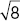
1.True
2.False
3.True
4.True
1.True
2.False
3.False
1.Congruent to
2.Less than
3.Perpendicular to
4.Greater than or equal to
1.C
2.D
3.E
4.F
5.A
6.H
7.B
8.G
1.True
2.True
3.True
4.False
1.15 degrees
2.150 degrees
3.90 degrees
4.110 degrees
1.95 degrees
2.5 degrees
3.50 degrees
1.True
2.False
3.True
4.False
1.31 degrees
2.168 degrees
3.25 degrees, 25 degrees
4.150 degrees
5.30 degrees
6.90 degrees, 90 degrees
Angle ACD ≅ angle BCE
Angle ACB ≅ angle DCE
Angle BED ≅ angle EDA ≅ angle DAB ≅ angle ABE
1.Right
2.supplementary
3.congruent
4.acute
5.complementary
6.Vertical
7.Obtuse
8.bisector
9.straight
1.165
2.15
3.165
4.180
5.180
6.180
7.180
8.360
1.False
2.False
3.False
4.True
5.True
1.A, S
2.A, S
3.V
4.C
5.S
6.S
7.AE
1.110
2.70
3.70
4.110
5.70
6.70
7.110
1.Yes
2.Don’t know
3.Don’t know
4.Yes
5.Yes
1.four
2.congruent
3.intersect
4.right
5.a.Corresponding
b.Alternate exterior
c.Alternate interior
6.supplementary
7.one
1.30 degrees
2.10 degrees
3.80 degrees
1.95 degrees
2.155 degrees
3.25 degrees
4.155 degrees
5.85 degrees
6.95 degrees
7.85 degrees
8.120 degrees
9.120 degrees
10.60 degrees
1.True
2.False
3.False
1.True
2.True
3.False
1.False
2.True
3.True
1.False
2.False
3.True
1.True
2.True
3.False
1.True
2.True
3.False
4.True
1.R, I
2.S, A
3.R, S
4.E, A
5.I, A
6.O, S
7.I, O
8.O, S
1.26
2.15
3.4 + 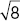
1.12 square inches
2.20 square inches
1.Yes
2.No
3.Yes
4.Yes
1.No
2.Yes
1.No
2.Yes
3.Yes
4.b = 9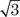 , c = 18
, c = 18
5.a = 6, c = 12
6.a = 4.5, b = 4.5
1.a = 10, b = 10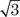 , c = 20
, c = 20
2.a = 5, b = 5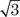 , c = 10
, c = 10
3.8
4.3
2.a = 100, b = 100
1.13 square inches
2.15 inches
3.4 inches
1.45-45-90
2.Obtuse and scalene
3.60-60-60
4.50 square inches
1. = 10
= 10
2. = 5
= 5
3. = 10
= 10
4.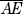 = 5
= 5
5.Equilateral
6.60 degrees
1.8 inches
2.4 inches
3.4 inches
4.8 inches
1.Angle Y, which is also angle XYZ
3.Angle X or angle YXZ
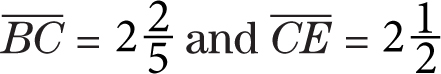
1.3
2.6
1. = 4
= 4
2. = 8
= 8
1.20 degrees
2.90 degrees
3.70 degrees
4.2
1.30 degrees
