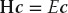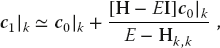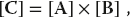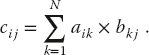11
Applied HPC: Optimization, Tuning, and GPU Programming
11.1 General Program Optimization
Rule 1 Do not do it.
Rule 2 (for experts only): Do not do it yet.
Rule 3 Do not optimize as you go: Write your program without regard to possible optimizations, concentrating instead on making sure that the code is clean, correct, and understandable. If it is too big or too slow when you have finished, then you can consider optimizing it.
Rule 4 Remember the 80/20 rule: In many fields you can get 80% of the result with 20% of the effort (also called the 90/10 rule – it depends on who you talk to). Whenever you’re about to optimize code, use profiling to find out where that 80% of execution time is going, so you know where to concentrate your effort.
Rule 5 Always run “before” and “after” benchmarks: How else will you know that your optimizations actually made a difference? If your optimized code turns out to be only slightly faster or smaller than the original version, undo your changes and go back to the original, clear code.
Rule 6 Use the right algorithms and data structures: Do not use an 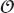 (n2) DFT algorithm to do a Fourier transform of a 1000 elements when there is an
(n2) DFT algorithm to do a Fourier transform of a 1000 elements when there is an 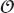 (n log n) FFT available. Similarly, do not store a thousand items in an array that requires an
(n log n) FFT available. Similarly, do not store a thousand items in an array that requires an 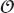 (n) search when you could use an
(n) search when you could use an 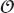 (log n) binary tree or an
(log n) binary tree or an 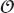 (1) hash table (Hardwich, 1996).
(1) hash table (Hardwich, 1996).
The type of optimization often associated with high-performance or numerically intensive computing is one in which sections of a program are rewritten and reorganized in order to increase the program’s speed. The overall value of doing this, especially as computers have become so fast and so available, is often a subject of controversy between computer scientists and computational scientists. Both camps agree that using the optimization options of compilers is a good idea. Yet on the one hand, CS tends to think that optimization is best left to the compilers, while computational scientists, who tend to run large codes with large amounts of data in order to solve real-world problems, often believe that you cannot rely on the compiler to do all the optimization.
11.1.1 Programming for Virtual Memory (Method)
While memory paging makes little appear big, you pay a price because your program’s run time increases with each page fault. If your program does not fit into RAM all at once, it will be slowed down significantly. If virtual memory is shared among multiple programs that run simultaneously, they all cannot have the entire RAM at once, and so there will be memory access conflicts which will decrease performance. The basic rules for programming for virtual memory are:
- Do not waste your time worrying about reducing the amount of memory used (the working set size) unless your program is large. In that case, take a global view of your entire program and optimize those parts that contain the largest arrays.
- Avoid page faults by organizing your programs to successively perform their calculations on subsets of data, each fitting completely into RAM.
- Avoid simultaneous calculations in the same program to avoid competition for memory and consequent page faults. Complete each major calculation before starting another.
- Group data elements close together in memory blocks if they are going to be used together in calculations.
11.1.2 Optimization Exercises
Many of the optimization techniques developed for Fortran and C are also relevant for Python applications. Yet while Python is a good language for scientific programming and is as universal and portable as Java, at present Python code runs slower than Fortran, C or even Java codes. In part, this is a consequence of the Fortran and C compilers having been around longer and thereby having been better refined to get the most out of a computer’s hardware, and in part this is also a consequence of Python not being designed for speed. Because modern computers are so fast, whether a program takes 1s or 3s usually does not matter much, especially in comparison to the hours or days of your time that it might take to modify a program for increased speed. However, you may want to convert the code to C (whose command structure is similar to that of Python) if you are running a computation that takes hours or days to complete and will be doing it many times.
Especially when asked to, compilers may look at your entire code as a single entity and rewrite it in an attempt to make it run faster. In particular, Fortran and C compilers often speed up programs by being careful in how they load arrays into memory. They also are careful in keeping the cache lines full so as not to keep the CPU waiting or having it move on to some other chore. That being said, in our experience compilers still cannot optimize a program as well as can a skilled and careful programmer who understands the order and structure of the code.
There is no fundamental reason why a program written in Java or Python cannot be compiled to produce a highly efficient code, and indeed such compilers are being developed and becoming available. However, such code is optimized for a particular computer architecture and so is not portable. In contrast, the byte code (.class file in Java and .pyc file in Python) produced by the compiler is designed to be interpreted or recompiled by the Java or Python Virtual Machine (just another program). When you change from Unix to Windows, for example, the Virtual Machine program changes, but the byte code is the same. This is the essence of portability.
In order to improve the performance of Java and Python, many computers and browsers run Just-in-Time (JIT) compilers. If a JIT is present, the Virtual Machine feeds your byte code Prog.class or Prog.pyc to the JIT so that it can be recompiled into native code explicitly tailored to the machine you are using. Although there is an extra step involved here, the total time it takes to run your program is usually 10–30 times faster with a JIT as compared to line-by-line interpretation. Because the JIT is an integral part of the Virtual Machine on each operating system, this usually happens automatically.
In the experiments below, you will investigate techniques to optimize both Fortran and Java or Python programs, and to compare the speeds of both languages for the same computation. If you run your program on a variety of machines you should also be able to compare the speed of one computer to that of another. Note that a knowledge of Fortran or C is not required for these exercises; if you keep an open mind you should be able to look at the code and figure out what changes may be needed.
11.1.2.1 Good and Bad Virtual Memory Use (Experiment)
To see the effect of using virtual memory, convert these simple pseudocode examples (Listings 11.1 and 11.2) into actual code in your favorite language, and then run them on your computer. Use a command such as time, time.clock() or timeit to measure the time used for each example. These examples call functions force12 and force21. You should write these functions and make them have significant memory requirements.
Listing 11.1 BAD program, too simultaneous.

