17
Routine examination of the newborn infant
All babies are examined shortly after birth to check that transition to extrauterine life has proceeded smoothly and there are no major abnormalities. A comprehensive medical examination within 24 hours of birth, the ‘routine examination of the newborn infant’, should be performed.
The purpose is to:
- detect any abnormalities – a significant congenital anomaly is present at birth in 10–20 per 1000 live births
- confirm and plan the further management of any abnormalities detected antenatally
- consider potential problems related to maternal pregnancy history or familial disorders
- allow the parents to ask any questions and raise any concerns about their baby
- determine whether there is concern by caregivers about the care of the baby following discharge.
- provide health promotion, especially prevention of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) (see Chapter 16).
Preparation
Maternal charts (records):
- Check maternal antenatal, labor and delivery charts.
Equipment:
- Tape measure.
- Stethoscope.
- Ophthalmoscope.
Environment:
- Warm room free from drafts.
- Privacy, suitably lit.
- Examine on firm mattress in crib (cot).
- Both parents present if possible.
- Always wash hands and clean stethoscope before each examination.
The infant
- The baby must be completely undressed during the course of the examination so that all the body is observed.
- Need a content, settled infant for successful examination.
- Examination is performed opportunistically, i.e. eyes when open, heart when quiet, hips left until last. However, the examination must be complete.
Routine examination of newborn infants
(Table 17.1, Figs 17.2 and 17.3) (see video: Newborn examination)
Table 17.1 Significant congenital abnormalities which may be identified on routine examination.
| Dysmorphic infant (see Chapter 9) |
| Cataracts (see Chapter 62) |
| Cleft lip and palate (see Chapter 40) |
| Congenital heart disease (see Chapter 49) |
| Urogenital – hypospadias, undescended testes (see Chapter 52) |
| DDH (developmental dysplasia of the hip) |
| Imperforate anus (see Chapter 48) |
| Spinal anomalies (see Chapter 59) |
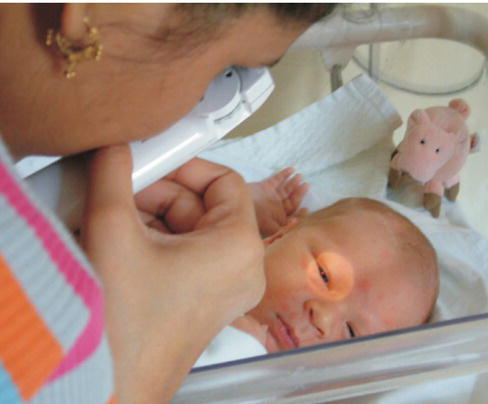
Fig. 17.2 Checking for red reflex. If absent, i.e. the pupil is white (cataracts, glaucoma, retinoblastoma), refer directly to an ophthalmologist. Also check eye looks normal, e.g. for a coloboma, a key-shaped defect in the iris. (see Chapter 62)
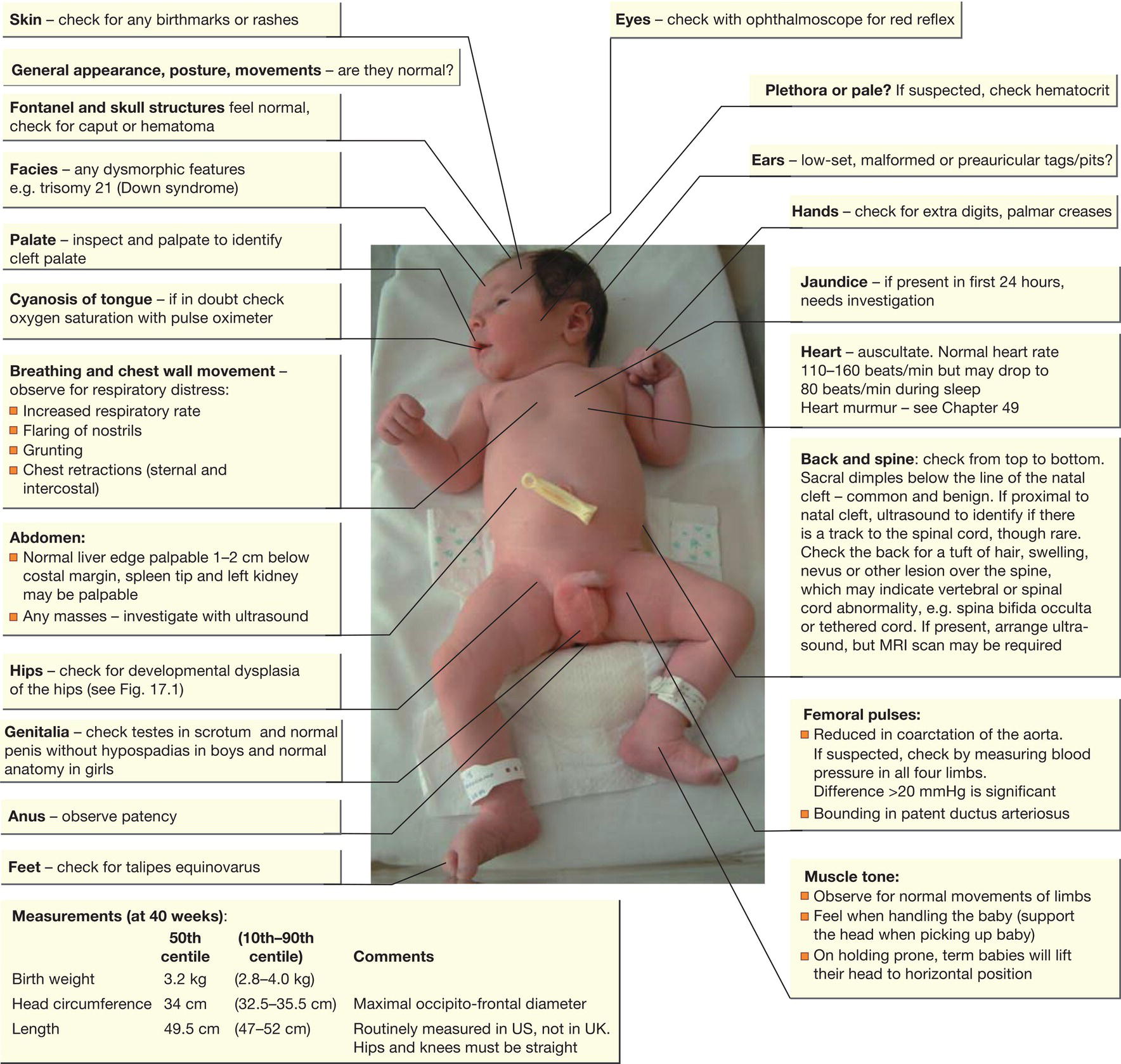
Fig. 17.3 Routine examination of newborn infants. In the UK the Newborn Infant Physical Examination (NIPE) checklist is recorded in the child health record and communicated to the family practitioner.