2.150 degrees
3.60 degrees
4.60 degrees
5.120 degrees
6.60 degrees
7.60 degrees
1.110 degrees
2.70 degrees
3.70 degrees
4.110 degrees
5.70 degrees
6.30 degrees
7.40 degrees
8.60 degrees
9.90 degrees
10.90 degrees
1.80 degrees
2.40 degrees
3.50 degrees
4.100 degrees
5.90 degrees
1.90 degrees
2.60 degrees
3.30 degrees
4.90 degrees
5.60 degrees
1.S, E
2.A, C, E
3.E, C
4.S, E
5.C, E
1.P, RH, R, S
2.R, S
3.RH, S
4.T
5.T
6.R, S
7.P, RH, R, S
8.R, S
1.1,620 degrees
2.17,640 degrees
3.156 degrees
4.165.6 degrees
1.10 degrees
2.150 degrees
3.12 sides
4.18 sides
1.2,340 degrees
2.158.82 degrees
3.140 degrees
4.10
1.6 inches
2.6 inches
1.Exterior of the circle
2.Exterior of the circle
3.On the circle
4.Interior of the circle
1.10π
2.10π
3.π
4.3
1.100π
2.π
3.100π
1.360 degrees
2.360 degrees
3.360 degrees
1.False
2.False
3.True
4.False
1.True
2.False
3.True
1.2π
2.7.5π
3.0.25π
1.90 degrees
2.30 degrees
3.60 degrees
4.120 degrees
5.30 degrees
6.90 degrees
7.55 degrees
8.70 degrees
1.36π
2.8π
3.6π
4.25π
5.4π
1.15 inches
2.9 inches
3.2 square inches
1.32 inches
2.40 meters
3.50 square inches
4.8 square centimeters
1.28 units
2.25 square units
3.9 square units
4.40 units
1.44 inches
2.72 square inches
3.24 square units
1.22 units
2.18 square units
3.28 units
4.36 square units
1.16 inches
2.24 square inches
3.1 square foot
1.540
2.360
3.900
4.360
5.A square, rectangle, rhombus, or parallelogram
1.16 inches
2.15 feet
3.48 square meters
4.75 square inches
1.A pentagon with sides 4 feet long is larger.
2.An equilateral triangle with sides 12 inches long is larger.
3.They are both the same.
4.They are both the same.
5.A square with sides 4 miles long is larger.
6.A square with sides 6 kilometers long is larger.
Perimeter = 28 units, Area = 48 square units
1.125 cubic inches
2.1 cubic inch
3.150 square inches
4.6 square inches
5.6 cubic inches
6.22 square inches
1.32π cubic units
2.10π cubic units
3.100π cubic units
1.36π cubic units
2.They are the same.
1.36π square units
2.36π cubic units
3.4π square units
4.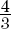 π cubic units
π cubic units
1.288π cubic units or 904.32 cubic units
2.5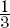 π cubic units or 16.74 cubic units