You see (Listing 11.1) that each iteration of the for loop requires the data and code for all the functions as well as access to all the elements of the matrices and arrays. The working set size of this calculation is the sum of the sizes of the arrays f12(N,N), f21(N,N), and pion(N) plus the sums of the sizes of the functions force12 and force21.
A better way to perform the same calculation is to break it into separate components (Listing 11.2):
Listing 11.2 GOOD program, separate loops.

Here, the separate calculations are independent and the working set size, that is, the amount of memory used, is reduced. However, you do pay the additional overhead costs associated with creating extra for loops. Because the working set size of the first for loop is the sum of the sizes of the arrays f12(N, N) and pion(N), and of the function force12, we have approximately half the previous size. The size of the last for loop is the sum of the sizes for the two arrays. The working set size of the entire program is larger than of the working set sizes for the different for loops.
As an example of the need to group data elements close together in memory or common blocks if they are going to be used together in calculations, consider the following code (Listing 11.3):
Listing 11.3 BAD Program, discontinuous memory.

Here the variables zed, ylt, and part are used in the same calculations and are adjacent in memory because the programmer grouped them together in Common (global variables). Later, when the programmer realized that the array med2 was needed, it was tacked onto the end of Common. All the data comprising the variables zed, ylt, and part fit onto one page, but the med2 variable is on a different page because the large array zpart2(50000) separates it from the other variables. In fact, the system may be forced to make the entire 4kB page available in order to fetch the 72 B of data in med2. While it is difficult for a Fortran or C programmer to establish the placement of variables within page boundaries, you will improve your chances by grouping data elements together (Listing 11.4):
Listing 11.4 GOOD program, continuous memory

11.2 Optimized Matrix Programming with NumPy
In Chapter 6, we demonstrated several ways of handling matrices with Python. In particular, we recommended using the array structure and the NumPy package. In this section, we extend that discussion somewhat by demonstrating two ways in which NumPy may speed up a program. The first is by using NumPy arrays rather than Python ones, and the second is by using Python slicing to reduce stride.
Listing 11.5 TuneNumPy.py compares the time it takes to evaluate a function of each element of an array using a for loop, as well as using a vectorized call with NumPy. To see the effect of fluctuations, the comparison is repeated three times.

A powerful feature of NumPy is its high-level vectorization. This is the process in which the single call of a function operates not on a variable but on an array object as a whole. In the latter case, NumPy automatically broadcasts the operation across all elements of the array with efficient use of memory. As we shall see, the resulting speed up can be more than an order of magnitude! While this may sound complicated, it really is quite simple because NumPy does this for you automatically.
For example, in Listing 11.5 we present the code TuneNumPy.py. It compares the speed of a calculation using a for loop to evaluate a function for each of 100 000 elements in an array, vs. the speed using NumPy’s vectorized evaluation of that function for an array object (Perez et al., 2010). And to see the effects of fluctuations as a result of things like background processes, we repeat the comparison three times. We obtained the following results:

Though a simple calculation, these results show that vectorization speeds the calculation up by a factor of nearly 50; really!
Now, recall from Chapter 10 our discussion of stride (the amount of memory skipped in order to get to the next element needed in a calculation). It is important to have your program minimize stride in order not waste time jumping through memory, as well as not to load unneeded data into memory. For example, for a (1000, 1000) array, there is a passage of 1 word to get to the next column, but of 1000 words to get to the next row. Clearly better to do a column-by-column calculation than a row-by-row one.
We start our example by setting up a 3 × 3 array of integers using NumPy’s arange to create a 1D array. We then reshape it into a 3 × 3 array and determine the strides of the matrix for rows and columns:

Line 11 tells us that it takes 12 bytes (three values) to get to the same position in the next row, but only 4 bytes (one value) to get to the same position in the next column. Clearly cheaper to go from column to column. Now, we show you an easy way to do that.
Recall Python’s slice operator that extracts just the desired part of a list (like taking a “slice” through the center of a jelly doughnut):
ListName[StartIndex:StopBeforeIndex:Step] .
The convention here is that if no argument is given, then the slice starts at 0 and stops at the end of the list. For example:

Once sliced, Python does not have to jump through memory to work with these elements, or even set up separate arrays for them. This is called view-based indexing, with the indexed notation returning a new array object that points to the address of the original data rather than store the values of the new array (think “pointers” in C). This does lead to improved speed, but you must remember that if you alter the new array, you are also altering the original array to which it points (think “pointers” in C).
For instance, you can optimize a finite difference calculation of forward- and central-difference derivatives quite elegantly (Perez et al., 2010):

