- k – steep
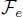 , 63
, 63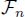 , 63
, 63 (E), 49
(E), 49- εne, 63
- εne, 76
- ϕn, 64
- δen, 76
- θ (p)
- ∞ – steep
- γe, 64
A, B, C
- adjunction, 53
- closing, 54
- dilation, 53
- erosion, 53
- opening, 54
- anti-extensive, 52
- antisymmetry, 49
- arc, 60, 99, 190
- arrow, 61, 188
- authorized pruning, 120
- bidirectional
- flowing edge, 72
- flowing path, 72
- black
- bounds
- button hole, 145, 183
- catchment zone, 68, 70, 72
- of a dead end, 102
- of a node-weighted graph, 68
- of an edge-weighted graph, 70
- closing, 53
- cocycle, 62
- commutes, 52
- complementation, 52
- complete lattice, 50
- concatenation
- connected component, 179
- core expanding flooding algorithm, 156, 157, 159, 161, 165, 168
- cycle, 62
D, E, F
- dead
- decreasing operator, 52
- digital elevation model (DEM), 148
- digraph, 60
- digraphs
- black holes, 145
- flat zones, 145
- flow digraph, 130
- gravitational digraphs, 131
- regional minima digraph, 158
- dilation, 52
- between node and edge weights, 63, 76, 77
- directed
- downstream, 109
- dual operator, 54
- edge, 60
- edge-weighted graph, 60
- edge weights opening, 64, 77
- equivalence classes
- even zone, 71
- node flat zones, 67, 69
- equivalence relation, 67, 69
- erosion, 52
- between edge and node weights, 63, 76, 77
- even zone, 71
- extensive, 52
- family of functions, 56, 62
- flat zone
- of a digraph, 103
- plateaus, 171
- flow digraph, 130, 156
- flowing
- flowing edge
- in a node-weighted graph, 67
- in an edge-weighted graph, 69
- flowing graph, 94, 95, 99
- coupling edge and node weights, 79
- e-flowing graph
- n-flowing graph
G, H, I
- Galois adjunction, 53
- geodesic distance, 179
- gradient operator, 64
- graph, 60
- e-flowing, 74, 99
- flowing, 76
- n-flowing, 75, 99
- subgraph, 61
- gravitational digraph, 106, 121, 123, 131
- greatest lower bound, 50
- grids, 188
- hierarchical queue, 159, 160
- core expanding algorithm, 169
- driven algorithms, 151, 181
- homotopic thickening, 179
- hydographic model, 88
- edge unstable filling, 91, 92
- node unstable filling, 91, 92
- totally unstable filling, 89
- idempotent, 52
- increasing operator, 52
- infimum
- in a lattice, 50
- of functions, 56
- invariants
- of an operator, 55
- of γe, 85
- of φn, 83
- involution, 52
K, L, M
- k-steep
- label, 66, 107, 192
- downstream propagation, 108, 152, 172
- priority order relation, 107
- upstream propagation, 108
- least upper bound, 50
- lexdist, 156
- lexicographic
- minimum spanning tree, 104
N, O, P
- node, 60
- closing, 64, 77
- flat zone, 67
- weights closing
- opening, 53
- operator, 52
- anti-extensive, 52
- extensive, 52
- idempotent, 52
- increasing, 52
- out-arrow, 188, 190
- overlapping
- partial
- digraph, 61
- graph, 61
- order relation, 49
- partially ordered set, 50
- partitions
- dead leaves partitions, 116, 150
- watershed partitions, 170
- pass point, 199
- path, 61
- directed path, 62
- undirected path, 61
- perpetuum mobile, 105
- plateau
- poset
- pruning, 120
- comet, 146
- directed erosion
- ↓k
 , 141
, 141
- factorization, 147
- infinite, 142
- iterated, 141
- operator, 192
- step, 140
- scissor operator
R, S, T
- Random Access Memory (RAM), 179
- reflexivity, 49, 67
- regional minimum, 72
- edge-weighted graph, 69
- node-weighted graph, 67
- scissor, 190
- skeleton by zones of influence, 179
- smooth zone, 101
- smoothly linked, 101
- steepness, 133
- subgraph, 61
- supremum, 50
- symmetry, 67
- tanks and pipes network, 88
- topographic
- total order relation, 50
- transitivity, 49
U, V, W
- unstable
- upper bound, 50
- upstream, 108
- vertex, 60
- waterfall hierarchy, 201
- watershed partition, 198
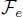 ,
, 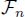 ,
, 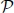 (E),
(E), 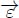 ,
, 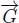 ,
,