π cubic units or 16.74 cubic units
3.1333 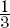 π cubic units or 4186.69 cubic units
π cubic units or 4186.69 cubic units
4.160π cubic units or 502.4 cubic units
5.512 cubic units
6.6 cubic units
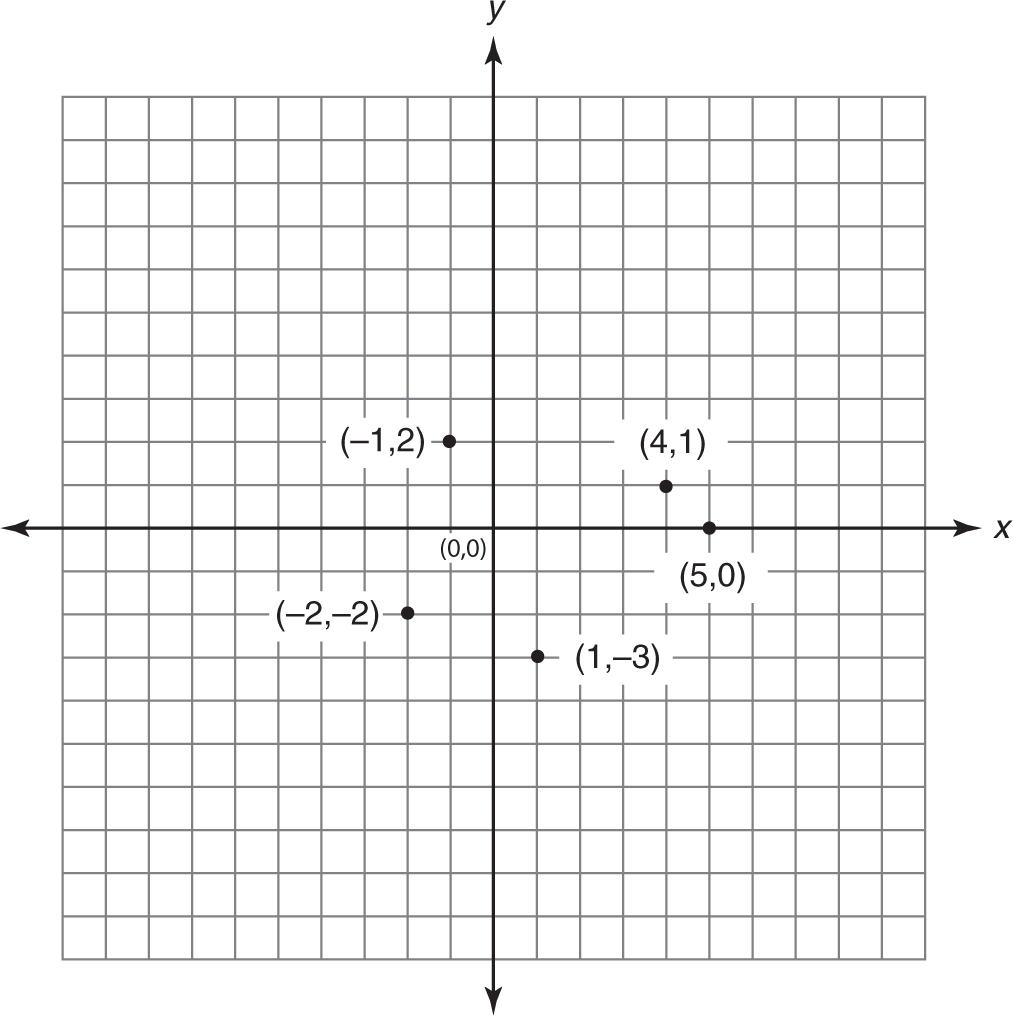
1.II
2.I
3.IV
4.III
5.The origin
1.(2, 5)
2.(5, 5)
3.(1, 1)
4.(2, –1)
1.5 units
2.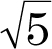 units
units
3.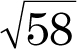 units
units
4.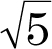 units
units
1.True
2.True
3.True
4.True
5.False
6.True
1.y = 5x + 2, slope = 5
2.y = –2x – 4, slope = –2
3.y = − 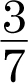 x, slope = −
x, slope = − 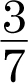
4.y = – 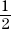 x +
x + 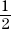 , slope = –
, slope = –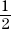
2.–1
1.Slope = 3, y-intercept = –2
2.Slope = 1, y-intercept = 0
3.Slope = 1, y-intercept = –2
4.Slope = 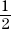 , y-intercept = –5
, y-intercept = –5
5.Slope = 0, y-intercept = 3
1.y = 2x – 12
2.y = x
3.y = 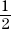 x – 1
x – 1
1.y = 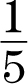 x +
x + 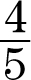
2.y = − 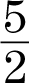 x + 5
x + 5
3.y = −x + 2
1.y = –2x + 11
2.y = x
3.y = −x – 8
4.y = 1
1.y = –2x + 15
2.y = 3
1.Perpendicular
2.Parallel
3.Neither
4.Parallel
1.Quadrant IV
2.(–2, 1)
4.y = − 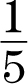 x + 4
x + 4
6.y = 4x
7.(0, 4)
8.Never
9.x = 0
10.y = − 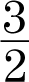 x + 9
x + 9 
11.Perpendicular
12.Parallel
1–7.Copy the constructions in Chapter 11 until you can replicate them easily.
1. Hint: Construct perpendicular lines to create four right angles. Bisect one of the angles to create two 45-degree angles.
2. Hint: Alternate interior angles are two angles between the parallel lines on the opposite sides of the transversal. When alternate interior angles are equal, the lines are parallel.
3.Hint: Construct a segment AB. Construct two equal segments starting at points A and B. These segments should be equal to each other but not equal to segment AB.