(We note that the values of the derivatives look quite different, yet the forward difference is evaluated at the start of the interval and the central difference at the center.)
11.2.1 NumPy Optimization Exercises
- We have just demonstrated how NumPy’s vectorized function evaluation can speed up a calculation by a factor of 50 via broadcast of an operation over an array rather than performing that operation on each individual element in the array. Determine the speedup for the matrix multiplication [A][B] where the matrices are at least 105 in size and contain floating-point numbers. Compare the direct multiplication to application of the elementary rule for each element:
(11.1)
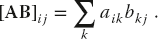
- We have just demonstrated how Python’s slice operator can be used to reduce the stride of a calculation of derivatives. Determine the speedup obtained in evaluating the forward-difference and central-difference derivatives over an array of at least 105 floating-point numbers using stripping to reduce stride. Compare to the same calculation without any stripping.
11.3 Empirical Performance of Hardware
The first step in optimization is to try asking the compiler to optimize your program. You control how completely the compiler tries to do this by adding optimization options to the compile command. For example, in Fortran (where this works better than in Python):
> f90 –O tune.f90
Here –O turns on optimization (O is the capital letter “oh,” not zero). The actual optimization that is turned on differs from compiler to compiler. Fortran and C compilers have a bevy of such options and directives that let you truly customize the resulting compiled code. Sometimes optimization options make the code run faster, sometimes not, and sometimes the faster-running code gives the wrong answers (but does so quickly).
Because computational scientists may spend a good fraction of their time running compiled codes, the compiler options tend to become quite specialized. As a case in point, most compilers provide a number of levels of optimization for the compiler to attempt (there are no guarantees with these things). Although the speedup obtained depends upon the details of the program, higher levels may give greater speedup. However, we have had the experience of higher levels of optimization sometimes giving wrong answers (presumably this may be related to our programs not following the rules of grammar perfectly).
Some typical Fortran compiler options include the following:
–OUse the default optimization level (–O3)–O1Provide minimum statement-level optimizations–O2Enable basic block-level optimizations–O3Add loop unrolling and global optimizations–O4Add automatic inlining of routines from the same source file–O5Attempt aggressive optimizations (with profile feedback).
The gnu compilers gcc, g77, and g90 accept –O options as well as
–malign–doubleAlign doubles on 64-bit boundaries–ffloat–storeFor codes using IEEE-854 extended precision–fforce–mem, –fforce–addrImproves loop optimization–fno–inlineDo not compile statement functions inline–nffast–mathTry non-IEEE handling of floats–funsafe–math–optimizationsSpeeds up float operations; incorrect result possible–fno–trapping–mathAssume no floating-point traps generated–fstrength–reduceMakes some loops faster–frerun–cse–after–loop–fexpensive–optimizations–fdelayed–branch–fschedule–insns–fschedule–insns2–fcaller–saves–funroll–loopsUnrolls iterative DO loops–funroll–all–loopsUnrolls DO WHILE loops
11.3.1 Racing Python vs. Fortran/C
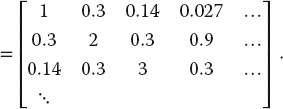
The various versions of the program tune that are given in the Codes/HPC directory solve the matrix eigenvalue problem
for the eigenvalues E and eigenvectors c of a Hamiltonian matrix H. Here the individual Hamiltonian matrix elements are assigned the values
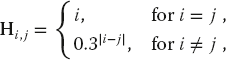
Listing 11.6 tune.f90 is meant to be numerically intensive enough to show the results of various types of optimizations, but you may have to increase sizes in it to make it more intensive. The programsolves the eigenvalue problem iteratively for a nearly diagonal Hamiltonian matrix using a variation of the power method.


