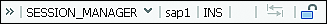5.4 The SAP Graphical User Interface
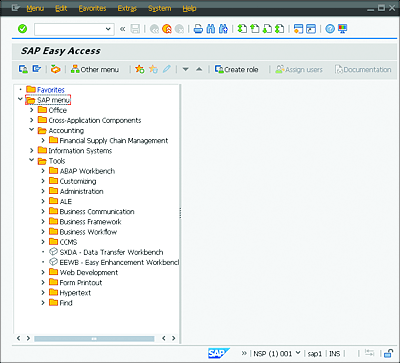
SAP GUI is the user interface in which you work; it displays the applications that run on the server on your PC. After successful logon to the system, the screen shown in Figure 5.7 is displayed.
Figure 5.7 SAP Easy Access (Initial Screen after Logon)
You can conveniently navigate to the desired application via the user menu, SAP Easy Access menu.
The SAP screen contains many buttons and fields. The following section details the various areas of the SAP GUI that will help you better orient yourself to SAP in your daily work. The elements that you can click in the SAP screen are indicated in Bold in this book.
5.4.1 Menu Bar
The menu bar is located at the top of the screen (Figure 5.8). The menus displayed depend on the respective application (transaction) and the level at which you’re located within the application. The menu items System and Help are always available in the menu bar regardless of the transaction you’re working on.
Figure 5.8 Menu Bar
You can call the menu items by clicking them. They may contain submenus. By clicking ![]() , you can activate a menu that offers the following functions:
, you can activate a menu that offers the following functions:
You can find the buttons for minimizing, maximizing, and closing the window on the right-hand side of the menu bar; these are listed in Table 5.1. They are comparable with the buttons you already know from Microsoft Windows.
| Button | Name | Use |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Minimize | The application window is minimized and displayed at the bottom of the screen. Its size is restored by clicking it. |
|
|
Maximize | The application window is displayed in its full size. |
|
|
Close | The open application window is closed. |
Table 5.1 Sizing Icons in the Menu Bar
5.4.2 Standard Toolbar
The standard toolbar is located below the menu bar (Figure 5.9). It contains icons for the most important functions, such as Save and Cancel. The buttons are displayed in all screens; inactive buttons are grayed out, and you can only use the buttons that are displayed in color. If you move the mouse pointer over the button without clicking it, the system displays brief information about the function, which is also referred to as tooltip.
Figure 5.9 Standard Toolbar
Some functions can also be called via the function keys, which are located at the top of your keyboard ((F1) through (F12)). Remember that some function keys have different settings, depending on the application. Table 5.2 lists the most essential buttons and function keys.
Table 5.2 Most Essential Buttons of the Standard Toolbar
For information on working with sessions, refer to Chapter 6. To learn more about links and adaptations of the local layout, read Chapter 7. The help function is described in Chapter 13.
5.4.3 Title Bar
The structure of the title bar always depends on the transaction you use (Figure 5.10). It can also contain other buttons in addition to the respective transaction name.
Figure 5.10 Example of a Title Bar
5.4.4 Command Field
You can navigate in the SAP system without a mouse by using the SAP Easy Access menu via the keyboard. This way, you can start transactions by directly entering the transaction code in the command field, as shown in Figure 5.11 (see also Chapter 6).
Figure 5.11 Command Field
5.4.5 Status Bar
The status bar is located at the bottom of the screen and extends over the entire screen width. On the left side, you can see an area that displays system messages. The right side displays four fields that provide current information on the system’s status.
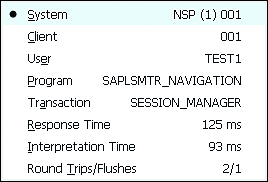
By clicking the Help ![]() button in the first status field, you get various pieces of information on the system and client you’re working with. The status bar indicates which program and transaction are currently active. You also find information on the response and interpretation time of the SAP system (Figure 5.12).
button in the first status field, you get various pieces of information on the system and client you’re working with. The status bar indicates which program and transaction are currently active. You also find information on the response and interpretation time of the SAP system (Figure 5.12).
Figure 5.12 Information in the Status Bar
Table 5.3 describes the most essential information available in the status bar.
| Description | Explanation |
|---|---|
| System | System and client to which you’re currently logged on |
| Client | Client |
| User | Logon name |
| Program | Program that is currently active |
| Transaction | Transaction that is currently active |
| Response Time | Time in milliseconds in which the SAP system responds |
| Interpretation Time | Time in milliseconds in which commands to the system are executed |
| Round Trips/Flushes | Connections to one or more SAP systems |
Table 5.3 Status Bar Information
In the second status field (Figure 5.13), you can view the name of the server to which you’re connected (here, sap1).
Figure 5.13 Additional Information in the Status Field
The third status field shows whether you’re in overtype mode (OVR) or in insert mode (INS) (refer to Figure 5.13). If OVR is set, you overwrite the existing data on the right side of the cursor when you enter data; if INS is set, you add or insert data. You can toggle between the modes by clicking this field.
The next section describes how to exit the SAP system.