$out = "$f °f equals $c °c";
}
elseif($c != '')
{
$f = intval((9 / 5) * $c + 32);
$out = "$c °c equals $f °f";
}
else $out = "";
echo <<<_END
<html><head><title>Temperature Converter</title>
</head><body><pre>
Enter either Fahrenheit or Celsius and click on Convert
<b>$out</b>
<form method="post" action="convert.php">
Fahrenheit <input type="text" name="f" size="7" />
Celsius <input type="text" name="c" size="7" />
<input type="submit" value="Convert" />
</form></pre></body></html>
_END;
function sanitizeString($var)
{
$var = stripslashes($var);
$var = htmlentities($var);
$var = strip_tags($var);
return $var;
}
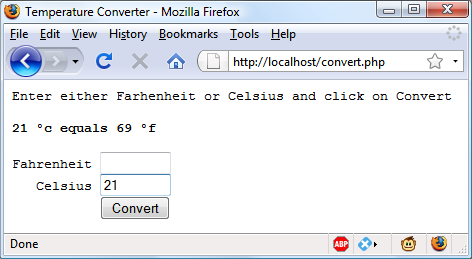
?>When you call up convert.php in a browser, the result should look something like the screen grab in Figure 11-8.
To break the program down, the first line initializes the variables
$c and $f in case they do not get posted to the
program. The next two lines fetch the values of either the field named
f or the one named c, for an input Fahrenheit or Celsius value. If
the user inputs both, the Celsius is simply ignored and the Fahrenheit
value is converted. As a security measure, the new function sanitizeString from Example 11-9 is also used.
So, having submitted either values or empty strings in both $f and $c,
the next portion of code constitutes an if...elseif...else structure that first tests
whether $f has a value. If not, it
checks $c; if $c does not have a value either, the variable
$out is set to the empty string (more
on that in a moment).
If $f is found to have a value,
the variable $c is assigned a simple
mathematical expression that converts the value of $f from Fahrenheit to Celsius. The formula used
is Celsius = (5 / 9) * (Fahrenheit – 32). The
variable $out is then set to a message
string explaining the conversion.
On the other hand, if $f is found
not to have a value but $c does, a
complementary operation is performed to convert the value of $c from Celsius to Fahrenheit and assign the
result to $f. The formula used is
Fahrenheit = (9 / 5) * Celsius + 32. As with the
previous section, the string $out is
then set to contain a message about the conversion.
In both conversions, the PHP intval function is called to convert the result
of the conversion to an integer value. This isn’t necessary, but it looks
better.
With all the arithmetic done, the program now outputs the HTML,
which starts with the basic head and title and then provides some
introductory text before displaying the value of $out. If no temperature conversion was made,
$out will have a value of NULL and nothing will be displayed, which is
exactly what we want when the form hasn’t yet been submitted. But if a
conversion was made, $out contains the
result, which is displayed.
After this, we come to the form, which is set to submit using the
POST method to the file convert.php (the program itself). Within the
form, there are two inputs for either a Fahrenheit or Celsius value to be
entered. A submit button with the text “Convert” is then displayed, and
the form is closed.
After outputting the HTML to close the document, we come finally to
the function sanitizeString from Example 11-9.
Note
All the examples in this chapter have used the POST method to send form data. I recommend
this, as it’s the neatest and most secure method. However, the forms can
easily be changed to use the GET
method, as long as values are fetched from the $_GET array instead of the $_POST array. Reasons to do this might include
to make the result of a search bookmarkable or directly linkable from
another page.