Because the Hamiltonian is almost diagonal, the eigenvalues should be close to the values of the diagonal elements, and the eigenvectors should be close to a set of N-dimensional unit vectors. For example, let us say that H has dimensions of N × N with N = 2000. The number of elements in the matrix is then 2000 × 2000 = 4 000 000, and so it will take 4 million × 8B = 32 MB to store this many double precision numbers. Because modern PCs have 4GB or more of RAM, this small a matrix should not have memory issues. Accordingly, determine the size of RAM on your computer and increase the dimension of the H matrix until it surpasses that size. (On Windows, this will be indicated as one of the “Properties” of “Computer” or in the information about “System” in the Control Panel.)
We find the solution to (11.2) via a variation of the power or Davidson method. We start with an arbitrary first guess for the eigenvector c and use it to calculate the energy corresponding to this eigenvector,1)
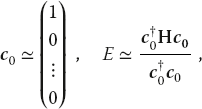
where  is the row vector adjoint of c0. Because H is nearly diagonal with diagonal elements that increase as we move along the diagonal, this guess should be close to the eigenvector with the smallest eigenvalue. The heart of the algorithm is the guess that an improved eigenvector has the kth component
is the row vector adjoint of c0. Because H is nearly diagonal with diagonal elements that increase as we move along the diagonal, this guess should be close to the eigenvector with the smallest eigenvalue. The heart of the algorithm is the guess that an improved eigenvector has the kth component
where k ranges over the length of the eigenvector. If repeated, this method converges to the eigenvector with the smallest eigenvalue. It will be the smallest eigenvalue because it gets the largest weight (smallest denominator) in (11.6) each time. For the present case, six places of precision in the eigenvalue are usually obtained after 11 iterations. Here are the steps to follow:
- Vary the value of
errin tune that controls precision and note how it affects the number of iterations required. - Try some variations on the initial guess for the eigenvector (11.6) and see if you can get the algorithm to converge to some of the other eigenvalues.
- Keep a table of your execution times vs. technique.
- Compile and execute
tune.f90and record the run time (Listing 11.6). On Unix systems, the compiled program will be placed in the filea.out. From a Unix shell, the compilation, timing, and execution can all be carried out with the commands
Here the compiled Fortran program is given the (default) name of
a.out, and thetimecommand gives you the execution (user) time andsystemtime in seconds to executea.out. - As indicated in Section 11.3, you can ask the compiler to produce a version of your program optimized for speed by including the appropriate compiler option:
> f90 –O tune.f90Execute and time the optimized code, checking that it still gives the same answer, and note any speedup in your journal.
- Try out optimization options up to the highest levels and note the run time and accuracy obtained. Usually
–O3is pretty good, especially for as simple a program as tune with only a main method. With only one program unit, we would not expect–O4or–O5to be an improvement over–O3. However, we do expect–O3, with its loop unrolling, to be an improvement over–O2. - The program
tune4does some loop unrolling (we will explore that soon). To see the best we can do with Fortran, record the time for the most optimized version oftune4.f95. - The program
Tune.pyin Listing 11.7 is the Python equivalent of the Fortran programtune.f90. - To get an idea of what Tune.py does (and give you a feel for how hard life is for the poor computer), assume ldim
=2and work through one iteration ofTuneby hand. Assume that the iteration loop has converged, follow the code to completion, and write down the values assigned to the variables. - Compile and execute
Tune.py. You do not have to issue thetimecommand because we built a timer into the Python program. Check that you still get the same answer as you did with Fortran and note how much longer it takes with Python. You might be surprised how much slower Python is than Fortran. - We now want to perform a little experiment in which we see what happens to performance as we fill up the computer’s memory. In order for this experiment to be reliable, it is best for you not to be sharing the computer with any other users. On Unix systems, the
who –acommand shows you the other users (we leave it up to you to figure out how to negotiate with them). - To get some idea of what aspect of our little program is making it so slow, compile and run
Tune.pyfor the series of matrix sizesldim= 10, 100, 250, 500, 750, 1025, 2500, and 3000. You may get an error message that Python is out of memory at 3000. This is because you have not turned on the use of virtual memory.Listing 11.7 Tune.py is meant to be numerically intensive enough to show the results of various types of optimizations, but you may need to increase sizes to make it more intensive. The program solves the eigenvalue problem iteratively for a nearly diagonal Hamiltonian matrix using a variation of the power method.
- Make a graph of run time vs.matrix size. It should be similar to Figure 11.1, although if there is more than one user on your computer while you run, you may get erratic results. Note that as our matrix becomes larger than ~ 1000 × 1000 in size, the curve sharply increases in slope with execution time, in our case increasing like the third power of the dimension. Because the number of elements to compute increases as the second power of the dimension, something else is happening here. It is a good guess that the additional slowdown is as a result of page faults in accessing memory. In particular, accessing 2D arrays, with their elements scattered all through memory, can be very slow.
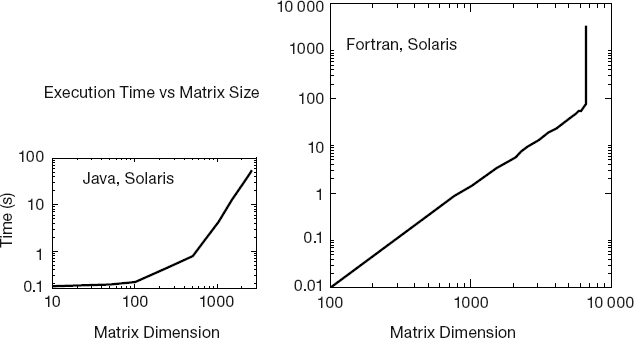
Figure 11.1 Running time
vs.dimension for an eigenvalue search usingTune.javaandtune.f90.Listing 11.8 Tune4.py does some loop unrolling by explicitly writing out two steps of a for loop
(steps of 2). This results in better memory access and faster execution.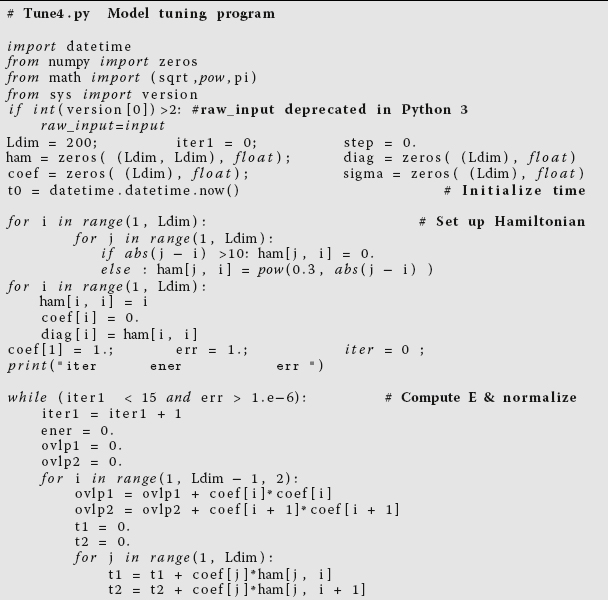
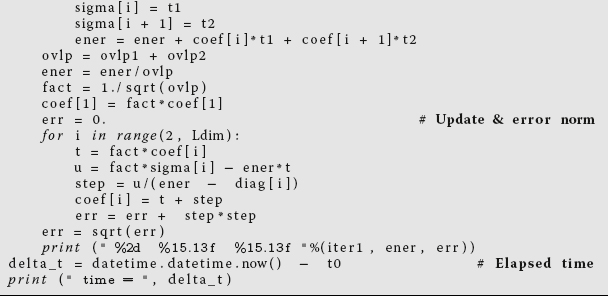
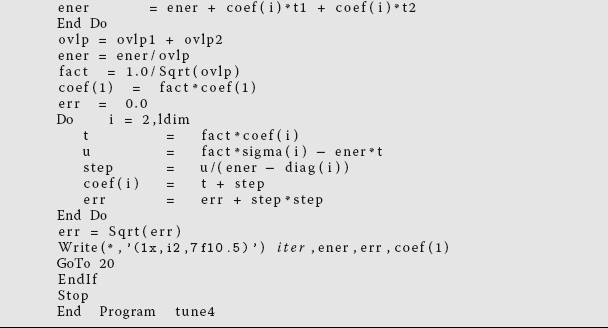
Listing 11.9 tune4.f95 does some loop unrolling by explicitly writing out two steps of a Do loop
(steps of 2). This results in better memory access and faster execution.
- Repeat the previous experiment with
tune.f90that gauges the effect of increasing thehammatrix size, only now do it forldim= 10, 100, 250, 500, 1025, 3000, 4000, 6000, … You should get a graph like ours. Although our implementation of Fortran has automatic virtual memory, its use will be exceedingly slow, especially for this problem (possibly a 50-fold increase in time!). So if you submit your program and you get nothing on the screen (though you can hear the disk spin or see it flash busy), then you are probably in the virtual memory regime. If you can, let the program run for one or two iterations, kill it, and then scale your run time to the time it would have taken for a full computation. - To test our hypothesis that the access of the elements in our 2D array ham[i,j] is slowing down the program, we have modified
Tune.pyintoTune4.pyin Listing 11.8 (and similar modification with the Fortran versions). - Look at
Tune4and note where the nestedforloop overiandjnow takes step of Δi = 2 rather the unit steps inTune.py. If things work as expected, the better memory access ofTune4.pyshould cut the run time nearly in half. Compile and executeTune4.py. Record the answer in your table. - In order to cut the number of calls to the 2D array in half, we employed a technique known as loop unrolling in which we explicitly wrote out some of the lines of code that otherwise would be executed implicitly as the
forloop went through all the values for its counters. This is not as clear a piece of code as before, but it evidently permits the compiler to produce a faster executable. To check thatTuneandTune4actually do the same thing, assumeldim = 4and run through one iteration ofTune4by hand. Hand in your manual trial.
11.4 Programming for the Data Cache (Method)
Data caches are small, very fast memory banks used as temporary storage between the ultrafast CPU registers and the fast main memory. They have grown in importance as high-performance computers have become more prevalent. For systems that use a data cache, this may well be the single most important programming consideration; continually referencing data that are not in the cache (cache misses) may lead to an order-of-magnitude increase in CPU time.
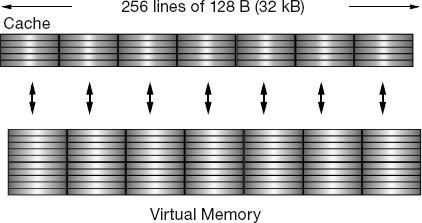
Figure 11.2 The cache manager’s view of RAM. Each 128-B cache line is read into one of four lines in cache.
As indicated in Figures 10.3 and 11.2, the data cache holds a copy of some of the data in memory. The basics are the same for all caches, but the sizes are manufacturer dependent. When the CPU tries to address a memory location, the cache manager checks to see if the data are in the cache. If they are not, the manager reads the data from memory into the cache, and then the CPU deals with the data directly in the cache. The cache manager’s view of RAM is shown in Figure 11.2.
When considering how a matrix operation uses memory, it is important to consider the stride of that operation, that is, the number of array elements that are stepped through as the operation repeats. For instance, summing the diagonal elements of a matrix to form the trace
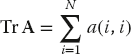
involves a large stride because the diagonal elements are stored far apart for large N. However, the sum
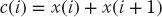
has stride 1 because adjacent elements of x are involved. Following is the basic rule in programming for a cache:
- Keep the stride low, preferably at 1, which in practice means:
- – Vary the leftmost index first on Fortran arrays.
- – Vary the rightmost index first on Python and C arrays.
11.4.1 Exercise 1: Cache Misses
We have said a number of times that your program will be slowed down if the data it needs are in virtual memory and not in RAM. Likewise, your program will also be slowed down if the data required by the CPU are not in the cache. For high-performance computing, you should write programs that keep as much of the data being processed as possible in the cache. To do this, you should recall that Fortran matrices are stored in successive memory locations with the row index varying most rapidly (column-major order), while Python and C matrices are stored in successive memory locations with the column index varying most rapidly (row-major order). While it is difficult to isolate the effects of the cache from other elements of the computer’s architecture, you should now estimate its importance by comparing the time it takes to step through the matrix elements row by row to the time it takes to step through the matrix elements column by column.
Run on machines available to you a version of each of the two simple codes given in Listings 11.10 and 11.11. Check that although each has the same number of arithmetic operations, one takes significantly more time to execute because it makes large jumps through memory, with some of the memory locations addressed not yet read into the cache:
Listing 11.10 Sequential column and row references.

Listing 11.11 Sequential column and row references.

11.4.2 Exercise 2: Cache Flow
Below in Listings 11.12 and 11.13, we give two simple code fragments that you should place into full programs in whatever computer language you are using. Test the importance of cache flow on your machine by comparing the time it takes to run these two programs. Run for increasing column size idim and compare the times for loop A vs. those for loop B. A computer with very small caches may be most sensitive to stride.
Listing 11.12 Loop A: GOOD f90 (min stride), BAD Python/C (max stride).

Listing 11.13 Loop B: BAD f90 (max stride), GOOD Python/C (min stride).

Loop A steps through the matrix Vec in column order. Loop B steps through in row order. By changing the size of the columns (the leftmost Python index), we change the step size (stride) taken through memory. Both loops take us through all the elements of the matrix, but the stride is different. By increasing the stride in any language, we use fewer elements already present in the cache, require additional swapping and loading of the cache, and thereby slow down the whole process.
11.4.3 Exercise 3: Large-Matrix Multiplication
As you increase the dimensions of the arrays in your program, memory use increases geometrically, and at some point you should be concerned about efficient memory use. The penultimate example of memory usage is large-matrix multiplication:
Listing 11.14 BAD f90 (max stride), GOOD Python/C (min stride).

This involves all the concerns with different kinds of memory. The natural way to code (11.9) follows from the definition of matrix multiplication (11.10), that is, as a sum over a row of A times a column of B. Try out the two codes in Listings 11.14 and 11.15 on your computer. In Fortran, the first code uses matrix B with stride 1, but matrix C with stride N. This is corrected in the second code by performing the initialization in another loop. In Python and C, the problems are reversed. On one of our machines, we found a factor of 100 difference in CPU times despite the fact that the number of operations is the same!
Listing 11.15 GOOD f90 (min stride), BAD Python/C (max stride).

11.5 Graphical Processing Units for High Performance Computing
In Section 10.16, we discussed how the trend toward exascale computing appears to be one using multinode-multicore-GPU computers, as illustrated in Figure 10.14. The GPU component in this figure extends a supercomputer’s architecture beyond that of computers such as IBM Blue Gene. The GPUs in these future supercomputers are electronic devices designed to accelerate the creation of visual images. A GPU’s efficiency arises from its ability to create many different parts of an image in parallel, an important ability because there are millions of pixels to display simultaneously. Indeed, these units can process 100s of millions of polygons in a second. Because GPUs are designed to assist the video processing on commodity devices such as personal computers, game machines, and mobile phones, they have become inexpensive, high performance, parallel computers in their own right. Yet because GPUs are designed to assist in video processing, their architecture and their programming are different from that of the general purpose CPUs usually used for scientific applications, and it takes some work to use them for scientific computing.
Programming of GPUs requires specialized tools specific to the GPU architecture being used, and while we do discuss them in Section 11.6.2, their low-level details places it beyond the normal level of this book. What is often called “compute unified device architecture (CUDA) programming” refers to programming for the architecture developed by the Nvidia corporation, and is probably the most popular approach to GPU programming at present (Zeller, 2008). However, some of the complications are being reduced via extensions and wrappers developed for popular programming languages such as C, Fortran, Python, Java, and Perl. However, the general principles involved are just an extension of those used already discussed, and after we have you work through some examples of those general principles, in Section 11.6 we give some practical tips for programming multinode-multicore-GPU computers.
In Chapter 10, we discussed some high-level aspects regarding parallel computing. In this section, we discuss some practical tips for multicore, GPU Programming. In the next section, we provide some actual examples of GPU programming using Nvidias CUDA language, with access to it from within Python programs via the use of PyCUDA (Klöckner, 2014). But do not think this is nothing more than adding in another package to Python. That section is marked as optional because using CUDA goes beyond the usual level of this text, and because, in our experience, it can be difficult for a regular scientist to get CUDA running on their personal computer without help. As is too often the case with parallel computing, one does have to get one’s hands dirty with lower level commands. Our presentation should give the reader some general understanding of CUDA. To read more on the subject, we recommend the CUDA tutorial (Zeller, 2008), as well as (Kirk and Wen-Mei, 2013; Sanders and Kandrot, 2011; Faber, 2010).
11.5.1 The GPU Card
GPUs are hardware components that are designed to accelerate the storage, manipulation, and display of visual images. GPUs tend to have more core chips and more arithmetic data processing units than do multicore central processing units (CPUs), and so are essentially fast, but limited, parallel computers. Because GPUs have become commodity items on most PCs (think gaming), they hold the promise of being a high powered, yet inexpensive, parallel computing environment. At present an increasing number of scientific applications are being adapted to GPUs, with the CPU being used for the sequential part of a program and the GPU for the parallel part.
The most popular GPU programming language is CUDA. CUDA is both a platform and a programming model created by Nvidia for parallel computing on their GPU. The model defines:
- threads, clocks, and grids,
- a memory system with registers, local, shared and global memories, and
- an execution environment with scheduling of threads and blocks of threads.
Figure 11.3 shows a schematic of a typical Nvidia card containing four streaming multiprocessors (SMs), each with eight streaming processors (SPs), two special function units (SFUs), and 16 kB of shared memory. The SFUs are used for the evaluation of the, otherwise, time-consuming transcendental functions such as sin, cosine, reciprocal, and square root. Each group of dual SMs form a texture processing cluster (TPC) that is used for pixel shading or general-purpose graphical processing. Also represented in the figure is the transfer of data among the three types of memory structures on the GPU and those on the host (Figure 11.3a). Having memory on the chip is much faster than accessing remote memory structures.
11.6 Practical Tips for Multicore and GPU Programming 
We have already described some basic elements of exascale computing in Section 10.16. Some practical tips for programming multinode-multicore-GPU computers follow along the same lines as we have been discussing, but with an even greater emphasis on minimizing communication costs.2) Contrary to the traditional view on optimization, this means that the “faster” of two algorithms may be the one that takes more steps, but requires less communications. Because the effort in programming the GPU directly can be quite high, many application programmers prefer to let compiler extensions and wrappers deal with the GPU. But if you must, here is how.
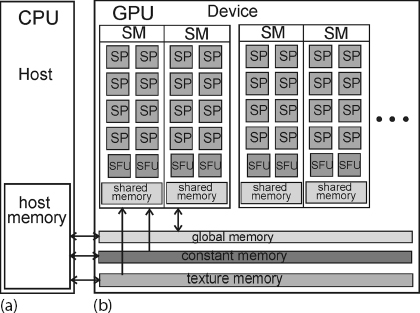
Figure 11.3 A schematic of a GPU (b) and its interactions with a CPU (a). The GPU is seen to have streaming multiprocessors, special function units and several levels of memory. Also shown is the communication between memory levels and with the host CPU.
Exascale computers and computing are expected to be “disruptive technologies” in that they lead to drastic changes from previous models for computers and computing. This is in contrast to the more evolving technology of continually increasing the clock speed of the CPU, which was the practice until the power consumption and associated heat production imposed a roadblock. Accordingly, we should expect that software and algorithms will be changing (and we will have to rewrite our applications), much as it did when supercomputers changed from large vector machines with proprietary CPUs to cluster computers using commodity CPUs and message passing. Here are some of the major points to consider:
Exacascale data movement is expensive The time for a floating-point operation and for a data transfer can be similar, although if the transfer is not local, as Figures 10.13 and 10.14 show happens quite often, then communication will be the rate-limiting step.
Exacascale flops are cheap and abundant GPUs and local multicore chips provide many, very fast flops for us to use, and we can expect even more of these elements to be included in future computers. So do not worry about flops as much as communication.
Synchronization-reducing algorithms are essential Having many processors stop in order to synchronize with each other, while essential in ensuring that the proper calculation is being performed, can slow down processing to a halt (literally). It is better to find or derive an algorithm that reduces the need for synchronization.
Break the fork-join model This model for parallel computing takes a queue of incoming jobs, divides them into subjobs for service on a variety of servers, and then combines them to produce the final result. Clearly, this type of model can lead to completed subjobs on various parts of the computer that must wait for other subjobs to complete before recombination. A big waste of resources.
Communication-reducing algorithms As already discussed, it is best to use methods that lessen the need for communication among processors, even if more flops are needed.
Use mixed precision methods Most GPUs do not have native double precision floating-point numbers (or even full single precision) and correspondingly slow down by a factor-of-two or more when made to perform double precision calculation, or when made to move double-precision data. The preferred approach then is to use single precision. One way to do this is to utilize the perturbation theory in which the calculation focuses on the small (single precision) correction to a known, or separately calculated, large (double precision) basic solution. The rule-of-thumb then is to use the lowest precision required to achieve the required accuracy.
Push for and use autotuning The computer manufactures have advanced the hardware to incredible speeds, but have not produced concordant advances in the software that scientists need to utilize in order to make good use of these machines. It often takes years for people to rewrite a large program for these new machines, and that is a tremendous investment that not many scientists can afford. We need smarter software to deal with such complicated machines, and tools that permit us to optimize experimentally our programs for these machines.
Fault resilient algorithms Computers containing millions or billions of components do make mistakes at times. It does not make sense to have to start a calculation over, or hold a calculation up, when some minor failure such as a bit flip occurs. The algorithms should be able to recover from these types of failures.
Reproducibility of results Science is at its heart the search for scientific truth, and there should be only one answer when solving a problem whose solution is mathematically unique. However, approximations in the name of speed are sometimes made and this can lead to results whose exact reproducibility cannot be guaranteed. (Of course exact reproducibility is not to be expected for Monte Carlo calculations involving chance.)
Data layout is critical As we discussed with Figures 10.3, 11.2, and 11.4, much of HPC deals with matrices and their arrangements in memory. With parallel computing, we must arrange the data into tiles such that each data tile is contiguous in memory. Then, the tiles can be processed in a fine-grained computation. As we have seen in the exercises, the best size for the tiles depends upon the size of the caches being used, and these are generally small.
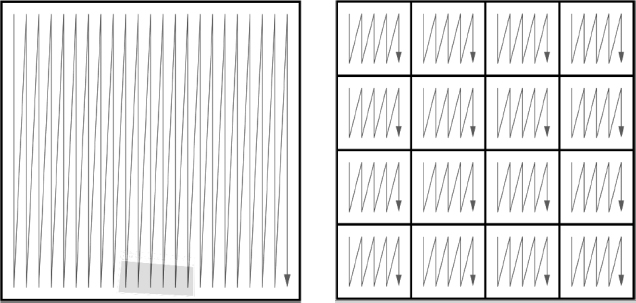
Figure 11.4 A schematic of how the contiguous elements of a matrix must be tiled for parallel processing (from Dongarra, 2011).
11.6.1 CUDA Memory Usage
CUDA commands are extensions of the C programming language and are used to control the interaction between the GPU’s components. CUDA supports several data types such as dim2, dim3, and 2D textures, for 2D, 3D, and 2D shaded objects, respectively. PyCUDA (Klöckner, 2014), in turn, provides access to CUDA from Python programs as well as providing some additional extensions of C. Key concepts when programming with CUDA are following:
Kernel A part or parts of a program that are executed in parallel by the GPU using threads. The kernel is called from the host and executed on the device (another term for the GPU).
Thread The basic element of data to be processed on the GPU. Sometimes defined as an execution of a kernel with a given index, or the abstraction of a function call acting on data. The numbers of threads that are able to run concurrently on a GPU depends upon the specific hardware being used.
Index All threads see the same kernel, but each kernel is executed with a different parameter or subscript, called an index.
As a working example, consider the summation of the arrays a and b by a kernel with the result assigned to the array c:
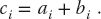
If these were calculated using a sequential programming model, then we might use a for loop to sum over the index i. However, this is not necessary in CUDA where each thread sees the same kernel, but there is a different ID assigned to each thread. Accordingly, one thread associated with an ID would see
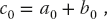
while another thread assigned to a different ID might see
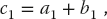
and so forth. In this way, the summation is performed in parallel by the GPU. You can think of this model as analogous to an orchestra in which all violins plays the same part with the conductor setting the timing (the clock cycles in the computer). Each violinist has the same sheet music (the kernel) yet plays his/her own violin (the threads).
As we have already seen in Figure 11.3, CUDA’s GPU architecture contains scalable arrays of multithreaded SMs. Each SM contains eight SPs, also called CUDA cores, and these are the parts of the GPU that run the kernels. The SPs are execution cores like CPUs, but simpler. They typically can perform more operations in a clock cycle than the CPU, and being dedicated just to data processing, constitute the arithmetic logic units of the GPU. The speed of dedicated SMs, along with their working in parallel, leads to the significant processing power of GPUs, even when compared to a multicore CPU computer.
In the CUDA approach, the threads are assigned in blocks that can accommodate from one to thousands of threads. For example, the CUDA GeForce GT540M can handle 1024 threads per block, and has 96 cores. As we have said, each thread runs the same program, which make this a single program multiple data computer. The threads of a block are partitioned into warps (set of lengthwise yarns in weaving), with each warp containing 32 threads. The blocks can be 1D, 2D, or 3D, and are organized into grids. The grids, in turn, can be ID or 2D.
When a grid is created or launched, the blocks are assigned to the SMs in an arbitrary order, with each block partitioned into warps, and each thread going to a different streaming processor. If more blocks are assigned to an SM than it can process at once, the excess blocks are scheduled for a later time. For example, the GT200 architecture can process 8 blocks or 1024 threads per SM, and contain 30 SMs. This means that the 8 × 30 = 240 CUDA cores (SPs) can process 30 × 1024 = 30 720 threads in parallel. Compare that to a 16 core CPU!
11.6.2 CUDA Programming 
The installation of CUDA development tools follows a number of steps:
- Establish that the video card on your system has a GPU with Nvidia CUDA. Just having an Nvidia card might not do because not all Nvidia cards have a CUDA architecture.
- Verify that your operating system can support CUDA and PyCuda (Linux seems to be the preferred system).
- On Linux, verify that your system has gcc installed. On Windows, you will need the Microsoft Visual Studio compiler.
- Download the Nvidia CUDA Toolkit.
- Install the Nvidia CUDA Toolkit.
- Test that the installed software runs and can communicate with the CPU.
- Establish that your Python environment contains PyCuda. If not, install it.
Let us now return to our problem of summing two arrays and storing the result, a[i]+b[i]=c[i]. The steps needed to solve this problem using a host (CPU) and a device (GPU) are:
- Declare single precision arrays in the host and initialize the arrays.
- Reserve space in the device memory to accommodate the arrays.
- Transfer the arrays from the host to the device.
- Define a kernel on the host to sum the arrays, with the execution of the kernel to be performed on the device.
- Perform the sum on the device, transfer the result to the host and print it out.
- Finally, free up the memory space on the device.
Listing 11.16 The PyCUDA program SumArraysCuda.py uses the GPU to do the array sum a + b = c.
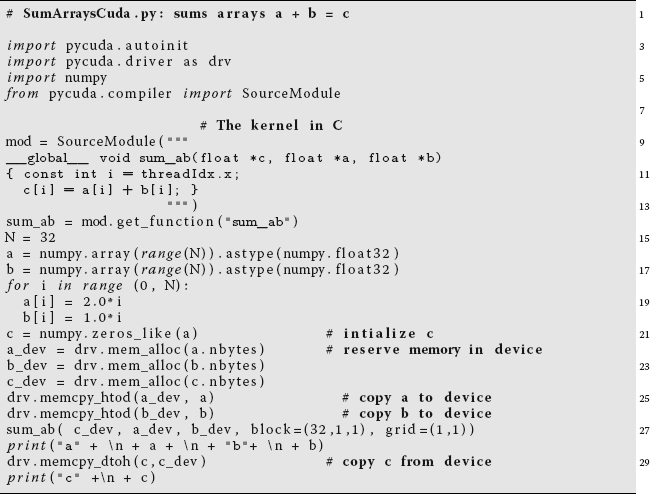
Listing 11.16 presents a PyCUDA program SummArraysCuda.py that performs our array summation on the GPU. The program is seen to start on line 3 with the import pycuda.autoinit command that initializes CUDA to accept the kernel. Line 4, import pycuda.driver as drv, is needed for Pycuda to be able to find the available GPU. Line 7, from pycuda.compiler import SourceModule prepares the Nvidia kernel compiler nvcc. The SourceModule, which nvcc compiles, is given in CUDA C on lines 10–14.
As indicated before, even though we are summing indexed arrays, there is no explicit for loop running over an index i. This is because CUDA and the hardware know about arrays and so take care of the indices automatically. This works by having all threads seeing the same kernel, and also by having each thread process a different value of i. Specifically, notice the command const int i = threadIdx.x on line 11 in the source module. The suffix .x indicates that we have a one dimensional collections of threads. If we had a 2D or 3D collection, you would also need to include threadIdx.y and threadIdx.z commands. Also notice in this same SourceModule the prefix __global__ on line 11. This indicates that the execution of the following summation is to be spread among the processors on the device.
In contrast to Python, where arrays are double precision floating-point numbers, in CUDA arrays are single precision. Accordingly, on lines 17 and 18 of Listing 11.16, we specify the type of arrays with the command
a = numpy.array(range(N)).astype(numpy.float32) .
The prefix numpy indicates where the array data type is defined, while the suffix indicates that the array is single precision (32 bits). Next on lines 22–24 are the drv.mem_alloc(a.nbytes) statements needed to reserve memory on the device for the arrays. With a already defined, a.nbytes translates into the number of bytes in the array. After that, the drv.memcp_htod() commands are used to copy a and b to the device. The sum is performed with the sum_ab() command, and then the result is sent back to the host for printing.
Several of these steps can be compressed by using some PyCUDA-specific commands. Specifically, the memory allocation, the performance of the summation and the transmission of the results on lines 22–28 can be replaced by the statements
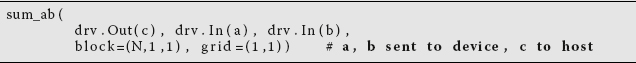
with the rest of the program remaining the same. The statement grid=(1,1) describes the dimension of the grid in blocks as 1 in x and 1 in y, which is the same as saying that the grid is composed of one block. The block(N,1,1) command indicates that there are N (= 32) threads, with the 1,1 indicating that the threads are only in the x direction.
Listing 11.17 The PyCUDA program SumArraysCuda2.py uses the GPU to do the array sum a + b = c, using four blocks with a (4,1) grid.

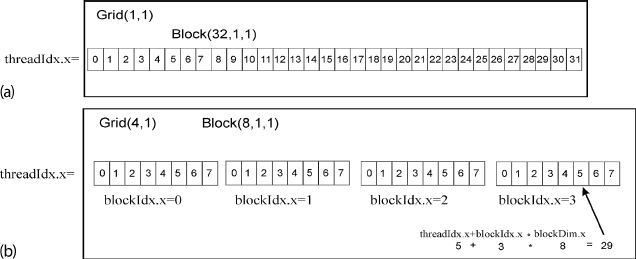
Figure 11.5 (a) A 1 × 1 grid with a 1D block containing 32 threads, and the corresponding threadIdx.x that goes from 0 to 31. (b) A 1D 4 × 1 grid, that has 4 blocks with 8 threads each.

Our example is so simple that we have organized it into just a single 1D block of 32 threads in a 1 × 1 grid (Figure 11.5a). However, in more complicated problems, it often makes sense to distribute the threads over a number of different block, with each block performing a different operation. For example, the program SumArraysCuda2.py in Listing 11.17 performs the same sum with the four-block structure illustrated in Figure 11.5b. The difference in the program here is the statement on line 23, block=(8,1,1), grid=(4,1) that specifies a grid of four blocks in 1D x, with each 1D block having eight threads. To use this structure of the program, on line 10 we have the command const int i = threadIdx.x+blockDim.x*blockIdx.x;. Here blockDim.x is the dimension of each block in threads (8 in this case numbered 0, 1,…,7), with blockIdx.x indicating the block numbering. The threads in each block have treadIdx.x from 0 to 7 and the corresponding IDs of the blocks are blockIdx.x = 0, 1, 2, and 3.